Cell bio chap18 M-phase cell division pt3
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
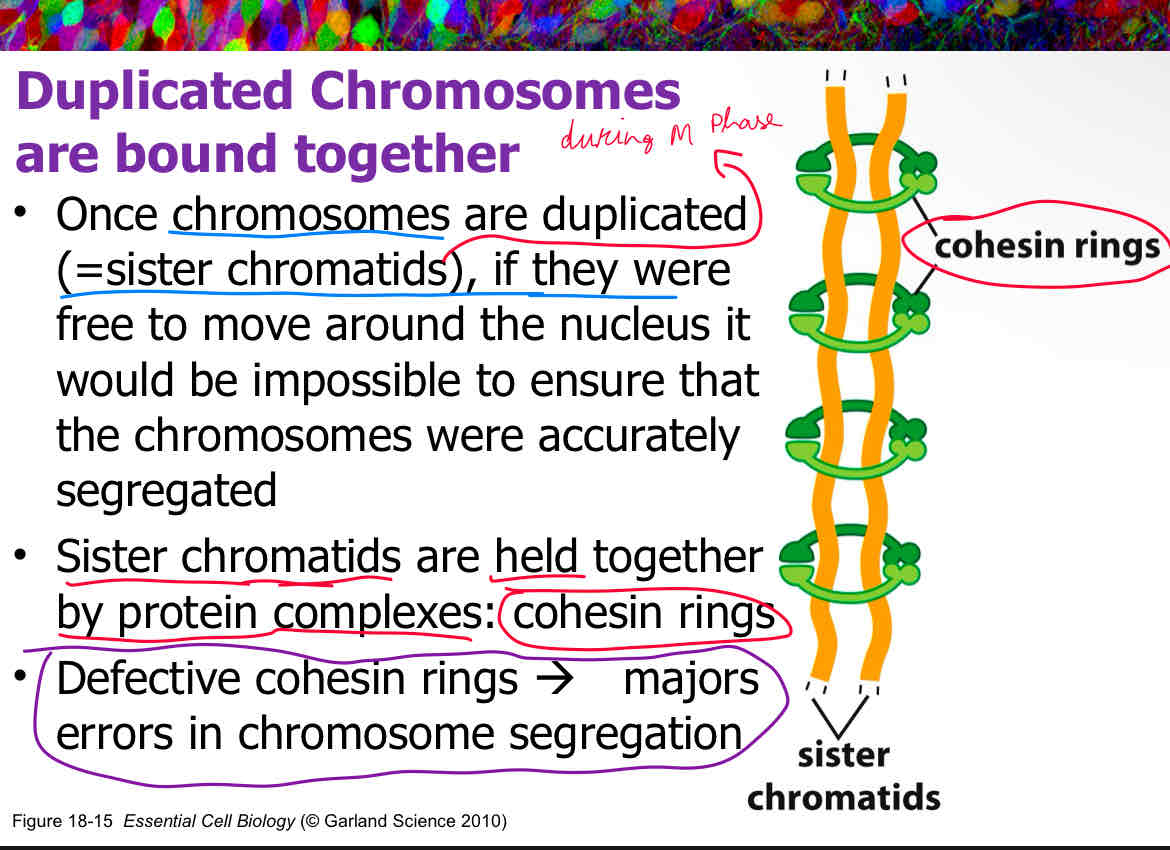
Sister chromatids are held together by protein complexes called __________.
