Important equations (Y1. Drug delivery + Y2 equations)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
The Stokes-Einstein Equation (diffusion coefficient)

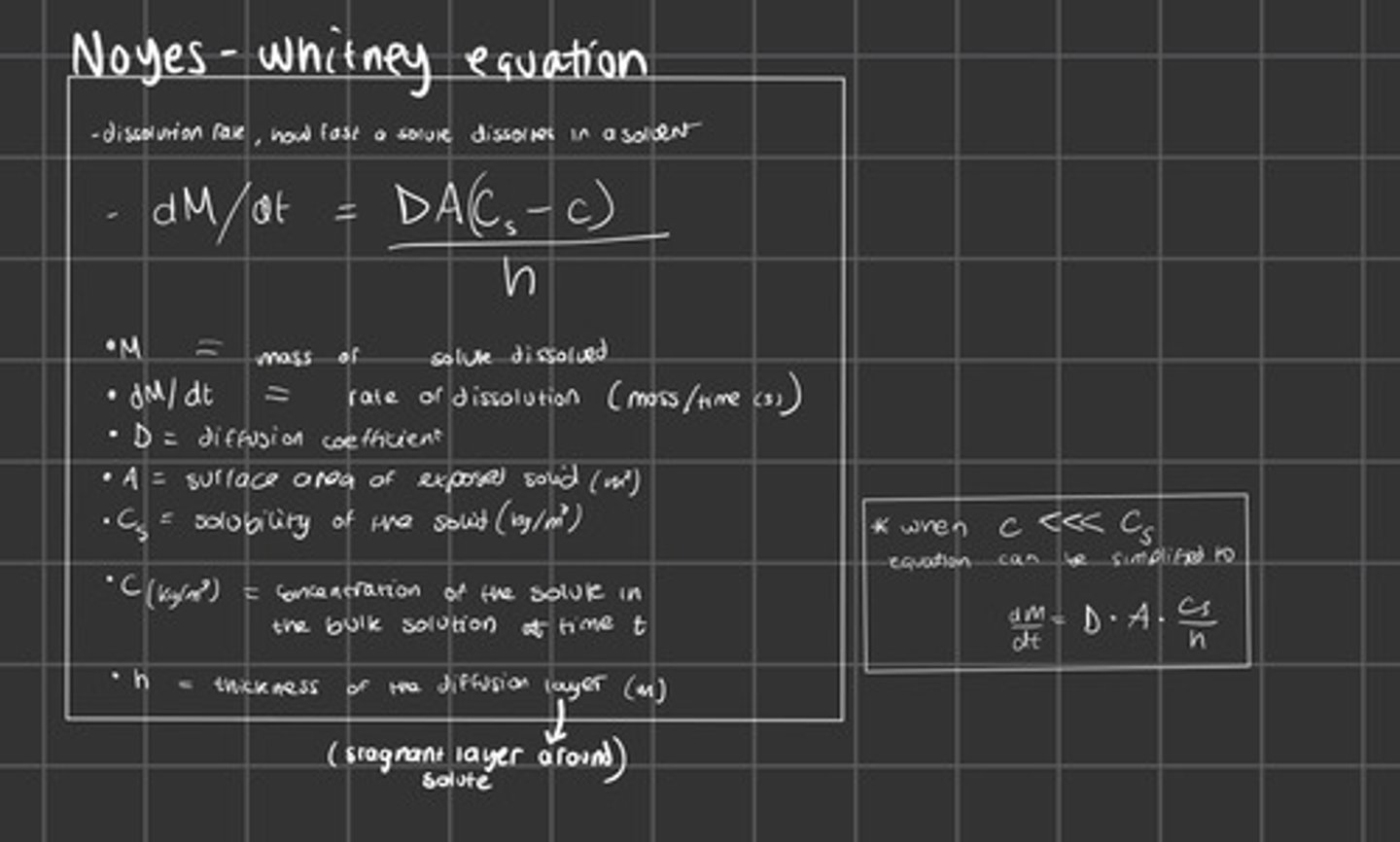
The Noyes-Whitney Equation
Concentration unit = mg/ml
A level equation for Gibbs
∆G (Jmol^-1) = ∆H - T∆S
Equation that links Gibbs, Ideal gas constant, Temperature and Equilibrium Constant.
