Cardio Electrophysiology/ Action Potentials/ ECG
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
work in progress
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
________________ is when the ventricles are filling, muscles are relaxed, and AV valves are open.
a. diastole
b. systole
a. Diastole
_______________ is when the ventricles are emptying, muscles are contracting, and AV valves are closed.
a. diastole
b. systole
b. Systole
What part of the heart has a pacemaker ability?
sinoatrial node
Are the action potentials in the nodes and myocytes the same?
no
Electrical signals flow from the SA node to the atria to the ______________.
AV node
What is the resting membrane potential (mV) in the SA node and the cardiac myocytes?
SA node: -60 mV
Myocytes: -90mV
How does sodium enter the cell of the SA node and depolarize? (aka which transporter)
F-type Na channels
What type of transporter causes the rapid depolarization in the SA node?
L-type voltage gated Ca channels
After rapid depolarization, what channels are opened to repolarize the membrane in the SA node?
K channels
How does sympathetic stimulation affect the SA node?
causes depolarization to occur more rapidly
steeper
faster heartbeats
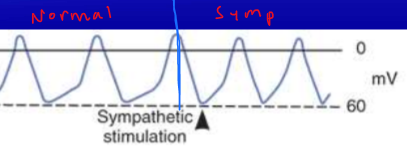
How does parasympathetic stimulation affect the SA node?
activates K channels
makes it harder to depolarize
slower heartbeats
In phase 0 of the cardiac myocyte action potential what happens?
voltage gated Na+ channels open
causes depolarization
What happens during phase 1 of the cardiac myocyte action potential?
transient K+ channels open
K+ leaves the cell
What happens during phase 2 of the cardiac myocyte action potential?
Calcium coming in the cell through voltage gated L-type channels
K+ still leaving the cells
causes a plateau
What happens during phase 3 of the cardiac myocyte action potential?
calcium channels close
K+ channels remain open
repolarizing
What happens during phase 4 of the cardiac myocyte action potential?
rest
leak K+ open
What measures change in polarity that occurs at the heart?
ECG
In an ECG, the P wave represents the…
atria depolarization
In an ECG, the QRS wave represents the…
ventricular depolarization
In an ECG, the T wave represents the…
ventricular repolarization
What event occurs right before the start of the P wave?
SA node depolarizes
What is happening during the PR interval?
We are measuring the conduction of signals from the SA node, AV node, and all the way down the heart before the ventricles
What does the QRS interval tell us about depolarization?
how RAPID/FAST we depolarize our ventricles
The QT interval measures how long our ________ __________ take.
measures how long our ACTION POTENTIALS take.