cohesin
defective cohesion rings lead to major errors in chromosome segregation
attach slide 4
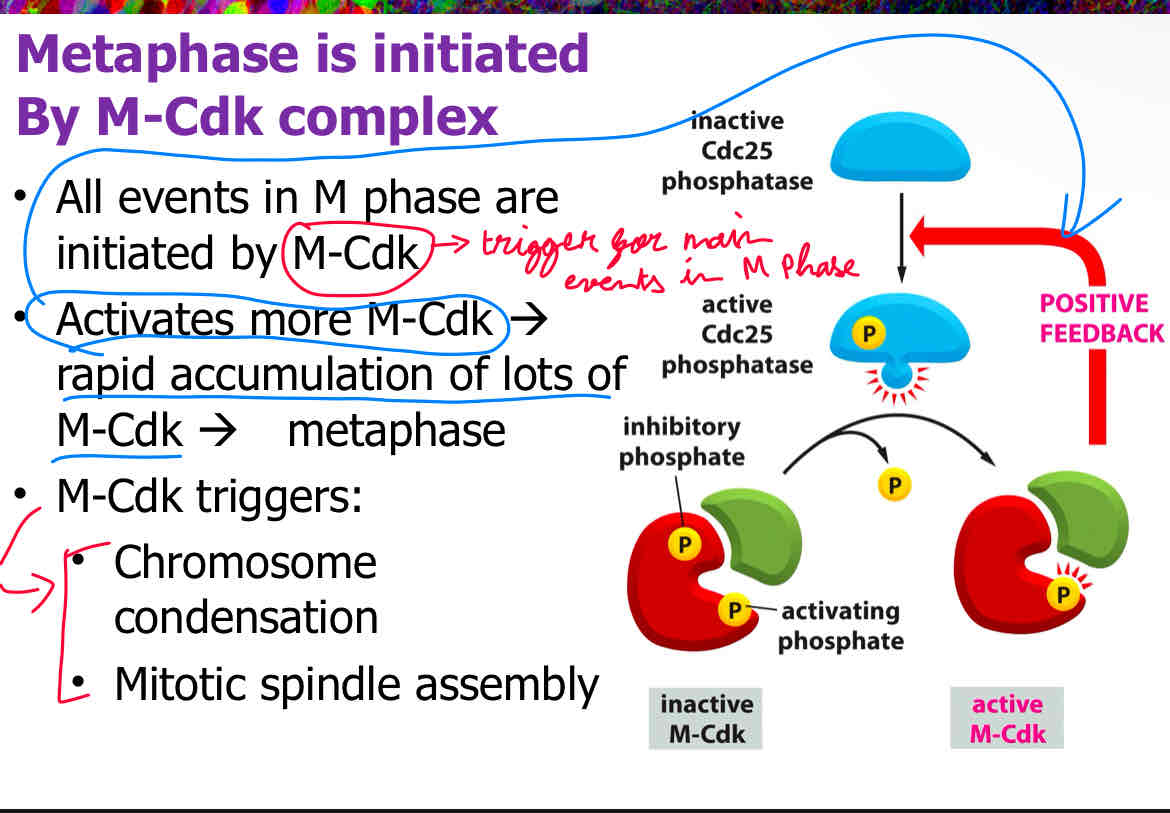
What initiates the M phase of cell division?
A) Cyclin D
B) M-Cdk complex
C) Separase
D) Cohesin rings
B
attach slide 6
True/False: The centrosome is responsible for the breakdown of the nuclear envelope during mitosis.