∆G (Jmol^-1) = -RTln(K). Can also be ka or kb
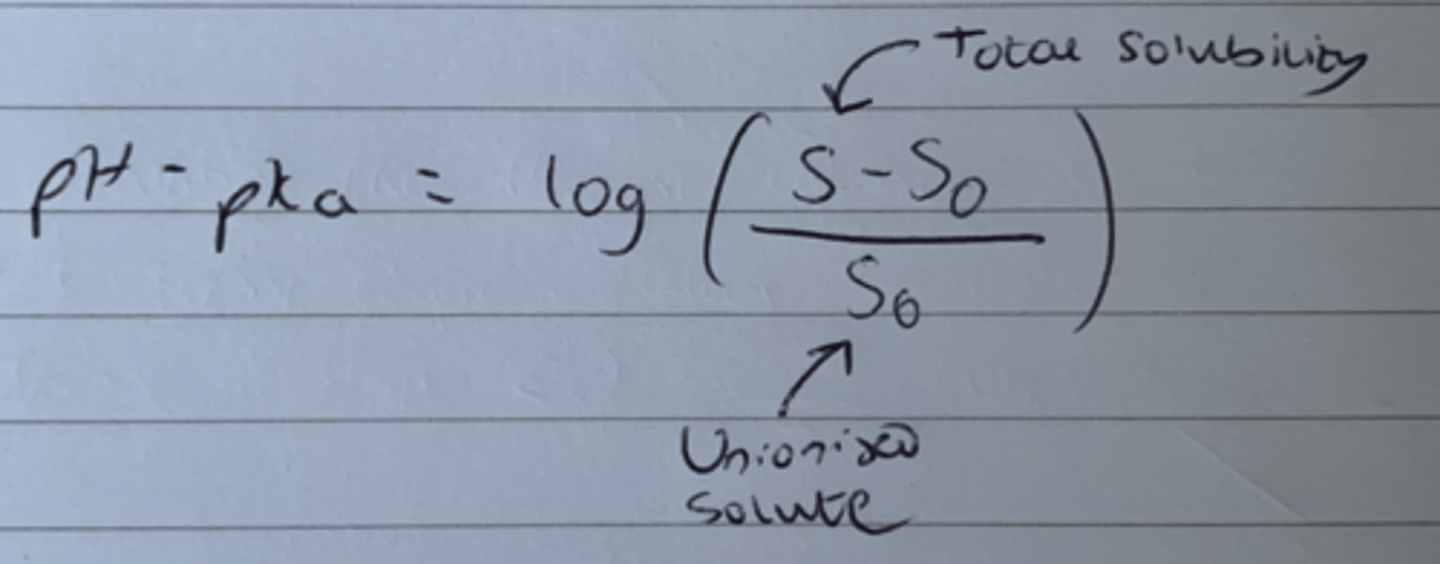
Equation that links pH, pKa, log(x), Total solubility and Unionised solubility.
Equation that links pKa and pKb
pKa + pKb = 14
Equation that links work, pressure and volume.
Work (J)= - Pressure (Pa) x Change in Volume (m^3)
Equation for Molar Enthalpy change (A-level).

Equation for enthalpy change (A-Level).
