Unit 2: AP HUG
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
population distribution
how population is spread out in an area
population density
The number of individuals in an area of a specific size
Arithmetic Density (Crude Density)
The total number of people divided by the total land area.
Pysiological Density
The number of people per unit of area of arable land, which is land suitable for agriculture.
Helpful in determining carrying capacity (how much food region can produce).
Agricultural Density
The ratio of the number of farmers to the total amount of land suitable for agriculture.
Wealthy countries have low agricultural density because of machines.
carrying capacity
maximum number of people an area can provide food and water for.
population composition
Structure of population in terms of age, sex and other properties such as marital status and education
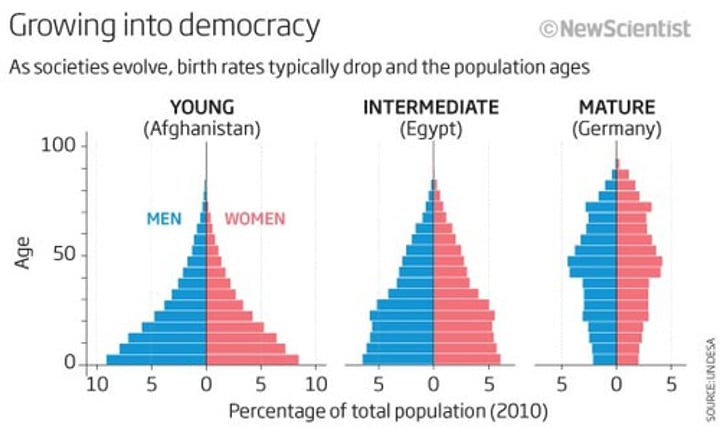
Population Pyramid (Age-Sex Pyramid)
visual representation of age and sex composition of a population
Demographics
the characteristics of a population with respect to age, race, and gender.
Demographic factors that determine population growth?
Fertility (birth), Mortality (death), Migration (immigrants moving to or emigrants moving away)
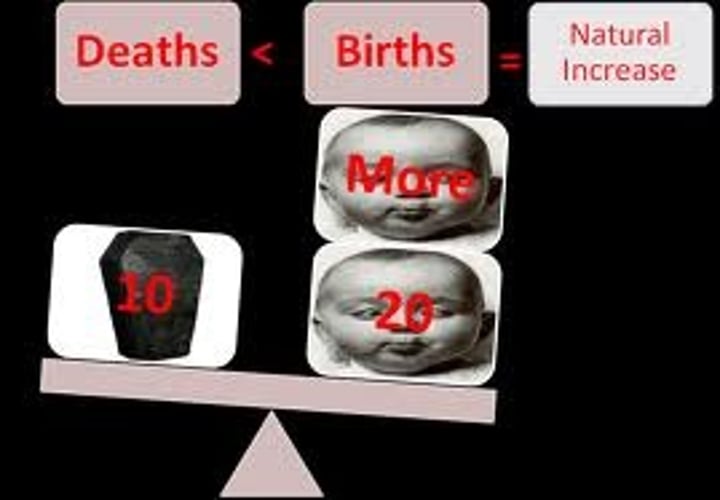
Rate of Natural Increase (RNI)
The percentage of annual growth in a population excluding migration.
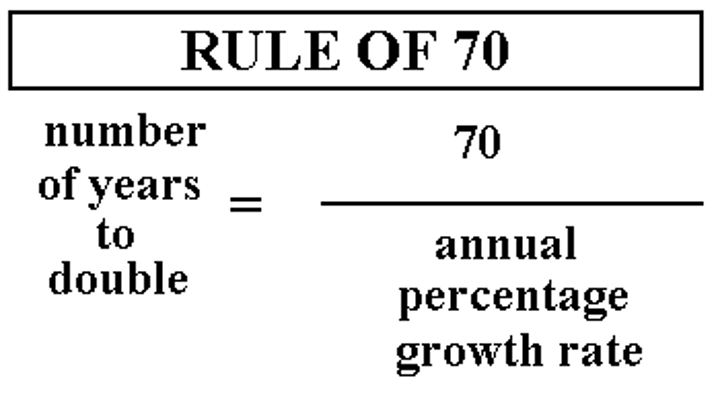
population doubling time
The number of years it takes a population to double; calculated by dividing the number 70 by the rate of natural increase
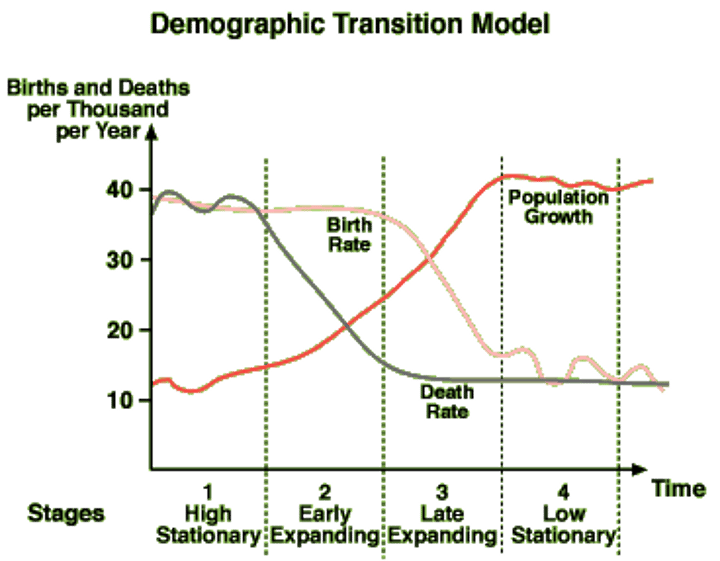
Demographic Transition Model
change in a population from high birth and high death rates (no population growth) to high births and low death rates (high population growth. Final stage is low birth rate and low death rate.