False (nuclear disassembly is the 1st event of pro metaphase and is not caused mitotic spindle of centrosome)
what are inerpolar microtubules
microtubules that interact with microtubules from other centrosome (those r said to be stable bcuz there’s no growing or shrinking)
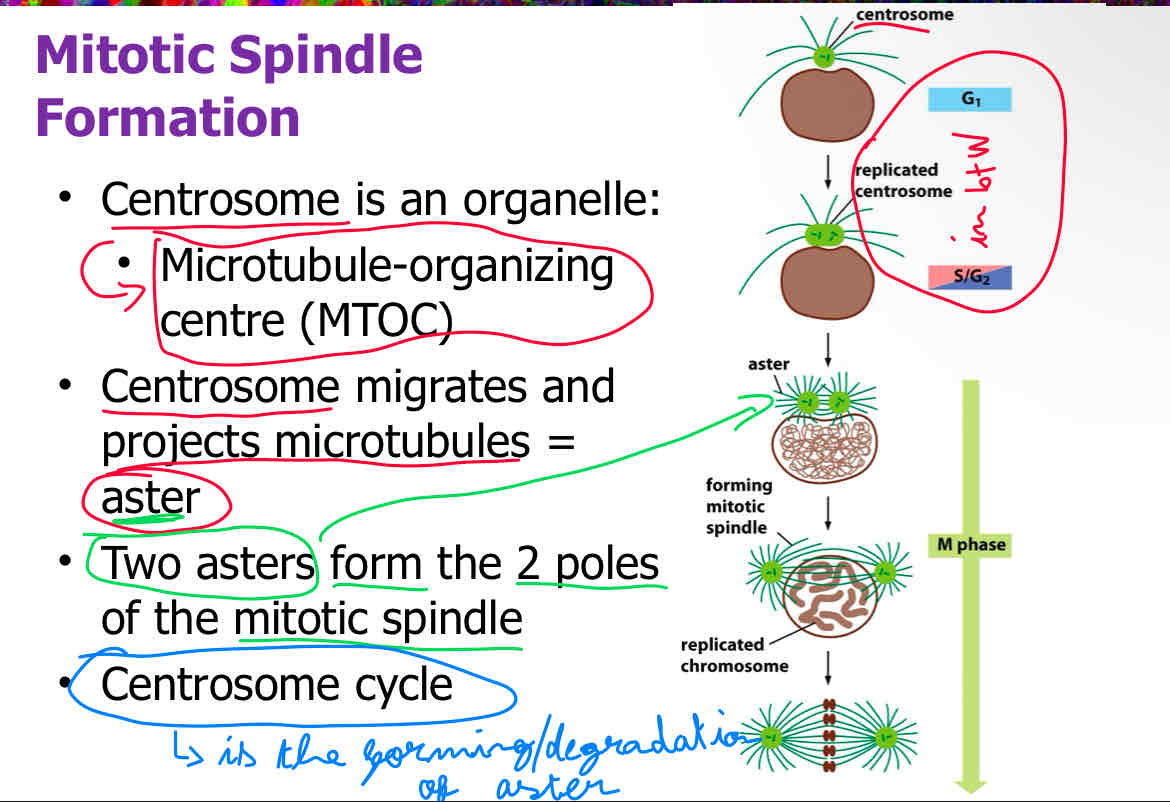
when does centrosome replication occurs
A) In between G1 and S/G2
B) During S phase
C) In between S and G2
D) During G1
A
attach slide 9

attach the M phase stages
Which phase of mitosis is characterized by the alignment of chromosomes at the spindle equator?
