Pharmacology Exam 1
1/213
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
214 Terms
What is the 6 Step Nursing Process
CAPPIE
Concept
Assessment
Pt Problems
Planning
Interventions
Evaluation
Patient Problems (Analysis)
3rd step of Nursing Process involving analysis of patient problems and needs. Based on assessment and is individualized
Planning
4th step of nursing process about generating solutions. This includes goals (SMART)
Specific
Measurable
Attainable
Relevant
Timed
Interventions
5th Step of nursing process about implementing planned activities. Involves patient teaching, promoting adherence to drug therapy, solving problems
Evaluation
Final step of nursing process about evaluating the goals. Did they reach their goal? If not why. Reassess, maybe revise plan
What are factors that help promote patient learning
The patients readiness to learn, their investment in learning, timing
What are the 3 core ethical principles in research
Respect for persons (including autonomy), beneficence (risk to benefit), justice (
What is the Controlled Substance Act
Act (passed in 1970) to regulate the manufactures distribution of drugs that may result in dependency. (STOPPING DRUG ABUSE)
It has 5 schedules.. 1 being not for medical abuse and high abuse potential.. and so on
Schedule 1 Drugs
Not approved for medical use, high abuse
Marijuana
LSD
Ecstasy
Heroin
Schedule 2 Drugs
High abuse potential, has medical use
Cocaine
Opium
High grade Morphine
Oxycodone
Methamphetamines (Adderall)
Schedule 3 Drugs
Less dependency then 1 and 2 but can lead to moderate dependence
Low grade Morphine
anabolic Steroids
Ketamine
Certain Codeine Mixtures
Schedule 4 Drugs
Ambien
Valium
Xanax
Rohypnol
Zolpidem
Soma
Darvon
Darvocet
Ativan
Talwin
Schedule 5 Drugs
Cough syrup
Lomotil
Motofen
How do nurses protect controlled substances
Accounting all controlled drugs though Drug counts with other nurses. Verify orders.
Controlled substance log
How do you account for Controlled Substances that are NOT used?
Any wastage must be witnessed by another nurse. If they already did it you CANNOT sign off on it
Who prescribed Controlled Substances stated by Nurse Practice Act
Physicians can only prescribe, nurses cannot administer either without provider order
What is the Chemical Name of a drug?
Describes the drug's chemical structure
What is a drug's Generic Name?
the official, nonproprietary name for a drug. This name is not owned by any drug company and is universally accepted.
nurses must know generic names
What is a drug's Brand Name
known as the proprietary name and is chosen by a drug company and is usually trademarked
ex. Lunesta is a brand name of a drug whose generic name is eszopiclone
Are generic drugs safe compared to brand name?
If the generic drug is found to be bioequivalent to the brand name by the FDA it can be marketed. If there is less than 20% variance in drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, a generic drug is considered equivalent to the brand name
What the biggest issue with OTC drugs for Nurses?
Patient side effects when taken with other drugs. Patient teaching with reading drug labels
What is Pharmacokinetics?
The process of drug movement through the body necessary to achieve drug action
what the body does to the drug
What is Drug Absorption? (1/4)
Process of drug transport from the site of administration to the systemic circulation by crossing a biologic membrane
ex- Oral to bloodstream
What factors impact Absorption?
Route, preparation, dosage, digestive motility and enzymes for oral drugs
Blood flow, lipid solubility, degree of ionization, pH, drug-drug, drug-food interactions
What is the route of an Oral Drug
Oral drugs from the GI tract pass from the intestinal lumen to the liver
What is the First-Pass Effect/Metabolism
Oral drugs when in the liver are metabolized to an inactive form and are excreted which REDUCES the amount of active drug available to exert effect
only part of drug reaches systemic circulation
What is Bioavailability
Refers to the percentage of administered drug available for activity. Bioavailability for Oral drugs is always less than 100% due to first pass and IV is always 100%
What are factors that ALTER Bioavailability
Drug form, such as tablet, capsule
Route of Administration- Enteral (gi tract), topical, parenteral
Gastric mucosa and motility
Administration of drug with food or other drugs
Changes in Liver function can increase Bioavailibility
Which drug form is most rapidly absorbed from the GI tract?
Sublingual
What is Drug Distribution? (2/4)
Movement of drug from blood circulation to body tissues. Carried by blood or tissue fluids to sites of action
What factors impact Distribution
Circulation
Tissue affinity
PROTEIN BINDING
What is drug protein binding
As drugs are distributed in plasma many bind with plasma proteins
Highly-bound protein drugs are less active
What are Free Drugs?
The portion that remains of a drug that is free and unbounded from a protein. These are ACTIVE
What happens when two highly protein-bound drugs are administered together
They compete for protein-binding sites resulting in increased free drugs and POSSIBILITY FOR ACCUMULATION AND TOXICITY
What would happen if there were LOW plasma protein levels
The decrease in the # of available binding sites can lead to increase in Free drugs resulting in accumulation and toxicity
What patients would be at risk for Low plasma protein levels?
Patients with Liver or Kidney disease,
What is the most abundant Plasma Protein available for binding?