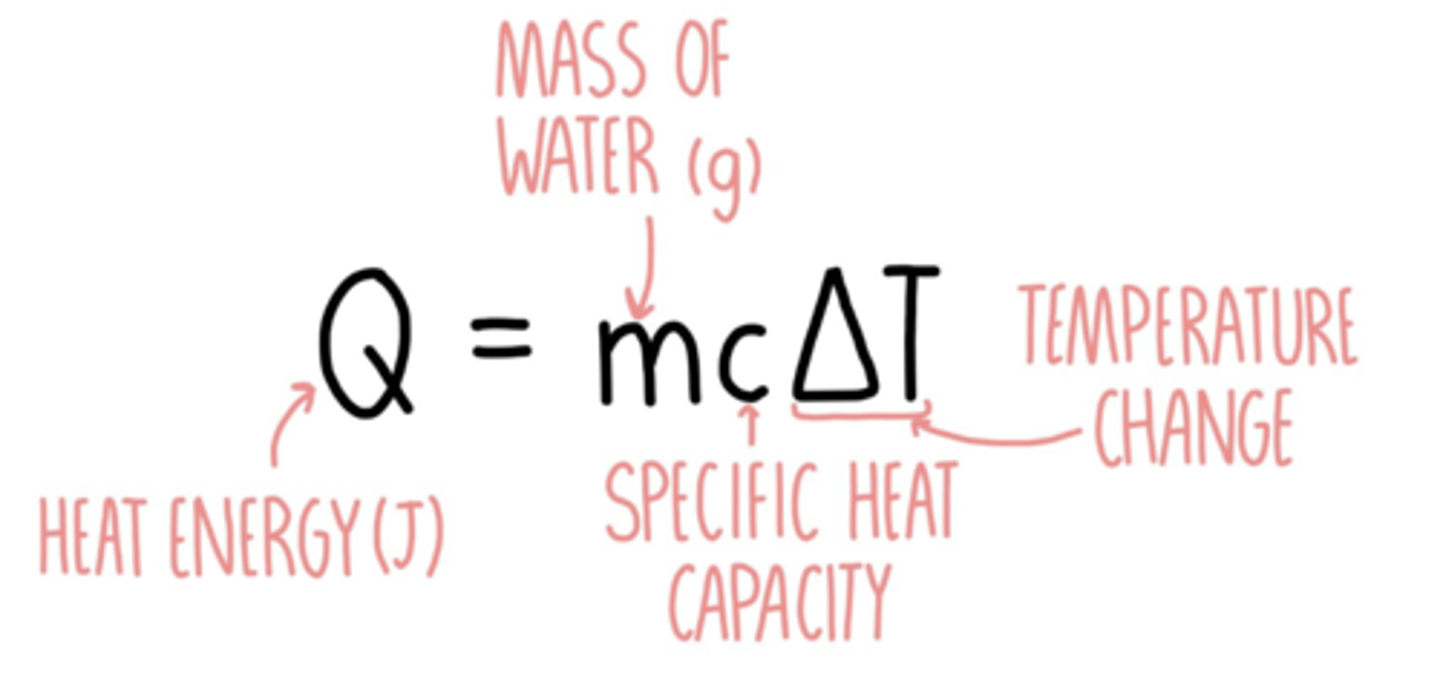
Equation that links Molar enthalpy change, Temperature and Change in entropy.
ΔH = TΔS
Equation that links Calorimeter constant (C), Change in internal energy of reactant (ΔU) and temperature (T).
ΔU (KJ) = C (kJ/K) x T (Kelvin)
Equation that links Internal energy of reactant (ΔU) , Moles and Enthalpy change.
ΔU (KJ) = mol (KJ) x ΔH (KJ/mol)
Van't Hoff's equation for ΔH.
If lots of values for Temp and K are available, Use the smallest values.
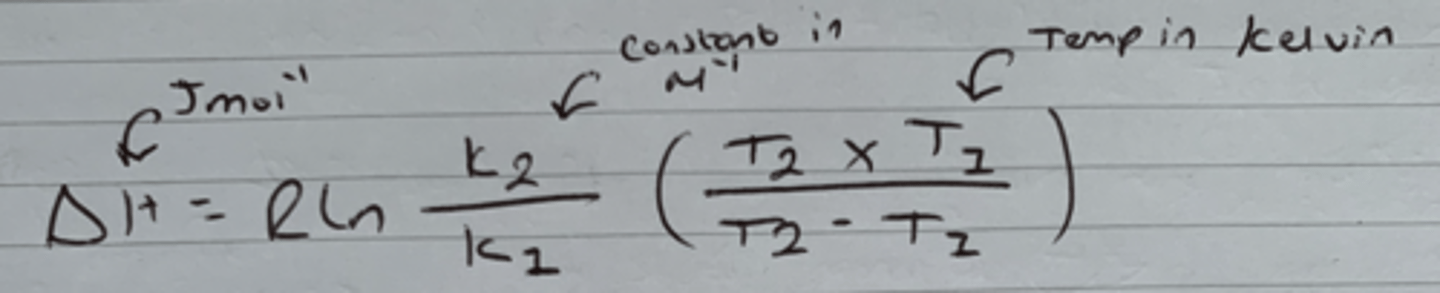
Show Van't Hoff's when rearranged to give an unknown equilibrium constant at a higher temperature (lnK2).
