Human Health and Environmental Hazards Overview
1/370
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
371 Terms
What is the Environment?
Everything affecting a living organism's health.
ex. Air, Water, Soil, Biota, Man Made environment
Gene-environment Interaction
Genetic and environmental factors as independent risk factors.
Environmental Health
Health aspects influenced by environmental factors.

Chemical Hazards
Toxins in air, water, soil, and food.
Biological Hazards
Pathogens and allergens affecting human health.
Physical Hazards
Natural disasters impacting health indirectly.
Social Hazards
Lifestyle choices affecting health outcomes.
Genetic Traits
Inherited characteristics influencing health risks.
Core Concerns
Focus on chemical, biological, and physical hazards.
Anthropogenic Hazards
Human-made environmental risks to health.
Public Health Perspective
Population-focused approach to health issues.
Industrialization
Shift from agriculture to manufacturing economy.
Atmospheric Change
30% CO2 increase since Industrial Revolution.
Hydrosphere Pollution
Contamination of water bodies like lakes.
Geosphere Transformation
Human alteration of ⅓ to ½ land surface.
Biosphere
Earth's region where life exists.
Deforestation
Clearing forests impacting biodiversity and climate.
Global Disparities
Unequal development and health across regions.
Sustainable Development
Development meeting needs without compromising future.
Ecosystem Interconnectedness
All materials and byproducts are interlinked.
Modern Western Lifestyle
Lifestyle contributing to environmental and health issues.
Lack of Foresight
Insufficient planning for new technologies' impacts.
Gas Emissions
Release of harmful gases into the atmosphere.
Overpopulation
Excessive population growth impacting resources.
Overconsumption
Using resources faster than they can be replenished.
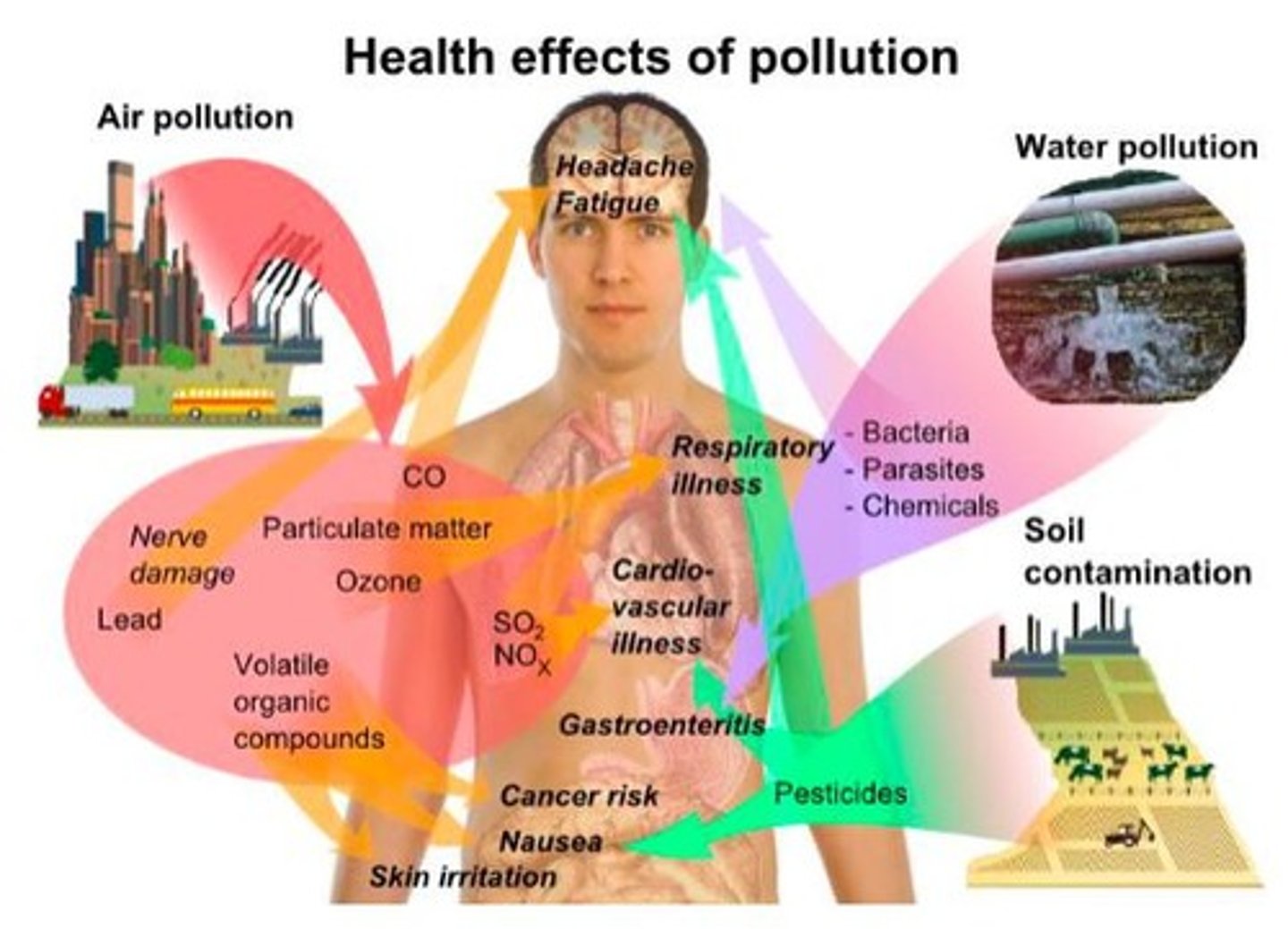
Health Effects of Pollution
Negative health impacts caused by environmental pollutants.
