Stereochemistry
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Primary Carbon
carbon atoms bonded to exactly one other carbon atom
secondary carbon
carbon atoms bonded to exactly two other carbon atoms
tertiary carbon
carbon atoms bonded to exactly 3 other carbon atoms
Quaternary carbon
carbon atoms bonded to exactly 4 other carbon atoms
methyl carbons
exactly 3 attached hydrogen atoms
methylene carbons
exactly 2 attached hydrogen atoms
methine carbons
exactly 1 attached hydrogen atom
normal line on 3D depiction
the bond is in the same plane as the page
hashed line on 3D depiction
the bond is projected into the page away from the viewer
bold wedged line on 3D depiction
bond is projected out of the page towards the viewer
Unambiguous depiction
the wedge and hash must be adjacent and the in plane bonds must be adjacent
stereoisomer
compounds with the same molecular formula and the same connectivity between atoms but a different 3D arrangement of those atoms in space
conformational isomers or conformers
stereoisomers arising from rotation around a single bond
Newman Projections
depicts the 3D arrangement of bonds on 2 adjacent atoms as viewed along the bond joining 2 atoms
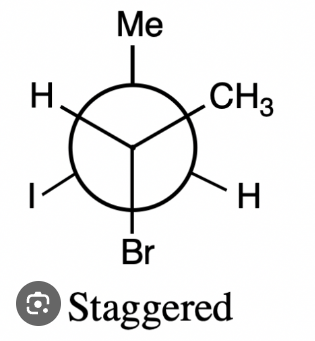
Staggered conformers
are a type of conformational isomer where substituents on adjacent carbons are oriented to minimize steric strain, resulting in a lower energy state.
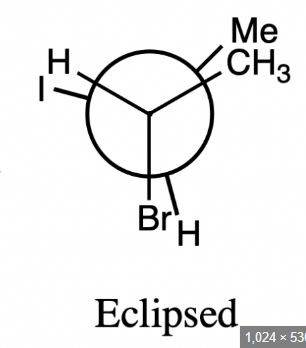
Eclipsed conformers
are conformational isomers where the substituents on adjacent carbons are aligned to maximize steric strain, resulting in a higher energy state.
torsional strain
energetic penalty for eclipsing interactions of hydrogen-hydrogen interactions on adjacent atoms
steric effects
in eclipsed conformers, the hydrogen atoms are closer in space and repel each other
result from repulsive interactions between atoms that are close in space
anti-conformer
the lowest energy, staggered conformer that has 180 degree angle between the two largest groups - the global minimum
gauche conformer
gauche conformation - local minimum with a 60 degree angle between the two largest groups, resulting in some steric strain
syn conformer
the staggered conformer with a 0 degree angle between the two largest groups, leading to increased steric strain. - global max
cycloalkanes
organic compounds containing only C-C and C-H single bonds and at least one ring
general formula for cycloalkanes with exactly 1 ring
CnH2n
naming cycloalkanes
same as IUPAC just use prefix cyclo- in name of parent hydrocarbon
cycloalkanes cannot rotate around single bonds bc…
there is not enough room for rotation to occur without rupturing the ring → results in cis/trans isomers
cis isomers
the groups are on the same side of the ring
trans isomers
the groups are on opposite sides of the ring
when are the cis/trans labels only used
disubstituted rings - two groups - although the ring can be of any size
angle strain
since an ideal sp3 hybridized carbon atom has bond angles of 109.5 degrees - significant bond angle distortions would be expected for very small rings and very large rings
overall ring strain
combination of angle strain, torsional strain, and steric strain
strain trends
-3 membered and 4 membered rings are highly strained
-6 membered rings and rings with 14 or more atoms are essentially strain free
-7-11 membered rings (medium rings) are moderately strained
most commonly encountered rings in Orgo
5-6 atoms - these are often found in naturally occurring compounds such as steroids' and sugars
cyclohexane
the most important ring in orgo
it is virtually strain free bc it can adopt 2 chair conformations with bond angles very close to the ideal 109.5
axial bond positions in a chair conformer
up and down alternate as you move around the ring
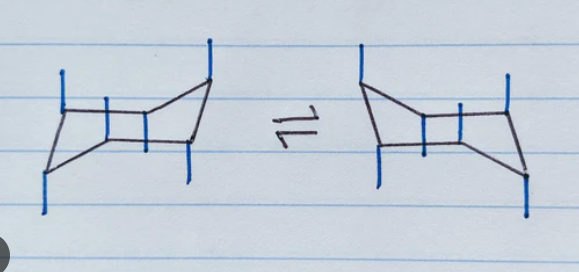
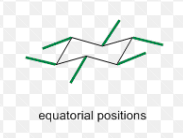
equatorial bonds in a chair conformer
up and down alternate as you move around the ring
ring flip or chair flip
the process of switching between the 2 chair conformers
“pulling down” one corner of the chair while simultaneously “pulling up” the other corner
there is significant energy available at room temp to make the interconversion rapid
Tracking substituent groups during chair flip
a chair flip converts all axial bonds into equatorial bonds and vice versa
a chair flip maintains the “up” or “down” designation of each bond within the ring
substituted cyclohexanes
one or more of the hydrogens have been replaced by a different group
axial vs equatorial positions relative energies
axial conformers have higher energy than equatorial conformers - bc there are more analogous gauche interactions in axial conformers
A-value
difference in energy between the axial and equatorial isomers for a particular monosubstituted cyclohexane
Trends in A-values