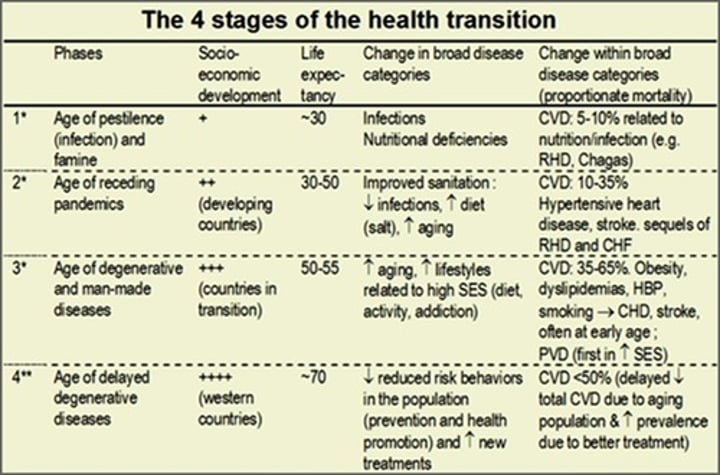
Epidemiological Transition Model
The theory that says that there is a distinct cause of death in each stage of the demographic transition model. It can help explain how a country's population changes so dramatically.
Malthusian Theory
Belief that population growth will lead to mass starvation because eventually there will be too many people to feed.
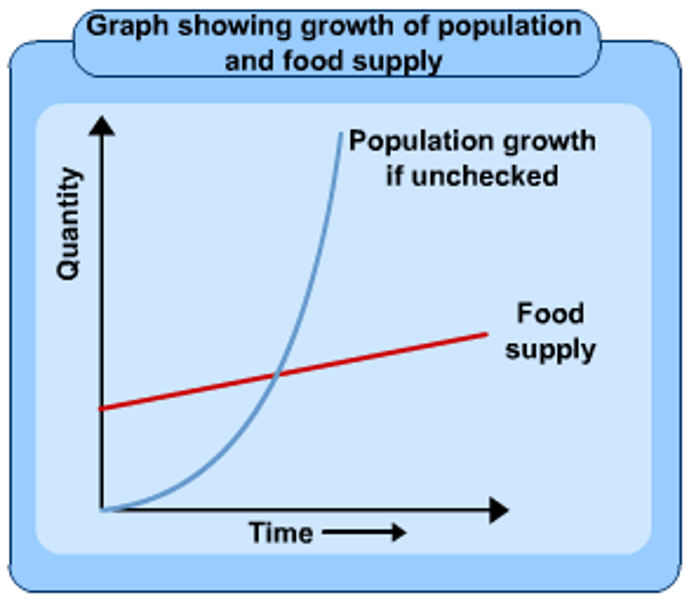
Flaws in Malthusian Theory
did not foresee chemical fertilizers, pesticides, machines, and refrigeration would increase the carrying capacity of the world.
Pro-Natalist Policies
Government policies to increase the rate of natural increase. Examples: tax cuts for having children, maternity leave

Anti-Natalist Policies
government policies to reduce the rate of natural increase. Examples: China's one child policy

Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
the average number of children a woman will have. TFR of 5 means women average 5 kids. TFR below 2 means the population is declining.

High fertility rate signifies?
a developing country where women have few rights, lack healthcare, children provide labor
Ravenstein's Laws of Migration
1. Most migration is over a short distance. 2. Migration occurs in steps. 3. Long-range migrants usually move to urban areas. 4. Each migration produces a movement in the opposite direction (although not necessarily of the same volume). 5. Rural dwellers are more migratory than urban dwellers. 6. Within their own country females are more migratory than males, but males are more migratory over long distances. 7. Most migrants are adults. 8. Large towns grow more by migration than by natural increase. 9. Migration increases with economic development. 2. Migration is mostly due to economic causes.
