Immune exam review
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
What is immunology?
the study of the immune system, immune response, and molecular mechanisms that help defend against microbial attacks or other foreign substances.
the immune system protects against…
pathogens (viruses, bacteria, protists, fungi, and parasites), cancer cells, and cells of differentiated blood types
define immune response
collective and coordinated response to the introduction of foreign substances
define the immune system
a system of cells, tissues, and their soluble products that recognize, attack, and destroy foreign entities that endanger health.
the ___ is the central player in maintenance of homeostasis and human health
immune system
malfunctioning of the immune system may result in…
autoimmune diseases, transplant rejection, hypersensitivity and allergy, immunodeficiency.
[transition of immunology into experimental science, role of modern molecular bio]
present at birth, highly nonspecific, no immunological memory, most evolutionarily conserved arm of the immune system
innate immunity
highly specific, activated after exposure to pathogens and acquired during one’s lifetime, highly specific and retains immunological memory
adaptive/acquired immunity
which immunity is only present in vertebrates?
acquired/adaptive immunity
what are the three phases of the host immune defense? just list
Non-induced, non-specific innate responses
induced innate responses
specific adaptive immune response
the innate response of immune defense involves ___ defense barriers. (give examples)
primary. ex: skin, epithelial barriers, mucous membranes, salivary enzymes, lacrimal secretions, pH
phagocytosis, target cell lysis, inflammatory responses, and complement action are all parts of which phase of innate immunity?
induced innate responses
specific adaptive immune response involves ___ and ___
B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes
along with epithelial barriers, ___ cells are major components of the innate immune response
phagocytic cells
what are epithelial barriers in immunity?
the major interfaces between the body and the external environment that provide physical and chemical barriers (defensins) against infection- skin, GI tract, respiratory tract, genitourinary tract.
The two types of circulating phagocytes, ___ and ___, are blood cells that are recruited to sites of infection, where they recognize and ingest microbes for intracellular killing
neutrophils and monocytes
the most abundant leukocytes in the blood. these cells ingest microbes in the circulation and rapidly enter extravascular tissues at sites of infection, where they also phagocytose and destroy microbes.
neutrophils
neutrophils are also called
polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs)
during inflammatory reactions, these cells enter extravascular tissues and differentiate into cells called macrophages.
monocytes
blood ___ and tissue ___ are two stages of the same cell lineage, which is often called the ___ system
monocytes, macrophages. mononuclear phagocyte system
these cells function as sentinels in tissues that respond to microbes by producing numerous cytokines, which serve two main functions: they initiate inflammation, and they stimulate adaptive immune responses
dendritic cells
dendritic cells capture ___. why?
protein antigens. they display fragments of these antigens to T cells (antigen presenting cells)
these cells recognize infected and stressed cells and respond by killing these cells and secreting interferons (macrophage-activating cytokine).
natural killer cells
describe how natural killer cells induce cell death.
they secrete perforin, a protein that creates pores in the target cell’s membrane. Unregulated diffusion of ions and molecules through the pores causes osmotic imbalance, causing swelling and rupture of infected cell.
the complement system is a collection of ___ that are important in ___
membrane-associated proteins, defense against microbes
complement activation culminates in…
the formation of a polymeric protein complex (membrane attack complex) that inserts into the microbial cell membrane, disturbing the permeability barrier and causing osmotic lysis
tissue reaction that delivers mediators of host defense—circulating cells and proteins—to sites of infection and t issue damage.
inflammation
describe the steps producing inflammation
bacteria introduced at wound site. activated macrophages engulf the pathogens and secrete cytokines and chemokines
mast cells in the area are activated by the tissue damage and release histamine
histamine and cytokines dilatate local blood vessels and increase their permeability. The cytokines also make the vessel wall sticky, causing neutrophils and monocytes to attach.
chemokines attract neutrophils and monocytes, which squeeze out of the blood vessel wall and migrate to the infection site
newly arrived monocytes differentiate into macrophages. neutrophils and macrophages engulf pathogens and destroy them.
