D202: Section Two
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Myelination
Process of insulating nerve cells, improving information processing speeds.
Oblivobesity
Lack of awareness about one's own obesity.
Average Age for Puberty
10 for girls and 12 for boys
early maturation in boys
favorable body image, higher popularity, earlier delinquency
early maturation in girls
-more self-conscious over developing body
-earlier sexual experiences, more unwanted pregnancies
-earlier exposure to alcohol and drug use
Menarche
the first menstrual period in girls
Primary Sex Characteristics
Sexual organs directly linked to reproduction, e.g., penis, testes, uterus, and ovaries.
Secondary Sex Characteristics
Physical traits that develop during puberty, e.g., breasts, widening hips, and pubic hair.
Acne Cause
Result of overactive sebaceous (oil-producing) glands.
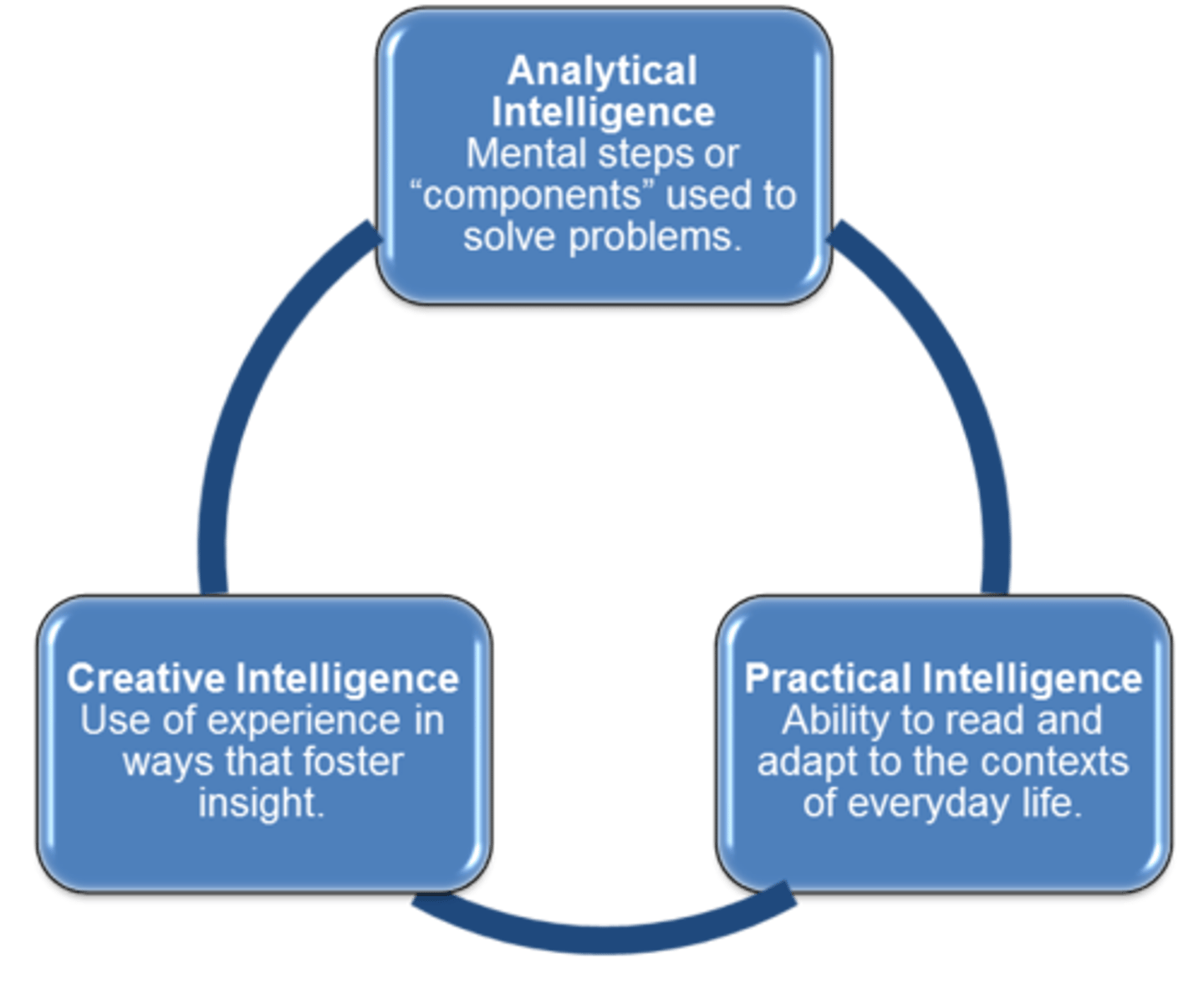
Creative Intelligence
Ability to generate new products, ideas, or novel solutions to problems. (Sternberg)
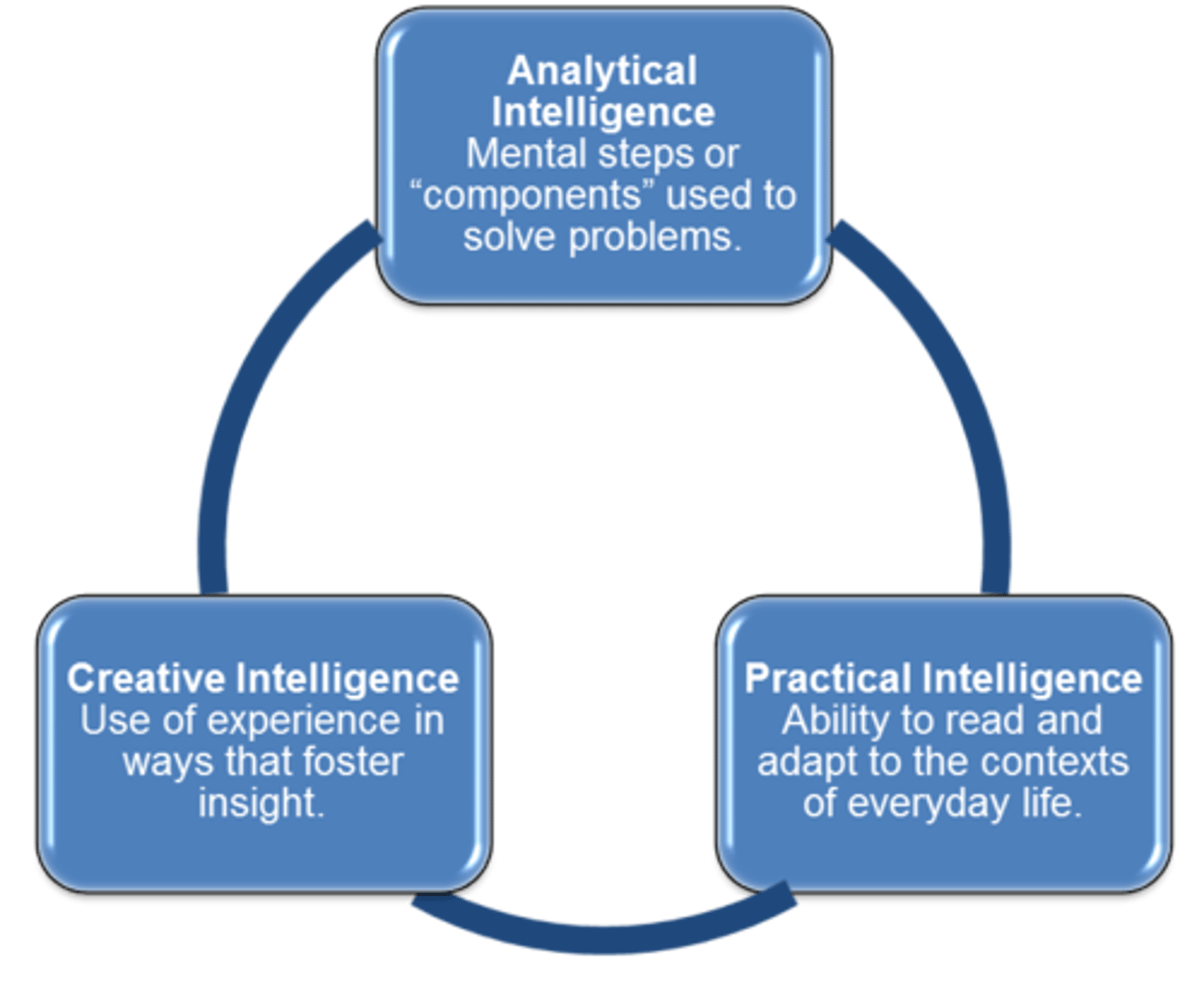
