y9 science
#ff8b00 - orange
UNIT 2: CHEMISTRY
1) Evolution of the Atom:
Matter - A substance that has volume (occupies space) and mass (weight). All matter is made up of atoms, which bond together to produce different substances.
Atoms - The building blocks of mater (classic definition)
First atomic theory: In 1802, John Dalton proposed that all matter is made up of tiny spherical particles that were indivisible and indestructible. We now know that this is wrong.
2) The Atomic World
Pure substances and mixtures:
Matter can be split into two types; pure substances and mixtures
Pure substances - Substances made up of only one type of particle throughout. They cannot be physically separated.
Mixtures - Substances that are made up of two or more types of particles throughout. These can be physically separated.
Elements:
Elements are types of atoms that share the same number of protons. In nature, some elements prefer to be formed in a monatomic form (individual atoms), while others form in a polyatomic form (e.g. molecules)
Regardless of the preferred arrangement, elements can also be considered pure substances, because if you have multiple particles, they will all be the same.
Compounds:
Compounds are substances that are made up of two or more different elements that are chemically bonded together. If they are not mixed with anything else, these compounds can also be considered pure substances, but not all pure substances are compounds.
3) Atomic Structure and Isotopes:
Atomic structure:
An atom is made up of three different types of particles:
Protons - positively charged
Neutrons - neutrally charged/no charge
Electrons - negatively charged
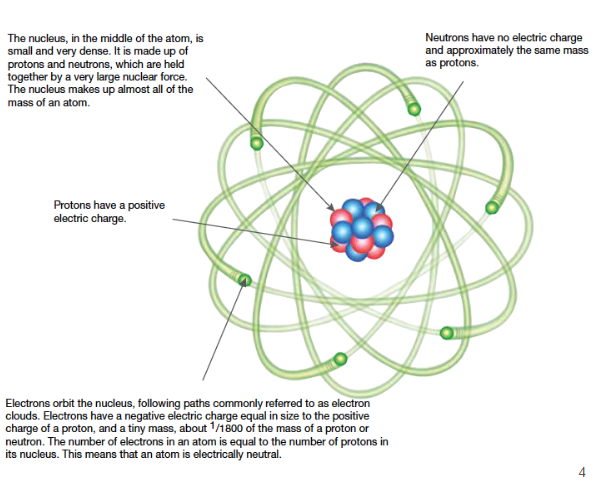
The protons and neutrons make up the nucleus, which has majority of the mass of an atom, due to its dense center.
The Bohr model:
In 1913, Niels Bohr developed a new model of the hydrogen atom, which explains emission spectra.
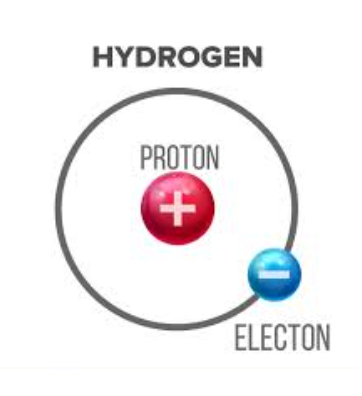
The Bohr model proposed that:
Electrons revolve around the nucleus in fixed, circular orbits
The electrons’ orbits refer to specific energy levels in atoms
Electrons can only occupy fixed energy levels and cannot exist between two energy levels
Scientists soon evolved the Bohr model to atoms other than hydrogen. They proposed that electrons were grouped in different energy levels, called electron shells. They will labelled with the number n = 1, 2, 3, etc.
Different types of atoms:
The type of atom that makes up each elements are determined by the number of protons (atomic number) in the nucleus.
Atomic number = number of protons
Mass number = number of protons + number of neutrons
Atoms are electrically neutral - number of electrons = number of protons
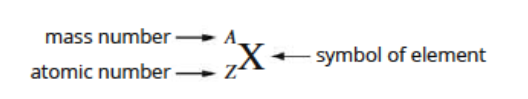
Isotopes:
Isotopes are when an atom has the same number of protons, but different number of neutrons. They have identical chemical properties, but different physical properties.
