4.4: Product
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/34
Last updated 6:56 AM on 10/6/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
1
New cards
the marketing mix
product, place, price, promotion
2
New cards
what does a good marketing strategy do
meet customer needs
3
New cards
what must a business do to have a good marketing strategy
- design and product high quality products
- charge an acceptable price
- promote products to consumers
- make products available in the right place
- charge an acceptable price
- promote products to consumers
- make products available in the right place
4
New cards
stages of product development
- generating ideas
- analysis
- development
- test marketing
- commercialisation and launch
- analysis
- development
- test marketing
- commercialisation and launch
5
New cards
generating ideas
- ideas for new products come from business stakeholders and market research
- sometimes businesses try to improve features of a rival's product
- sometimes businesses try to improve features of a rival's product
6
New cards
analysis
product ideas are analysed and evaluated as marketable, possible and suitably fit legally
7
New cards
development
involves carrying out tests for change and modifications in products
8
New cards
test marketing
- this involves testing the product in a sample of the market which represents the whole market
- it's used to gather information about consumer opinion
- it's used to gather information about consumer opinion
9
New cards
commercialisation and launch
- businesses add the final touches to the product
- problems are resolved and changes are made
- marketing strategy is designed
- press conferences are launched
- problems are resolved and changes are made
- marketing strategy is designed
- press conferences are launched
10
New cards
a risk of the development stage
a number of product ideas are likely to be rejected but tend to fall at each stage
11
New cards
products
goods and services sold by a business
12
New cards
two types of goods
- consumer goods
- producer goods
- producer goods
13
New cards
why is packaging important
customers link quality of products with the packaging
14
New cards
factors influencing choice of packaging
- protection
- environment
- cost-effectiveness
- information
- design
- convenience
- environment
- cost-effectiveness
- information
- design
- convenience
15
New cards
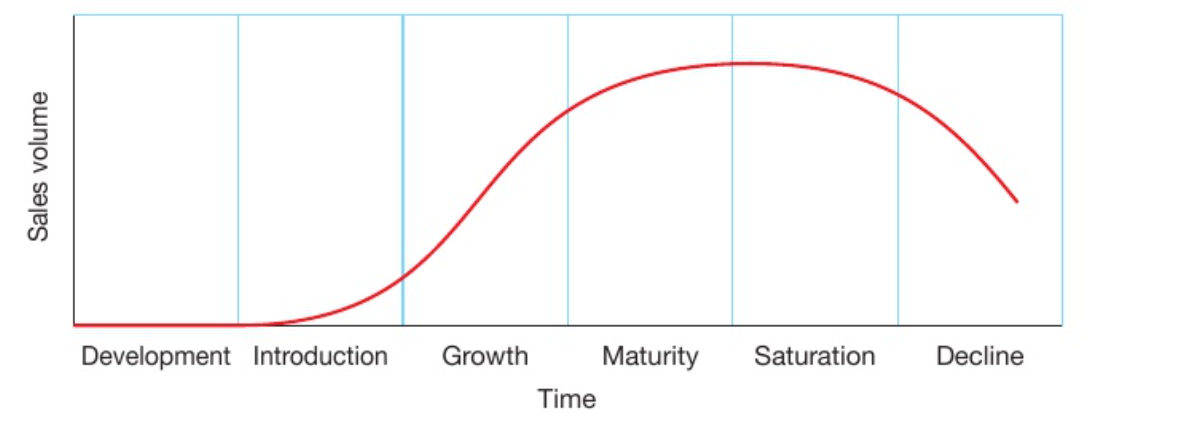
product life cycle
shows level of sales at different stages of the product
16
New cards
stages of the product life cycle
- development
- introduction
- growth
- maturity and saturation
- decline
- introduction
- growth
- maturity and saturation
- decline
17
New cards
development
- zero sales
- product research, design and testing
- high costs and can damage cash flow as most products don't make it past this stage
- product research, design and testing
- high costs and can damage cash flow as most products don't make it past this stage
18
New cards
introduction
- introduced through an official launch