Albumin
What drugs can get through the Blood Brain Barrier?
Highly lipid soluble and of low molecular weight
What is drug Metabolism? (3/4)
Biotransformation; method of drug inactivation.
PRIMARY SITE IS THE LIVER where drugs are turned into inactive Metabolites
What in the Liver converts drugs to Metabolites?
CYP450 Enzymes in the liver
What is a Pro Drug?
a compound that is metabolized into an active pharmacologic substance
drugs that are only effective when they are turned into metabolites
What is the Half-life of a drug?
Time that it takes for the amount of a drug to be reduced by half.
What is steady state?
Amount of drug administered is equal to the amount being eliminated
What is a Loading Dose?
A large dose given for drugs with long half-lives in order to achieve steady state
What is Drug Excretion? (4/4)
Getting rid of the metabolites from the body. Mainly from the KIDNEYS, can also be eliminated through bile, sweat, lungs.
Reason why kidney function is so important
What factors influence Excretion?
Urine pH, Renal function
What are some Renal Function Tests
Creatinine, BUN, CC (creatinine clearance)
What is Pharmacodynamics?
What the drug does to the body, the effect of the drug
What is a Drugs Primary Effect?
the desirable response from the drug
What is a Drug's Secondary Effect?
a response that may be desirable or undesirable
for example Benadryl with sedation
What is Dose-response Relationship?
the body's physiologic response to changes in drug concentration at the site of action
What does it mean for a drug to have High Potency?
a drug with high potency produces significant therapeutic responses at low concentrations
What is a drug's Maximal Efficacy?
The point when increasing a drug's dosage no longer increased the desired therapeutic response
What is the Therapeutic Index?
ratio of toxic dose to therapeutic dose
therapeutic dose of a drug (ED50) and the toxic dose (TD50). The number referring to the % of the population it effects
TD50 is toxic for 50% of the pop.
what is a drug's Onset?
time it takes for a drug to reach the minimum effective concentration
time it takes for the drug to work
what is a drug's Peak?
when a drug reaches its highest concentration in the blood
what is a drug's Duration of Action?
length of time the drug exerts its therapeutic effect
Where does a drug bind to a receptor?
Ligand-binding domain
What are Side Effects?
expected secondary effects of a drug that may be desirable or undesirable
What is an Adverse Reaction?
Unexpected reaction more severe than side effects, always undesirable.
anaphylaxis, jaundice, seizures, - WBC, kidney damage
What are Additive Drug Interactions
1+1= 2 sum of the effect of 2 drugs is greater than 1
What are Synergistic Drug Interactions
1+1= 3
2 drugs work together extremely well
What is the benefit of Synergistic and Additive drug interactions
You can give less drugs to pts which results in less side effects
What is a common Drug-food combo
Grapefruit juice
It inhibits CYP450 enzyme which alters metabolism
How might Pharmacogenetics affect patients?
Expensive, it can help pts with complex treatments that may be different if someone has genetic variance
What is Ethnopharmacology?
May combines traditional and Western health practices Healing remedies, herbs, powders, teas, etc
Why is Complementary and Alternative Medicine important to nurses
Pt teaching in safety, nurses must also be sensitive to beliefs and practices
What are Ethnohealers?
Folk medicine, traditional medicines, "healers"
Why is research related to Pediatrics limited?
Obtaining informed consent, companies investing less,
Pharmacodynamics is influenced by what in Pediatrics?
differences in body fat, decreased protein, etc.
Variability in organ function, development. and admin issues
what age group does immaturity in organs and systems effect the most in Pharmacokinetics?
Newborns and infants
what is different about Absorption in pediatric pts?
Reduced gastric acidity, irregular gastric emptying,
THINNER SKIN= TOPICALS EASILY ABSORBED
what is different about Distribution in pediatric patients?
More extracellular water/fluid= decreased drug concentration
what is different about metabolism in pediatric patients?
Higher metabolic rate
What is different about Excretion in pediatric patients?
Immature kidneys
How are drugs without pediatric dosing schedules dosed?
Dosing based on child's weight in kg or body surface area (BSA)
what is Family-Centered Care?
Patient teaching is for family and the child. Taking into account their culture. Parents choose involvement level, building rapport with parents
family members/care givers can assist in administration if possible
What is Atraumatic Care?
Care that minimizes the psychological and physical distress experienced by children and families.
Decreasing separation and pain, identifying stressors
What is the most common drug form for Pediatrics?
Oral medications
if IV or IM is needed it should be switched back ASAP
How are Oral drugs given in children under 6
Using oral syringe with exact dosing with possible flavoring
How are Infants given oral drugs
Syringe to the back of the cheek small amounts at a time
droppers, bottle nipples if necessary
Where are Immunizations given to Infants?