A) Prophase
B) Anaphase
C) Metaphase
D) Telophase
C
attach slide 16
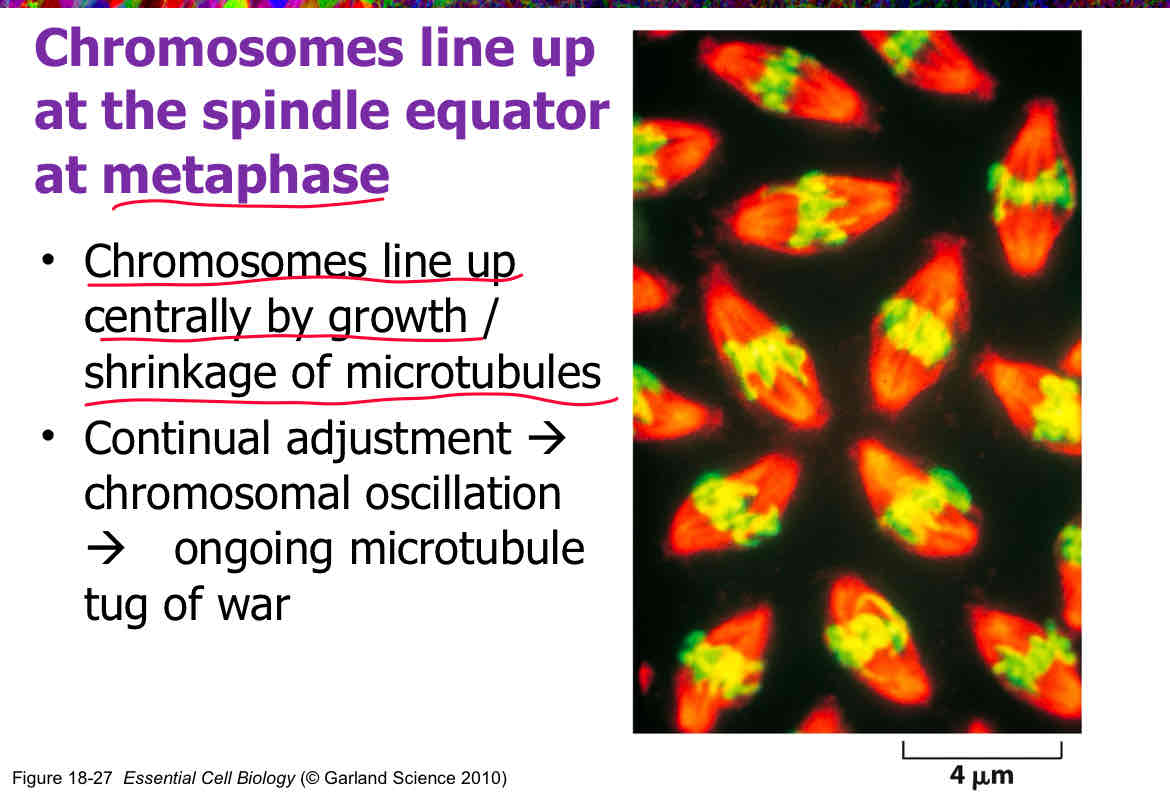
The protein complex that assembles on each centromere during prophase is called __________.
Kinetochore (it is bi orientated meaning there’s 1 on each side of the centromere. It also serves as checkpoint to prevent chromosomal separation when chromatids unattached to kinetochore microtubules)
attach slide 12
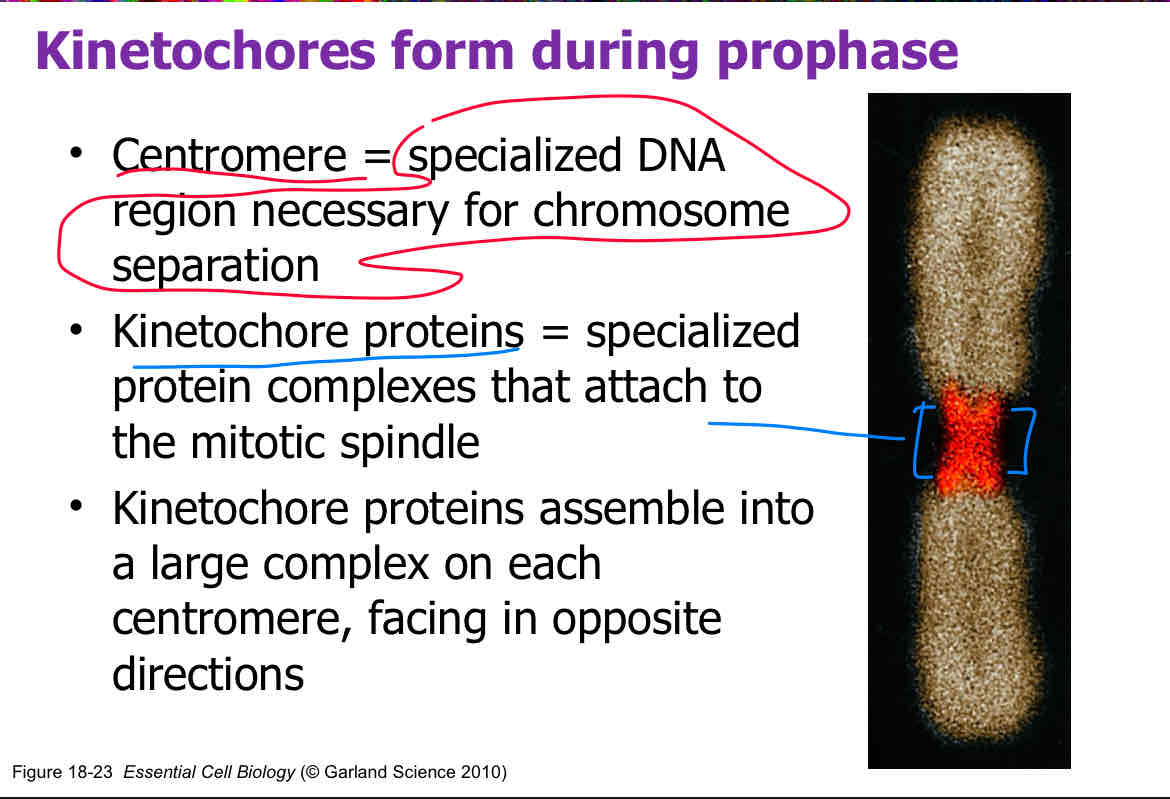
True/False: Cohesin rings are broken by a protease called separase during anaphase.