- promotion strategies
- high costs and spending
- some businesses start with skimming and some with penetration pricing
- promotion strategies
- high costs and spending
- some businesses start with skimming and some with penetration pricing
19
New cards
growth
- sales grow if a product is successful
- increased revenue
- recovery of cost
- falling cost
- profit
- end of stage: products grow less quickly as competitors launch their own versions of the product
- increased revenue
- recovery of cost
- falling cost
- profit
- end of stage: products grow less quickly as competitors launch their own versions of the product
20
New cards
maturity and saturation
- improving cash flow
- profit
- saturated market
- falling price
- change in promotion methods
- profit
- saturated market
- falling price
- change in promotion methods
21
New cards
decline
- sales decline and products are taken off the market
- change in consumer taste and new product emergence
- businesses replace declining products with new ones
- different products have different life cycles
- change in consumer taste and new product emergence
- businesses replace declining products with new ones
- different products have different life cycles
22
New cards
fads
short life cycle
23
New cards
long established products
long life cycle
24
New cards
extension strategies
- lengthen the life of a product before it starts to decline
- help businesses generate more cash
- help businesses generate more cash
25
New cards
3 examples of extension strategies
- finding new markets
- finding new uses
- changing the appearance
- finding new uses
- changing the appearance
26
New cards
benefits of extension strategies
- sales levels and revenues can recover and grow
- competitors will find it difficult to enter the market
- consumers will be loyal
- competitors will find it difficult to enter the market
- consumers will be loyal
27
New cards
product portfolio
range of products that a business currently has available on the market
28
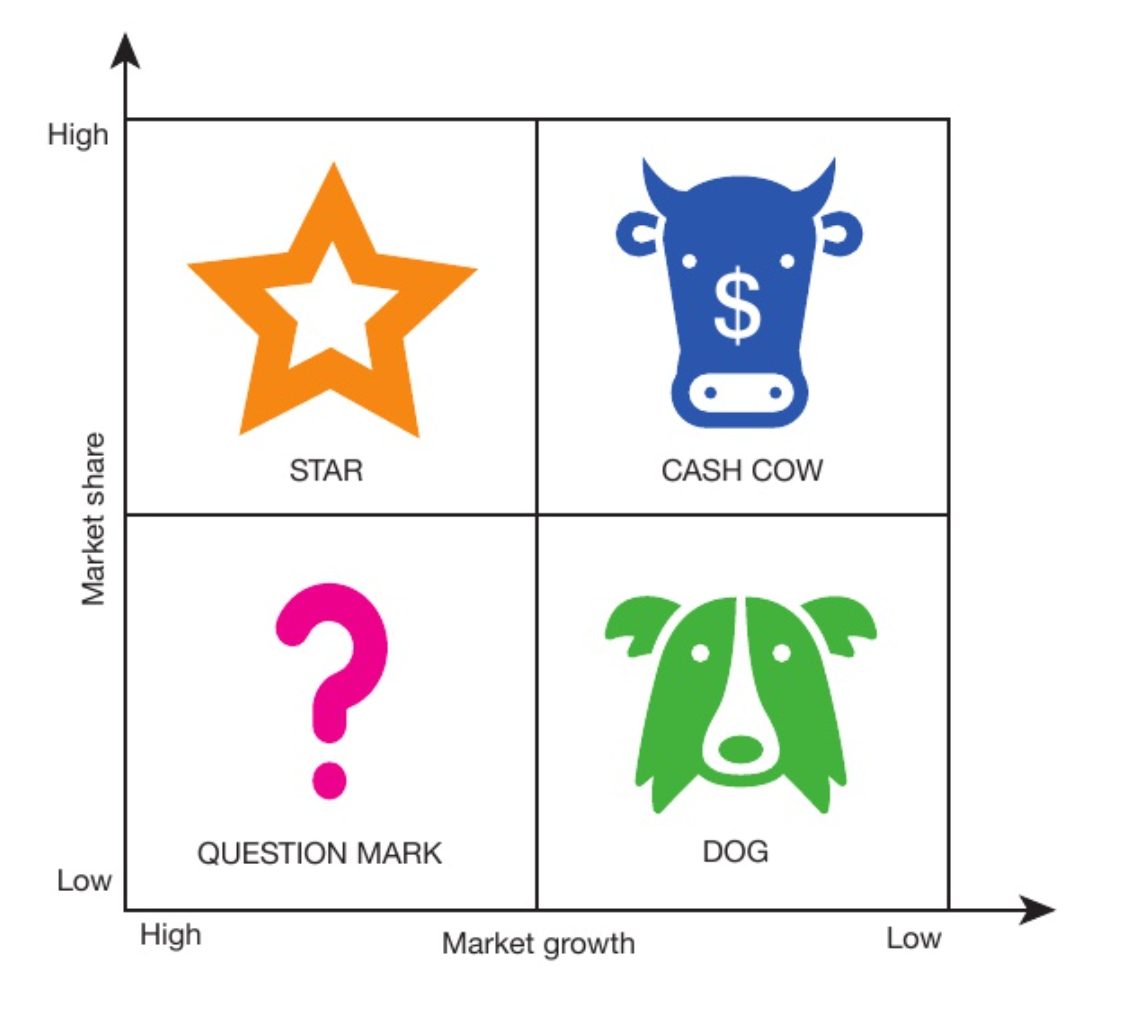
New cards
boston matrix
used to help analyse products marketed by a business
29
New cards
benefits of a product portfolio
- products decline and are replaced
- products are modified and extendes
- products are modified and extendes
30
New cards
significance of a boston matrix
helps businesses enable a product into appropriate categories according to market share and position in the life cycle
31
New cards
positions in the boston matrix
question mark, dog, star, cash cow
32
New cards
question mark
- low market share
- growing market
- potential
- growing market
- potential
33
New cards
dog
- end of life cycle
- low market share
- replaced
- low market share
- replaced
34
New cards
star
- valuable products
- high market share
- potential for growth
- profitable
- high market share
- potential for growth
- profitable
35
New cards
cash cow
- mature
- high market share
- not likely to grow
- steady flow of income
- high market share
- not likely to grow
- steady flow of income