Midterm 2 All Flashcards
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/116
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
1
New cards
-Multicellular eukaryotes
-Heterotrophs
-Cells lack cell walls
-Collagen
-Heterotrophs
-Cells lack cell walls
-Collagen
What is an animal?
2
New cards
-comprises fibers in connective tissues
-most abundant protein in animal bodies
-flexible, high tensile (stretchy), strength, high elastic resilience (returns energy)
-most abundant protein in animal bodies
-flexible, high tensile (stretchy), strength, high elastic resilience (returns energy)
What is collagen?
3
New cards
-skin: dense irregular arrangement of collagen
-ligament (connect bones): collagen arranged in sheets
-tendon (connects muscles to bones): cable-like arrangement of collagen
-ligament (connect bones): collagen arranged in sheets
-tendon (connects muscles to bones): cable-like arrangement of collagen
What are the different collagen arrangements?
4
New cards
-sexually with diploid stage dominating the life cycle
-sperm fertilizes egg → zygote
zygote undergoes rapid cell division → cleavage
-sperm fertilizes egg → zygote
zygote undergoes rapid cell division → cleavage
How do animals reproduce?
5
New cards
-collections of specialized cells with a common function, isolated from other tissues by membranous layers
What are tissues?
6
New cards
-germ layers give rise to the tissues and organs of the animal embryo
What are germ layers?
7
New cards
-cell cleavage
What leads to a blastula?
8
New cards
-hollow blastula undergoes gastrulation
-forms a gastrula with layers of embryonic tissues
-forms a gastrula with layers of embryonic tissues
What undergoes gastrulation and what does it form?
9
New cards
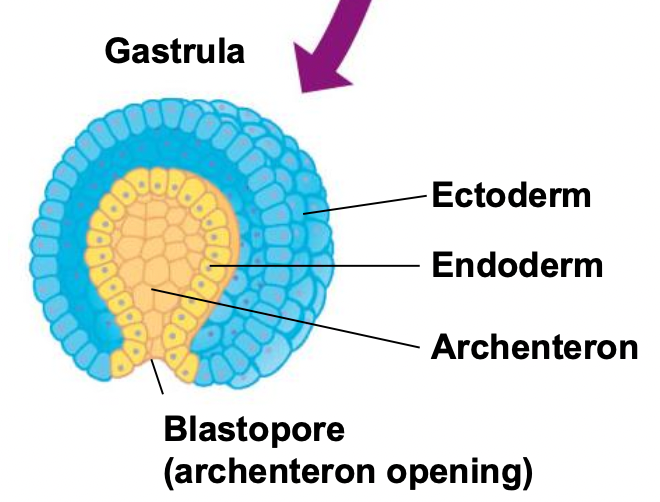
-ectoderm: covers embryo's surface
-endoderm: innermost germ layer and lines the developing digestive tube →archenteron
-archenteron
-endoderm: innermost germ layer and lines the developing digestive tube →archenteron
-archenteron
What are the different embryonic tissue layers in a gastrula?
10
New cards
-sponges
What animals lack true tissues?
11
New cards
-have ectoderm and endoderm
-coral, jellyfish, comb jellies
-coral, jellyfish, comb jellies
What are diploblastic animals and give some examples.
12
New cards
-have ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm layer (in between ectoderm and endoderm)
What are triploblastic animals?
13
New cards
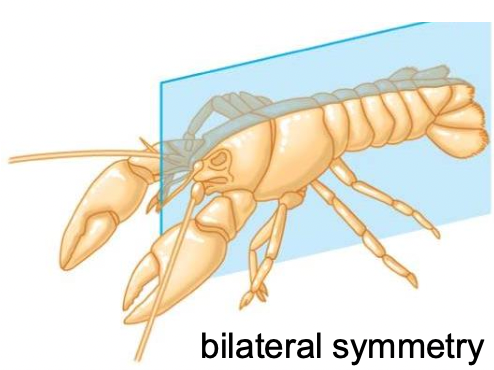
-multicellular animals other than sponges and cnidarians
-Characteristics: bilateral symmetry, cephalization (organization of senses and locomotion toward a head region)
-Characteristics: bilateral symmetry, cephalization (organization of senses and locomotion toward a head region)
What are bilaterians and what are some of their characteristics?
14
New cards
-larva: sexually immature and anatomically distinct from an adult; undergoes metamorphosis
-juvenile: resembles an adult but is not sexually mature
-juvenile: resembles an adult but is not sexually mature
What are some characteristics of a larval stage?
