Geography Exam Review
1/117
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for key concepts from the Geography Exam Review, covering definitions, important terms, and geographical theories.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
What does GIS stand for and what is its purpose?
Geographic Information Systems; it is a framework for gathering, managing, and analyzing spatial and geographic data to create layered maps and identify complex relations or patterns.
What is a Large Scale Map?
A map that shows a small area in great detail, such as a city street or a local neighborhood; it has a ratio where the second number is small (e.g., 1:25,000).
What is a Small Scale Map?
A map that shows a large area, such as a country or continent, with very little detail; it has a ratio where the second number is large (e.g., 1:10,000,000).
What are Latitude lines?
Imaginary lines that run horizontally across the Earth, parallel to the Equator, used to measure distance north or south of the Equator.
What are Longitude lines?
Imaginary lines that run vertically (north to south) from pole to pole, used to measure distance east or west of the Prime Meridian.
What is the definition of Absolute Location?
The exact position of a place on the Earth's surface, usually identified using a specific set of coordinates (latitude and longitude).
What is Relative Location?
The position of a place in relation to other landmarks or locations, often described using distance, direction, or travel time.
What is Spatial Significance?
The importance of a particular location based on its geographical characteristics and its relationship to other places in a specific context.
What are Convection Currents in geography?
The circular motion that occurs in the Earth's mantle when heated material rises and cooler material sinks, acting as the driving force behind the movement of tectonic plates.
What was Pangea?
A massive supercontinent that existed approximately 250 million years ago, incorporating almost all of Earth's landmasses before they drifted apart.
What does the Continental Drift Theory state?
Proposed by Alfred Wegener, it suggests that Earth's continents were once a single landmass and have since moved or 'drifted' across the ocean bed to their current positions.
What characterizes a Maritime Climate?
A climate influenced by the proximity to large bodies of water, resulting in relatively mild winters, cool summers, and high levels of annual precipitation.
What characterizes a Continental Climate?
A climate found in inland areas away from the ocean, marked by extreme temperature ranges (hot summers and cold winters) and relatively low precipitation.
What is a Linear Settlement Pattern?
A settlement that develops in a line, typically following a physical feature like a coastline or a human-made feature like a major highway or railway.
What is Shifting the Great Lakes/St. Lawrence Lowlands?
The smallest but most densely populated landform region in Canada, characterized by fertile soil, a moderate climate, and proximity to major urban centers.
How are fossil fuels created?
Non-renewable energy sources formed from the remains of dead organic matter that has been subjected to intense heat and pressure within sedimentary rock layers over millions of years.
What does the Ecological Footprint measure?
A tool that quantifies how much biologically productive land and water an individual or population requires to produce the resources they consume and to absorb the waste they generate.
What is Fast Fashion?
A contemporary term used for the rapid mass production of inexpensive clothing by retailers in response to the latest fashion trends, often resulting in significant environmental waste.
What is the Natural Increase Rate Formula?
The difference between the number of births and deaths in a population, adjusted for migration: (Birth\ Rate - Death\ Rate) + (Immigration\ Rate - Emigration\ Rate)..
What is the Canadian Shield?
The largest landform region in Canada, consisting of ancient igneous and metamorphic rock, thin soil, and vast forests, often referred to as the 'storehouse' of metallic minerals.
What does the acronym LOWERN stand for?
The six factors that affect climate: - Latitude - Ocean currents - Wind and air masses - Elevation - Relief (mountains) - Nearness to water.
What is early definition of Population Density?
The average number of people living in a specific area, usually calculated as people per square kilometer (km^{2}).
What are 'Push Factors'?
Negative reasons that compel or 'push' people to leave their current place of residence, such as political instability, unemployment, or environmental degradation.
What are 'Pull Factors'?
Positive reasons that attract or 'pull' people to a new location, such as better economic opportunities, political freedom, or a better quality of life.
What is Urban Sprawl?
The uncontrolled and often car-dependent expansion of urban areas into the surrounding rural landscape, leading to the loss of agricultural land and increased infrastructure costs.
What does GPS stand for?
Global Positioning System; a satellite-based navigation system used to determine the exact position of an object or person on Earth.
What characterizes the Appalachian Mountains region?
One of Canada's oldest landform regions, located in the east, consisting of rounded, eroded mountains and valleys formed hundreds of millions of years ago.
What characterizes the Western Cordillera?
A region in Western Canada featuring high, jagged, snow-capped mountains and deep valleys, formed by the collision of tectonic plates.
What characterizes the Interior Plains?
A vast, relatively flat landform region in central Canada, composed of sedimentary rock and known for being the 'breadbasket' due to its extensive grain farming.
What is Orographic (Relief) Precipitation?