Environmental Health
Impact of environmental factors on human health.
Preventable Diseases
Diseases that can be avoided through environmental protection.
Diarrhea
Leading cause of disease in developing countries.
Respiratory Infections
Common health issue in developing nations.
Cancer
Leading health issue in developed countries.
Cardiovascular Diseases
Major health concern in affluent societies.
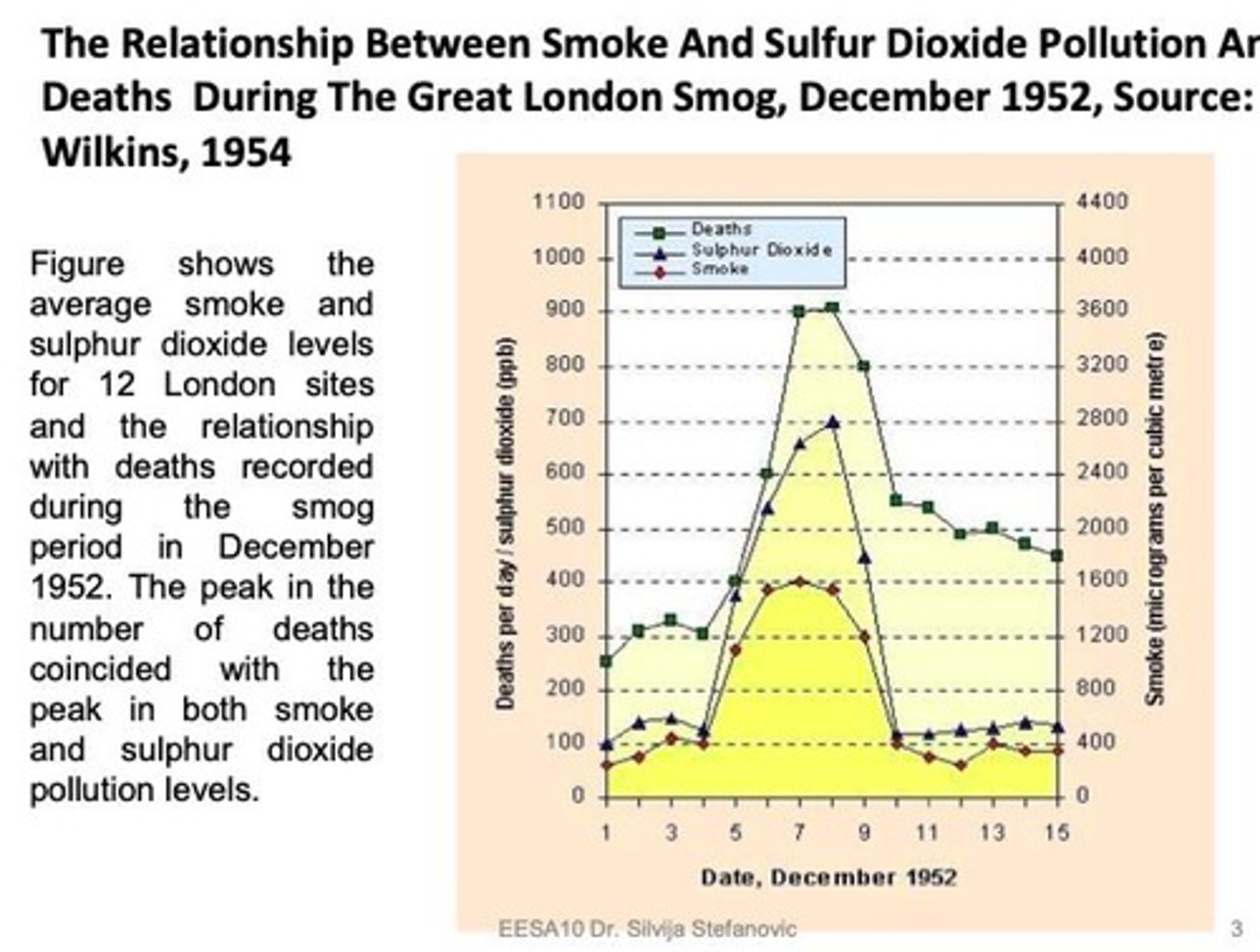
London Smog, 1952
Severe air pollution event caused by coal burning.