True (the breaking of cohesion rings allows for kinetochore separation)
attach slide 18

Which structure serves as the microtubule-organizing center (MTOC)?
A) Centrosome
B) Kinetochore
C) Cleavage furrow
D) Contractile ring
A
True/False: The contractile ring disassembles after cytokinesis is complete.
True
attach slide 24

What happens to the nuclear envelope during telophase?
A) It breaks down completely for each set of chromosomes
B) It condenses into chromatin
C) It remains intact
D) It reassembles for each set of chromosomes
D
attach slide 21

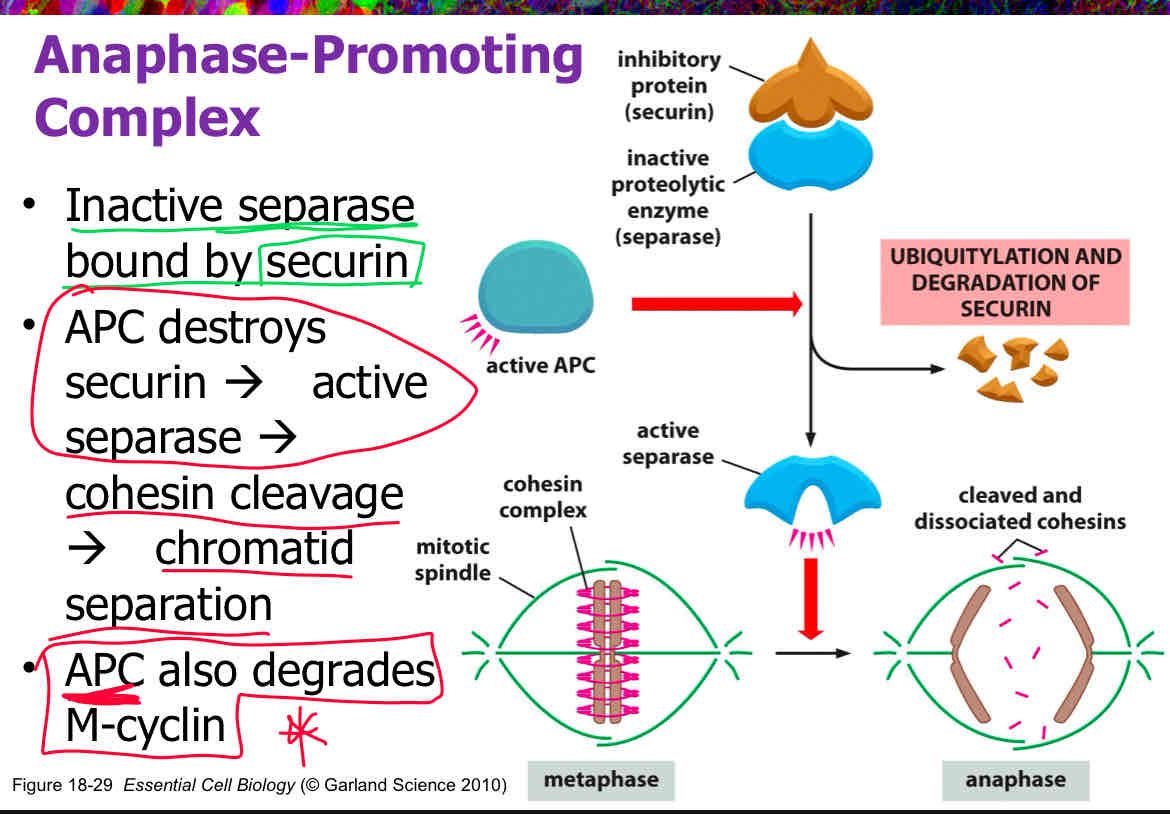
What is the role of the Anaphase-Promoting Complex (APC)?