4) Electron Configuration:
Electron configuration - Bohr model:
Using the Bohr Model, the basic electron configuration can be found for different types of atoms. Remember, this rule ONLY applies to the first 18 elements.
Shell 1 - 2 electrons
Shell 2 - 8 electrons
Shell 3 - 18 electrons
An overall approach can be 2, 8, 8, …
There are two rules to the electron configuration model:
Rule 1 - Each shell can only contain a specific number of electrons
Rule 2 - Lower energy shells must be filled before higher energy shells
6) Ions:
The octet rule:
The octet rule is the tendency of atoms to prefer having eight valence electrons, because a valence shell with eight electrons is very stable, and equivalent to a full shell. When given the opportunity, atoms will either gain, lose or share electrons to follow the octet rule.
Ions:
Ions are atoms with a charge. They are formed when a neutral atom gains or loses electrons. Losing electrons can cause an imbalance between positive and negative charges, thus creating an ion.
When an atom gains electrons, it is more negative. If it loses electrons, it becomes more positive.
There are two types of ions; cations and anions.
Cations - positively charged ions
Anions - Negatively charged ions
To become stable, ions take the path of least resistance, or the most effective way, between either losing or gaining valence electrons.
For example, if an ion has 3 valence electrons, it will lose all of them to be stable.
Metals and nonmetals:
Metals have low amounts of valence electrons (1, 2, 3), so they usually lose electrons and become cations.
Nonmetals have high amounts of valence electrons (5, 6, 7) and they gain electrons and become anions, with the exception of noble gases (group 18), since they already have eight valence electrons.
Naming monatomic ions:
With cations, you put the word ‘cation’ next to the element.
e.g. Aluminium cation
With anions, replace the suffix with -ide
e.g. Oxide anion

7) Electron Transfer and Ionic Bonding:
Ionic bonding:
Ionic bonding is the electrostatic attraction between two oppositely charged atoms. They typically involve a metal cation and a nonmetal anion.
Lattice structures:
Some ionic compounds involve more than two ions. As more ions bond together, they form an ionic lattice.

Electron transfer diagrams:
Electron transfer diagrams are used to show what path electrons take during ionic bonding.
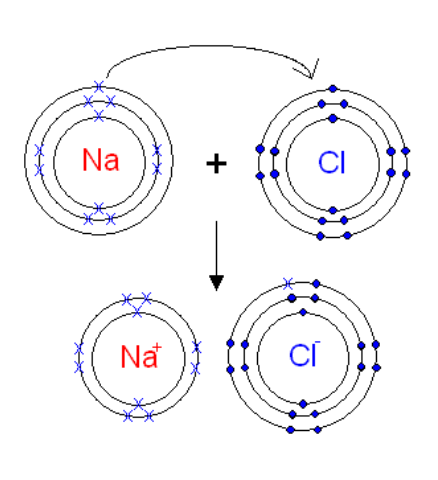
NOTE - for lattices, cations are always next to anions, and vice versa.
8) Naming Ionic Compounds:
Rules for naming ionic compounds:
Names of cations (metals) should come before names of anions
e.g. sodium chloride
Names of cations remain constant
e.g. sodium
Names of anions have -ide at the end
e.g. chloride
Chemical formulas for simple ionic compounds:
Rules for writing chemical formulas:
Write the symbol of the positively charged ion first
Use subscripts to indicate the number of each ion, writing them after the ion they match to.
If there is only one ion of an element, don’t put subscript 1.
Don’t include the charges of ions in the balanced formula.
Example:
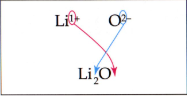
In this example, the Lithium symbol is first, since it is positively charged. The Oxygen ion is negatively charged, so it is second. The number of the negative charge of the Oxygen ion goes as a subscript next to the Lithium ion, and vice versa.