Analytical Intelligence
Involves analyzing, evaluating, judging, comparing, and contrasting. (Sternberg)
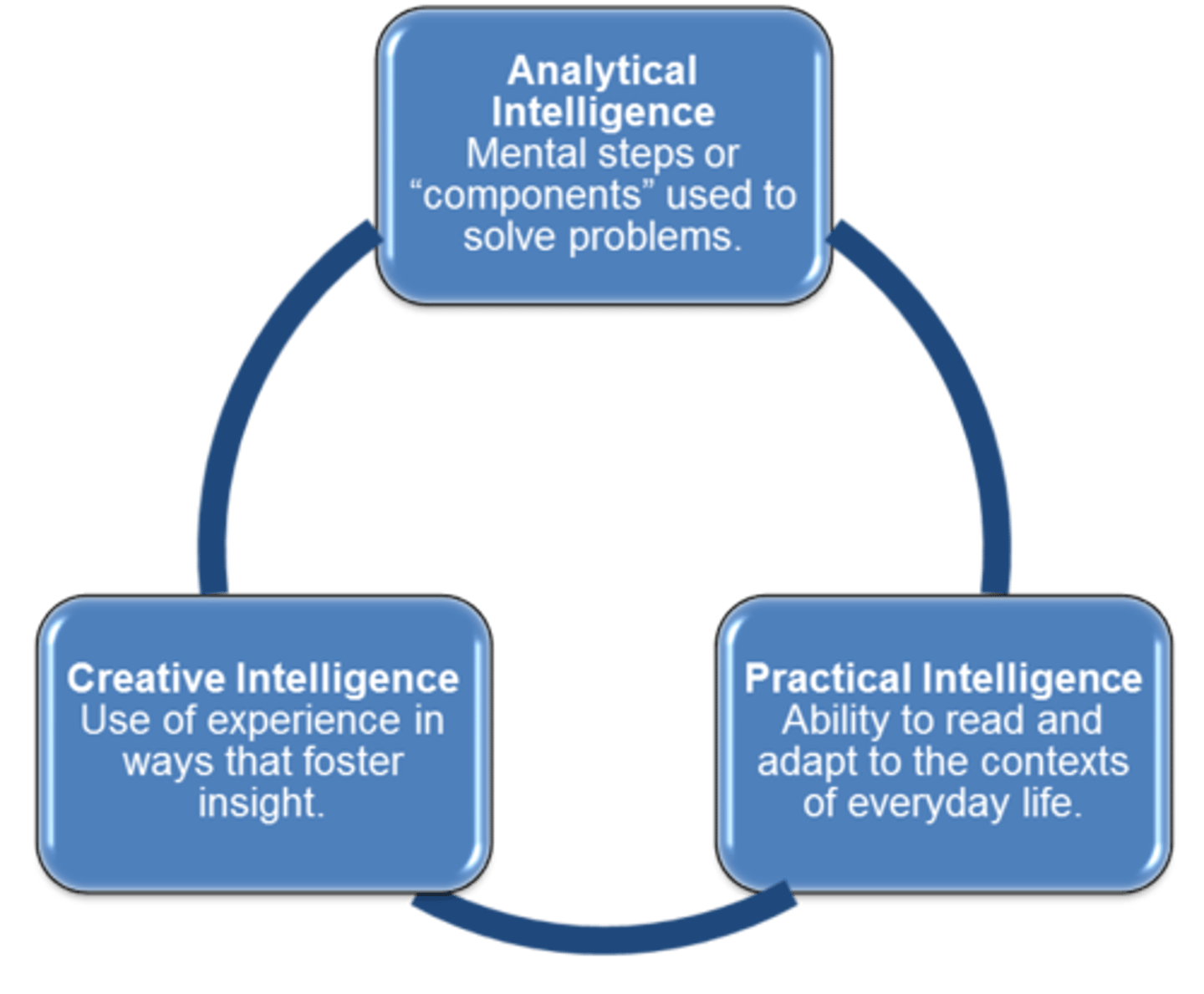
Practical Intelligence
Finding optimal fit between oneself and the environment through adaptation or shaping. (Sternberg)
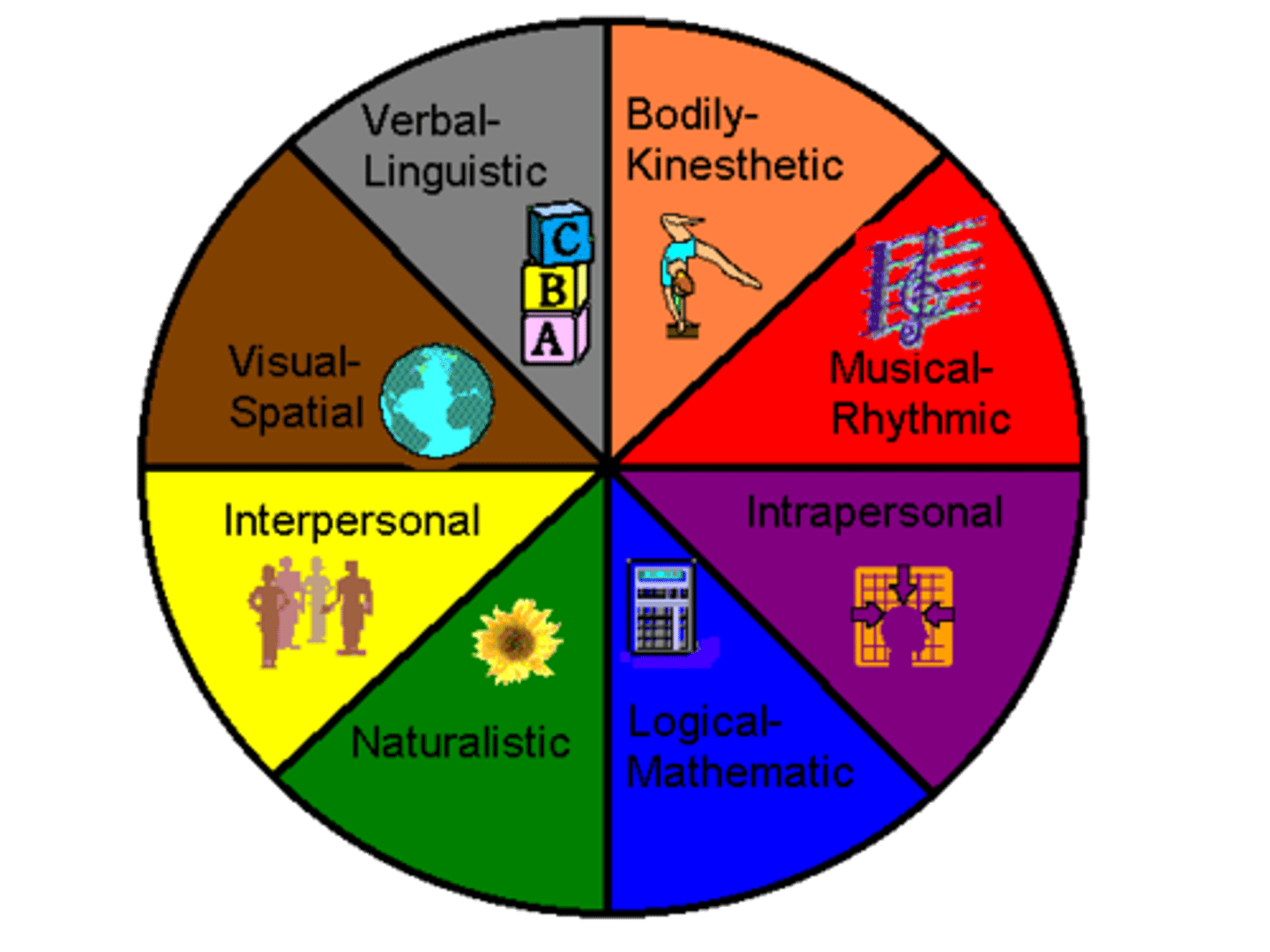
Gardner's Multiple Intelligences
our abilities are best classified into eight independent intelligences, which include a broad range of skills beyond traditional school smarts
intellectual disability
a condition of limited mental ability, indicated by an intelligence score of 70 or below and difficulty in adapting to the demands of life; varies from mild to profound
Learning Disability (LD)
Neurological disorder affecting brain function, unrelated to intelligence.
Dopamine and Oxytocin in Adolescent Brain
Dopamine peaks, involved in reward circuits; oxytocin facilitates bonding and social connections.
Formal Operational Thinking