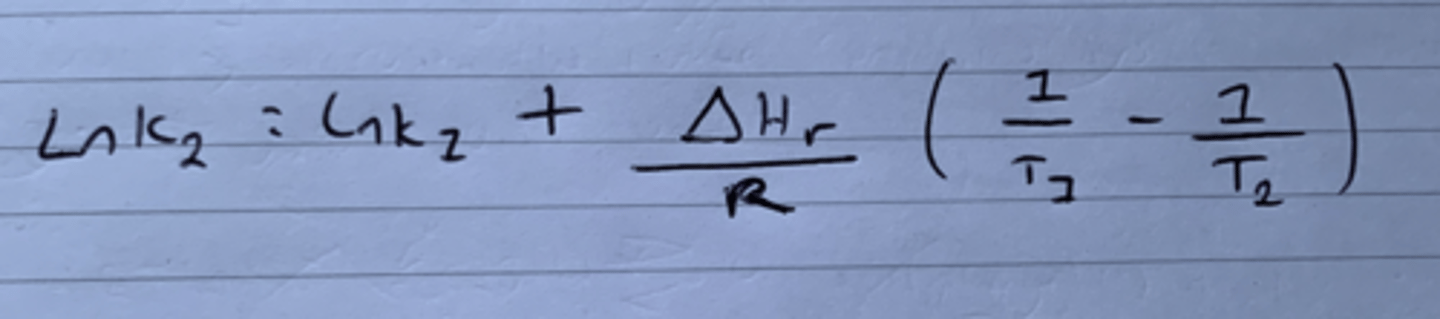
Equation that links Change in temp, Cryoscopic constant and molality.
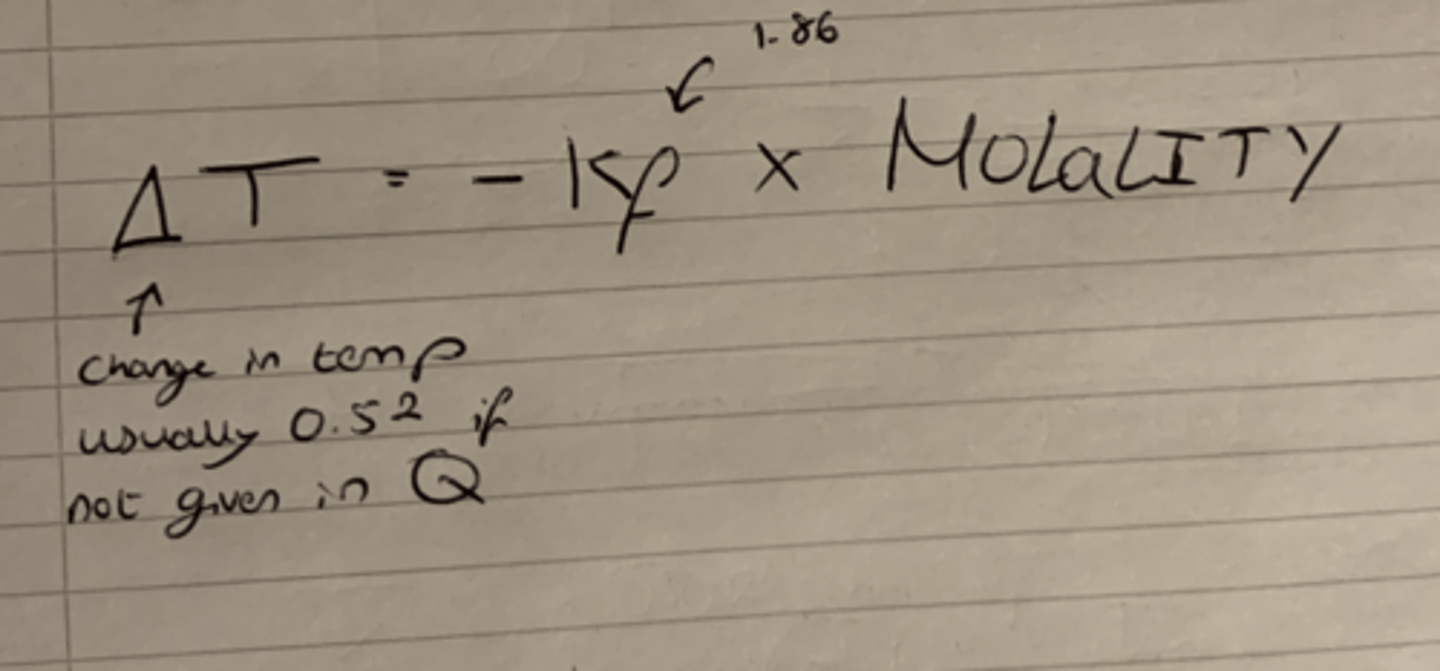
How to calculate molality?