More examples:
K2O = K1+O2- Potassium Oxide
NaOH = Na1+OH1- = Sodium Hydroxide
CaBr2 = Ca2+Br1- Calcium Bromide
Al2S3 = Al3+S2- = Aluminium Sulfide
Li3N = Li1+N3- = Lithium Nitride
Be(NO3) = Be2+NO3- = Beryllium Nitrate
9) Properties of Ionic Compounds:
Ionic compounds are called ‘salts’, and they are solid in room temperature. They have strong electrostatic bonds between cations and anions and form a lattice. Very high levels of energy are required to break these bonds, so they stay solids.
Why are ionic compounds brittle?
When an ionic compound is struck with a hammer, the ions shift, and go next to like ions. Due to this, they repel, and the bond is broken.
Some ionic compounds are soluble, since the ions are attracted to water’s particle charges, and therefore, the bonds break. Since the atoms are free, they can conduct electricity, hence, solid ionic compounds can’t conduct electricity, but liquids can.
Molten ionic compounds can conduct electricity, but solids can’t, due to the kinetic/thermal energy of the liquid compounds loosens the bonds between the ions, and making them conductive, due to the free moving ions.
10) Metallic Bonds:
Ionic bonds:
Valence electrons from the cation go to the anion
The cation (transition metal)‘donates’ its valence electrons to the anion (nonmetal).
Solid crystals with repeating patterns of cations and anions.
Covalent bonds:
They share valence electrons
Usually liquid or solid
Between two nonmetals
Metallic bonds:
Metallic bonds are surrounded by electron clouds (delocalised sea of electrons)
Valence electrons move freely around the metal ions.
There is only one type of metal cation
They are uniformly structured
Occurs in pure metals
Occur as ‘crystal lattice”.
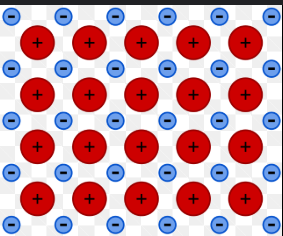
A crystal lattice of a metallic bond. The red circles are cations, while the blue circles are the delocalised sea of electrons.
This type of non-directional bond is called metallic bonding.
Metal atoms are hard to separate, but relatively easy to move (malleable).
Alloys: A mixture of two or more elements, where one element is a metal combined via metallic bonding.
Alloys are generally harder than the pure elements, due to the cations having different sizes and radii.
Examples of alloys:
Steel: combination of iron (metal) and carbon (nonmetal)
Bronze: Combination of copper (metal) and tin (metal)
Brass: Mixture of copper (metal) and zinc (metal)
Metallic properties:
Metals are:
Lustrous (due to the presence of free moving electrons, which can reflect light.
Good conductors of electricity (due to the delocalised sea of electrons being free to move, and an electric current being able to form)
Malleable (can be hammered into shapes without breaking)
Have a high melting point (due to strong metallic bonding)
Good conductors of heat (delocalised sea of electrons are able to gain kinetic energy, then collide with other electrons and conduct heat)
Ductile (able to be drawn into a thin wire without breaking)
Dense (has a tightly packed lattice)
Flame test logbook task:
The colour of the flame changes, due to the energy levels of the metallic cations. The heat makes their electrons jump to higher energy levels. As these excited electrons jump back down to their original energy levels, they release the energy in the form of light. The colour depends on the amount of energy released. Each metal has a unique outcome.
11) Covalent Bonding:
Covalent bonds refer to bonds that involve sharing electrons, instead of donating, to satisfy the octet rule, and always involves two or more non-metals.
There is only one pair of shared electrons, called a ‘bonding pair’.
One bonding pair is called a single bond, two bonding pairs are a double bond, etc.
All halogens can covalently bond with themselves, or other halogens.
Steps to draw covalent bonds:
Draw the symbol of the element that will form the most bonds in the center
Draw the other atoms around the central atom
Determine how many electrons are needed to achieve chemical stability, either following the octet rule or the duet rule
The atom which needs the most atoms to achieve chemical stability is the one that needs to be in the middle
Add a pair of electrons between any two atoms that are forming a covalent bond
Determine how many electrons each atom has left and add these as non-bonding pairs
Check to see that the octet or duet rule is satisfied for all atoms and that all the valence electrons have been drawn.