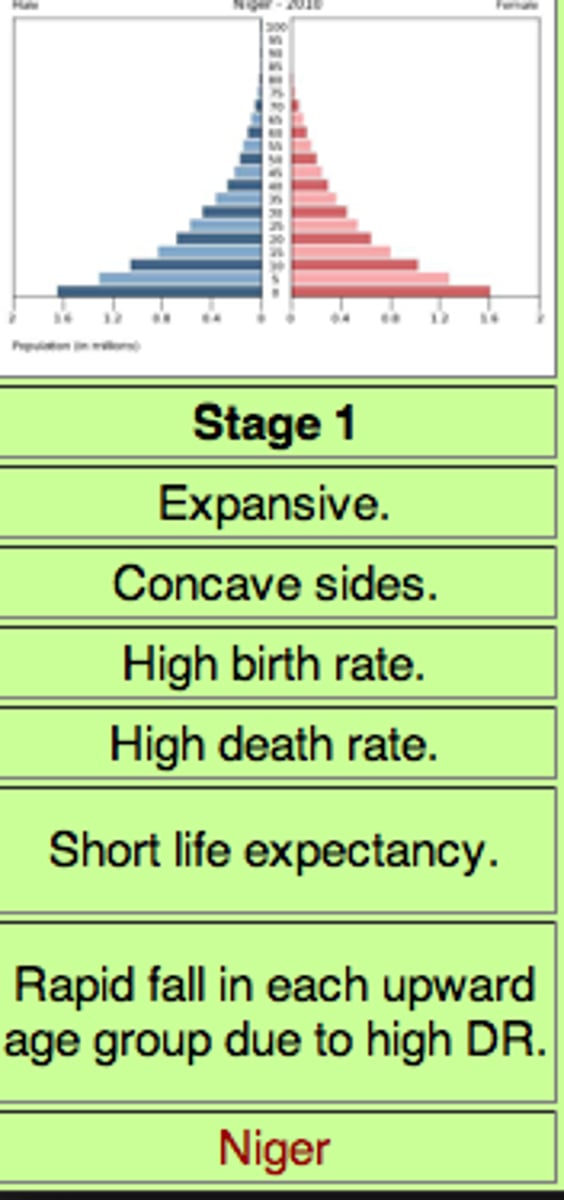
Stage 1 of Demographic Transition Model
low growth - high birth rate, high death rate, (birth and death rate cancel each other out), and low population growth. ONLY EXISTS IN HUNTERS AND GATHERERS
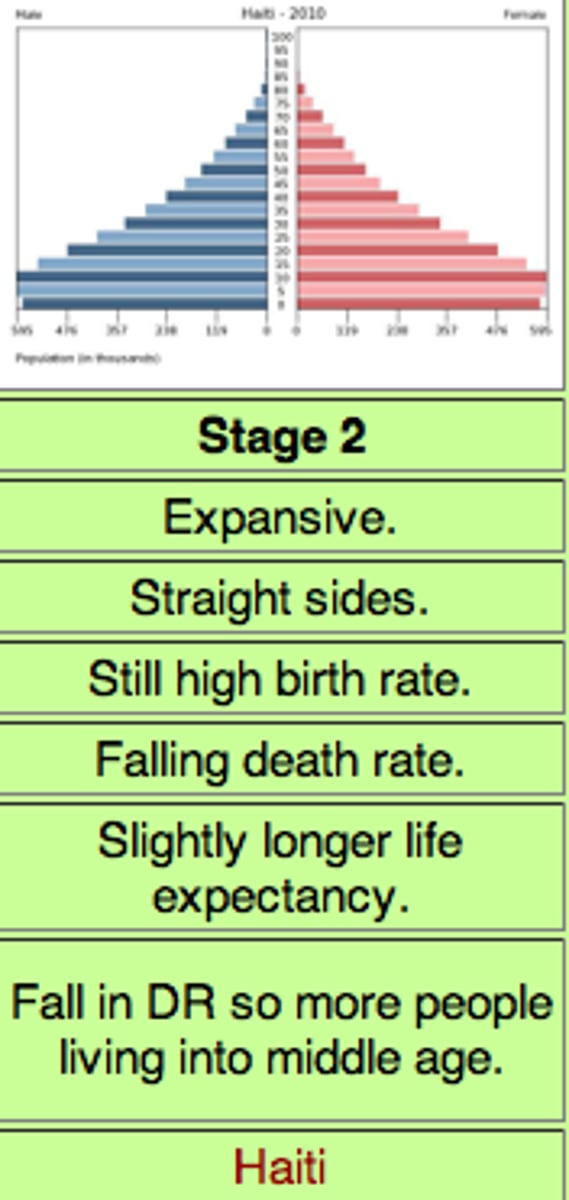
Stage 2 of Demographic Transition Model
high birth rate (Above 35), falling death rate, high population growth (society: from agricultural to urbanized, raising quality of life) PERIPHERY COUNTRIES (Sub-Saharan Africa, Afghanistan)