15
New cards
-(535 to 525 million years ago) marks the earliest fossil appearance of many major groups of living animals
-new predator-prey relationships
-rise in atmospheric oxygen
-evolution of the Hox gene complex
-new predator-prey relationships
-rise in atmospheric oxygen
-evolution of the Hox gene complex
What is the Cambrian explosion and what are some possible causes?
16
New cards
-regulate other genes and control the development of body form
What are Hox genes?
17
New cards
-deuterostomes
-lophotrochozoa
-ecdysozoa
-lophotrochozoa
-ecdysozoa
What are the three major groups that separate bilateral animals?
18
New cards
-cell proliferation following fertilization by spiral cleavage
-coelom (body cavity) forms within the middle tissue germ layer
-initial opening into the gut becomes the mouth
-coelom (body cavity) forms within the middle tissue germ layer
-initial opening into the gut becomes the mouth
What is a protostome?
19
New cards
-cell proliferation following fertilization by radial cleavage
-coelom forms from outpocketing of the middle tissue germ layer
-initial opening into the gut becomes the anus
-coelom forms from outpocketing of the middle tissue germ layer
-initial opening into the gut becomes the anus
What is a deuterostome?
20
New cards
-smallest genome
-only four cell types
-no symmetry
-no organs
-no muscles
-no nervous system
-only four cell types
-no symmetry
-no organs
-no muscles
-no nervous system
What are the characteristics of the phylum placozoa?
21
New cards
-sponges
-Characteristics: specialized cell types but no true tissues; sessile → no locomotion; collar cells → responsible for movement, in flagella, create water currents that move through the body of the sponge
-Characteristics: specialized cell types but no true tissues; sessile → no locomotion; collar cells → responsible for movement, in flagella, create water currents that move through the body of the sponge
What are some characteristics of the phylum porifera and give an example of an animal in this phylum.
22
New cards
-tiny calcium or silica structures
-support sponge body
-support sponge body
What are spicules and what animal has them?
23
New cards
-function in digestion of food particles pulled from the water current by the collar cells
What are amoebocytes?
24
New cards
-modern choanoflagellates → protists
What does the hypothesized ancestor responsible for animal diversity resemble?
25
New cards
-sponges
-sperm is released into the environment
-sperm is released into the environment
What are hermaphrodites and what animal is one?
26
New cards
-jellyfish, anemones, corals
-radial symmetry
-two specialized cell layers (tissues)
-nerve cells
-feeding is done by capturing food particles or prey from water
-radial symmetry
-two specialized cell layers (tissues)
-nerve cells
-feeding is done by capturing food particles or prey from water
What are some characteristics of the phylum cnidaria and what are some animals in this phylum?
27
New cards
-sessile polyp
-free-swimming medusa
-free-swimming medusa
What are the two body forms for cnidarians?
28
New cards
-way to get prey by launching a venomous spine
What is a nematocyst?
29
New cards
-lophophore: horse-shoe shaped feeding structure or
-trocophore: ciliated larva
-trocophore: ciliated larva
What are characteristics of the lophotrochozoa?
30
New cards
-flatworms
-lack circulatory, respiratory, and skeletal systems
-coelom is absent and gut is incomplete
-large range in size (less than 1 mm to several m)
-lack circulatory, respiratory, and skeletal systems
-coelom is absent and gut is incomplete
-large range in size (less than 1 mm to several m)
What are characteristics of the phylum platyhelminthes and what are some examples of this phylum?
31
New cards
-turbellaria
-monogenea
-trematoda
-cestoda
-monogenea
-trematoda
-cestoda
What are some of the classes of the phylum platyhelminthes?
32
New cards
-mostly marine, some fresh water, a few terrestrial
-predators and scavengers
-body surface is ciliated
-mostly hermaphordites but can also reproduce asexulally
-flatworms, planarian
-predators and scavengers
-body surface is ciliated
-mostly hermaphordites but can also reproduce asexulally
-flatworms, planarian
What are some characteristics of the class tubellaria and what are some animals in this class?
33
New cards
-marine and freshwater parasites
-most infect external surfaces of fishes (skin and gills)
-life history is simple
-ciliated larva starts infection on host
-unciliated synctial outer layer (cells connected so that cytoplasm is shared
-monogeans
-most infect external surfaces of fishes (skin and gills)
-life history is simple
-ciliated larva starts infection on host
-unciliated synctial outer layer (cells connected so that cytoplasm is shared
-monogeans
What are some characteristics of the class monogea and what are some animals in this class?