UNIT 3: PHYSICS
1) Introduction to Electricity:
Electricity:
Electricity is the movement of energy through charged particles, such as electrons or ions.
Electric charge can be either positive or negative, opposite charges attract and similar charges repel.
Electrons:
Electrons are the most involved in electricity.
Most materials have electrons tightly bound to their atoms, but with electrical conductors (like metals), the electron (delocalised sea of electrons) are free to move.
Conductors and Insulators:
Conductors are able to conduct, because of their electrons that are free to move.
Insulators, however, have electros that hold on tightly to their atoms, and electrons don’t move along these materials very well.
Static electricity:
Some insulators can get electrons from conductors when rubbed together.
The insulator has a more negative charge, while the conductor has a more positive charge.
Static electricity is the abundance of electric charge on a surface.
Static electricity can only be generated by two materials rub against each other, an electric charge is present, and there is an electrical imbalance.
When two materials rub against each other, there are loose electrons, that escape to the other object, making one positively charged, and the other negatively charged.
Like magnets, opposite charges attract, while like charges repel.
Static electricity practical investigation:
Hypothesis:
The object that loses electrons will be positive, and the object that the positive object sticks to will be negative.
Results:
Questions:
How did you determine the charge on each material after they had been in contact?
The material that the other material was stuck to had a negative charge, due to the loose electrons. The object that is attracted has a positive charge, due to loss of electrons.
Illustrate this charge differential with a picture.
Given that you did not rub the balloon with the pieces of paper or coke can, what was the charge on each?
The balloon would be charged, while the can and confetti would be neutral.
When you placed a ‘charged’ object (for example, the balloon) next to uncharged objects (coke can or pieces of paper), what happened?
The balloon would either attract or repel electrons from the uncharged objects, and temporarily change the charge of specific areas of the neutral objects.
Why do you believe this was the case?
This would be the case, because of charge induction.
Using your current understanding of static electricity - how do you think it might be applied to larger examples, such as lightning?
Lightning is caused by an imbalance of electrons between clouds and the ground, with the cloud being charged, and the ground being neutral. Due to this, electrons transfer to the ground, and strike as lightning.
Reflection:
What did you learn from this activity? How did you add to what you already knew?
Charge induction:
This occurs when a charged object comes near a neutral object. The charged object either attracts or repels electrons in the neutral object, and they will move to one side. The overall charge will be unchanged, but there will be temporary charges on different areas of the object.
2) Electrical Circuits
Components that make an electrical circuit:
A power supply to provide electrical energy.
A load (or loads) in which electrical energy is converted to other forms of energy (e.g. heat, light, etc.).
A conducting path which allows electric charge to flow around the circuit
Drawing electrical circuits:
There are some symbols that are needed to draw electrical circuits, so that everyone can understand it.
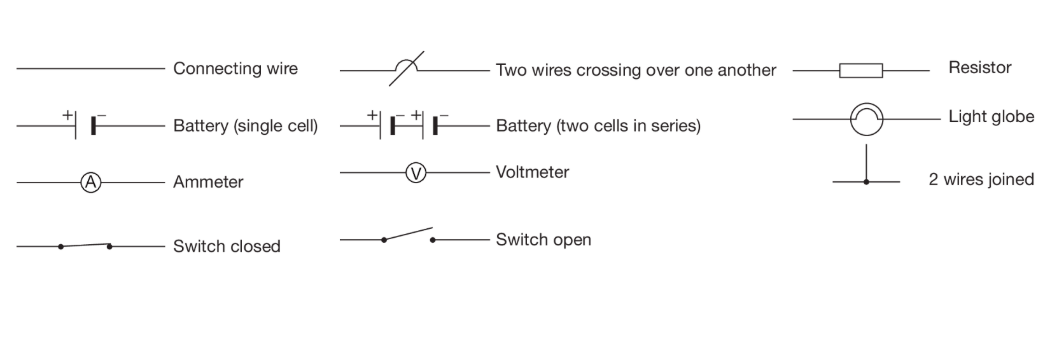
3) Current and Voltage + Series and Parallel Circuits:
Water flowing through a hose:
Current - How many coulombs (num of electrons that represent one ampere) of electrons flow through a conductor per second
Direction of conventional current = from cathode to anode
Direction of current flow = anode to cathode
1 coulomb = 6 × 10^18 electrons per ampere per second.