Vastus lateralis
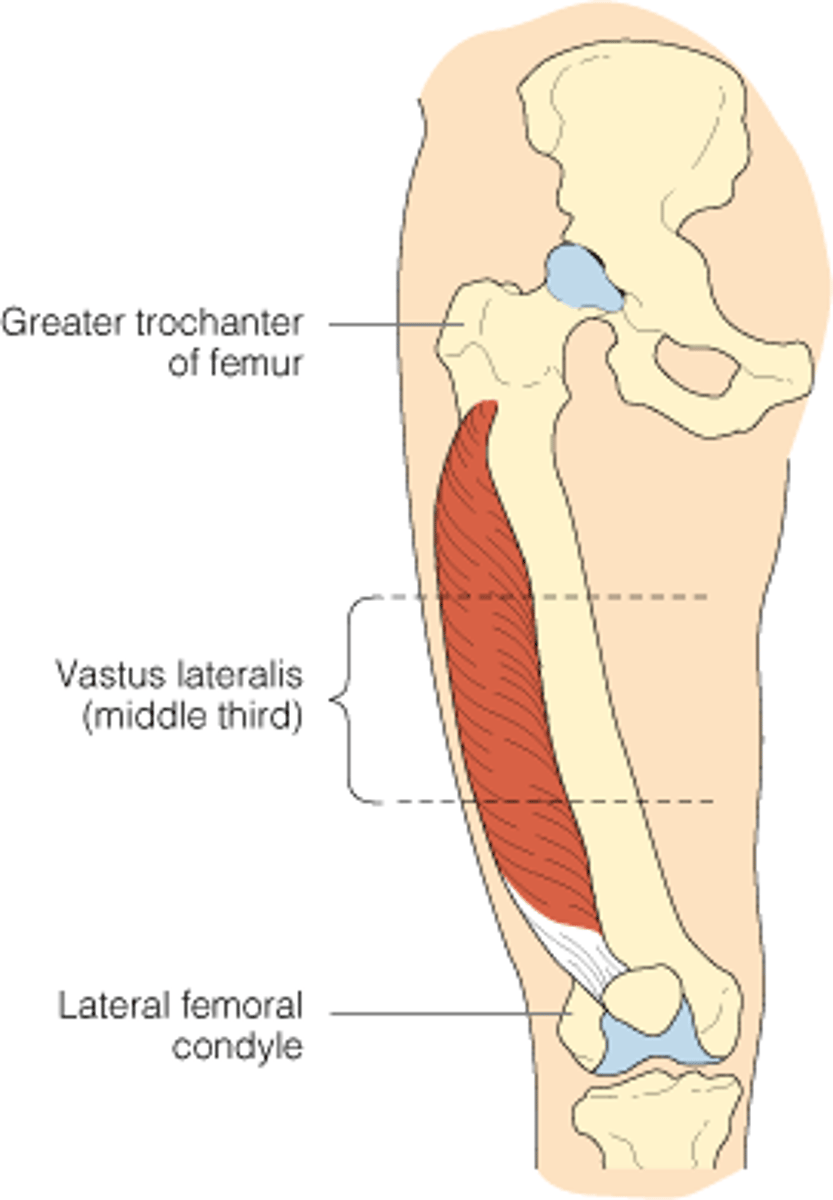
How should drugs be administered to Geriatrics?
Start low and go slow
Low dosages first and gradually increase
Physiological Changes that affect Pharm in Older Adutls
increased body fat, reduction in kidney mass and blood flow, reduced clearance of drugs
Reduction in liver size and blood flow, reduced hepatic clearance of drugs
What influences Pharmacodynamics in Geriatric?
decreased receptors, affinity, altered response to drugs, decreased compensatory responses
decreased protein binding sites (free drugs)
What is the significance in Pharmacodynamic changes in Geriatric?
increased risk of adverse reactions
May need a lower dose
may need increase in dosing interval
what is Polypharmacy?
use of more medications than is medically necessary, usually 5 drugs
risk factors- advanced age, female,
Beers Criteria for Potentially Inappropriate Medication Use in Older Adults
document that is used as a guide for safe presciptions
5 types of Adverse Drug Events
adverse reactions
Medication errors
Therapeutic failures
Adverse drug withdrawal events
overdose
Which age group is Adherence to a drug regimen a problem
Older adult geriatric
what are some reasons for Nonadherence to a drug regimen?
Polypharmacy (too many), economic factors, lack of knowledge, lack of symptoms, impairments, cognitive decline
The older adult patient has questions about oral drug metabolism. Information on what subject is most important to include in this patient teaching plan?
First pass effect
What is Substance Use Disorder
when the recurrent use of alcohol and/or drugs causes clinically and functionally significant impairment
What do drugs do to the Limbic System of the brain?
increase Dopamine for the brain's Reward Circuit making us feel pleasure
what words do you NOT use for Substance Use Disoder?
Abuse and dependency
What is Tolerance?
Requiring a significantly increased amount of a drug to achieve the desired effect
What is remission?
None of the 11 criteria for substance use disorder for at least 3 months
What is Recovery
a process of change through which an individual improves health and wellness, lives a self-directed life, and strives to reach full potential
What is Relapse?
a return to drug use after a period of abstinence, often accompanied by reinstatement of substance use disorder
How is Alcohol absorbed?
It is absorbed mainly through Small Intestines but also in the Stomach