Chapter 5 - Animal Nutrition : Diet
Nutrition:
There are %%7 types of nutrients%% that humans consume namely, %%carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, fiber and water%%. The following pyramid shows their dietary requirements:

Simple carbohydrates
- Carbohydrates are %%organic molecules%% made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen with the general formula for most carbohydrates being CnH2nOn.
- Carbohydrates are classified into 3 main groups: %%monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides%% depending on the number of basic sugar units they have.
- Monosaccharides are the most basic unit of carbohydrates and are the simplest form of sugars. Common examples are %%glucose, fructose and galactose%%.
- Disaccharides are formed when two monosaccharides undergo a condensation reaction. Common examples are %%maltose%% (formed by 2 glucose units), %%sucrose%% (1 glucose, 1 fructose) and %%lactose%% (1 galactose, 1 glucose).
- A %%condensation reaction%% is a chemical reaction when two molecules combine together to form a single molecule with the elimination of a water molecule.
- A disaccharide can be split into its component monosaccharides by undergoing %%hydrolysis%% in which a water molecule is added to the disaccharide to break it down into its component monosaccharides. Enzymes are usually required for this process.
Complex carbohydrates
Polysaccharides include %%starch, glycogen and cellulose%%. They are long chains of glucose molecules linked together in condensation reactions. Each chain may contain thousands of glucose molecules.
In starch, the glucose molecules are linked together in long straight chains or branched chains. It is a storage molecule in plants.
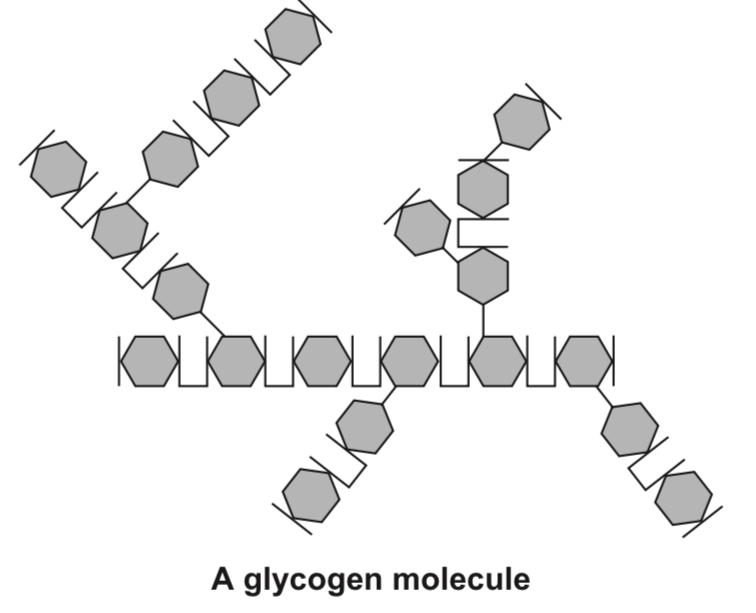
In glycogen, the glucose molecules are linked together in highly branched chains. It is a %%storage molecule in animals and fungi.%%
In cellulose, the glucose molecules are linked in long straight chains. The linkage between the glucose molecules is not the same as that in starch. Cellulose is the tough material %%found in cell walls of plants%%. Cellulose is the %%fibre%% necessary in a healthy diet.
Glycogen and starch are the storage forms of glucose in animal and plant cells respectively. This is because
(a) they are %%insoluble in water%% and do not affect water potential in cells,
(b) they are %%too large to diffuse out%% of the cells and thus remain within the cells,
(c) they have compact shapes, and
(d) they can be easily hydrolysed into glucose for %%cellular respiration%%.
Fats
- Fats (lipids) are organic molecules made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. There is no general formula for fats. The ratio of hydrogen to oxygen is much higher in fats than in carbohydrates, where the ratio of hydrogen to oxygen is 2 : 1.
- Fats are made from two types of smaller molecules: %%glycerol and fatty acids.%% Each fat molecule contains a glycerol molecule and 3 fatty acids. Each fatty acid is linked to the glycerol backbone in a condensation reaction.
- When 3 water molecules are added to a fat molecule with the help of enzymes in a hydrolysis reaction, the fat molecule breaks down into fatty acids and glycerol.
- Fats are storage molecules that can store a large amount of energy.
- They are also an important %%component of cell membranes.%%
- Fats are used to make %%steroids%% and %%certain hormones.%%
- Fats are also used as %%insulating material%% to prevent the loss of body heat.
- Fat is also a %%solvent for fat-soluble vitamins%%.
Proteins
Proteins are complex organic molecules made up of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. They may also contain %%sulfur%%.
In the form of %%enzymes%%, proteins participate in all cellular processes and are responsible for almost everything living organisms do.
There are tens of thousands of different proteins, each serving a different function and having a unique structure.
Proteins are made up of %%amino acids%%.
