Natural Hazards and Their Impact on Society
1/202
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
203 Terms
Geological Hazards
Natural hazards from land and tectonic processes.
Meteorological Hazards
Natural hazards from weather and climate phenomena.
Natural Hazards
Events causing social impact, property damage, or casualties.
Tectonic Hazards
Natural hazards like earthquakes and tsunamis.
Biological Hazards
Natural hazards such as forest fires.
Geomorphological Hazards
Natural hazards including mudslides and avalanches.
Atmospheric Hazards
Natural hazards related to wind, like hurricanes.
Vulnerability
Population exposure increases risk from natural hazards.
Capacity to Cope
Ability to manage extreme events reduces risk.
Hazard Risk
Likelihood of being affected by natural hazards.
Economic Factors
Job dependency may prevent relocation from hazards.
Social Factors
Language barriers can hinder evacuation efforts.
Flood Risk
Living near rivers for fertile land increases risk.
Cost of Land
Affordability drives habitation in hazardous areas.
Climate Change
Increased CO2 leads to more extreme weather events.
Densely Populated Areas
High population density amplifies hazard impact.
Tectonic Plates
Large sections of Earth's crust that move.
Extreme Weather
Severe weather events like heatwaves or cold spells.
Tsunamis
Large ocean waves caused by underwater tectonic activity.
Avalanche
Rapid flow of snow down a slope.
Oceanic Crust
Thin layer of Earth's crust beneath oceans.
Continental Crust
Thick layer of Earth's crust forming continents.
Destructive Plate Margin
Where plates collide, forming mountains and earthquakes.
Continental-Continental Collision
Plates crumple to create mountains without volcanoes.
Continental-Oceanic Subduction
Oceanic plate subducts, forming magma and volcanoes.
Friction in Plate Boundaries
Causes earthquakes due to plate movement.
Conservative Plate Margin
Plates slide past each other, causing earthquakes.
San Andreas Fault
Example of a conservative plate margin in California.
Constructive Plate Margin
Plates move apart, allowing magma to form new rocks.
Shield Volcanoes
Formed by long-flowing lava from constructive margins.
Primary Effects
Immediate impacts of natural hazards on people/property.
Secondary Effects
Long-term consequences of natural hazards.
Immediate Response
Actions taken immediately after a natural hazard.
Long-term Response
Actions taken over time after a natural hazard.
Gross National Income (GNI)
Total income of a country divided by its population.
High Income Country (HIC)
Country with GNI over $12,616 per person.
Low Income Country (LIC)
Country with GNI less than $12,000 per person.
Nepal Earthquake 2015
LIC earthquake causing 9000 deaths and homelessness.
Avalanches from Earthquake
Triggered by Nepal earthquake, killing 18 on Everest.
Immediate Response in Nepal
250,000 ex-servicemen recalled for disaster assistance.
Long-term Preparedness in Nepal
Government education schemes to improve disaster readiness.
Amatrice Earthquake 2016
HIC earthquake causing 229 deaths and €21.9 billion damage.
Psychological Damage
Long-term mental health effects from disasters.
Monitoring Earthquakes
Seismometers track movements for early warning systems.
Monitoring Volcanoes
Signs of eruptions include gas and shape changes.
Building Protection Strategies
Reinforced structures reduce earthquake damage.
Emergency Planning
Evacuation routes and supplies prepared for disasters.
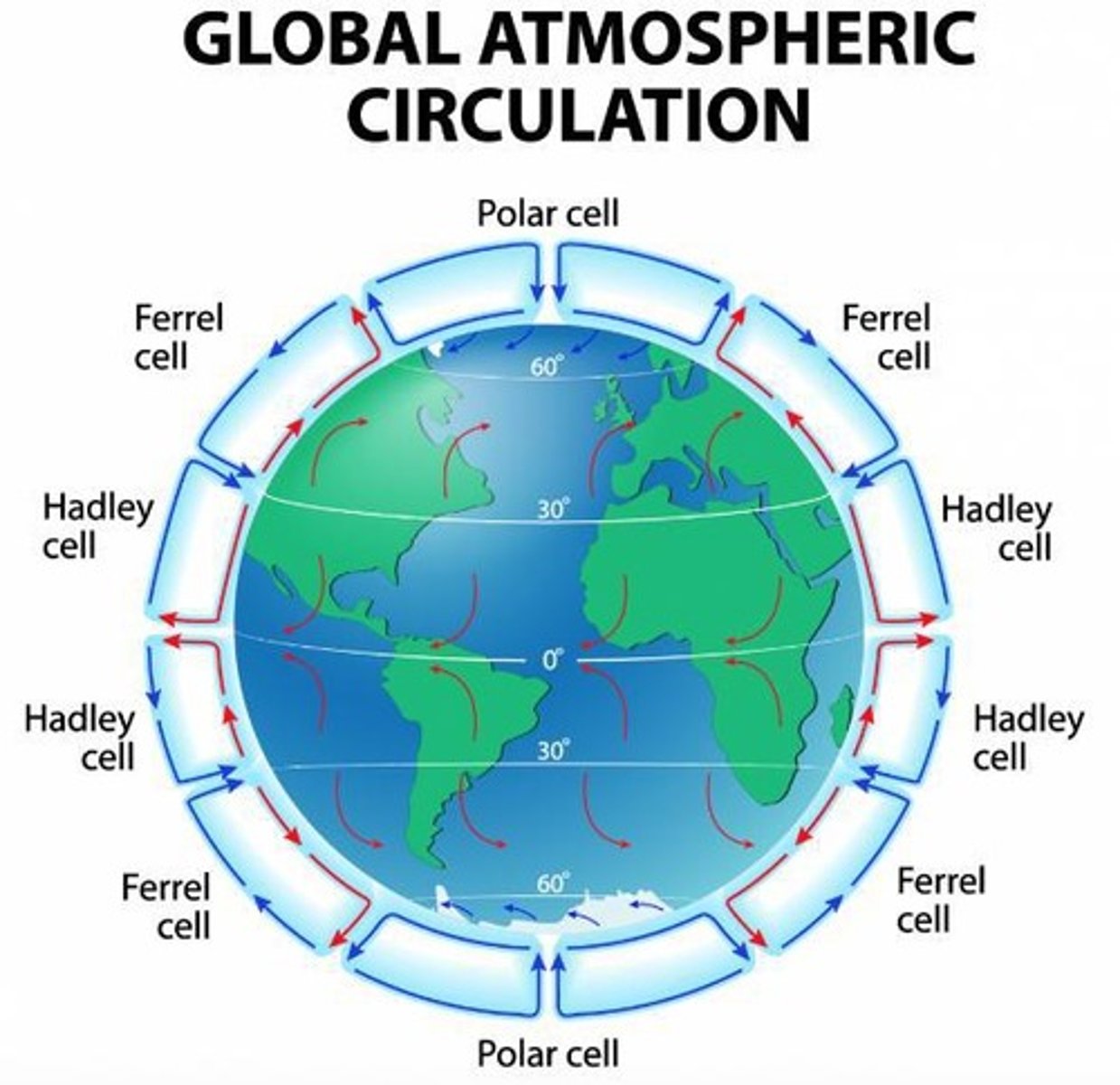
Global Atmospheric Circulation