Unit for current - Ampere (can be abbreviated to amp).
Electric current:
Electric current is the amount of electric charge that flows through a wire per second. It is measured in amperes/amps, and the electric charge comes from the electrons.
Types of circuits:
There are two ways a circuit can be arranged:
Series circuit: There is only one ‘loop’ (conducting pathway) in the circuit, and multiple loads are on a single line.
Parallel circuits: There are many ‘loops’, and there are loads on each loop.
4) Resistance and Ohm’s Laws
Resistance: The measure of how much an object resists flow of electrons.
Ohm’s Law: Shows the relationship between voltage, current and resistance.
Voltage (Volts) = Resistance (Ohms Ω) x I (current/Amps)
5) Magnets
Faraday and magnetism:
Generation of electricity by power plants depends on electricity and magnetism. Faraday suggested that magnetic fields may be able to produce an electric current and proved it in 1831.
Magnetism | Magnets:
Spinning of a magnet inside a metal coil or vice versa can create a large electric current, which can be connected to a turbine and it can create renewable energy.
Magnetic materials:
Magnetic materials are attracted to magnets.
Only iron, nickel and cobalt are magnetic.
Metals can also be polarised, where some ions in metals can be made to face another direction, and they can become magnets.
However, if it is too close to a large magnetic field, it can lose its magnetism. This is called reverse polarisation.
Magnetism:
Magnetism is the force of attraction and repulsion between magnets.
Permanent magnets can produce their own magnetic field, and the magnetic field lines go from the north pole to the south pole.
The closer you get to the magnets, the stronger the magnetic field.
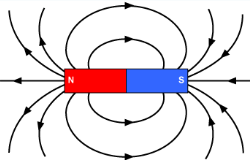
Notice how there are lines from the north pole to the south pole between the two magnets. This indicates the magnetic pull of magnets that have opposite poles facing each other.
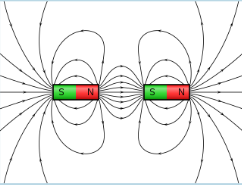
Whenever there are two of the same poles facing each other, the magnetic field lines NEVER connect both magnets.
2) Cycles in the Biosphere
Earth’s four spheres:
Atmosphere:
Consists of the gases above Earth’s surface (around 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 1% argon, and <1% trace gases)
It is around 500km thick and contains 5 layers
Lithosphere:
All the natural and lifeless arts of earth’s surface, crust and core.
Includes the rocks and sand from dry land, as well as magma, lava and minerals below the earth’s surface.
Hydrosphere:
Made up of all the water on the Earth (includes all the water vapor in the atmosphere
Includes large bodies of water, as well as ice, glaciers and rain.
Biosphere:
Consists of all areas of earth and the atmosphere that contain life.
It includes all living organisms on the planet(e.g. humans, microorganisms, fungi, plants, etc.)
The carbon cycle:
The carbon cycle describes the movement of carbon throughout all four spheres. Carbon is one of the most important chemicals for life on earth.

The carbon cycle can be summarised into seven processes which either increase or decrease the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Photosynthesis:
Input: Sunlight, minerals, CO2, water, glucose (C6H12O6)
carbon dioxide + water = glucose + oxygen
Transfer of carbon via food chain:
The building block of all living organisms are made of carbon
From producer to primary consumer (herbivores) then secondary consumers (omnivores) and tertiary consumers, etc.