moles of solute/ solvent in kg
Quadratic equation
Always use + after -b
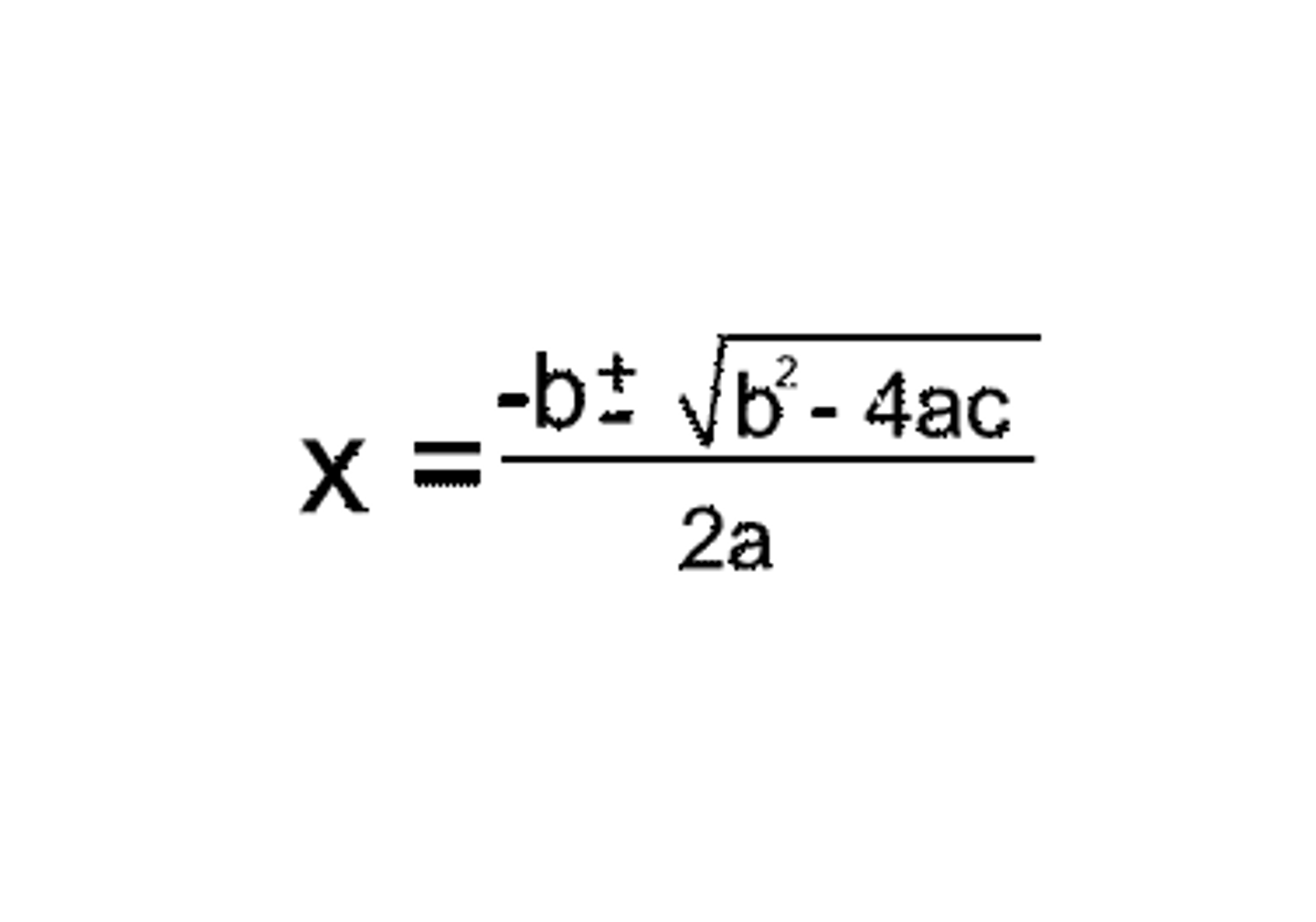
What does each letter in the quadratic equation refer too when calculating H+ and how do you calculate H+ from the calculated x value?