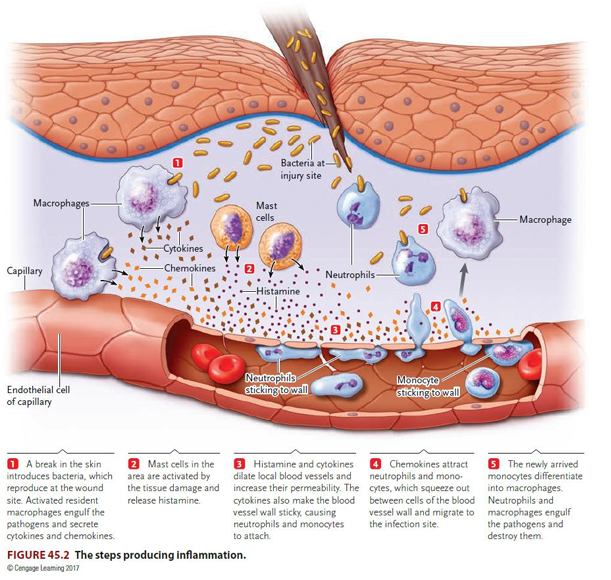
in response to pathogens, the initial release of ___, ___, and other mediators by mast cells and macrophages causes ___
histamine, prostaglandins; causes increased blood flow and exudation of plasma proteins, which contributes to redness, warmth, and swelling associated with inflammation
adaptive immune responses are carried out by
white blood cells called lymphocytes
what are the two broad classes of active immune responses?
antibody-mediated/humoral responses
cell-mediated responses
are T/B-lymphocytes the same as T/B cells?
yes
antibody/humoral responses are carried out by ___ lymphocytes, while cell-mediated responses are carried out by ___ lymphocytes
antibody - B
cell - T
describe the antibody-mediated immune response
B cells are activated to secrete antibodies, which are proteins called immunoglobulins.The antibodies circulate in the bloodstream and permeate the other body fluids, where they bind to the foreign antigen that stimulated their release.
antibodies are secreted forms of ___, secreted by ___.
immunoglobulins are present as cell surface-bound molecules on ___
antibodies are secreted forms of immunoglobulins, secreted by plasma B-cells.
immunoglobulins are present as cell surface-bound molecules on naive B-cells.
binding of antibody inactivates viruses and microbial toxins by
blocking their ability to bind to receptors on host cels.
___ marks invading pathogens for destruction by making it easier for phagocytic cells of the immune system to ingest them
antibody binding
describe the cell-mediated immune response
T cells recognize foreign antigens that are bound to MHC proteins on the surface of host cells such as dendritic cells, which are specialized for presenting antigen to T cells (therefore often referred to as antigen-presenting cells (APCs).
because MHC proteins carry fragments of pathogen proteins from inside a host cell to the cell surface, T cells can detect pathogens hiding inside a host cell and either kill the infected cell or stimulate phagocytes of B cells to help eliminate the pathogens.
T cells can only recognize antigens presented on antigen presenting cells in the context of
an MHC
T cells develop in the ___, B cells develop in the ___
T cells: thymus
B cells: bone marrow
list the 5 phases of adaptive immune response
antigen recognition, lymphocyte activation, antigen elimination, contraction and restoration of homeostasis, development of immunological memory
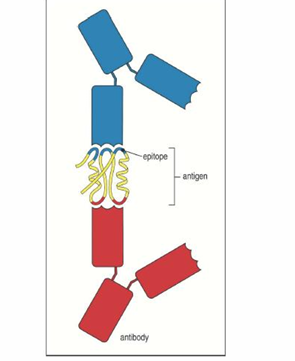
define the following: antigen, epitope, paratope
antigen - any foreign molecule that triggers an adaptive immune response
epitope (or antigenic determinant) - the small specific part of the antigen that the antibody molecules bind to
paratope - the corresponding site on the antibody that binds to an epitope
list the three ways antibody-bound antigens are processed to protect the host from infection
neutralization - inhibit the toxic effects or infectivity of pathogens by binding to them
opsonization - by coating the pathogens, they can enable accessory cells that recognize the Fc portions of arrays of antibodies to ingest and kill the pathogen
complement system activation
how are the polypeptide chains in antibodies, B cell receptors, and T cell receptors different?
B cell receptor - Y shaped immunoglobulin molecule with a transmembrane tail that anchors it in the plasma membrane. it has 2 identical antigen binding sites
antibody - differentiated from a B cell receptor, so very similar but without the transmembrane region
T cell receptor - one antigen binding site
antigens bind to the ___ regions
variable
differences in the ___ regions define 5 main isotopes/classes of immunoglobulin, which have different functions in the immune response
heavy-chain C
which immunoglobulins are monomers? What are the structures of the others?
monomers: IgG, IgD, IgE
IgA is a dimer
IgM is a pentamer
___ is always the first class of antibody to be secreted in an immune response. it is secreted as a ___ of immunoglobulin
IgM, pentamer
___, ___, and ___ are the main antibodies present in blood, lymph, and the fluid in connective tissues
IgM, IgA, and IgG
What is the most abundant antibody circulating in the blood and lymphatic system? It is produced in large amounts when the body is exposed a second time to the same antigen
IgG(γ)
these antibodies are produced in response to parasites and, in genetically susceptible individuals, to otherwise harmless environmental antigens (allergens).
