Biochem - Lecture 4 Learning Objectives
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Proteins structure and peptide bond learning objectives
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
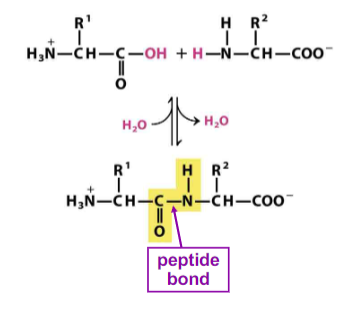
equation for peptide bond formation
condensation reaction
peptide bond conformation refers to what?
the spatial arrangement of atoms around the peptide bond, which can be cis or trans
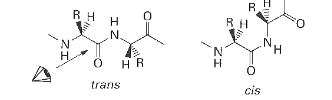
are peptide bond conformations typically cis or trans?
trans except Pro
why is Pro not always trans?
due to its cyclic shape
N-terminus
amino acid with a free amino group, marks the beginning of the protein
C-terminus
the amino acid with a free carboxyl group, marks the end of the chain
In what direction do we read an amino acid chain?
N-terminus to C-terminus
How are amino acid residues in a protein numbered?
they are numbered starting at the N-terminus and move toward the C-terminus, you know a new amino acid residue starts when you see another alpha carbon, so you can essential count the alpha carbons
linear projection structure of a short peptide of any given sequence
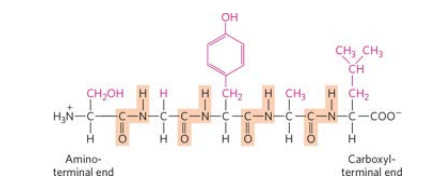
What is the charge of this peptide chain at pH = 8: TNMFDKR?
+1
what does the partial double bond character of a peptide bond do?
due to resonance, it prevents rotation around the bond and forces the atoms in the peptide bond to be in a planar configuration. which will significantly restrict the possible conformations of the chain
what is a steric effect?
a nonbonding interaction in a molecule that occurs when atoms occupy space too close to one another
what does the steric affect do?
influences the chain’s folding by favoring conformations that minimize interactions between bulky groups, determining the overall protein structure
what do steric effects arise from?
the spatial arrangement of side chains
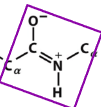
6-atom planar peptide group
refers to the six atoms that lie in the same plane within a peptide bond
what are the 6-atoms in the planar peptide group?
the carbonyl carbon, the carbonyl oxygen, the amide nitrogen, the amide hydrogen, and the two alpha carbons
What three categories can be found in the secondary structure of a protein?
alpha helix, beta sheet, and loops
alpha helix
backbone coiled (spiral) conformation with regular repeating rotation, residue by residue
in an alpha helix, what group is the hydrogen bond donor?
the amide nitrogen group
in an alpha helix, what group is the hydrogen bond acceptor?
the carbonyl oxygen
what is the chirality of the alpha helix?
right handed helix
how many residues per turn in an alpha helix?
4 amino acid residues
R groups point ___ from the helix axis
outward
what direction does the dipole moment move in on an alpha helix?
from C-terminus to the N-terminus
What terminus is negative on an alpha helix?
C-terminus
What terminus is positive on an alpha helix?
N-terminus
the packing density in an alpha helix is
relatively high, but depends on the amino acid and the environment
what components of amino acid residues in one helix directly contact what components of residues in the other helix?
the side chain of amino acid residues on one helix directly interact with the side chain of another amino caid residue
beta conformation (sheets)
an element of secondary structure in which the protein chain is nearly linear
in a beta sheet, what is the hydrogen bond acceptor group?
carbonyl oxygen group of the polypeptide backbone
in a beta sheet, what is the hydrogen bond donor group?
amide nitrogen group of the polypeptide backbone
What is the orientation of R groups in a beta pleated sheet?
the R groups on the peptide strand alternate sides in both parallel and antiparallel configurations
Are parallel beta sheets more stable or less?
less stable due to their hydrogen bond arrangement being bent
Are antiparallel beta sheets more stable or less?
more stable due to their hydrogen bond arrangement being straight
what is parallel beta conformation?