a = Concentration in question.
b = ka
c = -ka
Then multiply the calculated x value with the concentration in the question again to the H+ concentration.
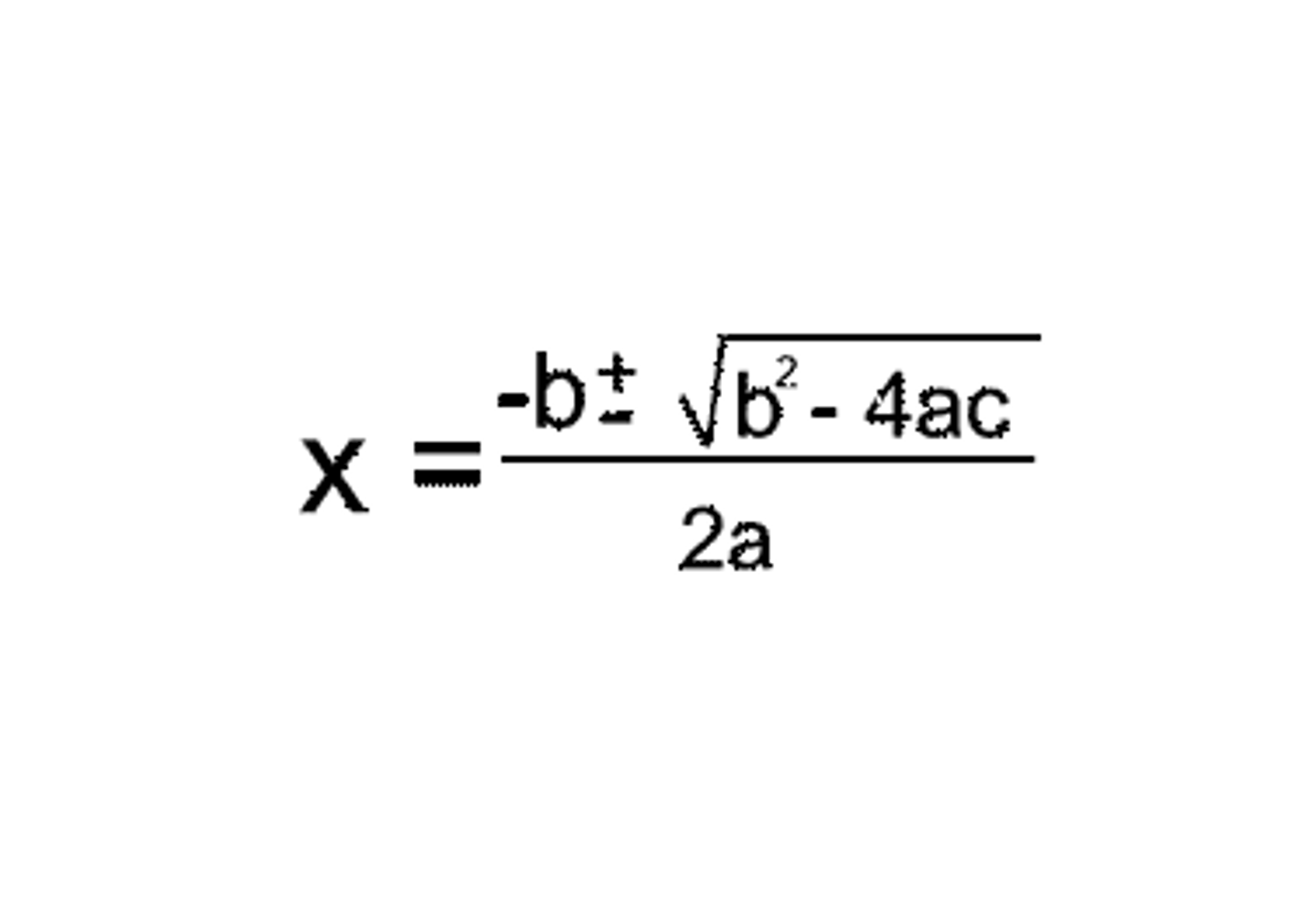
Show the equation to find K using the rate of diffusion, surface area, solubility and concentration. (From the Noyes-Whitney equation)