Heat transfer from equator to poles via air movement.
Air Pressure
Differences in atmospheric pressure causing wind movement.
Wind
Air movement from high to low pressure areas.
Atmospheric Circulation
Global air movement in loops called cells.
Cells
Loops of air circulation in the atmosphere.
Polar Cell
Circulation cell at polar regions with cold air.
Ferrel Cell
Mid-latitude circulation cell between polar and Hadley cells.
Hadley Cell
Tropical circulation cell with warm rising air.
Surface Winds
Winds created by atmospheric pressure differences.
Tropical Storms
Storms forming between 5-30 degrees latitude.
Sea Temperature
Must be 27°C or higher for tropical storms.
Wind Shear
Change in wind speed/direction with altitude.
Evaporation
Process of water turning into vapor from heat.
Condensation
Process of water vapor turning back into liquid.
Typhoon Haiyan
Devastating tropical storm impacting the Somerset levels.
Primary Effects
Immediate impacts like flooding and damage.
Secondary Effects
Consequences like job loss and crop destruction.
Economic Impact
Financial losses due to disasters and recovery costs.
Management Strategies
Plans to mitigate future flooding risks.
Prediction and Monitoring
Using technology to forecast storm paths.
Protection Strategies
Designing buildings to withstand storm impacts.
UK Weather Hazards
Severe weather events affecting the UK.
Heat Waves
Extended periods of excessively high temperatures.
Climate Change
Long-term alteration in temperature and weather patterns.
Quaternary Period
Time of fluctuating climate between warm and cold.
Ice and sediment cores
Analyze trapped gases to determine historical temperatures.
Tree rings
Count rings to assess tree age and climate conditions.
Burning fossil fuels
Releases CO2, contributing to climate change.
Methane production
Farming generates significant methane emissions.
Deforestation
Removes CO2 absorbers, increasing atmospheric CO2.
Volcanic eruptions
Eject materials that can cool Earth's surface.
Reduced solar output
Lower solar energy can cool certain areas.
Mitigation
Actions to reduce long-term risks from climate hazards.
Adaptation
Adjusting to climate change impacts to minimize damage.
CO2 emissions reduction
Methods to lower carbon emissions for climate mitigation.
Biodiversity increase
Planting trees can enhance ecosystem diversity.
Debt for nature swaps
Financial agreements to protect forests in developing countries.
Carbon capture and storage
Storing CO2 emissions in geological formations.
Desalination plant
Produces drinking water from salty river water.
Reverse osmosis
Process used in desalination to filter water.
Flood warning systems
Improved alerts for rising sea levels and floods.
Flood barriers
Physical defenses to protect against flooding.
Agricultural adaptation
Changing crops or locations for better climate suitability.
Tree planting project
UK initiative to increase forests in Brazil.
CO2 storage potential
Trees could store 55% of global CO2 emissions.
Water meters
Devices to discourage excessive water usage.
Climate vulnerability reduction
Actions to make populations less susceptible to climate impacts.
Tundra
High latitude ecosystem with mosses and low shrubs.
Grassland
Savannahs have distinct dry and wet seasons.
Hot Deserts
Very hot, dry, little rainfall, cacti present.
Tropical Rainforest
Equatorial ecosystem with dense, layered vegetation.
Polar Regions
Icy, dry areas with short growing seasons.
Boreal Forest
Coniferous forest found at 50-60 degrees North.