when the C-terminus of one sheet is next to the C-terminus of another sheet and their N-terminus are also next to each other
What is an antiparallel beta conformation?
when the C-terminus of one sheet is next to the N-terminus of another sheet
what is the most important noncovalent interactions stabilizing the alpha helix and beta conformations?
hydrogen bonding between the backbone amino group of one amino acid and the carbonyl oxygen of another amino acid located further down the peptide chain
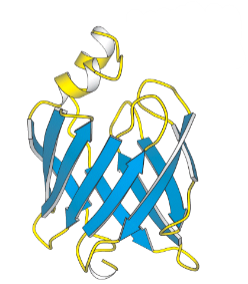
what do the blue arrows represent?
beta sheets
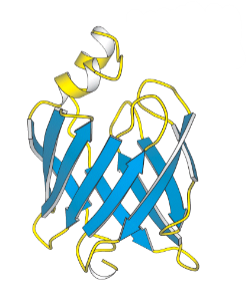
what do the yellow and white ribbons represent?
alpha helix
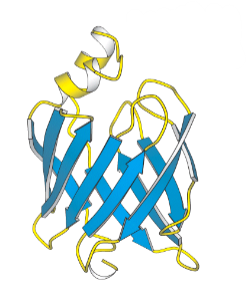
what do the yellow strings represent?
loops
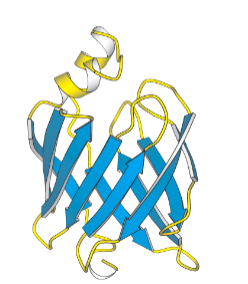
what does the head of the arrow represent?
C-terminus
what does the flat end of the arrow represent?
N-terminus
collagen
what is the chirality of collagen?
left handed
how many residues in a turn in a collagen helix?
3 amino acid residues
what is the pitch of a helix?
the vertical distance traveled along the axis of a helix to complete one full turn around the axis
what is the pitch of an alpha helix?
5.4 A/turn
what is the pitch for a collagen helix?
10 A/turn
collagen can form a very stable ___ ____
triple helix
collagen’s primary structure is made of
Proline, hydorxyproline (Hyp), and glycine
the individual polypeptide chain secondary structure of collagen is a
collagen helix
supersecondary structure for collagen is a
3-standard coiled coil, a triple helix
what is collagen in the human body?
a structural protein in connective tissue
is collagen flexible or inflexible?
collagen is very inflexible, or rigid
what is collagen helix stabilized by?
inherent kins in Pro and Hyp rings
the triple helix of collagen is stabilized by
H bonds between the backbone groups on different chains
secondary structure of alpha keratins
right handed alpha helix
supersecondary structure of alpha keratin
2 polypeptides with right handed alpha helices, coiled together in a left handed twist to give a 2 stranded supercoil
what is the quaternary structure of alpha keratin?
higher levels of assembly of multiple polypeptide chains
the supercoiled structure of alpha helices has great
tensile strength
What role do disulfide bridges play in alpha keratins?
they act as strong covalent bonds between cysteine amino acids, effectively cross-linking the protein chains and providing significant stability to the overall structure
What is the molecular basis for ascorbic acid definiency?
ascorbic acid acts as a cofactor for the enzymes responsible for hydroxylating Pro and Lys residues in collagen, and without it, collagen synthesis is impaired leading to weak and fragile blood vessels, skin, etc.
conformation
the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule
configuration
the fixed 3-D relationship of the atoms in a molecule, defined by the bonds between them
secondary structure
local regular conformations for parts of the peptide backbone of a protein
what is the rise of a helix?
the distance traveled along the axis of the helix for each amino acid residue
tertiary structure
3-D conformation of whole
polypeptide in its folded state
domain
a distinct, independently folding structural unit within a protein that carries a specific function
fibrous protein
big long extended cables (fibers) made up of proteins
globular protein
spherical proteins that are the most common and abundant proteins in nature
coiled coil (supercoil)
structural motif in proteins where two to seven alpha helices are coiled together like rope strands
amphipathic helix
an alpha helix with opposing polar (hydrophilic) and nonpolar (hydrophobic) sides
stacked beta sheets
a protein supersecondary structure where the beta sheets stack to form ribbons, then fibrils, and finally fibers