Rate unit = kg s^-1
A unit = m^2
Cs unit = mg/ml
C unit = Kg m^3
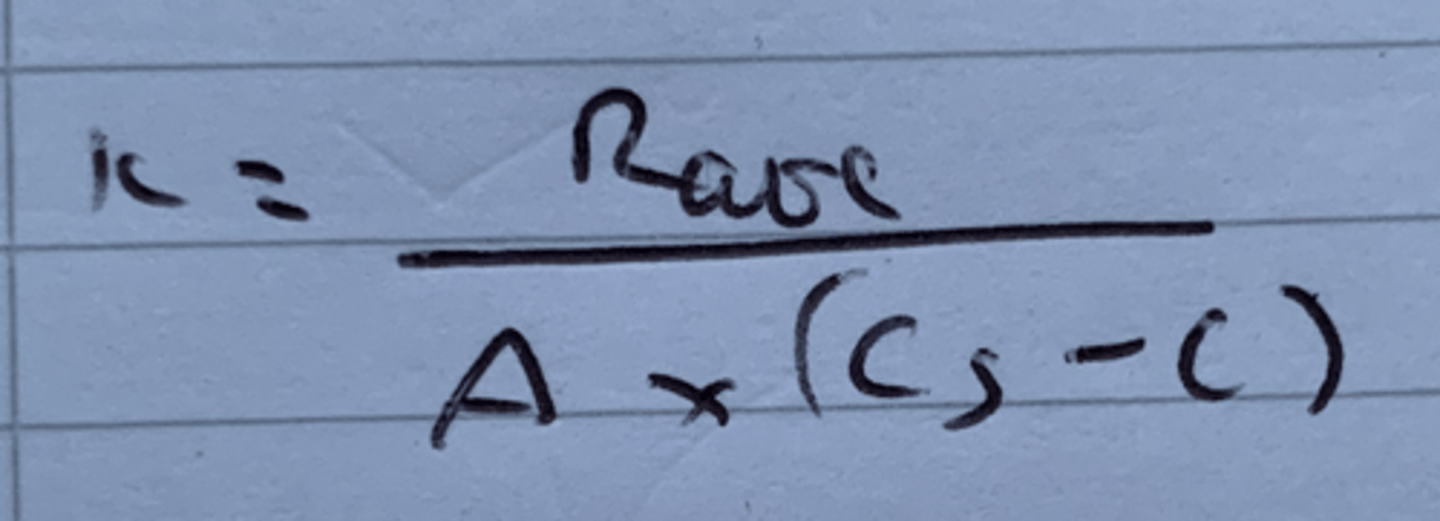
How can rate of diffusion be calculated?
Noyes Whitney equation
or
Change in mass ÷ Change in time
Equation that links diffusion coefficient (D), K and thickness (h).
