Astrophysics
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Comparing Red-Shift with Elements (1)
Most galaxies are moving away from each other
Comparing Red-Shift with Elements (2)
Different elements absorb different frequencies of light
Comparing Red-Shift with Elements (3)
Light passes through forming dark lines at each frequency of visible light the element absorbs
Comparing Red-Shift with Elements (4)
More distant galaxies have the same patterns at a lower frequency
Comparing Red-Shift with Elements (5)
The patterns are shifted towards the red end of the spectrum
Big Bang
More distant galaxies = greater red shifts
More distant galaxies = moving away faster
Whole universe must be expanding
Microwave Radiation
Coming from all directions in all parts of the universe called CMBR. As the universe expands and cools, the radiation drops in frequency.
Star Colour
All stars emit visible light. Frequency and amount is dependent on surface temperature. The hotter the star, the bluer the light emitted.
White stars
All frequencies of visible light produced equally
Brightness of a star
Brightness depends on size and temperature.
Brightness in terms of distance from Earth
Closer stars appear brighter
Absolute Magnitude
How bright a star would appear to be if it was a fixed distance from Earth. The lower the absolute magnitude the brighter the star.
HR Diagrams
Absolute Magnitude vs Temperature
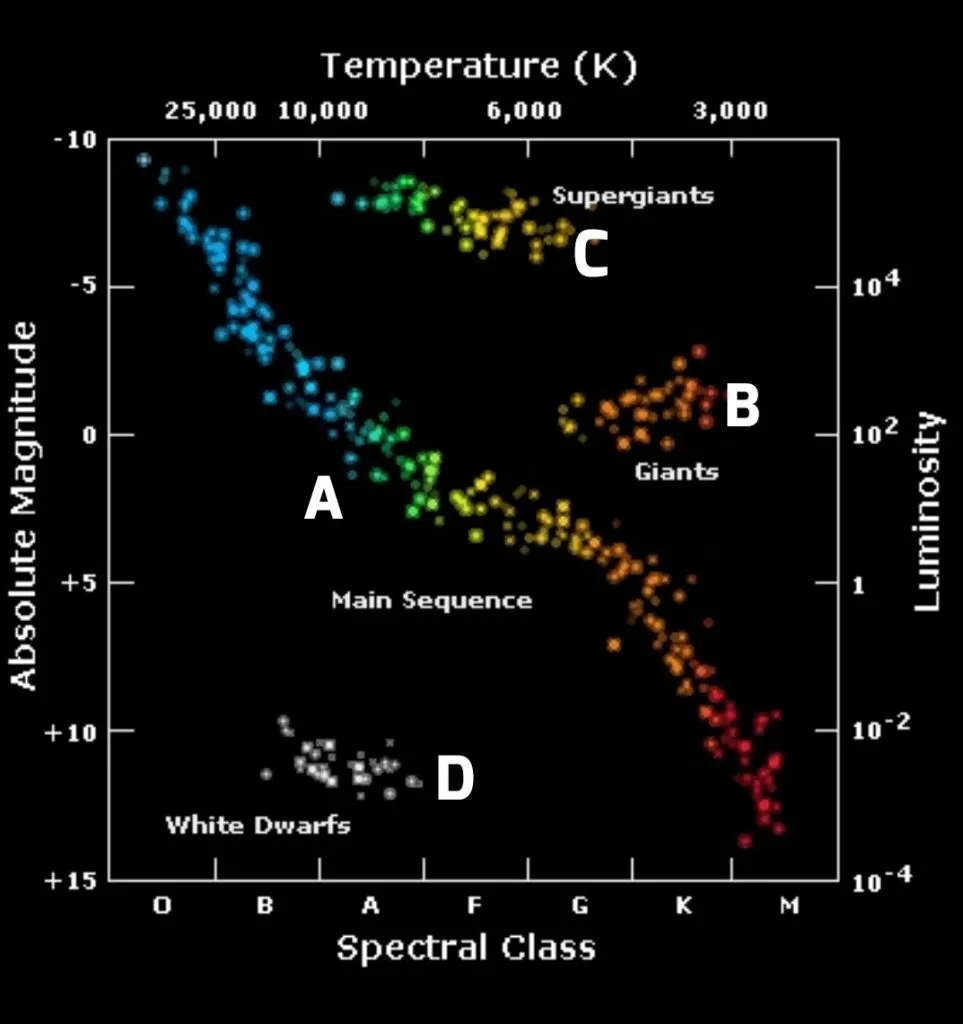
Where are the red giants and supergiants?
Top right

Where are the main sequence stars?
Middle of the HR diagram stretching from top left to bottom right

Where are the white dwarfs?
Bottom left of the HR diagram
Red-shift
A change in frequency that is shifted towards the red end of the spectrum showing that the source is moving away from the observer.
Planet Orbits
Around the Sun, almost circular.
Gravity in Orbits
Gravity is always acting on the object and pushing towards the centre of the orbit so the object constantly changes direction.
Orbital Radius
Faster objects will have smaller orbital radii than slower ones.
Comet vs Planet/Satellite
Very elliptical vs slightly elliptical
Longer orbital periods vs shorter orbital periods
Travels much faster when closer to the Sun vs Travels at an even speed throughout
Geostationary Satellites
They have the orbit of one day so they are always in the same place above the Earth