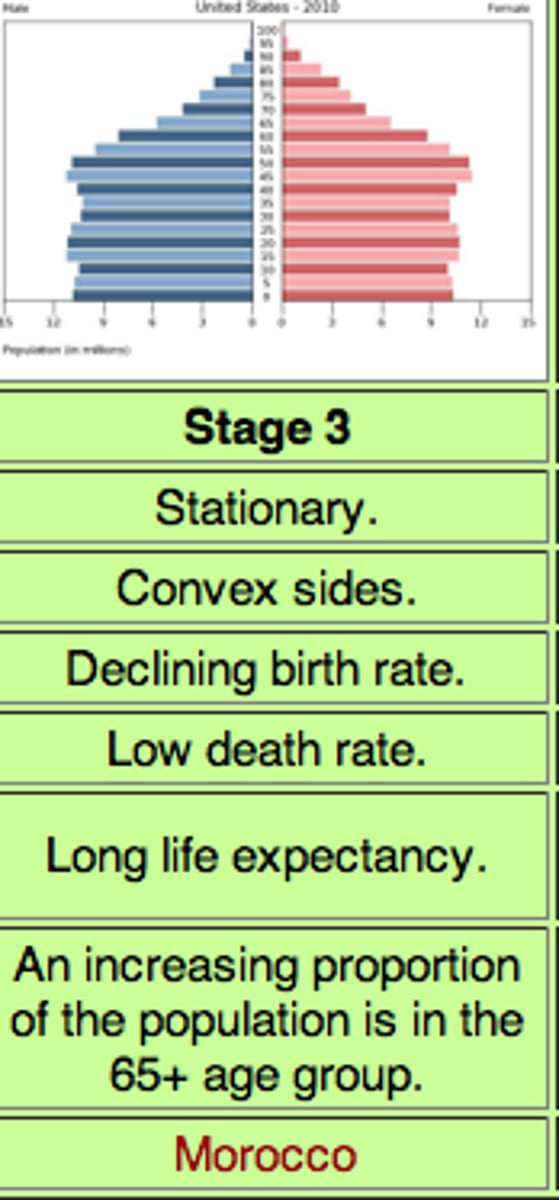
stage 3 of the demographic transition model
moderate growth - falling birth rate (Birth rate between 35 and 15), low death rate, steady population growth (urbanized and more industrialized families have less children) SEMI-PERIPHERY COUNTRIES (Mexico, India)
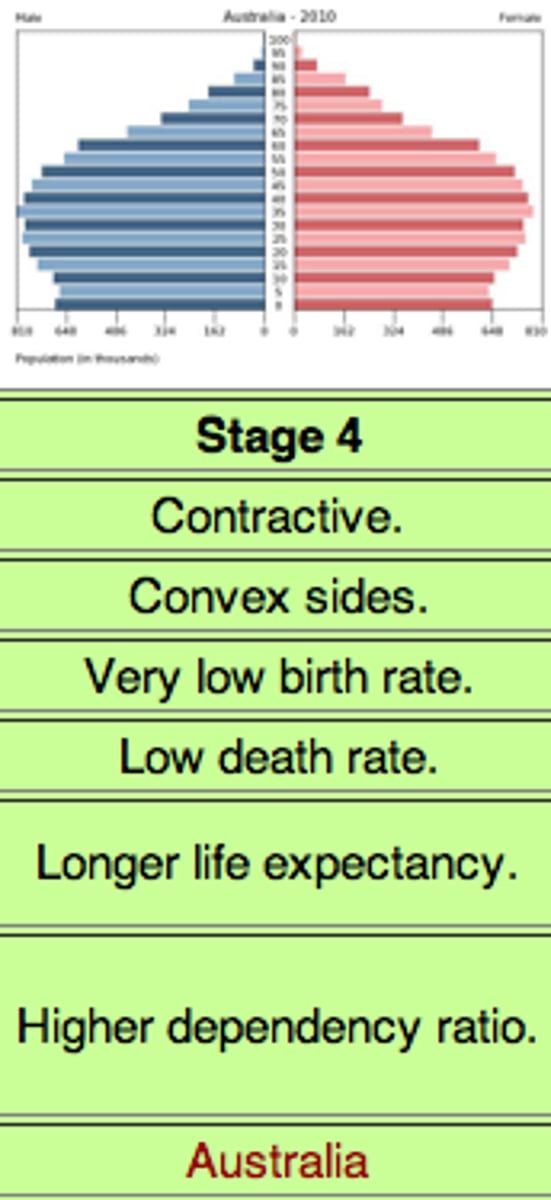
stage 4 of the demographic transition model