Piaget's 4th stage of cognitive development, characterized by the ability to think abstractly. No longer limited to the here and now, they can think hypothetically and imagine what might be. They can use symbols for symbols as in algebra. They can also imagine multiple possibilities and form and test hypotheses.
Abstract Reasoning
Thinking based on broad ideas rather than specific facts and experiences.
hypothetical-deductive reasoning
Piaget's formal operational concept that adolescents have the cognitive ability to develop hypotheses, or best guesses, about ways to solve problems
Transitivity
The ability to understand that relationships between two objects can extend to a third object.

Pseudostupidity
The tendency of young adolescents to interpret situations in more complex ways than called for
Personal Fable
Belief in the uniqueness of adolescent feelings and immortality.

Imaginary Audience
Psychological state where an individual imagines multitudes enthusiastically listening or watching them.

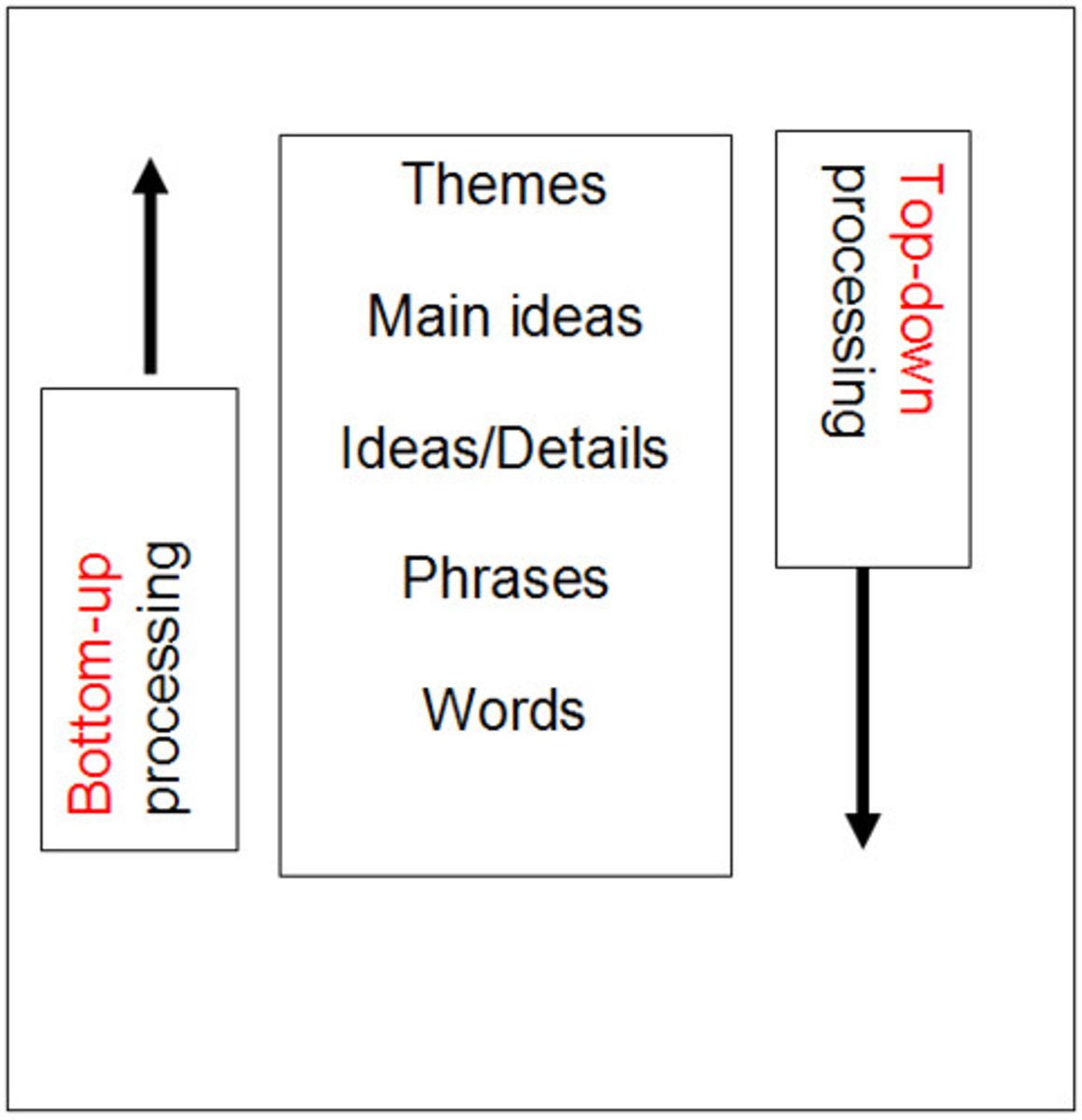
Bottom-Up Processing
Inductive reasoning based on specific observations to draw general conclusions.