34
New cards
-parasites, mostly vertebrates
-two suckers attach to host (mollusc and vertebrate)
-most life cycles include intermediate and finals hosts
-infections from this class can cause pain, anemia, dysentery, and liver damage
-trematodes (flukes)
-two suckers attach to host (mollusc and vertebrate)
-most life cycles include intermediate and finals hosts
-infections from this class can cause pain, anemia, dysentery, and liver damage
-trematodes (flukes)
What are some characteristics of the class trematoda and what are some animals in this class?
35
New cards
-parasites of vertebrates
-scolex (hooked structure) attaches to host (via intestine)
-proglottids produce eggs and break off after fertilization
-no head, digestive system, and no sense organs
-life cycle with one or more intermediate hosts
-proglottids → comprise the body and contains both male and female sex organs
-tapeworms
-scolex (hooked structure) attaches to host (via intestine)
-proglottids produce eggs and break off after fertilization
-no head, digestive system, and no sense organs
-life cycle with one or more intermediate hosts
-proglottids → comprise the body and contains both male and female sex organs
-tapeworms
What are some characteristics of the class cestoda and what are some animals in this class?
36
New cards
-Rotifer
-max size is 3mm (super small)
-wide range of aquatic and marine habitats
-some can survive in extremely dry and cold conditions
-predators, parasites, filter feeders (some are sessile)
-mouth has hard, muscular jaws
-have separate sexes or are asexual
-max size is 3mm (super small)
-wide range of aquatic and marine habitats
-some can survive in extremely dry and cold conditions
-predators, parasites, filter feeders (some are sessile)
-mouth has hard, muscular jaws
-have separate sexes or are asexual
What are some characteristics of the phylum syndermata and an example of an animal in this phylum?
37
New cards
-need moisture in habitat, but has a huge range of habitats
-large variety of sizes
-one of the largest animal phyla
-used as food, crop pests, and intermediate hosts for human parasites
-protective mantle enclosing a mantle cavity and muscular foot
-radula → scraping, tongue-like feeding organ; in all major mollusc classes except bivalves
-large variety of sizes
-one of the largest animal phyla
-used as food, crop pests, and intermediate hosts for human parasites
-protective mantle enclosing a mantle cavity and muscular foot
-radula → scraping, tongue-like feeding organ; in all major mollusc classes except bivalves
What are some characteristics of the phylum mollusca?
38
New cards
-calcium carbonate
What are mollusc shells composed of?
39
New cards
-polyplacophora
-gastropoda
-bivalvia
-cephalopoda
-gastropoda
-bivalvia
-cephalopoda
What are some of the classes of the phylum mollusca?
40
New cards
-marine
-shell with 8 plates
-foot used for locomotion
-radula
-no head
-chitons
-shell with 8 plates
-foot used for locomotion
-radula
-no head
-chitons
What are some characteristics of the class polyplacophora and what are some animals in this class?
41
New cards
-marine, freshwater, or terrestrial
-head present
-symmetrical body, usually with a coiled shell
-shell reduced or absent
-foot for locomotion
-radula
-mostly herbivores but some are scavengers or active predators
-some have a complex genital apparatus from the side of its head which hermaphroditic slugs use to pass sperm
-some snails have "love darts" to inject hormones into their mate to increase the success of their sperm in fertilizing eggs
-snails, slugs
-head present
-symmetrical body, usually with a coiled shell
-shell reduced or absent
-foot for locomotion
-radula
-mostly herbivores but some are scavengers or active predators
-some have a complex genital apparatus from the side of its head which hermaphroditic slugs use to pass sperm
-some snails have "love darts" to inject hormones into their mate to increase the success of their sperm in fertilizing eggs
-snails, slugs
What are some characteristics of the class gastropoda and what are some animals in this class?
42
New cards
-marine and freshwater
-flattened shell with two valves
-head reduced
-paired gills → modified for filter-feeding
-no radula
-locomotion is by extension and anchoring of the foot or by propelling water between the valves (shells)
-clams, mussels, scallops, oysters
-flattened shell with two valves
-head reduced
-paired gills → modified for filter-feeding
-no radula
-locomotion is by extension and anchoring of the foot or by propelling water between the valves (shells)
-clams, mussels, scallops, oysters
What are some characteristics of the class bivalvia and what are some animals in this class?