chloro-, bromo-, and iodo- substituents have almost the same a-value - due to atoms getting bigger but bonds getting longer which cancels
methyl, ehtyl, and isopropyl groups have almost the same A-value - bond rotation minimizes unfavorable steric interactions
tert-butyl group has a very lg A-value - no way to minimize steric interactions via bond rotation
Wedge and hash in chair conformers
wedge = up position in chair conformer
hash = down position in chair conformer
hidden gauche interactions
there are “hidden” gauche interactions for any chair conformer in which at least one of the substituent groups is equatorial
in general only occur when 2 of the same group are right next to each other
bicyclic compound
organic compound that contains 2 rings
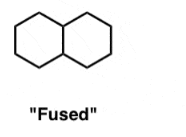
fused bicycles
2 rings share a common bond and the ring fusion can be either trans or cis
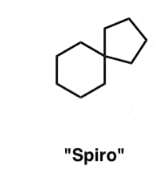
spiro compounds
2 rings share a common atom
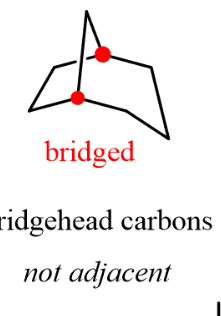
bridged bicycles
contain a chain of one or more atoms that bridge a larger ring
atoms at the intersection of the larger ring and bridge - bridgehead atoms
polycyclic compounds
compounds that contain more than 2 rings
superimposable
when 2 objects are superimposable - they can be overlapped such that all corresponding parts match up exactly
can completely align all atoms and bonds
chiral
not superimposable with its mirror image
mirror images but cannot rotate in space and make identical
best way for an atom to be chiral - sp3 hybridized with 3 different groups attached
4 different groups (chiral center) and no symmetry
achiral
is superimposable with its mirror image
any object that has an internal plane of symmetry MUST be achiral
has symmetry and can have a chiral center
chiral center/stereogenic center/stereocenter
most common way for an organic molecule to be chiral is for it to contain an atom with tetrahedral geometry bonded to 4 different substituent groups (chiral center)
such carbon atom is an asymmetric carbon or chiral carbon
Meso compound
specific molecule with 2 chiral centers but has symmetry
cannot have enantiomers bc have symmetry
enantiomers
have a mirror-image relationship
needs to be chiral (4 different groups and no symmetry)
flip all wedges to hashes and vice versa or draw mirror image
S and R flip
S + S → R + R
R + S → S + R
enantiomers always come in pairs
a compound and its non-superimposable mirror image
enantiomer configuration
the configuration at a chiral carbon CANNOT be changed via molecular rotations or translations → would require breaking or reforming bonds
a molecule or atom’s configuration
the specific molecular geometry arising from the spatial arrangement of atoms and bonds
enantiomer physical properties
in achiral environment
enantiomers have identical chemical and physical properties
in a chiral environment
enantiomers can have different physical properties
Diastereomer
2 compounds to be stereoisomers but are not mirror images
typically arise when we have more than 1 chiral center in a particular molecule
Meso or achiral compound
cis/trans association switching
How to draw a diastereomer
Keep 1 dash or hash and switch others or switch cis/trans depending on molecule
S/R - keep 1
RRS → RSS or RSR
R S → RR or SS
If you see a double bond you usually have a diastereomer - can distinguish between cis/trans - rotation about the pi bond
Diastereomer physical properties
Have completely different chemical and physical properties
racemic mixture
50:50 mixture of two enantiomers
optically inactive - does not rotate plane-polarized light
half of the molecules rotate light clockwise and other half rotate light counter-clockwise - canceling
What compounds are optically inactive?
racemic mixtures and achiral compounds
Absolute configuration of an individual stereocenter
R or S configuration
lowest priority must be pointing back in space (hash)
if not pointing back and is pointing forward (wedge) switch R and S
R or S included in front of name if there are stereogenic centers
R configuration
moving around the circle in clockwise direction based on priority groups
S configuration
moving around the circle in counter-clockwise direction based on priority groups
How to determine total possible number of stereoisomers
determine number of stereogenic centers = n
2^n = total possibilities
What is the stereochemical relationship between axial and equatorial chair conformers?
They are either enantiomers or diastereomers due to the differences in the axial and equatorial positions. If the original structure is achiral it cannot be an enantiomer so it is a diastereomer.
When are cis/trans applicable to naming?
In achiral molecules - have symmetry
When is R and S applicable to naming?
In chiral molecules - have stereocenters
Can chirality occur at any atom?
Yes, not just carbon