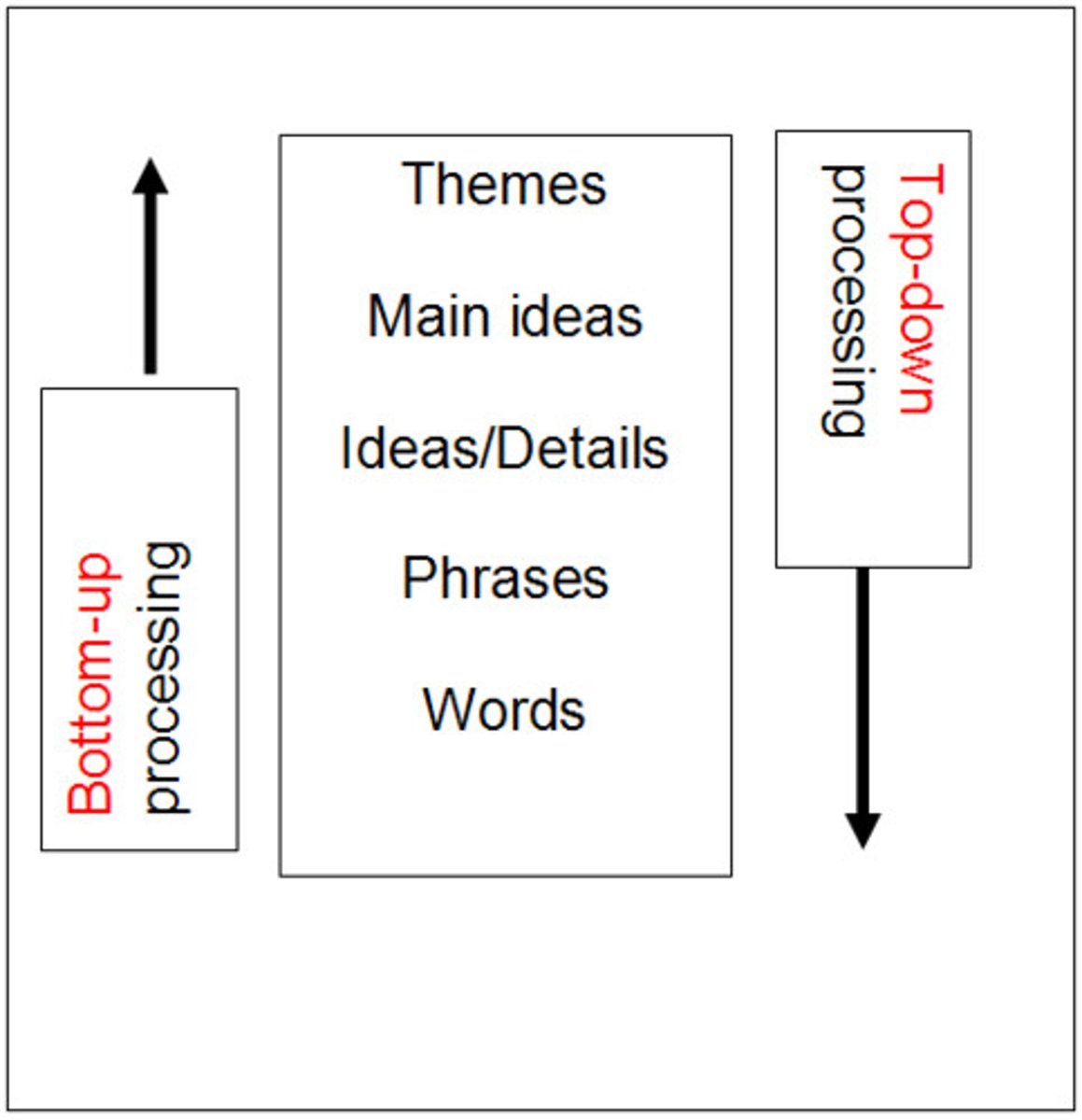
Top-Down Processing
Deductive reasoning starting with overarching principle to propose specific conclusions.
intrinsic motivation
a person performs an action because the act is fun, challenging, or satisfying in an internal manner
Intuitive Thought
Automatic, unconscious, experiential, and emotional thought process.

Erikson's 4th Stage: Industry vs inferiority
productivity in work and play is emphasized and children of all cultures strive for compencncy; if children don't master social and academic tasks while learning to cooperate they develop a sense of inferiority
Analytic Thought
Deliberate, conscious, and rational thought process.
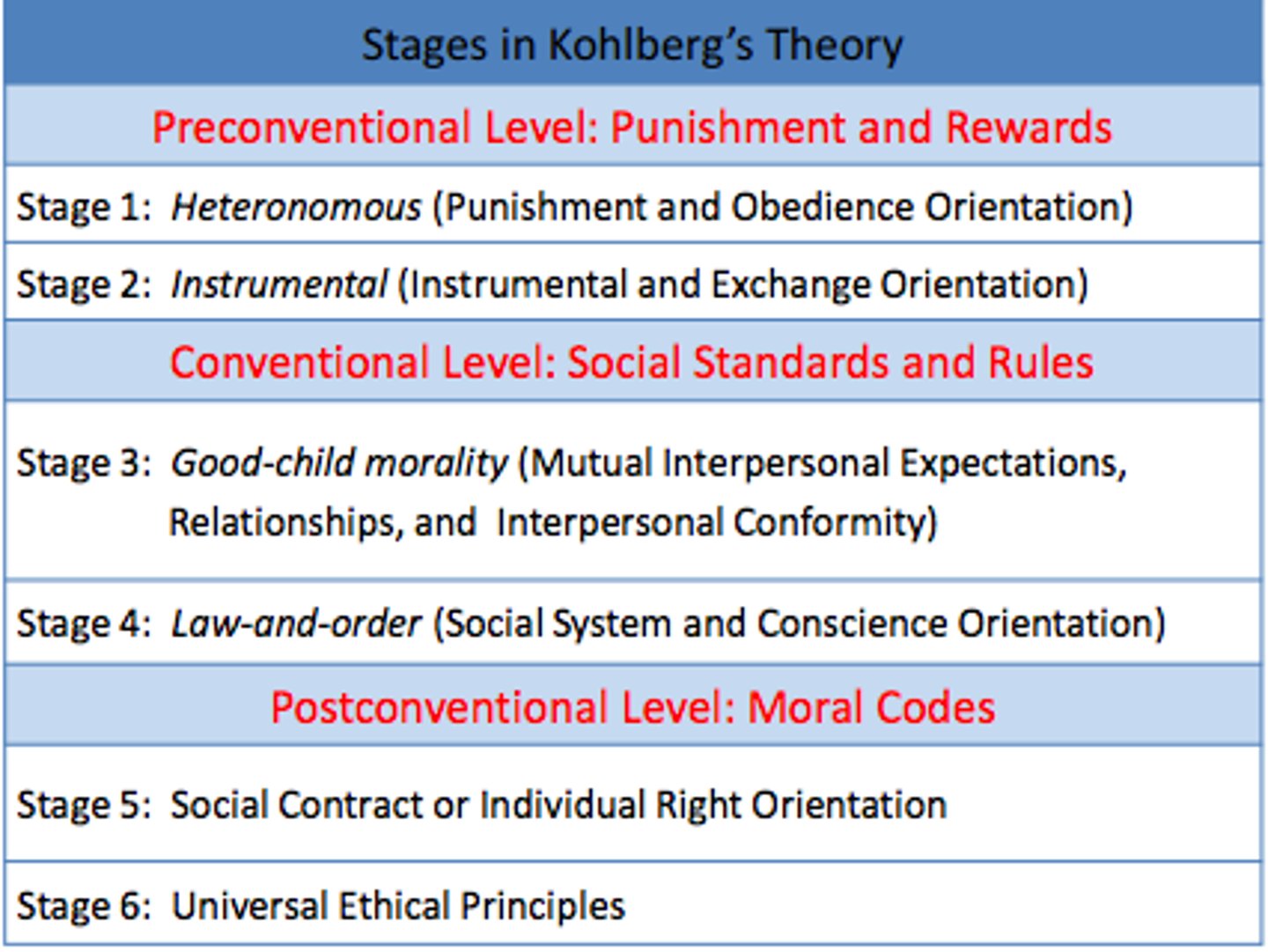
Preconventional Morality
Self-centered sense of right and wrong focused on rewards and punishment.