43
New cards
-marine predators
-head surrounded by grasping tentacles, usually with suckers
-shell external, internal, or absent
-mouth with or without radula
-locomotion via jet propulsion; foot is modified into a siphon for propulsion
-sexes are separate
-highly developed nervous and sensory systems
-squids, octopuses, cuttlefishes, chambered natiluses
-head surrounded by grasping tentacles, usually with suckers
-shell external, internal, or absent
-mouth with or without radula
-locomotion via jet propulsion; foot is modified into a siphon for propulsion
-sexes are separate
-highly developed nervous and sensory systems
-squids, octopuses, cuttlefishes, chambered natiluses
What are some characteristics of the class cephalopoda and what are some animals in this class?
44
New cards
-true coelom
-closed circulatory system
-body plan exhibits distinct repetition of segments → metameric
-reproduction by separate sexes, hermaphroditic sexual reproduction, or by fission and regeneration
-marine
-closed circulatory system
-body plan exhibits distinct repetition of segments → metameric
-reproduction by separate sexes, hermaphroditic sexual reproduction, or by fission and regeneration
-marine
What are some characteristics of the phylum annelida?
45
New cards
-errantia
-sedentaria
-sedentaria
What are the two major clades of the phylum annelida?
46
New cards
-mostly mobile and marine
-pair of paddle/ridge-like parapodia (beside feet) on each body segment
each parapodium (foot) has numerous chaetae → bristles made of chitin
-pair of paddle/ridge-like parapodia (beside feet) on each body segment
each parapodium (foot) has numerous chaetae → bristles made of chitin
What are some characteristics of the clade errantia?
47
New cards
-less mobile than errantians
-some burrow into substrate or live in protective tubes
-tube-dwelling sedentarians have elaborate gills or tentacles used for filter feeding
-leeches and earthworms
-some burrow into substrate or live in protective tubes
-tube-dwelling sedentarians have elaborate gills or tentacles used for filter feeding
-leeches and earthworms
What are some characteristics of the clade sedentaria?
48
New cards
-parasites/predators
-lack chaetae and have suckers on anterior and posterior ends
-blood-sucking leeches produce an anti-clotting enzyme, hirudin, to facilitate feeding
-lack chaetae and have suckers on anterior and posterior ends
-blood-sucking leeches produce an anti-clotting enzyme, hirudin, to facilitate feeding
What are leeches?
49
New cards
-ecdysis → periodic shedding of a cuticle
What is a defining characteristic of the ecdysozoa?
50
New cards
-cuticle → non-living external layer secreted by the epidermis
-cuticle is periodically shed as the nematode grows → ecdysis
-only have longitudinal muscles
-hydrostatic skeleton → resists compression and transmits muscular forces due to the high internal pressure in the pseudocoelom allowing it to function with the cuticle
-cuticle is periodically shed as the nematode grows → ecdysis
-only have longitudinal muscles
-hydrostatic skeleton → resists compression and transmits muscular forces due to the high internal pressure in the pseudocoelom allowing it to function with the cuticle
What are some characteristics of the phylum nematoda?
51
New cards
-ascaris lumbricoides
-necator americanus (hookworm)
-trichinella spiralis
-caenorhabditis elegans
-necator americanus (hookworm)
-trichinella spiralis
-caenorhabditis elegans
What are some animals that are part of the phylum nematoda?
52
New cards
-largest and most common parasite of the human intestine
-one female can lay over 200,000 eggs each day
-intestinal infection is acquired by ingesting eggs present in the soil
-one female can lay over 200,000 eggs each day
-intestinal infection is acquired by ingesting eggs present in the soil
What are some characteristics of ascaris lumbricoides?
53
New cards
-juveniles feed on bacteria in the soil and infect humans by penetrating the skin
-adults feed on blood sucked from the lining of the intestines
-adults feed on blood sucked from the lining of the intestines
What are some characteristics of necator americanus (hookworm)?
54
New cards
-responsible for the potentially lethal disease trichinosis contracted by consuming undercooked pork
-juveniles enter muscle cells and alter the host's gene expression to change the muscle into a nurse cell that protects and nourishes the nematode
-juveniles enter muscle cells and alter the host's gene expression to change the muscle into a nurse cell that protects and nourishes the nematode
What are some characteristics of trichinella spiralis?
55
New cards
-most studied "model organisms"
What are some characteristics of caenorhabditis elegans?