low birth rate (Birth rate below 15), low death rate, Very little population growth. CORE COUNTRIES (USA)
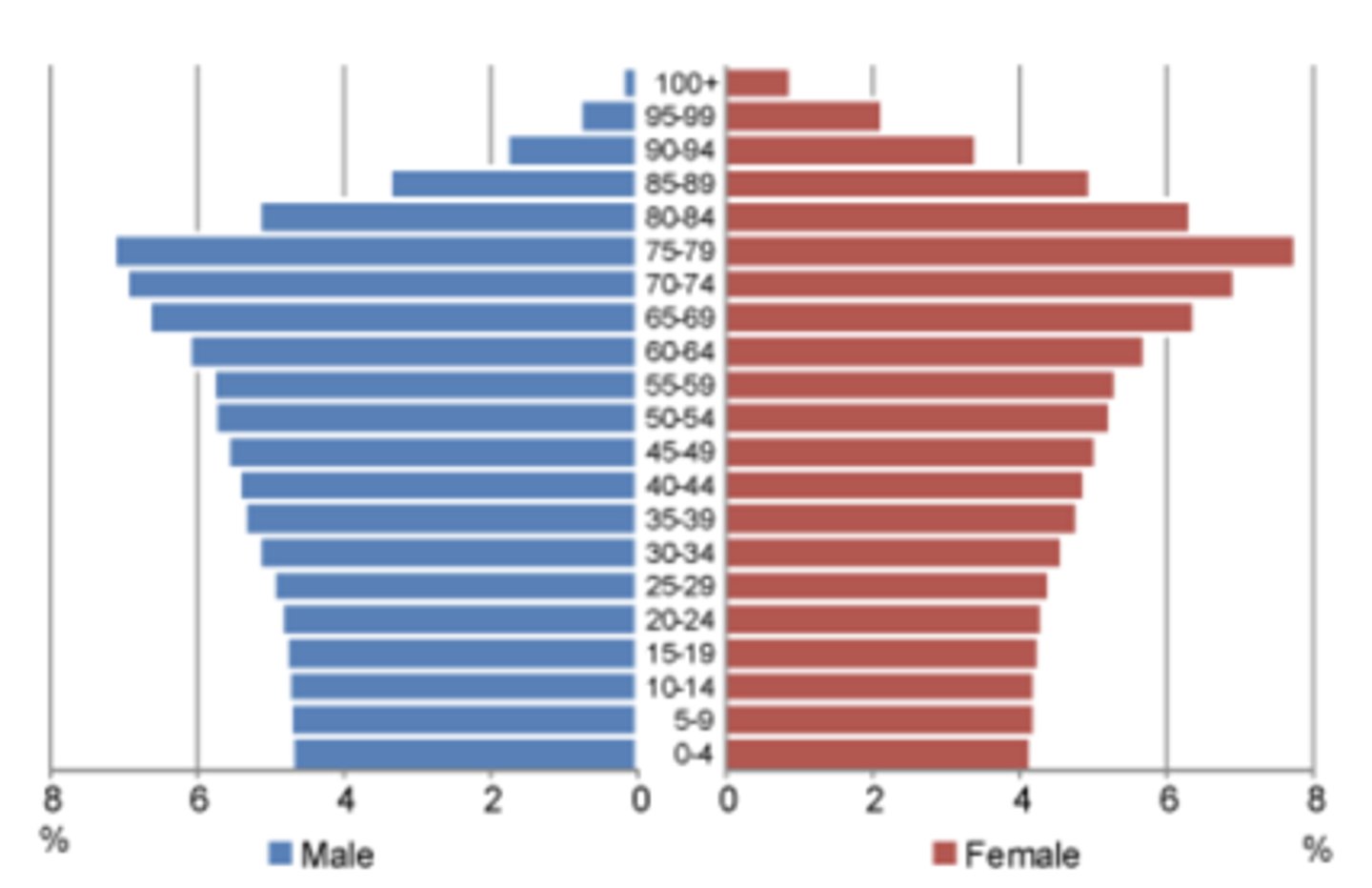
elderly dependency ratio
the number of persons aged 65 or older per 100 persons of working age. High dependency ratio means more elderly than workers. Stage 4 Countries
youth dependency ratio
The ratio of the number of people 0-14 to those 15-64 years of age. High youth dependency means too many kids to take care of.