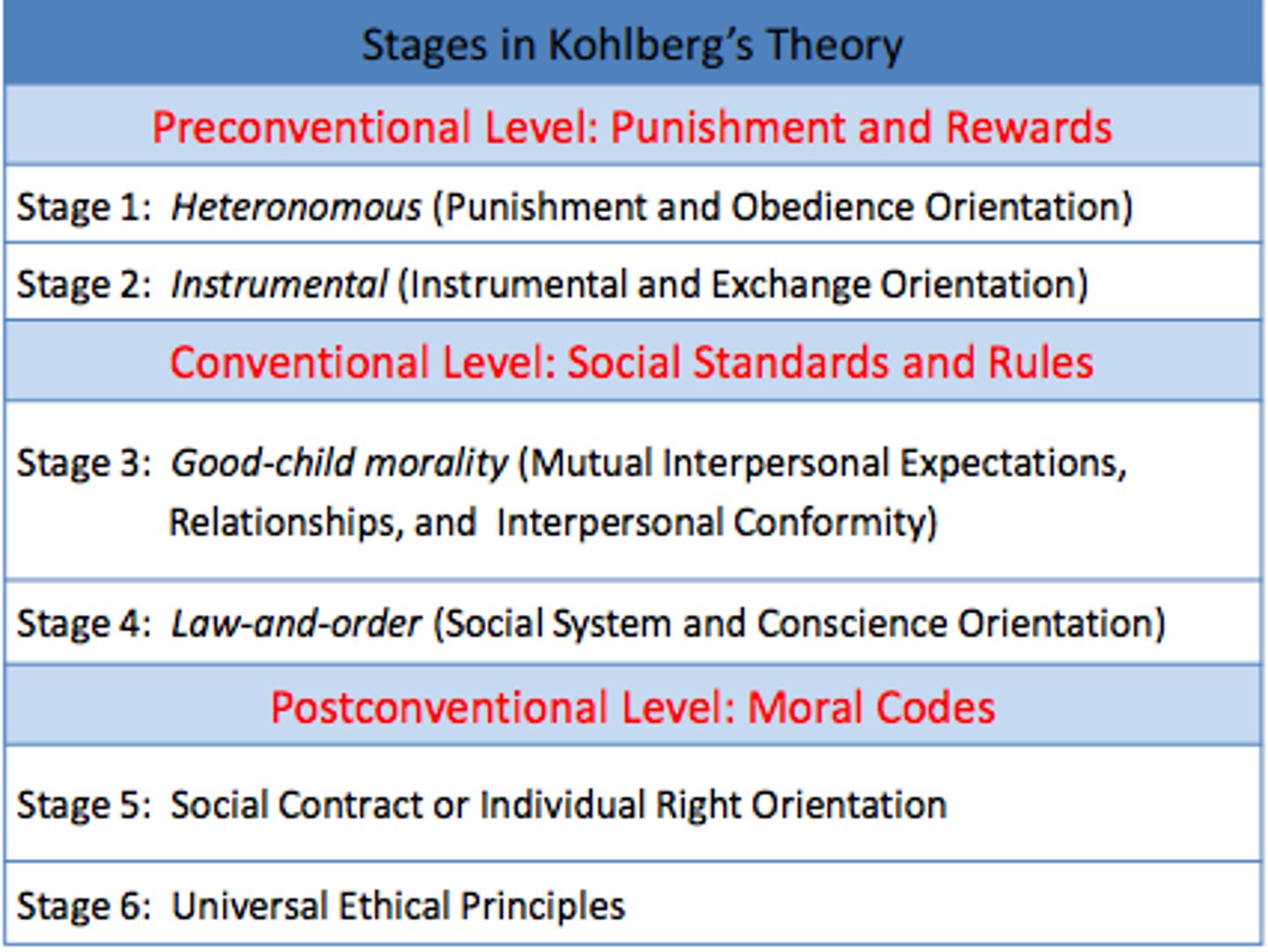
Conventional Morality
Accepted sense of right and wrong without involvement of rewards or punishments.
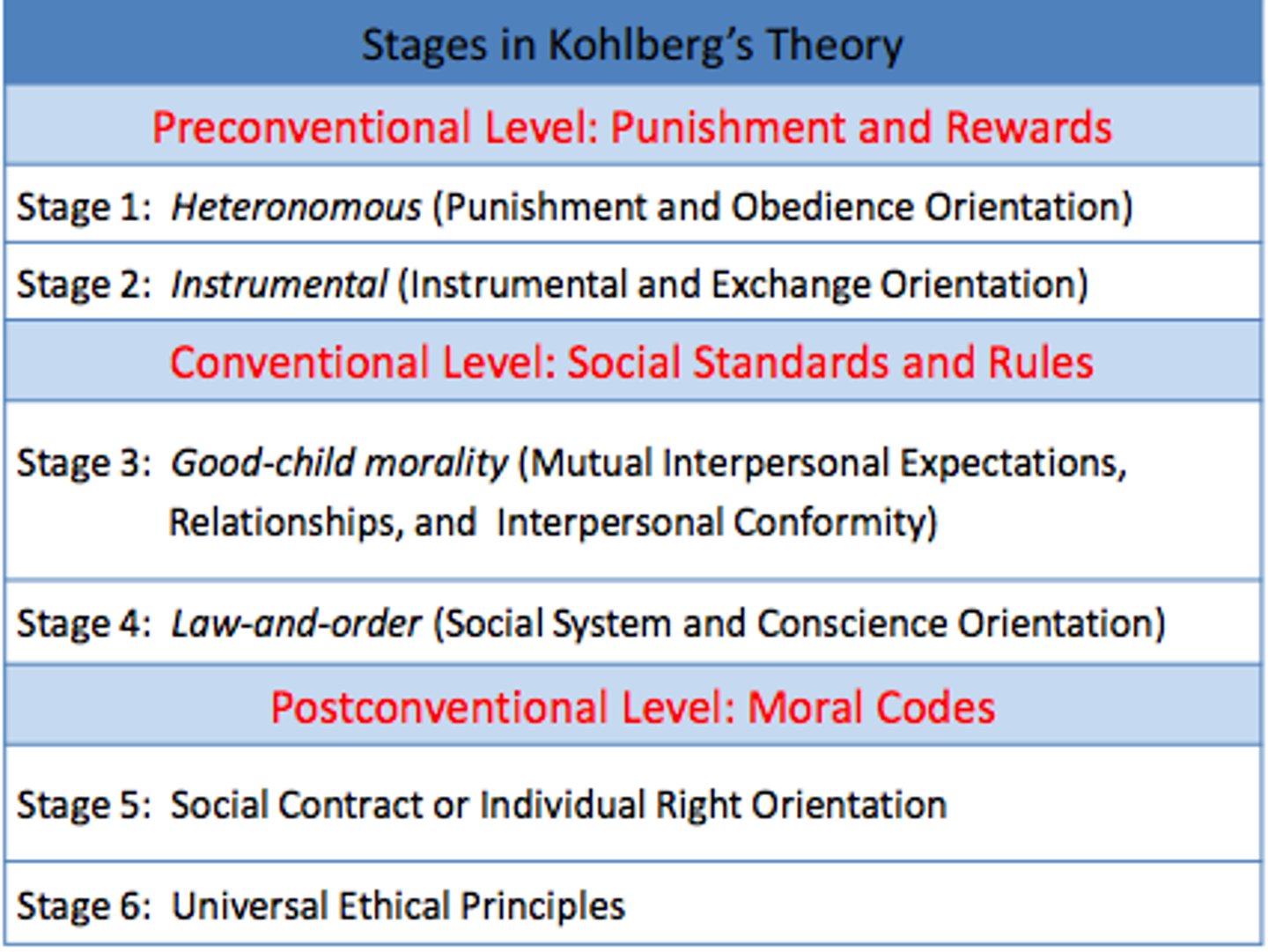
Postconventional Morality
Sense of right and wrong considering the welfare of society as a whole.