56
New cards
-tropical predators that prey on ground-dwelling insects, snails, and worms
-unjointed appendages and a body form that changed very little
-paired slime glands spray an entangling fluid to catch prey
-onychophorans or velvet worms
-unjointed appendages and a body form that changed very little
-paired slime glands spray an entangling fluid to catch prey
-onychophorans or velvet worms
What are some characteristics of the phylum onychophora?
57
New cards
-water bears; microscopic inhabitants of water films on mosses or marine sands that feed by sucking fluids from other tiny animals or plants
-cryptobiosis → state of suspended metabolism
-in cryptobiotic state, tardigrades can survive: heating to 149°C and cooling to -272°C; radiation; lack of oxygen
-cryptobiosis → state of suspended metabolism
-in cryptobiotic state, tardigrades can survive: heating to 149°C and cooling to -272°C; radiation; lack of oxygen
What are some characteristics of the phylum tardigrada?
58
New cards
-cuticle hardened by proteins
-exoskeleton made of chitin
-jointed appendages that are modified for special functions
-segmented bodies into functional units → tagmata
-open circulatory system emptying into body cavity → hemocoel
-complete digestive system, complex muscle and nervous systems
-respiration through a complex system of air canals → trachea
-exoskeleton made of chitin
-jointed appendages that are modified for special functions
-segmented bodies into functional units → tagmata
-open circulatory system emptying into body cavity → hemocoel
-complete digestive system, complex muscle and nervous systems
-respiration through a complex system of air canals → trachea
What are some characteristics of the phylum arthropoda?
59
New cards
-cheliceriformes
-myriapoda
-hexapoda
-crustacea
-myriapoda
-hexapoda
-crustacea
What are some of the subphyla of the phylum arthropoda?
60
New cards
-body having one or two main parts
-six pairs of appendages
-mostly terrestrial or marine
-horseshoe crabs, spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites
-six pairs of appendages
-mostly terrestrial or marine
-horseshoe crabs, spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites
What are some characteristics of the subphylum cheliceriformes and what are some animals in this subphylum?
61
New cards
-distinct head bearing antennae and chewing mouthparts
-terrestrial
-millipedes and centipedes
-terrestrial
-millipedes and centipedes
What are some characteristics of the subphylum myriapoda and what are some animals in this subphylum?
62
New cards
-body divided into head, thorax, and abdomen
-antennae present
-three pairs of legs and usually two pairs of wings
-mostly terrestrial
-insects, springtails
-antennae present
-three pairs of legs and usually two pairs of wings
-mostly terrestrial
-insects, springtails
What are some characteristics of the subphylum hexapoda and what are some animals in this subphylum?
63
New cards
-body of two or three parts
-antennae present
-chewing mouthparts
-three or more pairs of legs
-elaborate serial homology
-mostly marine and freshwater
-crabs, lobsters, crayfishes, shrimps
-antennae present
-chewing mouthparts
-three or more pairs of legs
-elaborate serial homology
-mostly marine and freshwater
-crabs, lobsters, crayfishes, shrimps
What are some characteristics of the subphylum crustacea and what are some animals in this subphylum?
64
New cards
-study of insects is called entomology
-openings in the exoskeleton lead to a system of trachea and tracheoles that supply the body with oxygen
-growth in insects result in molting of exoskeleton; the life stages between molts are called instars
-has the protein resilin which plays a large role in locomotion
-flexible chitinous exoskeleton
-asynchronous flight muscles
-openings in the exoskeleton lead to a system of trachea and tracheoles that supply the body with oxygen
-growth in insects result in molting of exoskeleton; the life stages between molts are called instars
-has the protein resilin which plays a large role in locomotion
-flexible chitinous exoskeleton
-asynchronous flight muscles
What are some characteristics of insects?
65
New cards
-ametabolous: growth without major change in form
-hemimetabolous: nymph stage is followed by increased development of wings from buds with each successive molt
-holometabolous: complete metamorphosis from stages specialized for feeding to stages specialized for mating and dispersal
-hemimetabolous: nymph stage is followed by increased development of wings from buds with each successive molt
-holometabolous: complete metamorphosis from stages specialized for feeding to stages specialized for mating and dispersal
What are the three stages of insect development?
66
New cards
-hemichordata
-echinodermata
-chordata
-echinodermata
-chordata
What phylums are classified as deuterstomes?