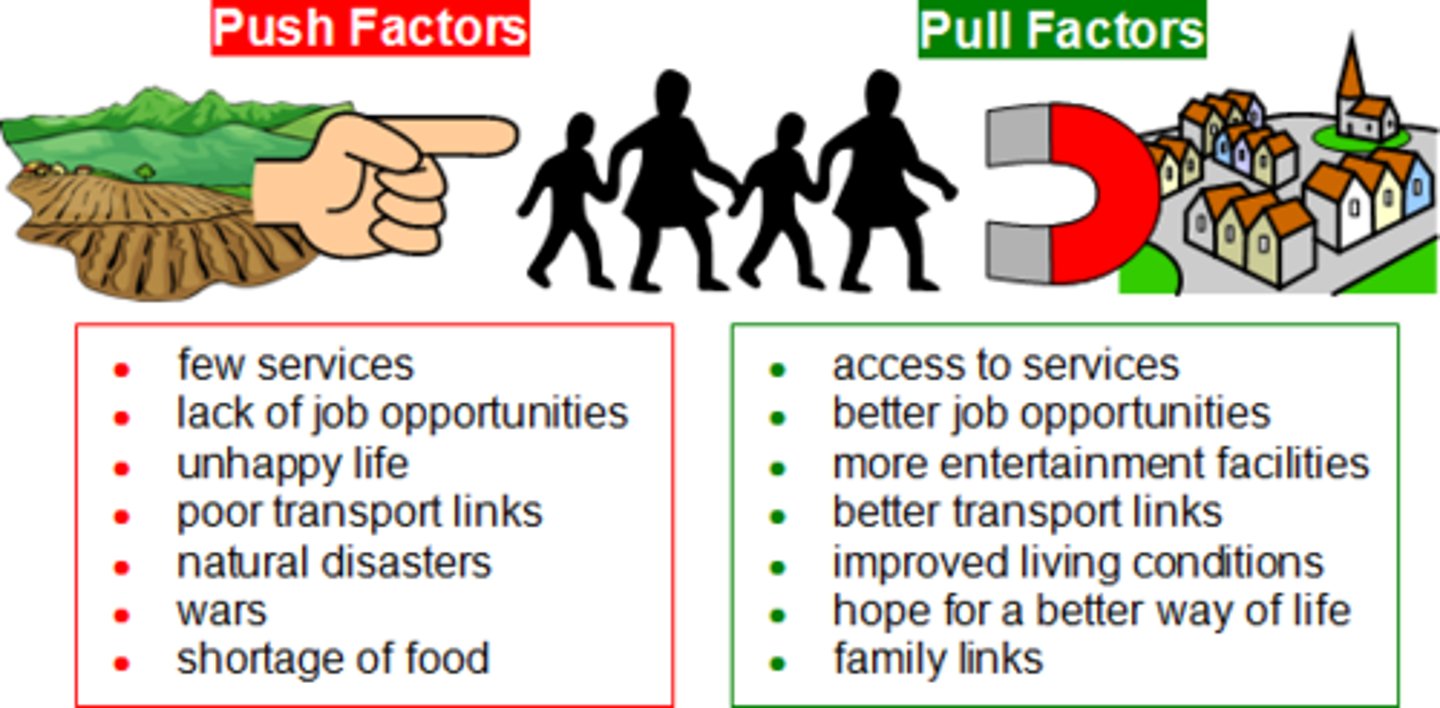
Push Factors of Immigration
economic troubles, overcrowding, poverty, persecution, war
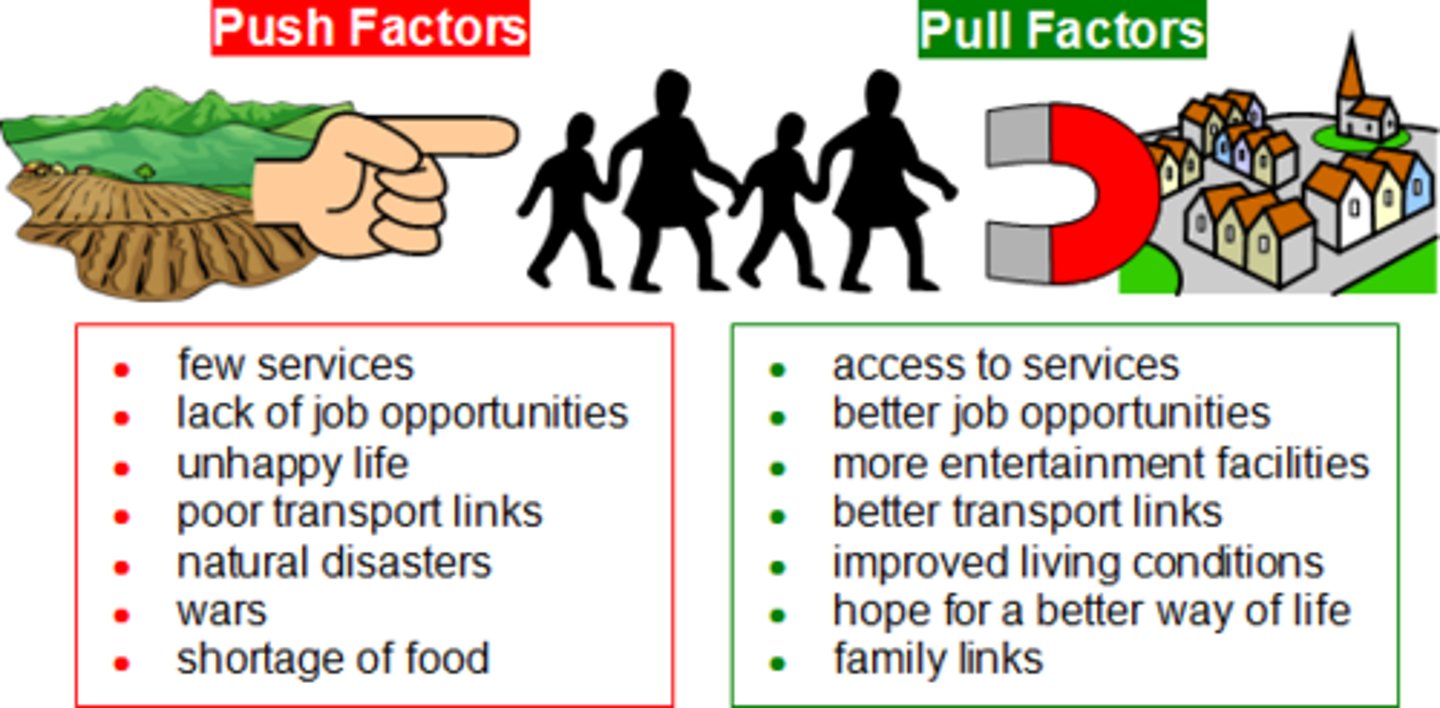
Pull Factors of Immigration
Economic Opportunity ($)
Jobs/ workers were needed
Land
Peace and stability
Freedom to make a better life
Forced Migration
forcing people to move usually as a result of persecution. Native Americans moved to reservations, Slave trade
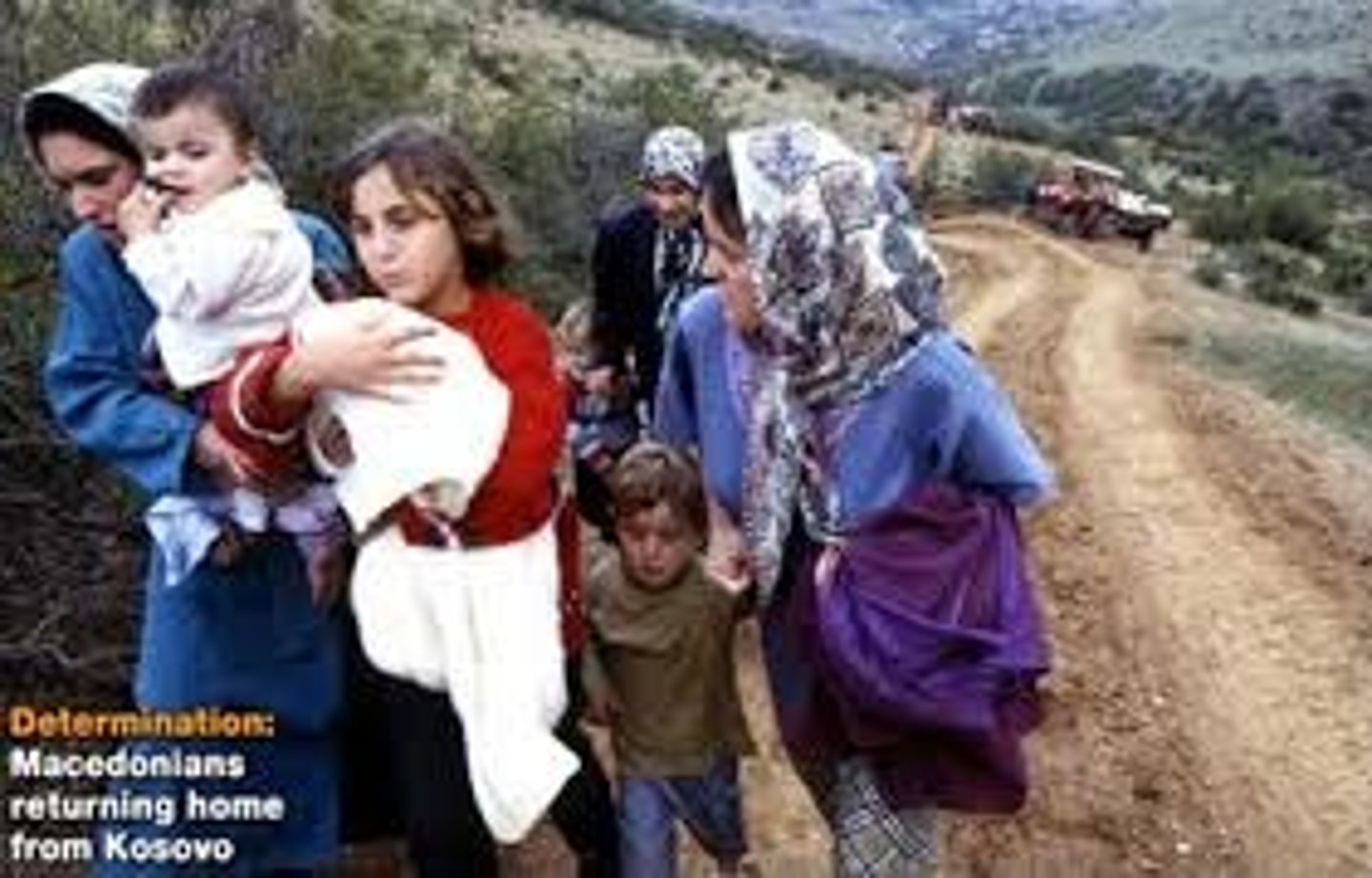

refugee
A person who has been forced to leave their country in order to escape war, persecution, or natural disaster