Rain or snow that occurs when moist air is forced to rise over a mountain range, where it cools, condenses, and falls on the windward side.
What is Convectional Precipitation?
Rainfall that results from the sun heating the Earth's surface, causing air to rise, cool, and condense rapidly, often resulting in intense afternoon thunderstorms.
What is Frontal (Cyclonic) Precipitation?
Precipitation produced when two air masses of different temperatures (warm and cold) meet, forcing the lighter warm air to rise over the denser cold air.
How is Igneous Rock formed?
Rock formed by the cooling and solidification of molten rock, either underground as magma or on the surface as lava.
How is Sedimentary Rock formed?
Rock formed by the accumulation and compression of sediment layers, such as sand, mud, and organic matter, over millions of years.
How is Metamorphic Rock formed?
A type of rock that has been changed from its original form (igneous or sedimentary) by subjected to intense heat and pressure within the Earth's crust.
What is Glaciation?
The process by which large ice sheets move across the landscape, eroding the Earth's surface and depositing materials, significantly shaping Canada's current geography.
What is the Dependency Load?
The portion of the population that is generally non-working and relies on the working-age population (15 to 64 years old), specifically those under 15 and over 64.
Who are the Baby Boomers?
The significant demographic group born during the post-World War II period between 1946 and 1964, who have greatly influenced social and economic trends.
What is a Population Pyramid?
A graphical illustration that shows the distribution of various age groups in a population, typically split by gender, used to analyze demographic trends.
What is the formula for Net Migration Rate?
The difference between the number of people entering a country and the number of people leaving, expressed as: Net\ Migration\ Rate = (Immigration\ Rate - Emigration\ Rate)..
What is Rural Settlement?
Low-density settlement located outside of urban centers, typically characterized by agriculture, resource extraction, or wild spaces.
What is the Central Business District (CBD)?
The commercial and economic core of a city, characterized by high property values, high-density development, and a concentration of offices and retail stores.
What is Residential Land Use?
The use of land for housing purposes, typically occupying the largest portion of land within a city.
What is Commercial Land Use?
Land designated for business purposes, including the sale of goods and services, such as shops, restaurants, and professional offices.
What is Industrial Land Use?
Land used for manufacturing, processing, assembling, or storing goods, often located near major transportation routes.
What are Renewable Resources?
Natural resources that can be replenished naturally over time, such as solar energy, wind, and forests, if managed sustainably.
What are Non-renewable Resources?
Resources that are finite and take millions of years to form, such as fossil fuels and minerals, meaning they cannot be replaced once they are consumed.
What is Sustainable Development?
Development that meets the needs of the current generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
What is Remote Sensing?
The collection of data about the Earth's surface from a distance using sensors on satellites or aircraft, used to monitor environmental changes or map remote areas.
What is an Alphanumeric Grid?
A coordinate system using a combination of letters (usually for the x-axis) and numbers (usually for the y-axis) to locate specific squares on a map.
What is the difference between Weather and Climate?
Weather refers to the short-term atmospheric conditions (e.g., temperature, precipitation) at a specific time and place, while Climate is the long-term pattern of weather conditions averaged over a period of at least 30 years.
What is this plate movement called
What is a Primary Industry?
An industry involved in the extraction or harvesting of raw materials directly from the natural environment, such as farming, mining, fishing, and logging.
What is a Secondary Industry?
An industry that processes raw materials into finished goods through manufacturing and construction, such as a car assembly plant or a bread factory.
What is a Tertiary Industry?
Commonly known as the service sector, this industry provides services to individuals and other businesses rather than producing goods, such as retail, healthcare, and education.
What is a Quaternary Industry?
A highly specialized sector of the economy focused on knowledge-based activities, including research and development (R&D), information technology, and financial consulting.
What is the Rule of 70 used for?
A simple formula used to estimate how many years it will take for a population to double in size:
Doubling\ Time = \frac{70}{Population\ Growth\ Rate\ (\%)}
What is the Total Population Growth Rate formula?
The combined effect of natural increase and net migration, expressed as a percentage:
Total\ Growth\ Rate = \left( \frac{Natural\ Increase + Net\ Migration}{Total\ Population} \right) \times 100
What is Permafrost?
Ground (soil or rock, including ice or organic material) that remains at or below 0^\circ C for at least two consecutive years, commonly found in the Arctic regions.
What is a Compass Rose?
A figure on a map or chart used to display the orientation of the cardinal directions (North, South, East, and West) and their intermediate points.
What is the difference between Cardinal and Ordinal directions?
Cardinal directions are the four main points: North (N), South (S), East (E), and West (W). Ordinal directions are the points in between: Northeast (NE), Southeast (SE), Southwest (SW), and Northwest (NW).