67
New cards
-asteroidea
-ophiuroidea
-echinoidea
-crinoidea
-holothuroidea
-ophiuroidea
-echinoidea
-crinoidea
-holothuroidea
What are some classes in the phylum echinodermata?
68
New cards
-marine animals
-secondarily evolved radial symmetry from a bilateral ancestor (larva are still bilateral)
-calcium-containing endoskeleton (internal skeleton) of plates or tiny bony elements
-none of the echinoderms are parasites
-water-vascular system for movement
-fluid is pushed from muscular ampullae into tube feet causing them to extend
-external surface is covered with spines and pedicellariae → tiny jaws that keep the surface clear of debris and parasites
-catch collagen → unique connective tissue of echinoderms, changes rapidly between solid and liquid states in response to stimulation from the nervous system
-secondarily evolved radial symmetry from a bilateral ancestor (larva are still bilateral)
-calcium-containing endoskeleton (internal skeleton) of plates or tiny bony elements
-none of the echinoderms are parasites
-water-vascular system for movement
-fluid is pushed from muscular ampullae into tube feet causing them to extend
-external surface is covered with spines and pedicellariae → tiny jaws that keep the surface clear of debris and parasites
-catch collagen → unique connective tissue of echinoderms, changes rapidly between solid and liquid states in response to stimulation from the nervous system
What are some characteristics of the phylum echinodermata?
69
New cards
-star-shaped body with multiple arms
-mouth directed to substrate
-sea stars
-mouth directed to substrate
-sea stars
What are some characteristics of the class asteroidea and what are some animals in this class?
70
New cards
-distinct central disk
-long, flexible arms
-incomplete digestive system
-brittle stars
-long, flexible arms
-incomplete digestive system
-brittle stars
What are some characteristics of the class ophiuroidea and what are some animals in this class?
71
New cards
-roughly spherical or disk-shaped
-no arms
-five rows of tube feet
-mouth ringed by complex, jaw-like structure
-sea urchins, sand dollars
-no arms
-five rows of tube feet
-mouth ringed by complex, jaw-like structure
-sea urchins, sand dollars
What are some characteristics of the class echinoidea and what are some animals in this class?
72
New cards
-feathered arms surrounding upward-pointing mouth
-sea lilies, feather stars
-sea lilies, feather stars
What are some characteristics of the class crinoidea and what are some animals in this class?
73
New cards
-cucumber-shaped body
-five rows of tube feet
-reduced skeleton
-no spines
-secondarily evolved bilateral symmetry
-can digest organic matter in sediment and can expel and regenerate their digestive system
-sea cucumbers
-five rows of tube feet
-reduced skeleton
-no spines
-secondarily evolved bilateral symmetry
-can digest organic matter in sediment and can expel and regenerate their digestive system
-sea cucumbers
What are some characteristics of the class holothuroidea and what are some animals in this class?
74
New cards
-notochord → semi-rigid rod of cells enclosed by a fibrous sheath that functions as a skeletal element
-dorsal, hollow nerve cord → runs along the length of the body
-pharyngeal slits or clefts → openings in the pharyngeal cavity (throat) to the outside of the animal; leads to the structures of the middle ear, tonsils, and internal gills
-muscular, post-anal tail → aquatic locomotion
-dorsal, hollow nerve cord → runs along the length of the body
-pharyngeal slits or clefts → openings in the pharyngeal cavity (throat) to the outside of the animal; leads to the structures of the middle ear, tonsils, and internal gills
-muscular, post-anal tail → aquatic locomotion
What are the characteristics of the phylum chordata?
75
New cards
-cephalochordata
-urochordata
-urochordata
What are the two chordate lineages that diverged early in the evolution of vertebrates?
76
New cards
-lancelets
-small, thin filter-feeders
-found on the sandy bottoms in coastal waters
-lack gills and heart
-closed circulatory system
-small, thin filter-feeders
-found on the sandy bottoms in coastal waters
-lack gills and heart
-closed circulatory system
What are some characteristics of the cephalochordates?
77
New cards
-also known as tunicates
-more closely related to other chordates than lancelets
-as an adult, draws in water through an incurrent siphon which filters food particles
-more closely related to other chordates than lancelets
-as an adult, draws in water through an incurrent siphon which filters food particles
What are some characteristics of the urochordata?