A) To degrade securin and inactivate separase
B) To degrade securin and activate separase
C) To condense chromosomes
D) To promote the separation of sister chromatids
B
attach slide 18
Define the centrosome cycle
It is the forming/degradation of asters
attach slide 9

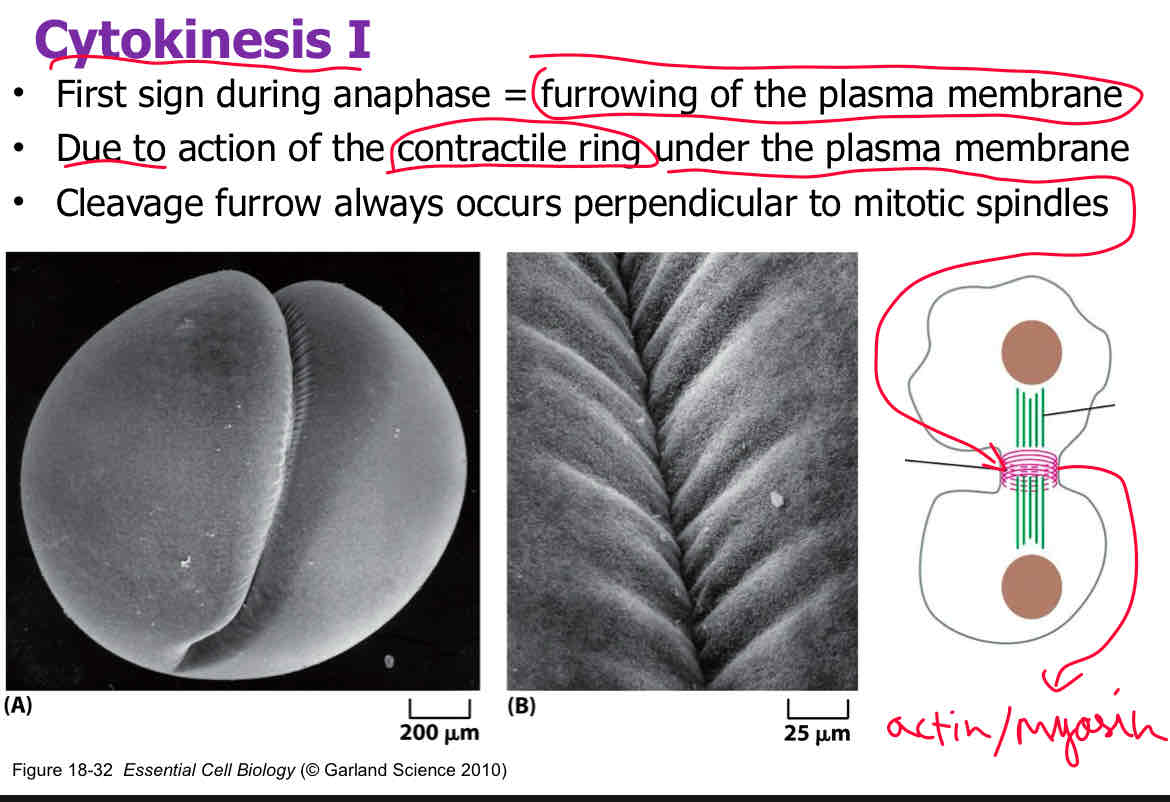
The sliding filament mechanism during cytokinesis involves overlapping ______ and __________ filaments.
actin and myosin (happens after cell division)
If a mutation occurs that prevents separase from being activated, what would be the consequence for sister chromatids?