Divorce Impact on Child's Development
Negative impact on forming intimate relationships, lower education, and occupational status.
parental gatekeeping
Parents directly intervene and choose/provide access to certain friends or relationships over others.
Anorexia Nervosa
Medical condition characterized by lack or loss of appetite for food.
Bulimia Nervosa
Emotional disorder characterized by distorted body image and obsessive desire to lose weight.
Binge Eating Disorder
Frequent consumption of unusually large amounts of food and inability to stop eating.
Self-Esteem
Perception and valuation of oneself based on one's personal opinions and beliefs.
Self-Concept
all our thoughts and feelings about ourselves, in answer to the question, "Who am I?"
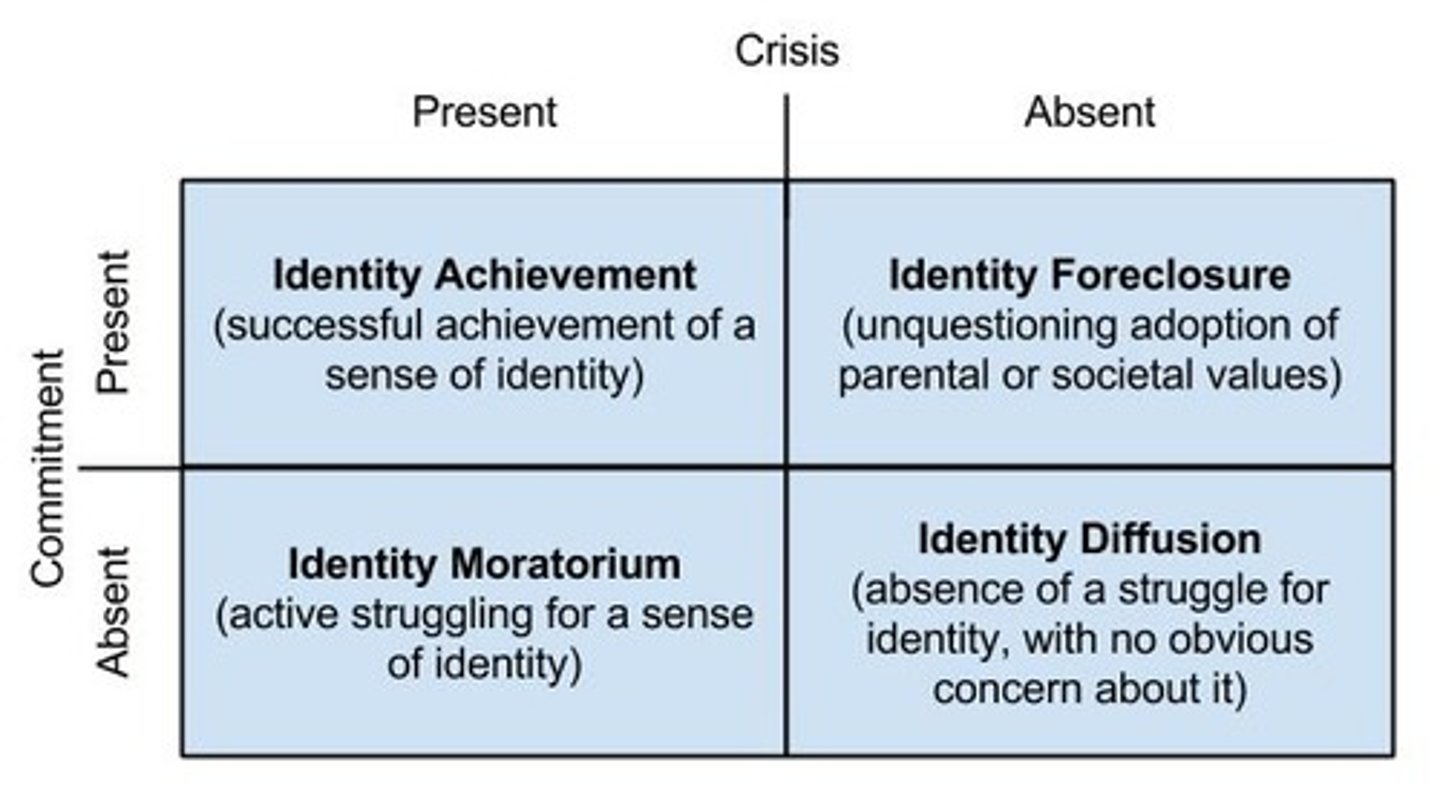
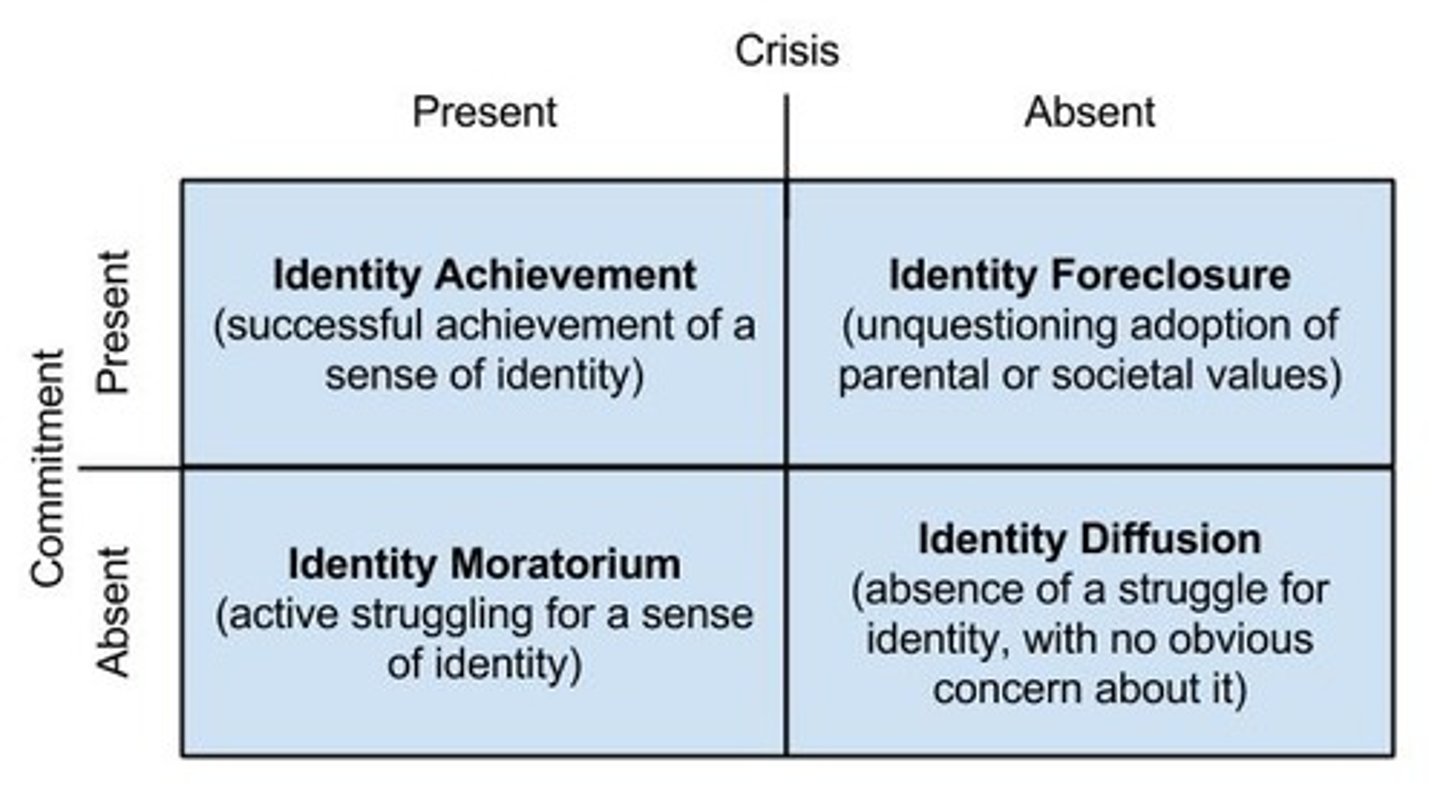
Identity-Diffusion
Lack of strong sense of self and not actively working on it.
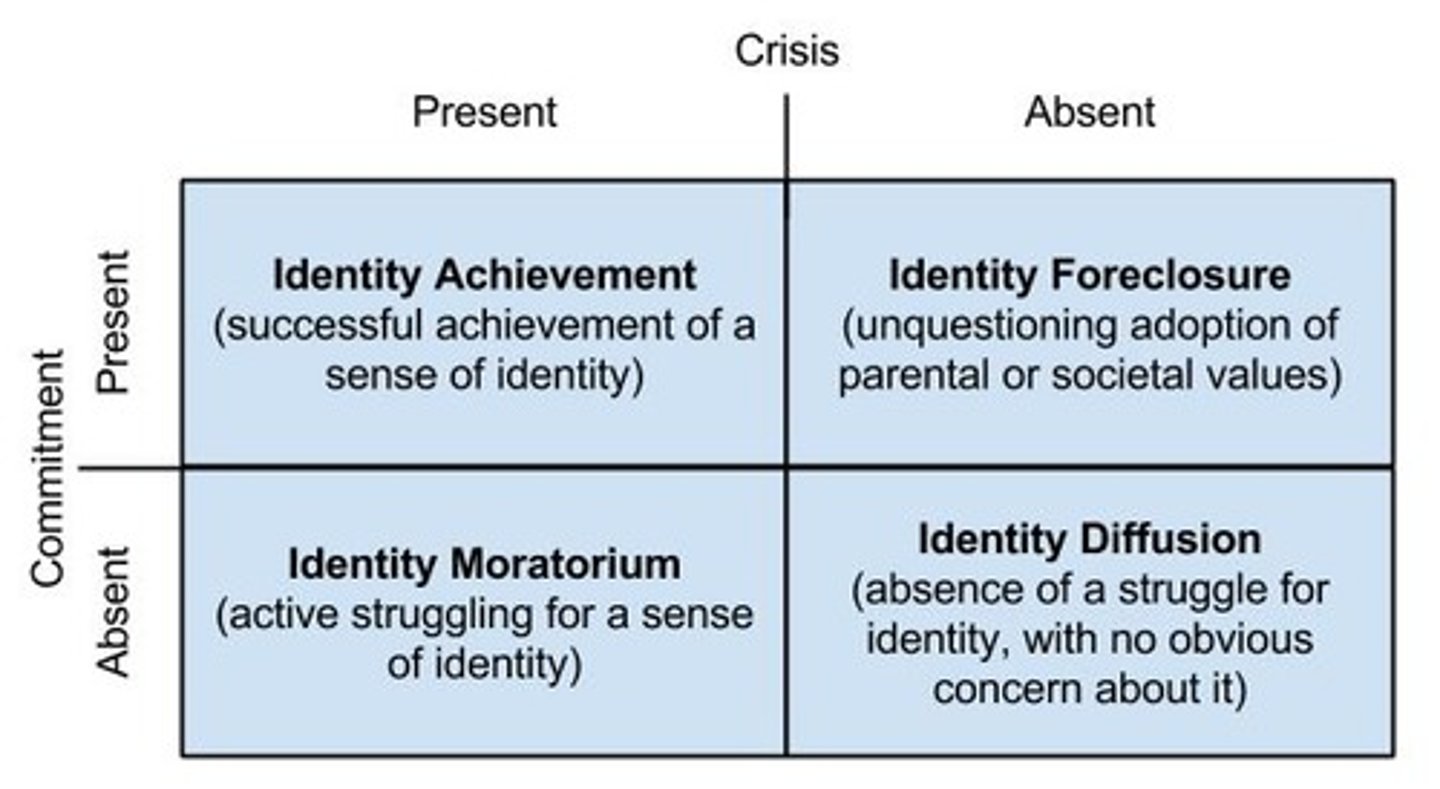
Identity-Moratorium Status
Exploring to establish an identity without making a commitment.