IgE
5 steps of antibody-mediated immunity
Engulfment of bacterium
degradation of bacterium and release of antigens
Presentation of antigens on dendritic cell surface
Interaction of APC with lymphocyte
Activation of T cell
in antibody-mediated immunity, a bacterium is taken up by a ___ cell by ___
dendritic cell by phagocytosis
in antibody-mediated immunity, the bacterium is degraded within a ___. the released bacterial protein fragments act as ___
lysosome; antigens
in antibody-mediated immunity, antigens bind to ___ within the cell, resulting in an antigen-presenting cell (APC).
class II MHC proteins
in antibody-mediated immunity, the APC presents the antigen to ___ with a receptor that recognizes the antigen.
a CD4+ T cell
in antibody-mediated immunity, the ___ receptor binds directly to the ___ protein, resulting in the APC and T cell becoming linked.
CD4+ receptor binds to the class II MHC protein
in antibody-mediated immunity, the APC secretes ___, which ___
interleukins, which activate the T cell
the phenomenon whereby we develop long-lasting immunity to many common infectious diseases after our initial exposure to the pathogen, either through natural infection or vaccination.
immunological memory
how does the response to the same antigen change upon multiple exposures?
the secondary response is much quicker and more specific to a certain antigen the second time the immune system encounters it.
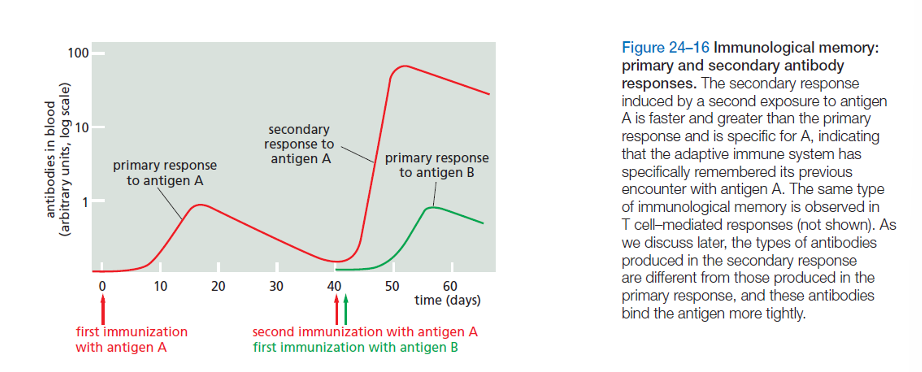
active immunity
production of antibodies in the body in response to exposure to a foreign antigen. immunological memory is produced by a primary immune response
passive immunity
acquisition of antibodies from another person, including antibodies passed from parent to child through the placenta or breast milk.
what are the uses of antibodies in research?
immunohistochemistry techniques: ELISA, immunoblotting
monoclonal antibody production - hybridoma technology
What are the steps of cell-mediated immunity?
Presentation of antigens on cell surface
activation of T cell
Production of cytotoxic T cells
Attack of infected cell by cytotoxic T cell
Destruction of infected cell
in cell-mediated immunity, viral proteins are degraded into fragments that act as antigens. The antigens are displayed on the cell surface bound to ___, making the cell an antigen presenting cell APC
class I MHC proteins
in cell-mediated immunity, the APC presents the antigen to a ___ cell with a receptor that recognizes the antigen. this cell receptor binds directly to the ___, resulting in ___
APC presents antigen to a CD8+ T cell
CD8 receptor binds directly to the class I MHC protein, resulting in the APC and T cell linking, which in addition to the secretion of interleukins by the T cell, activate the T cell.
in cell-mediated immunity, what happens after the CD8+ T cell is activated?
it proliferates to form a clone. Many of these cells differentiate into cytotoxic T cells, which fight infection. Some differentiate into memory cytotoxic T cells, which live long and respond rapidly if the same antigen is encountered later
cytotoxic cells are a type of ___
effector T cell
in cell-mediated immunity, what happens after the T cell receptor on a cytotoxic T cell recognizes the antigen bound to a class I MHC protein on the infected cell?
the T cell releases perforins
type 1 diabetes, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis are all ___
autoimmune diseases (increased immune response)
type 1 diabetes
an autoimmune reaction against the pancreatic beta cells producing insulin
lupus
produces antibodies against blood cells, platelets, mitochondria, and proteins associated with DNA
rheumatoid arthritis
attacks connective tissues in the joints, causing pain and inflammation
multiple sclerosis
attacks myelin sheaths of neurons
substances responsible for allergic reactions form a distinct class of antigens called allergens, which induce ___ to secrete an overabundance of ___. This results in ___
B cells, IgE antibodies. this results in the release of histamine, producing severe inflammation.
antihistamines counter the effects of what type of cell?
mast cells