The further down the food chain you go, the less the original energy from the producer.
Energy can be lost via digestion
Respiration:
Plants and animals break down glucose using oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water.
glucose + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water
Decomposition or excretion:
Some of the carbon content of animals and plants enters the soil as waste
Dead organic matter is broken down by decomposers, which respire, release carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere.
Organic matter = matter with carbon and hydrogen
Formation of fossil fuel:
The carbon content of these organic matter are broken down into usable fuels to provide us with energy.
Combustion:
When fossil fuels are burned in oxygen (combustion), carbon dioxide and water are formed.
Octane + Oxygen = Carbon dioxide + Water
Formation of limestone:
Carbonic acid along with calcium ion mineral deposits make calcium carbonate - the major component of shells.
Shells from dead animals compact to make limestone.
The Greenhouse Effect:
The greenhouse effect happens when greenhouse gases, such as water vapor, chlorofluorocarbons (cfcs), etc. let sunlight in, but don’t let it out. This mimics a greenhouse, since greenhouses are designed to let sunlight and heat energy in, but doesn’t let it escape.
The greenhouse effect can lead to global warming.
Tectonic plates:
Subduction zones are where two tectonic plates collide
Continental crust (30-70km) is thicker than oceanic crust (5-10km)
Oceanic crust is more dense and heavy
Continental crust is around 4 billion years old
Oceanic crust is around 200 million years old
Continental crust is made when magma cools slowly (granitic rocks)
Oceanic crust is made from basaltic rocks (when magma cools quickly)
When tectonic plates merge, the heavier plate goes down (subduction)
Convention currents:
As the centre of the earth is hotter, the heat will flow by convection currents
Heat causes the rock in the mantle
Types of plate boundaries:
Convergent - destructive plate boundaries, because crust enters the mantle
Divergent boundaries - made when oceanic crust separates and forms a rift, and hot mantle melts into magma and fills in the rift, which creates a chain of small underwater volcanoes, and eventually cools to form new oceanic crust.
Transform boundaries - Also known as conservative plate boundaries, since crust is conserved, not created nor destroyed. Describes two plates sliding along each other along a fault line. Large earthquakes occur when something prevents the plates from sliding, and pressure builds up until there is just enough to start the sliding with a jolt.
Subduction: Occurs when old oceanic crust moves towards or converges towards continental crust or younger oceanic crust
Earthquakes:
Epicentre: The epicentre of an earthquake is the point on the surface of the Earth that is directly above the underground point (the focus) where a fault rupture begins.
Triangulation:
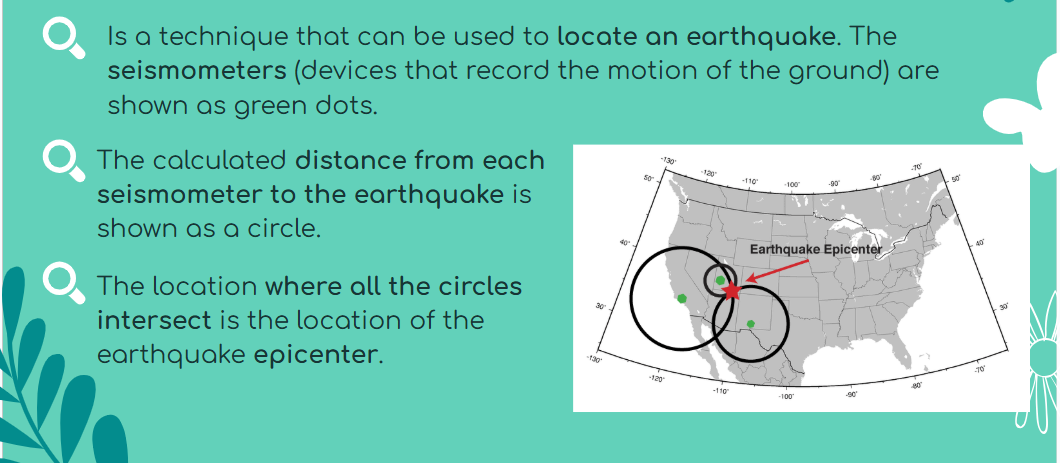
Measuring earthquakes:
Earthquakes are measured using a seismograph, and the most well known way of measuring the strength of an earthquake is the Richter scale.