Internally Displaced Person (IDP)
someone who is forced to flee his or her home but who remains within his or her country's borders
asylum seeker
Someone who has migrated to another country in the hope of being recognized as a refugee

guest worker programs
allows foreign workers to temporarily reside and work in a host country. Workers migrate from poor countries to wealthy countries for temporary work.
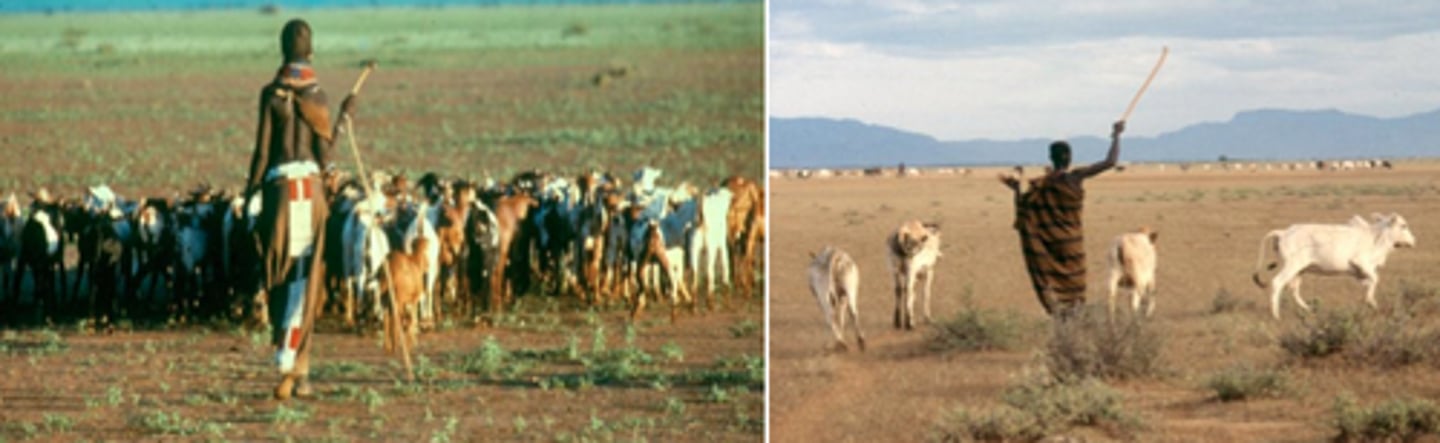
Transhumance
The seasonal migration of livestock between mountains and lowland pastures.

Chain Migration
migration of people to a specific location because relatives or members of the same nationality previously migrated there

Who would be most likely to immigrate to another country according to ravenstein?
Single man in his 20s.
infant mortality rate
The percentage of children who die before their first birthday within a particular area or country.
Remittances
Money migrants send back to family and friends in their home countries, often in cash, forming an important part of the economy in many poorer countries
immigrant vs. emigrant
immigrant comes to a country; emigrant leaves a country
Effects of Immigration
-Conflict over jobs
-Possible housing shortages