78
New cards
-backbone
-two or more sets of hox genes that regulate anterior-posterior development
-embryos have neural crest cells that give rise to a variety of structures (bones, cartilage)
-two or more sets of hox genes that regulate anterior-posterior development
-embryos have neural crest cells that give rise to a variety of structures (bones, cartilage)
What are some characteristics of vertebrates?
79
New cards
-Scavengers: myxini, hagfish, petromyzontida
-Parasites: lampreys
-Parasites: lampreys
What are some examples of jawless fish (cyclostomes)? Which ones are scavengers and which ones are parasites?
80
New cards
-notochord is the only "backbone"
-cartilage braincase rather than bone
-no paired fins
-no stomach
-partially open circulatory system (4 hearts)
-cartilage braincase rather than bone
-no paired fins
-no stomach
-partially open circulatory system (4 hearts)
What some characteristics of the myxini?
81
New cards
-fibrous and cartilage skeleton
-cartilage braincase
-no paired fins
-distinct stomach
-closed circulatory system with single heart
-cartilage braincase
-no paired fins
-distinct stomach
-closed circulatory system with single heart
What are some characteristics of the petromoyzontida?
82
New cards
-glands that secrete huge amounts of mucous and protein threads that surround the body in defensive slime
What are some characteristics of hagfishes?
83
New cards
-attach to fish by suction and rasp a wound through the skin with their spiny tongues
-anticoagulant allows lamprey to acquire blood and body fluids while attached to the host
-anticoagulant allows lamprey to acquire blood and body fluids while attached to the host
What are some characteristics of lampreys?
84
New cards
-chordates with jaws
-sharks, ray-finned fish, lobe-finned fish, amphibians, reptiles (including birds), mammals
-placoderms → earliest gnathostomes in fossil records
-sharks, ray-finned fish, lobe-finned fish, amphibians, reptiles (including birds), mammals
-placoderms → earliest gnathostomes in fossil records
What are gnathostomes and what are some examples?
85
New cards
-improved respiratory efficiency (closing jaws prevents backflow when water is passed over the gills)
-grasping, biting, suction feeding
-may have evolved from the skeletal supports of the pharyngeal slits
-grasping, biting, suction feeding
-may have evolved from the skeletal supports of the pharyngeal slits
What is the significance of jaws?
86
New cards
-aka chondrichthyes
-skeleton composed primarily of cartilage
-sharks, rays, skates
-lack of mineralization in the cartilage skeleton
-calcified bony skeletal elements
-scales are a type of placoid → form horns, spines, teeth
-spiral valve → slows passage of food and increases surface area for absorption
-males have claspers → modified pelvic fins for copulation
-oviparous, ovoviviparous, viviparous
-skeleton composed primarily of cartilage
-sharks, rays, skates
-lack of mineralization in the cartilage skeleton
-calcified bony skeletal elements
-scales are a type of placoid → form horns, spines, teeth
-spiral valve → slows passage of food and increases surface area for absorption
-males have claspers → modified pelvic fins for copulation
-oviparous, ovoviviparous, viviparous
What are some characteristics of the chondrichthyans?
87
New cards
-eggs hatch outside the mother's body
Define oviparous.
88
New cards
-embryo develops within the uterus and is nourished by the egg yolk
Define ovoviviparous.
89
New cards
-embryo develops within the uterus and is nourished through a yolk sac placenta from the mother's blood
Define viviparous/
90
New cards
-bony fish, tetrapods
-bone replaces cartilage in the skeleton
-operculum → plate-like, covers gills and allows fish to breathe efficiently without forward movement
-gills maximize surface area for gas exchange by having folding on multiple levels
-more diverse teeth and digestive systems than chondrichthyes
-gas bladder increased swimming efficiency and maneuverability by contributing to neutral buoyancy
-bone replaces cartilage in the skeleton
-operculum → plate-like, covers gills and allows fish to breathe efficiently without forward movement
-gills maximize surface area for gas exchange by having folding on multiple levels
-more diverse teeth and digestive systems than chondrichthyes
-gas bladder increased swimming efficiency and maneuverability by contributing to neutral buoyancy
What are some characteristics of the osteichthyans?
91
New cards
-lateral line → "distant touch" detection of water movements via neuromasts
-neuromasts have extensions that trigger signals to the nervous system when displaced by water movement
-lateral lines are arranged on the head and along the side of the body
-neuromasts have extensions that trigger signals to the nervous system when displaced by water movement
-lateral lines are arranged on the head and along the side of the body
What are is a shared characteristics between the chondrichthyes and osteichthyans?