The Richter scale is measured in tenfold, instead of a constant scale.
Seismic waves:
The energy formed in earthquakes are released in waves. there are three types of waves:
P-waves: A type of compression wave that travels through the ‘body’ of the earth (the crust) and liquids.
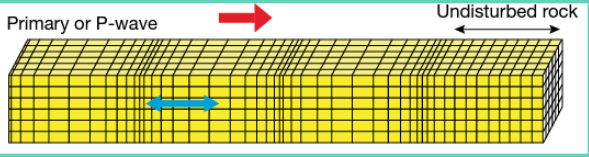
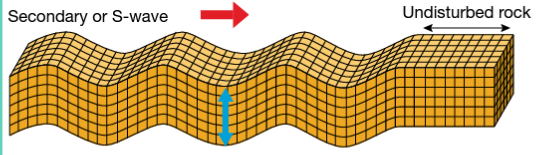
S-waves: Moves only through liquids, and the energy moves perpendicularly
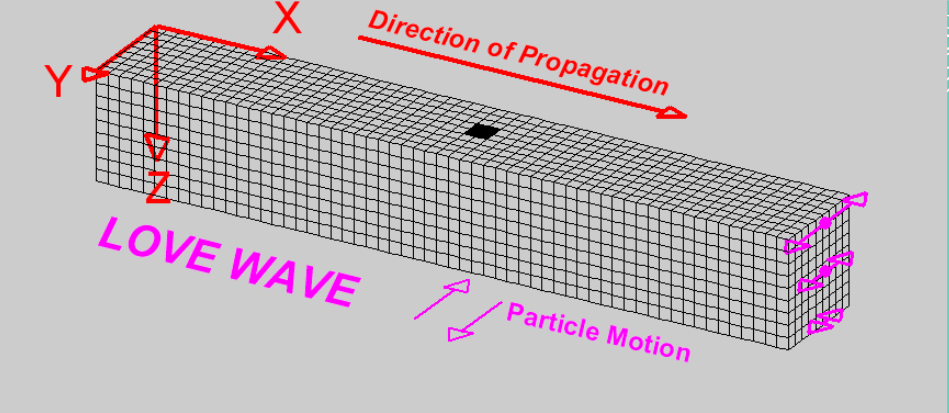
L-waves: Moves side to side, and are the most dangerous types of waves; combination of P and S waves
Greenhouse effect:
Greenhouses:
Some areas are too cold to grow plants, so they are grown in greenhouses.
This allows farmers to control the conditions of where the plant grows
Greenhouse gases:
Gases that absorb and re-emit infrared radiation in the atmosphere
Infrared (~50%): Invisible light that we can’t see, but can feel as heat. Much is absorbed and re-emitted by greenhouse gases in the upper atmosphere.
Visible light (~45%): The light from the EM spectrum we are able to see. It is absorbed by the earth (and other opaque objects).
Ultraviolet (~5%): Another type of invisible light that is damaging to the skin, but is luckily mostly absorbed by the ozone layer.
Infrared light:
Infrared radiation has a really long wavelength (difference in length between two peaks or two troughs)
Greenhouse gases:
Carbon dioxide
Methane
Nitrous oxide
Water vapour
Fluorinated gases
Why can’t infrared light get out?
After the Earth absorbs the solar radiation, it warms up and emits its own IR radiation. Since the Earth is much cooler than the sun, this IR radiation has a longer wavelength. Many greenhouse gases absorb and re-emit this longwave IR radiation, trapping heat in the atmosphere.
catalyst- speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction
Radiation is reflected off the atmosphere, and also directly off the earth’s crust.
You are very likely to get sunburnt when you are in snow, because white reflects light, while black absorbs light.