Sulfur Dioxide
Toxic gas primarily responsible for London Smog deaths.
Coal Burning
Main heating source contributing to air pollution.
Clean Air Act
Legislation aimed at reducing air pollution.
Indonesian Fires, 1997
Forest fires caused by agricultural land clearing.

Slash-and-Burn Agriculture
Farming method involving burning forests for land.
Monsoon
Seasonal rains affecting fire conditions in Indonesia.
Stagnant Air
Cold air trapped near the ground, worsening pollution.
Toxic Chemicals
Harmful substances affecting wildlife and human health.
UV Increase
Rising ultraviolet radiation impacting environmental health.
Fungi and Bacteria Infections
Pathogens contributing to health decline in organisms.
Environmental Changes
Alterations in the ecosystem affecting pollution dynamics.
Outdoor air pollution
Contaminants in the atmosphere from various sources.
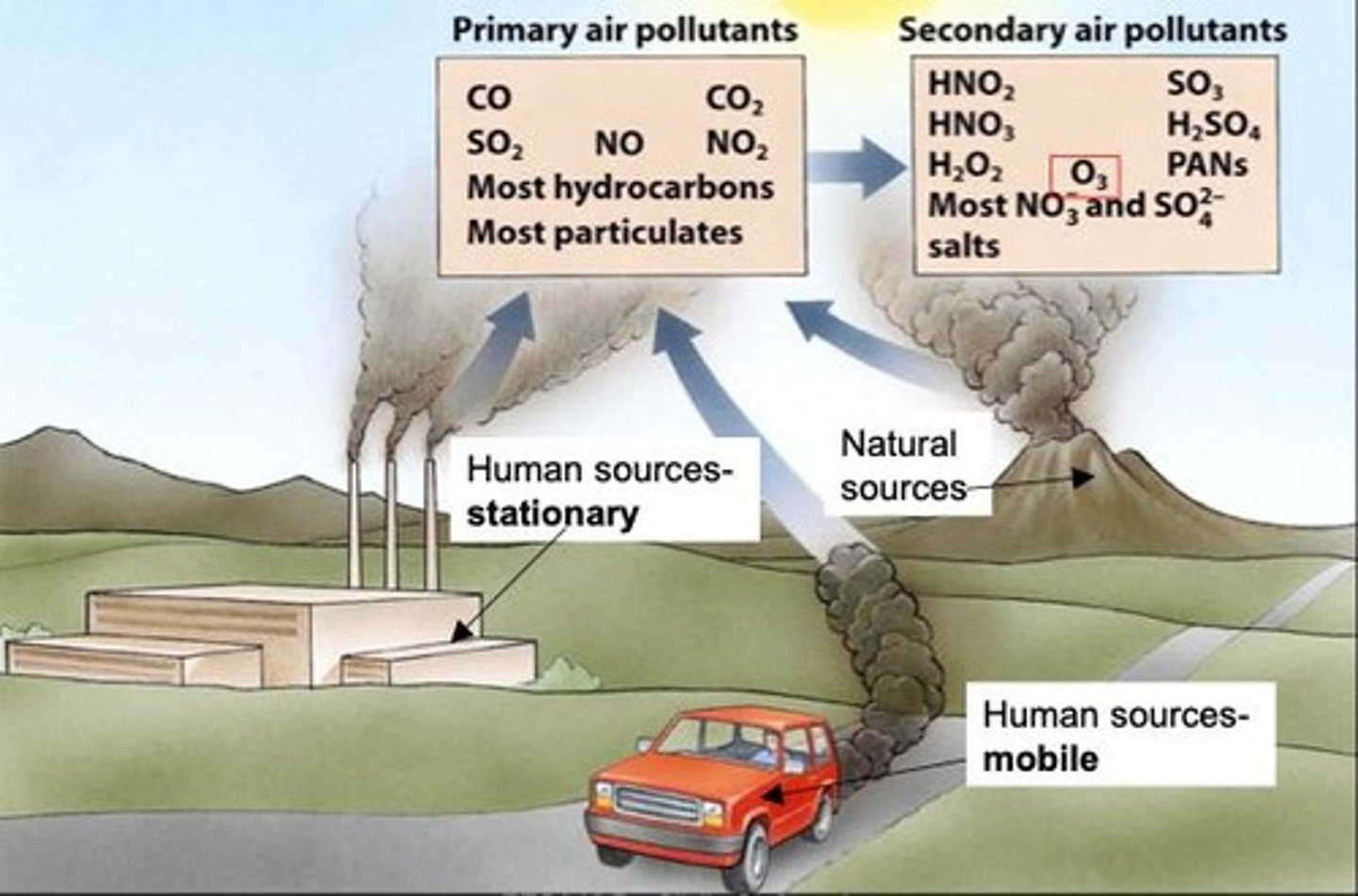
Indoor air pollution
Pollutants found within buildings affecting health.
Human sources - stationary
Pollutants from fixed sources like factories.
Natural sources