An amino acid is a molecule with the general structure:
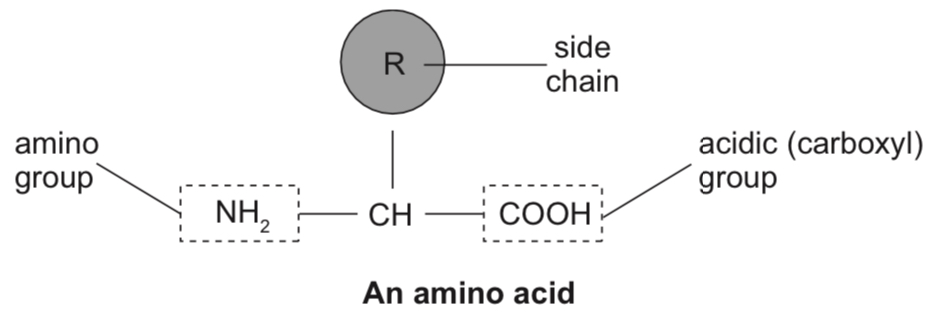
There are about 20 different naturally-occurring amino acids which have different side chains (also known as R groups).
Amino acids are combined in many different ways to form different protein molecules.
Amino acids link up in a condensation reaction to form a %%polypeptide chain%%. The bonds between the amino acids are known as %%peptide bonds%%.
Proteins are made of one or more polypeptide chains twisted, folded and coiled into a %%unique 3-dimensional structure.%%
The bonds between the amino acids, peptide bonds, are strong but the bonds that hold the 3-dimensional coiled structures together are weak and can easily be broken by heat or by changes in pH. Examples of such bonds are hydrogen bonds, ionic interactions and %%van der Waals interactions.%%
When these bonds are broken ,the protein loses its 3-dimensional conformation. This process is called %%denaturation%%. Proteins can be %%denatured%% if they are heated or placed in an environment with unsuitable pH. Denaturation usually leads to loss of function as proteins require their 3-dimensional shape to function. Denaturation can also cause proteins to lose their solubility and precipitate out of the solution.
Many %%proteins are enzymes%%, which catalyze chemical reactions with in our body.
Structural proteins found in muscle cells play a role in movement.
Other proteins take part in %%cell growth, repair and reproduction.%%
%%Antibodies%% are proteins in our body that help us fight diseases.
Water:
About 70% of the human body consists of water. %%Water%% is %%found in cell cytoplasm, blood, digestive juices, tissue fluid, fluid in joints and contained within organs i.e. spinal cord, the brain, the eyes, gastrointestinal tract, etc%%.
Water %%moderates body temperature%%. It has a %%high specific heat capacity%%, which means that a lot of energy is required to raise the temperature of water by 1°C. Hence, water helps the cell resist changes in temperature.
It plays a role in %%evaporative cooling%%. Water is a %%component of sweat%%, which removes heat from the body when it evaporates.
Water is a %%reactant in certain chemical reactions%% in the body, such as the hydrolysis of food molecules during digestion.
Water is a component of %%body fluids%% with %%lubricative%% or protective properties such as %%lubricants in joints%%, %%coating the stomach lining,%% %%mucus%% in the %%oesophagus%%, and %%cervical mucus%% in the female reproductive system.
Water is an extremely %%versatile solvent%%. More things dissolve in water than in any other solvent.
Because of this property,
(a) water is the medium in which chemical reactions take place in living organisms, and
(b) water serves as a %%transportation medium%%. It transports water-soluble food products from the small intestine to other parts of the body and waste materials from cells to the excretory organs for removal. It %%transports hormones%% to the target organs or tissues. Blood is the main transport medium in the body.
Testing for the presence of Nutrients:
Reducing Sugars
- The test for %%reducing sugars%% is known as the %%Benedict’s test%%.
- The main reagent is Benedict’s solution which contains %%copper(II) sulfate%%.
- Reducing sugars can reduce copper(II) ions in Benedict’s solution to copper(I) in the form of copper(I) oxide, a %%brick-red precipitate.%%
- Reducing sugars are %%glucose%%, %%fructose%%, %%galactose%%, %%maltose%% and %%lactose%%. %%Sucrose is not a reducing sugar.%%
- %%Procedure%%: Add 2 cm3 of Benedict’s solution to 2 cm3 of sample solution and mix the contents thoroughly. Heat the test tube in a boiling water bath for 5 minutes. If the sample is an insoluble solid, crush it or cut it into small pieces before adding 2 cm3 of water and 2 cm3 of Benedict’s solution.
- The colour of the solution changes from %%green to orange to brick-red%% with increasing amounts of reducing sugars present.
Starch
- The test for %%starch%% is called the %%iodine test%%. Iodine is added to the sample and the colour change (if any) is observed.
- %%Procedure%%: Add a few drops of iodine solution to the sample. If the sample contains starch, it will turn %%blue-black%% in colour.
Fats
- The test for %%fats%% is known as the %%ethanol emulsion test%%.
- Ethanol is added to the sample to allow the fats present in it to dissolve. Water is then added to the ethanolic mixture. Since fats do not dissolve in water, they precipitate out of the solution to give a %%cloudy white emulsion.%%
- %%Procedure%%: Add 2 cm3 of ethanol to the sample in a test tube and shake the contents thoroughly. Add 2 cm3 of water and mix the contents. If fats are present, a white emulsion will be observed.
Proteins
- The test for %%proteins%% is known as the %%biuret test%%.
- The main reagents are %%sodium hydroxide and copper(II) sulfate.%%
- %%Procedure%%: Add 1 cm3 of sodium hydroxide solution to 1 cm3 of sample solution in a test tube and mix thoroughly. Add a few drops of 1% copper(II) sulfate solution dropwise into the mixture, shaking after each drop. Allow the mixture to stand for 5 minutes.
- If proteins are present, a %%violet colouration will be observed.%%