A) They would separate normally.
B) They would condense further.
C) They would be lost during cell division.
D) They would remain attached.
D
What is the typical range of kinetochore microtubules that attach to each sister chromatid during cell division in human cells?
A) 20 to 40
B) 10 to 20
C) 40 to 60
D) 60 to 80
A
attach slide 14
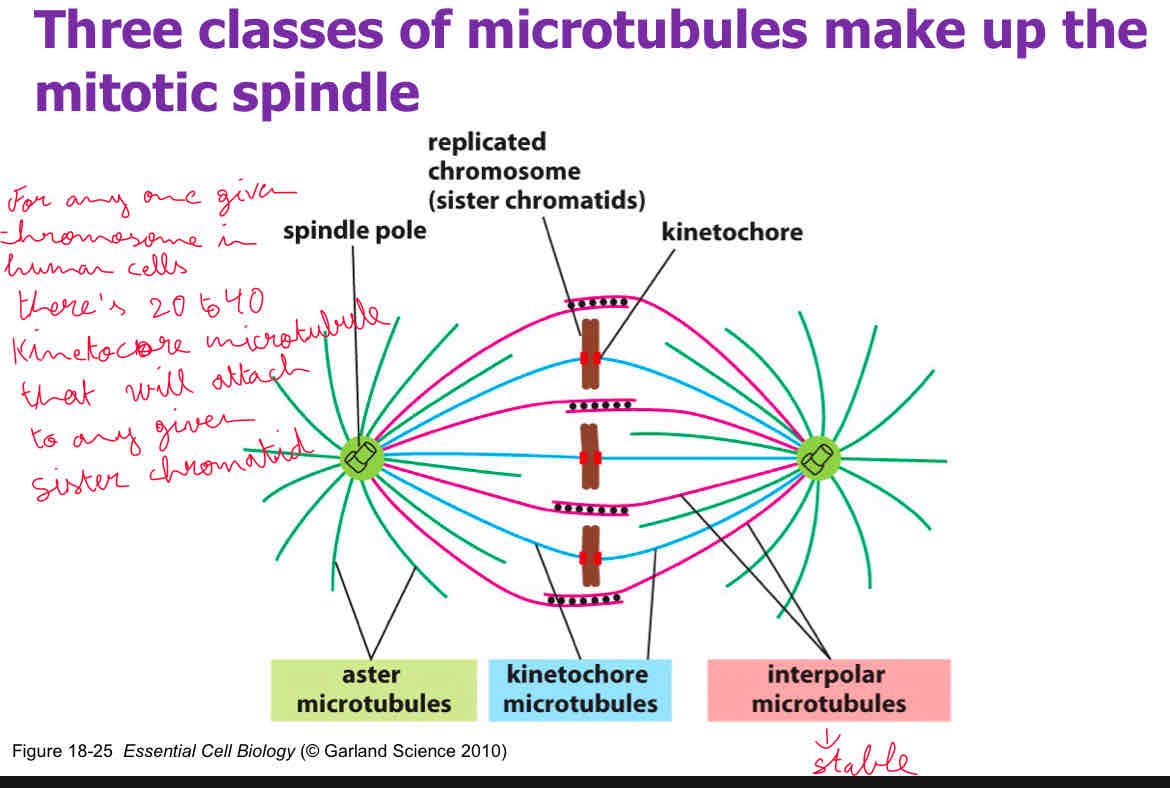
Which phase marks the transition from metaphase to anaphase?