Pollutants originating from natural events, e.g., volcanoes.
Human sources - mobile
Pollutants from moving sources like vehicles.
Secondary air pollutants
Pollutants formed by reactions of primary pollutants.
Particulate matter
Airborne particles like dust and smoke.
PM10
Respirable particulate matter with diameter ≤10 micrometers.
PM2.5
Fine particulate matter with diameter ≤2.5 micrometers.
Carbon monoxide (CO)
Odorless gas from incomplete combustion of fuels.
Health effects of outdoor air pollution
Adverse health outcomes dependent on pollutant concentration.
Asthma
Respiratory condition worsened by particulates and SO2.
Chronic bronchitis
Persistent cough due to excess mucus in bronchi.
Pulmonary emphysema
Alveoli damage causing shortness of breath.
Lung cancer
Malignant growth in lung tissue due to pollutants.
Heart disease
Cardiovascular issues exacerbated by air pollution.
Toxic poisoning
Health effects from exposure to harmful substances.
Eye irritation
Discomfort in eyes due to airborne pollutants.
Birth defects
Congenital anomalies linked to environmental pollutants.
Nitrogen oxides (NOx)
Gases from combustion contributing to ozone formation.
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Organic chemicals that can vaporize and affect health.
Lead (Pb)
Heavy metal from industrial sources affecting children.
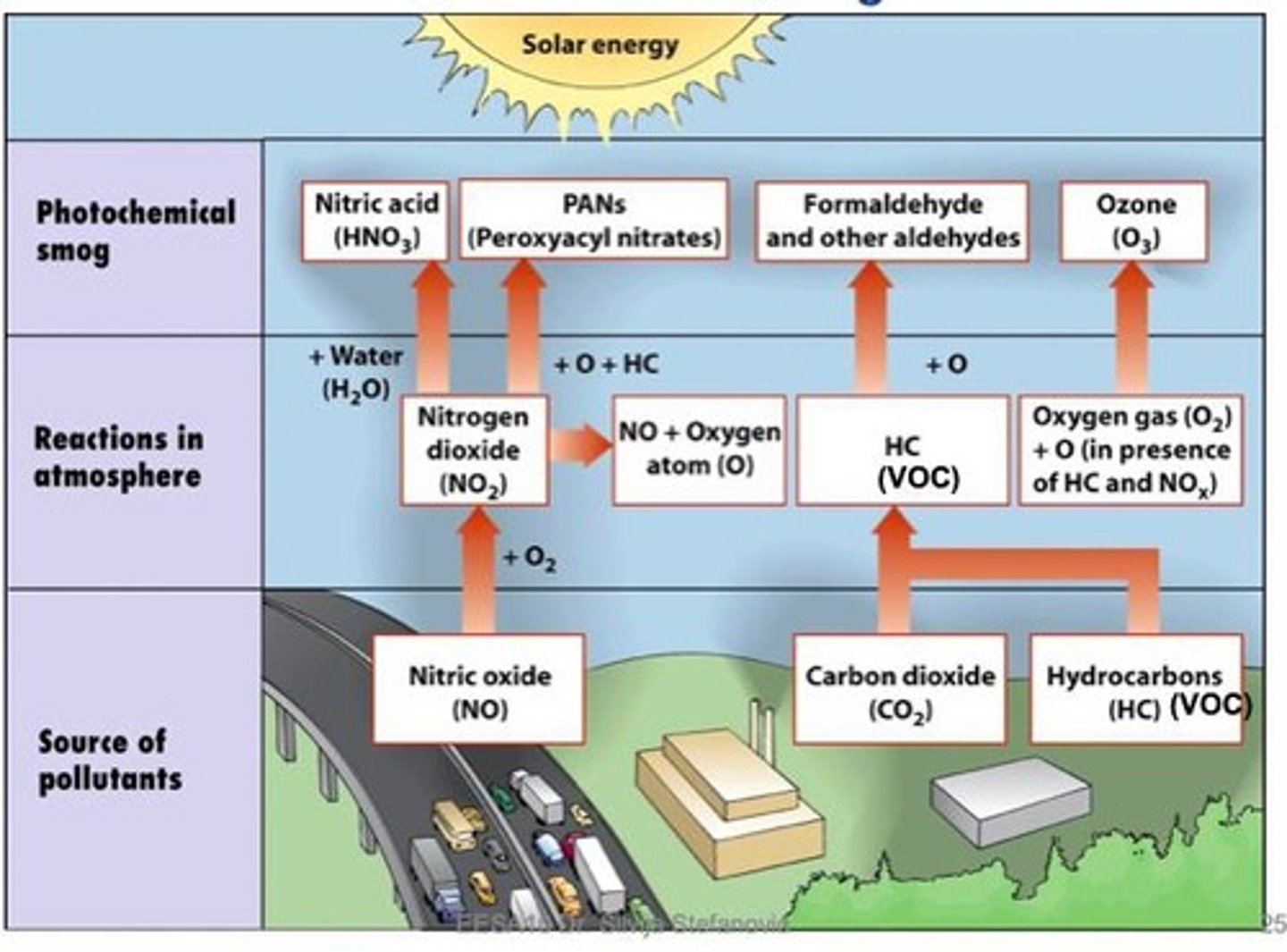
Ground level ozone
Secondary pollutant formed from NOx and VOCs.
Neurotoxicant
Substance causing damage to nervous system.
Lead Exposure
Affects IQ, cognitive function, and health.
Ground Level Ozone
Harmful pollutant formed from VOCs and NOx.
Ozone Formation
Occurs from VOC + NOx + heat + sunlight.
Smog
Air pollution combining smoke and fog.
Sulphurous Smog
Industrial smog, prevalent in London.
Photochemical Smog
Brown air smog, common in Los Angeles.
Indoor Air Pollution
Higher pollutant concentration than outdoor air.
Sick Building Syndrome
Nonspecific symptoms from building occupancy.
Building Related Illness
Diagnosable illness linked to building features.
Common Indoor Pollutants
Includes asbestos, formaldehyde, mold, and smoke.