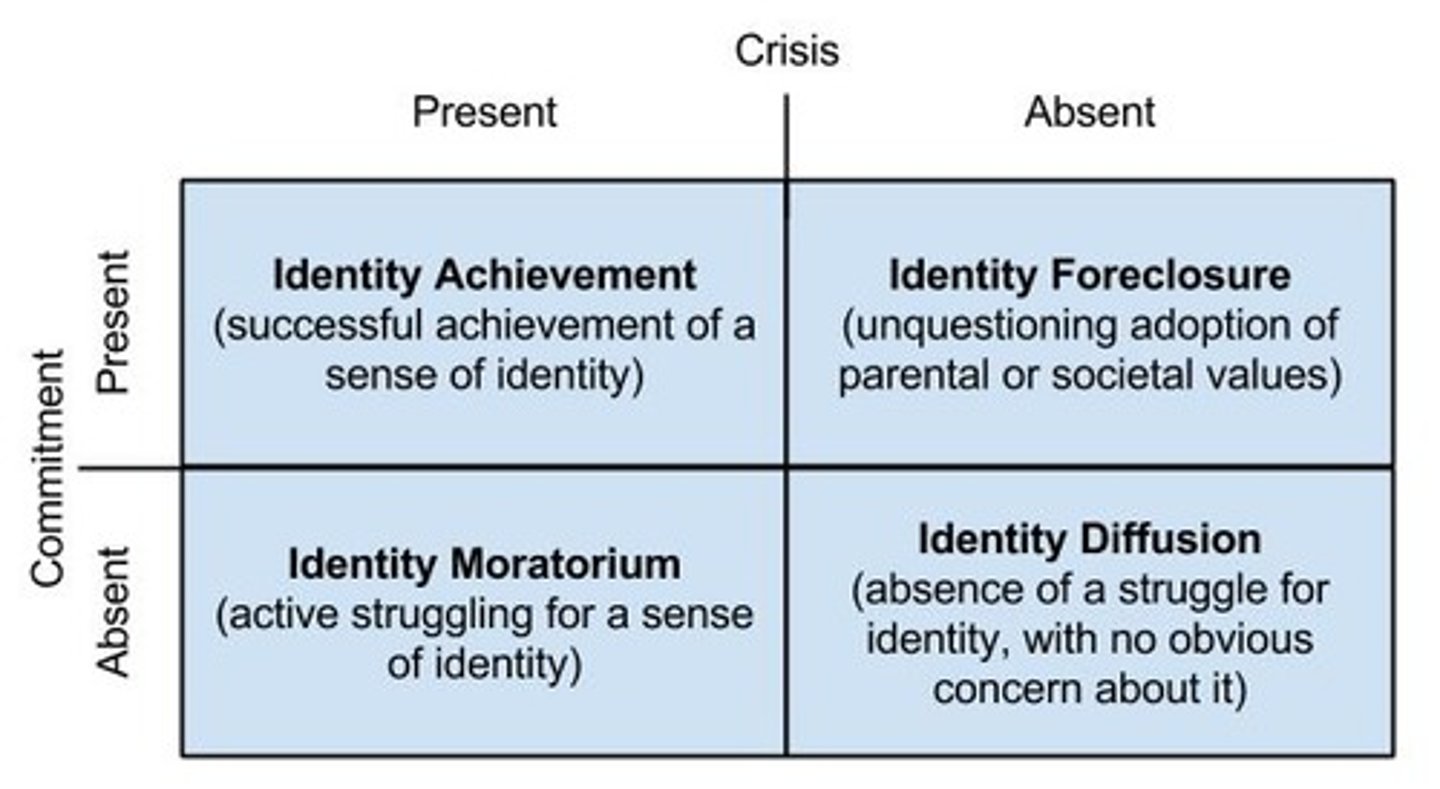
Identity-Foreclosure
Committing to an identity without exploring options.
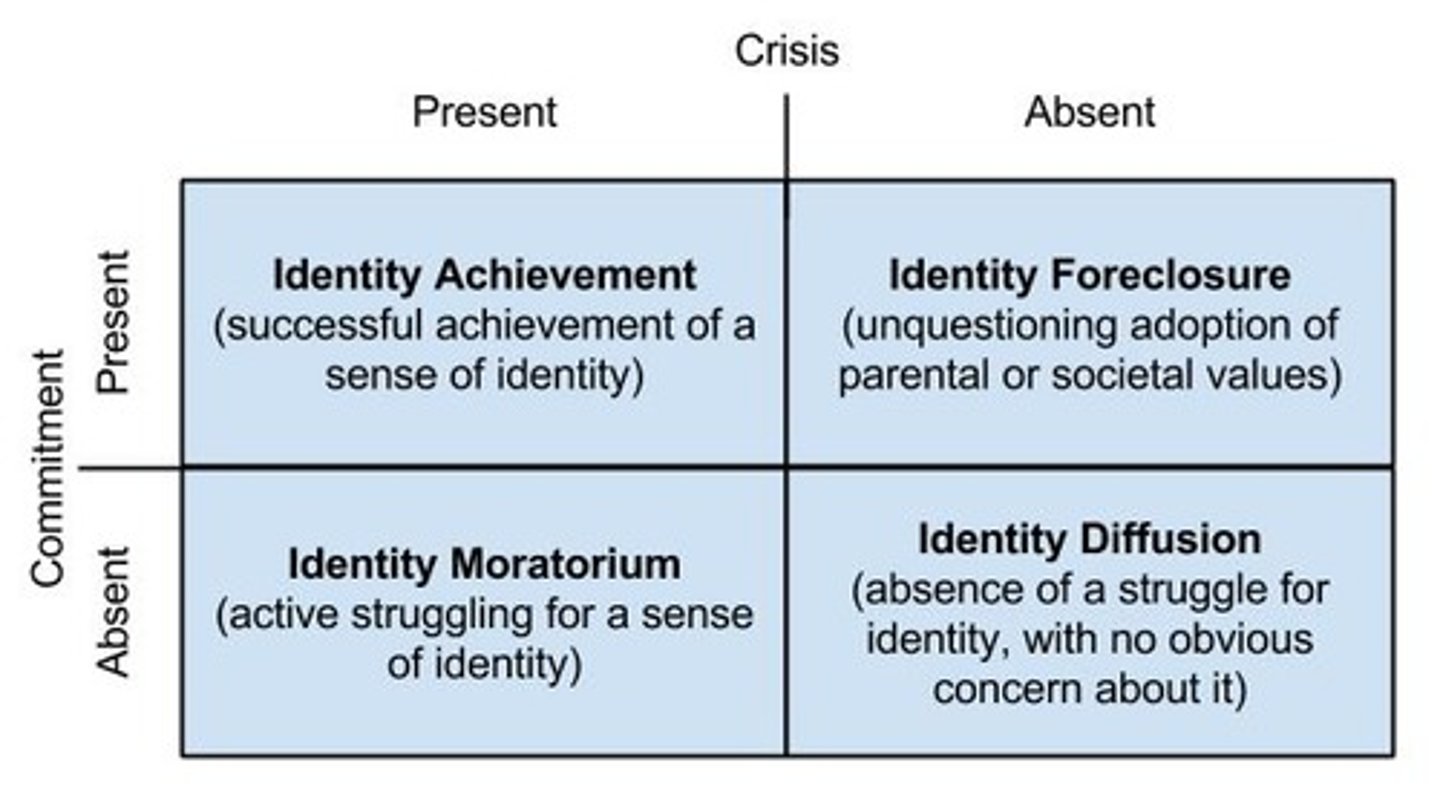
Identity Achievement
Settling on an identity after exploring multiple roles or options.
MAMA Cycling
Moving back and forth between moratorium and achievement in identity exploration.
Homophily
Tendency for peer group members to be similar in behavior and attitudes.
Rejected-Withdrawn Children
Shy, withdrawn, and unlikely to retaliate when bullied, making them more likely to be victims of bullies.
Rejected-Aggressive Children
Ostracized due to being loud, aggressive, and confrontational.
living arrangements in 21st century
There is an increase in children living with solo or cohabiting parents, mainly due to a decline in marriages and an increase in divorces.