A) Cohesin cleavage
B) Chromosome alignment
C) Nuclear envelope breakdown
D) Cytokinesis initiation
A
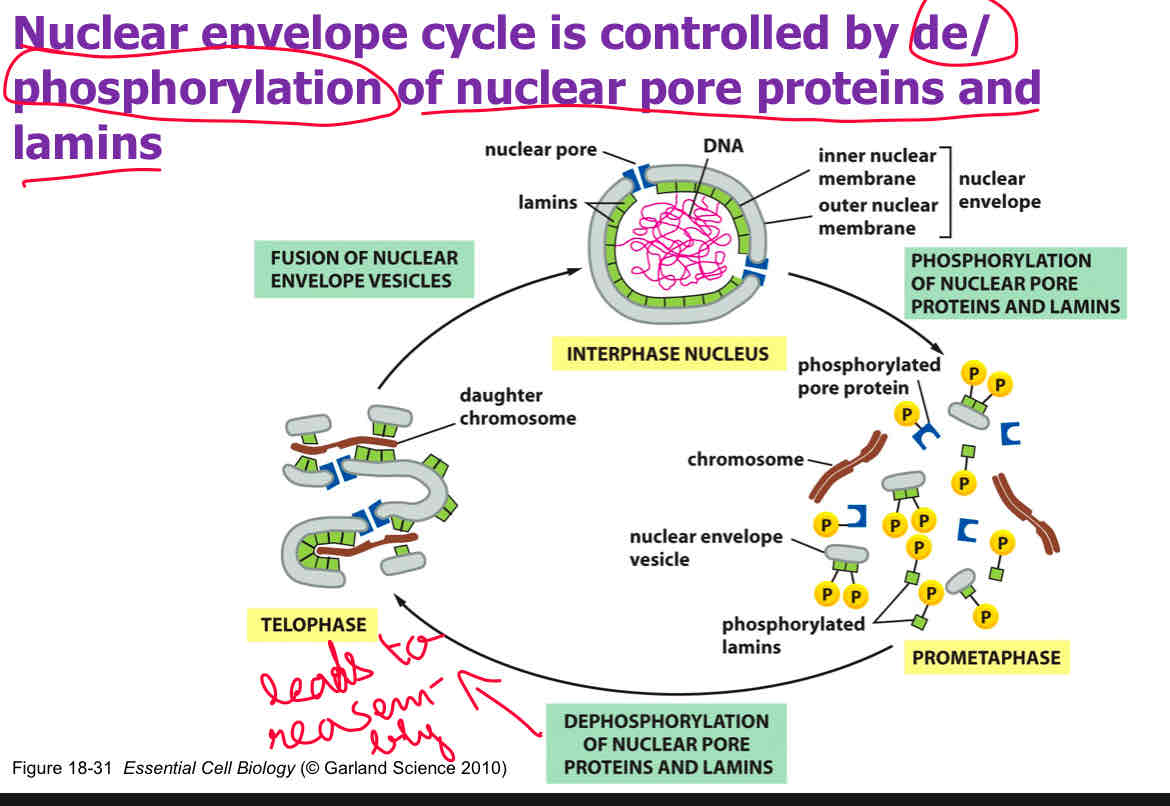
The __________ proteins enter through nuclear pores during telophase to help reform the nuclear envelope.
Nuclear (Nuclear envelope cycle is controlled by de/phosphorylation of nuclear pore proteins and lamins)
attach slide 22
Describe the role of cohesin rings in chromosome segregation during cell division.
Cohesin rings are protein complexes that hold sister chromatids together from the time they are replicated until they are separated during anaphase. if the sister chromatids were free to move around the nucleus it would be impossible to ensure that the chromosomes were accurately segregated. This is why cohesion is very important.
Explain how the Anaphase-Promoting Complex (APC) contributes to the separation of sister chromatids.
The Anaphase-Promoting Complex (APC) is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that triggers the transition from metaphase to anaphase by marking specific proteins for degradation. It degrades securin, a protein that inhibits separase. Once securin is degraded, separase is activated, which then cleaves cohesin rings, allowing sister chromatids to separate and be pulled toward opposite poles of the cell during anaphase.
The process by which the plasma membrane begins to cleave during cell division is known as __________.
Furrowing
attach slide 23