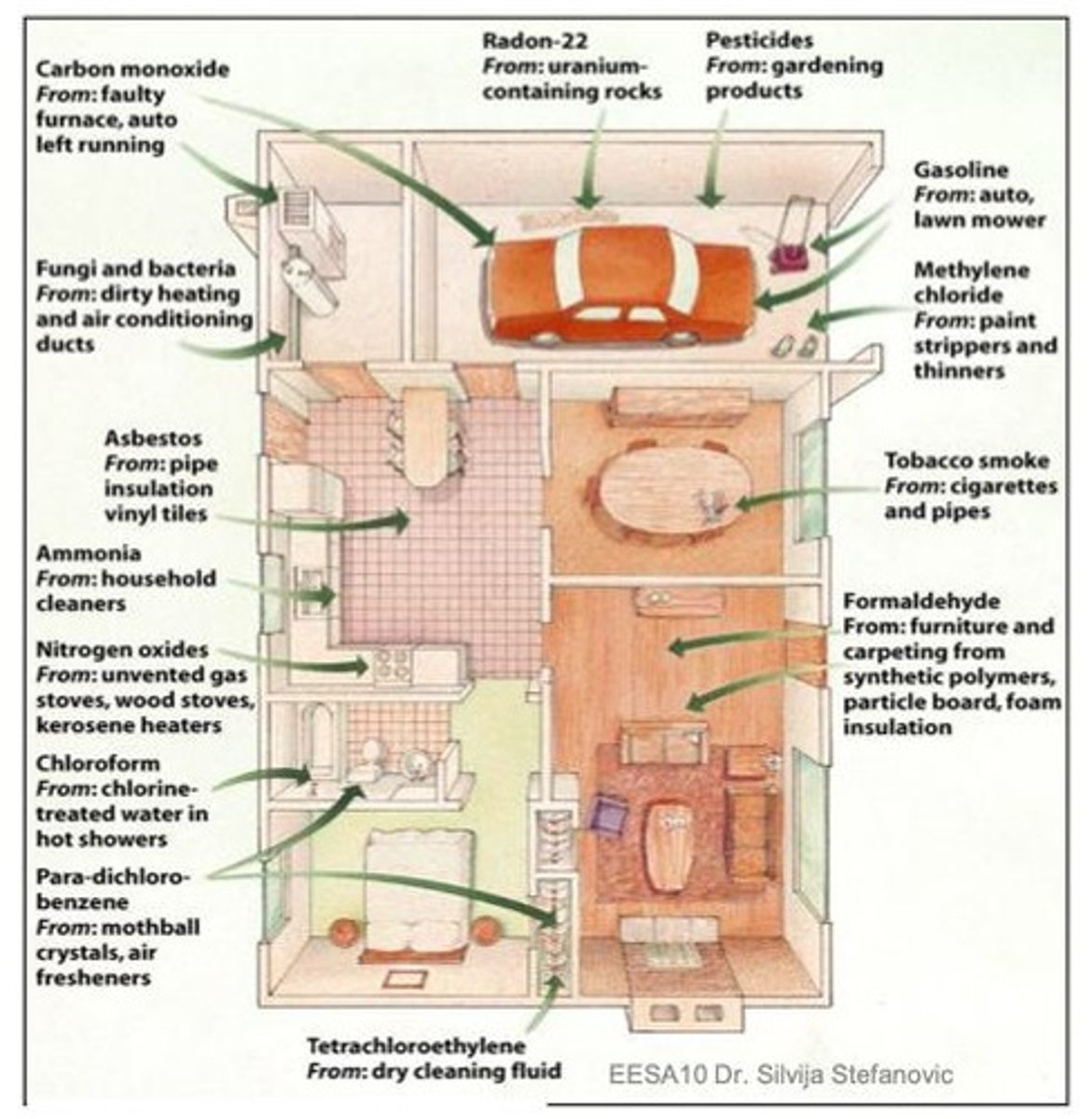
Asbestos
Fibrous mineral used in construction materials.
Formaldehyde
Common indoor pollutant from building materials.
Mold
Fungi thriving in damp indoor environments.
Secondhand Smoke
Tobacco smoke inhaled by non-smokers.
Radon Gas
Radioactive gas from soil, harmful indoors.
Air Dust
Particles suspended in indoor air.
Inadequate Ventilation
Primary cause of sick building syndrome.
Health Effects of Indoor Pollution
Symptoms include headaches, dizziness, and asthma.
Vulnerable Populations
Children, elderly, and ill are more sensitive.
Pollutant Sources
Includes building materials, cleaning products, and cooking.
Environmental Reaction
Process creating ground-level ozone, affected by climate.
Asbestos
Fibers linked to lung diseases and cancer risk.
Asbestosis
Scar-like lung tissue causing breathing difficulties.
Lung Cancer
Mesothelioma associated with asbestos exposure.
Formaldehyde
Colorless gas causing allergic reactions and cancer.
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Organic chemicals that evaporate at room temperature.
Mold
Fungi thriving in moist environments, causing allergies.
Moisture Control
Maintaining humidity between 30-60% to prevent mold.
Secondhand Smoke
Contains 4000 compounds, increasing lung cancer risk.
Radon Gas
Radioactive gas from uranium decay, linked to lung cancer.
Environmental Tobacco Smoke
Secondhand smoke causing health issues in adults and children.
Cancer Carcinogens
Substances that increase cancer risk, found in smoke.