What are the three layers of the Earth's interior?
Crust: The thin, outermost rocky shell.
Mantle: The thick layer of hot, solid rock between the crust and the core.
Core: The extremely hot center, divided into a liquid outer core and a solid inner core.
What is Inshore Fishing?
A type of commercial fishing that takes place within a few kilometers of the shoreline, typically involving small, independently-owned boats and seasonal operations.
What is Offshore Fishing?
A large-scale commercial fishing operation featuring company-owned vessels that stay at sea for several days, allowing for fishing in deep waters away from the coast.
What led to the collapse of the Atlantic Cod fishery?
A combination of overfishing triggered by advanced technology, poor management, and changes in environmental conditions, leading to a total moratorium in 1992.
What is Aquaculture?
The farming of fish, shellfish, and aquatic plants in controlled environments, often seen as a way to reduce the pressure on wild fish stocks.
What is the Clear-cutting method in forestry?
The most common and economical harvesting method where every tree in a designated area is cut down, though it can lead to significant soil erosion and habitat loss.
What is the Selective Cutting method in forestry?
A harvesting technique where only mature trees of a specific quality or species are removed, leaving the rest of the forest intact to maintain the ecosystem.
What is the Shelterwood Cutting method in forestry?
A process where a part of an old-growth forest is cleared, but enough trees are left to provide seed and shade for new seedlings to grow naturally.
What is Sustained Yield Management?
An approach to resource management which ensures that the amount of timber or fish harvested does not exceed the amount that can grow back or reproduce during the same period.
What is a Tariff?
A tax or duty placed on imported goods coming into a country, designed to make foreign products more expensive and encourage consumers to buy domestic goods.
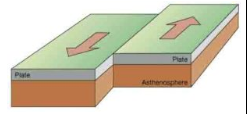
What is this type of plate movement called?
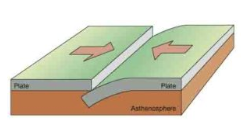
What is this type of plate movement called?
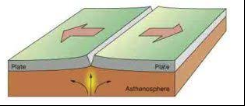
What is this type of plate movement called?
What does the acronym LOWERN stand for?
The six factors that affect climate: - Latitude - Ocean currents - Wind and air masses - Elevation - Relief (mountains) - Nearness to water.
What is Protectionism?
An economic policy of restricting imports to protect domestic industries.
What is Gill Netting?
A fishing method where a net is suspended in the water and fish are caught by their gills as they try to swim through the mesh.
What is Otter Trawling?
A fishing technique where a large bag-shaped net is dragged along the ocean floor to catch bottom-dwelling species.
Longlining?
A commercial fishing method that uses a long main line with hundreds or thousands of shorter lines and baited hooks attached.
Purse Seining?
A fishing method that uses a large wall of netting to encircle
Concentrated Settlement Pattern
A settlement pattern where buildings are clustered together, often around a central point or resource.
Dispersed Settlement Pattern
A settlement pattern where buildings are spread out over a large area, often seen in rural regions.Traditional Ecological Knowledge
Traditional Ecological Knowledge
The knowledge and practices developed by Indigenous peoples over generations regarding their local ecosystems.
Surface Mining
A method of mining that involves removing soil and rock layers to access minerals near the Earth's surface.
Open Pit Mining
A type of surface mining where a large excavation is made to extract minerals, often used for metals and coal.
Shaft Mining
A mining technique used to access deep mineral deposits by creating tunnels or shafts below the surface.
Underground Mining is also known as?
Land Reclamation
The process of restoring land that has been disturbed or degraded, often to make it suitable for agriculture or development.
Bycatch
The unintentional capture of non-target species during fishing, which can lead to ecological imbalances.

Ugly Food
Produce that is misshapen or imperfect in appearance but still perfectly edible and nutritious.
Emigrant
A person who leaves their country to live in another country.
Immigrant
A person who comes to live permanently in a foreign country.
Refugee
A person who flees their home country due to persecution, war, or violence and seeks safety in another country.
Developed Country
A nation with a high level of industrialization, high standards of living, and advanced technological infrastructure.
Developing Country
A nation with a lower level of industrialization, lower standards of living, and less advanced technological infrastructure compared to developed countries.
Newly Industrializing Country
A nation that is transitioning from an agrarian economy to an industrialized economy, often experiencing rapid growth.
NGO
A non-governmental organization that operates independently from the government, often focused on social, environmental, or humanitarian issues.
Median Age
The age that divides a population into two equal halves, with half the population being younger and half older.
Green Infrastructure
An approach to water management that protects, restores, or mimics the natural water cycle. Protects from flooding.
Urban Heat Island
An urban area that experiences higher temperatures than its rural surroundings due to human activities and infrastructure.