92
New cards
-osteichthyans that share some characteristics of the first terrestrial vertebrates
-coelacanth → paired fins at the end of appendages with internal bony elements, notochord as the primary anterior-posterior support, jointed braincase
-coelacanth → paired fins at the end of appendages with internal bony elements, notochord as the primary anterior-posterior support, jointed braincase
What are lobe-fins? (characteristics, significance)
93
New cards
-notochord
-developed vertebrae
-functional lungs
-withstand drying of their habitat
-estivation → state of reduced physiological activity during drought (air-breathe, lower heart rate, retain urea and other wastes, break down body fat and protein)
-developed vertebrae
-functional lungs
-withstand drying of their habitat
-estivation → state of reduced physiological activity during drought (air-breathe, lower heart rate, retain urea and other wastes, break down body fat and protein)
What are some characteristics of lungfish?
94
New cards
-ancestrally terrestrial and four-limbed vertebrates
-amphibia
-amphibia
What are tetrapods?
95
New cards
-oxygen is more concentrated in air than in water
-air is less dense and less thick than water
-air experiences far greater temperature extremes
-terrestrial environments comprise greater diversity of habitats than marine environments
-air is less dense and less thick than water
-air experiences far greater temperature extremes
-terrestrial environments comprise greater diversity of habitats than marine environments
What are some difference between marine life and terrestrial life?
96
New cards
-skeleton is mostly bone
-usually have four limbs
-skin is moist and functional in respiration (oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse across skin)
-mucous glands that keep skin moist so it functions as a respiratory surface (cutaneous respiration), produce adhesives that function in locomotion and defense
-skin can produce caustic and toxic poisons
-aquatic larva and terrestrial adult
-frogs, salamanders, caecilians
-usually have four limbs
-skin is moist and functional in respiration (oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse across skin)
-mucous glands that keep skin moist so it functions as a respiratory surface (cutaneous respiration), produce adhesives that function in locomotion and defense
-skin can produce caustic and toxic poisons
-aquatic larva and terrestrial adult
-frogs, salamanders, caecilians
What are some characteristics of amphibians?
97
New cards
-elongate, tailed, four limbs (except for some fully aquatic forms)
-larvae have external gills and laterally flattened tails
-most fully terrestrial salamanders hatch from eggs as miniatures of the adult with no aquatic larval stage
-paedomorphosis → evolution of retention of larval characteristics into adulthood (many reach sexual maturity while retaining external gills and an aquatic habitat)
-may have gills, lungs, both, or neither
-larvae have external gills and laterally flattened tails
-most fully terrestrial salamanders hatch from eggs as miniatures of the adult with no aquatic larval stage
-paedomorphosis → evolution of retention of larval characteristics into adulthood (many reach sexual maturity while retaining external gills and an aquatic habitat)
-may have gills, lungs, both, or neither
What are some salamander characteristics?
98
New cards
-most eggs are fertilized internally by sperm passed to the female in a packet or spermatophore
-eggs are either deposited on the spermatophore or it is drawn into the female's cloaca
-few species are viviparous (birth live young)
-eggs are either deposited on the spermatophore or it is drawn into the female's cloaca
-few species are viviparous (birth live young)
How do salamanders reproduce?
99
New cards
-warning (aposomatic) coloration
-poison that is fast acting on lips or epithelial tissue of mouth to rapidly deter predation
-poison that is fast acting on lips or epithelial tissue of mouth to rapidly deter predation
What are some defensive and offensive options that salamanders have?
100
New cards
-skeletal features specialize anurans for locomotion by jumping with hindlimbs generating the power to propel the frog through the air or water
-pelvis is elongate and reaches far anteriorly and the posterior vertebrae are fused into a urostyle
-vertebral column is short and overlapping projections restrict side to side bending
-closed circulatory system with a three-chambered heart and separate pulmonary and systemic circuits
-external fertilization with eggs deposited in aquatic habitats
-larval tadpole have external then internal gills with the full process of metamorphosis taking 2-3 years in some species
-pelvis is elongate and reaches far anteriorly and the posterior vertebrae are fused into a urostyle
-vertebral column is short and overlapping projections restrict side to side bending
-closed circulatory system with a three-chambered heart and separate pulmonary and systemic circuits
-external fertilization with eggs deposited in aquatic habitats
-larval tadpole have external then internal gills with the full process of metamorphosis taking 2-3 years in some species
What are some characteristics of frogs?