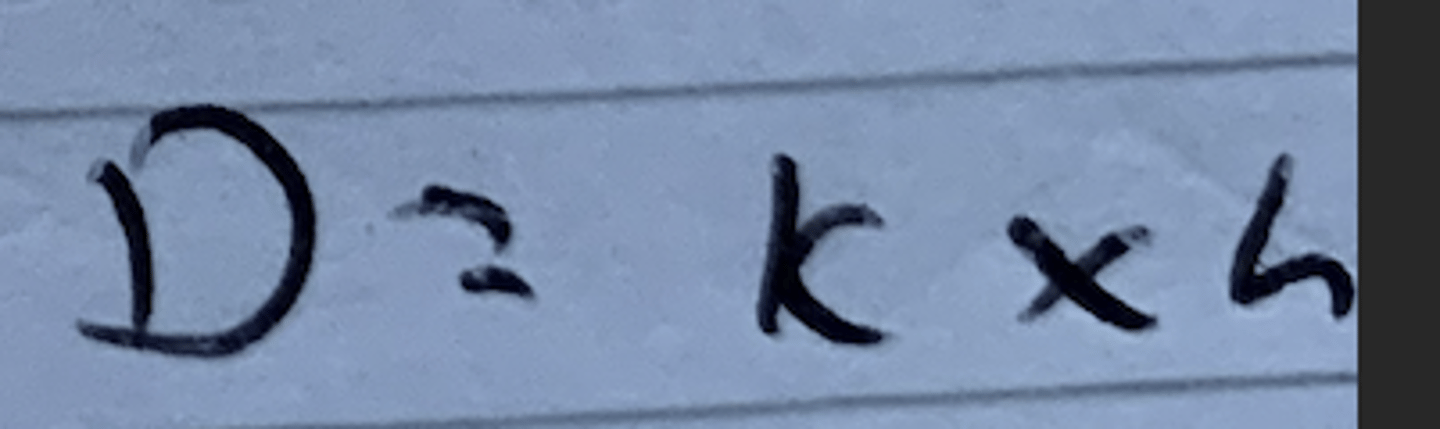
How do you calculate Osmolarity?
OsM = number of ions x moles
number of ions of NaCl = 2 as 1 Na+ and 1 Cl-
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
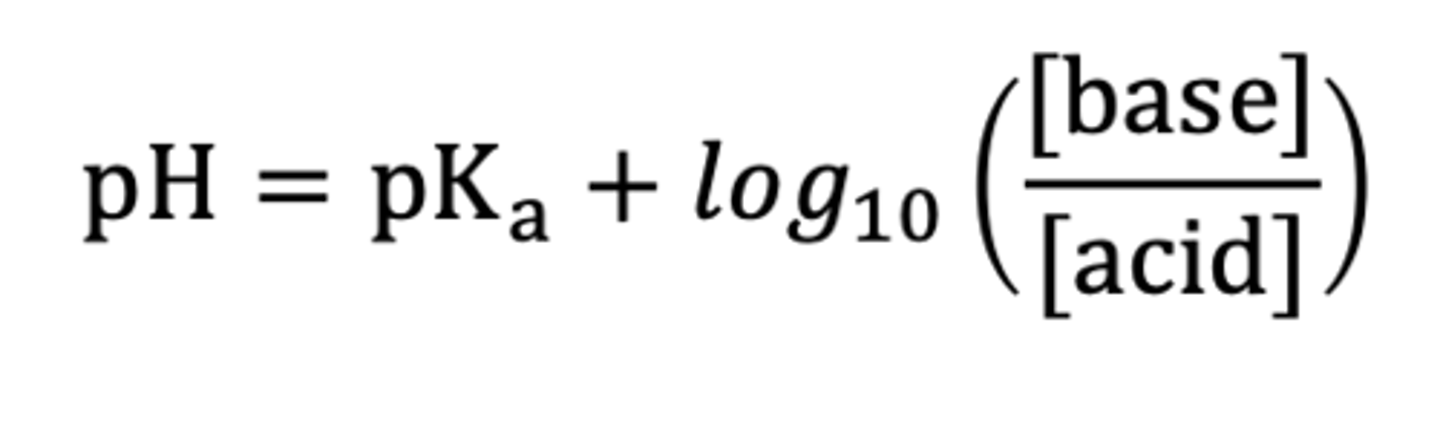
Equation that links desired change in temp, change in temp at specific concentration and the difference of temp.
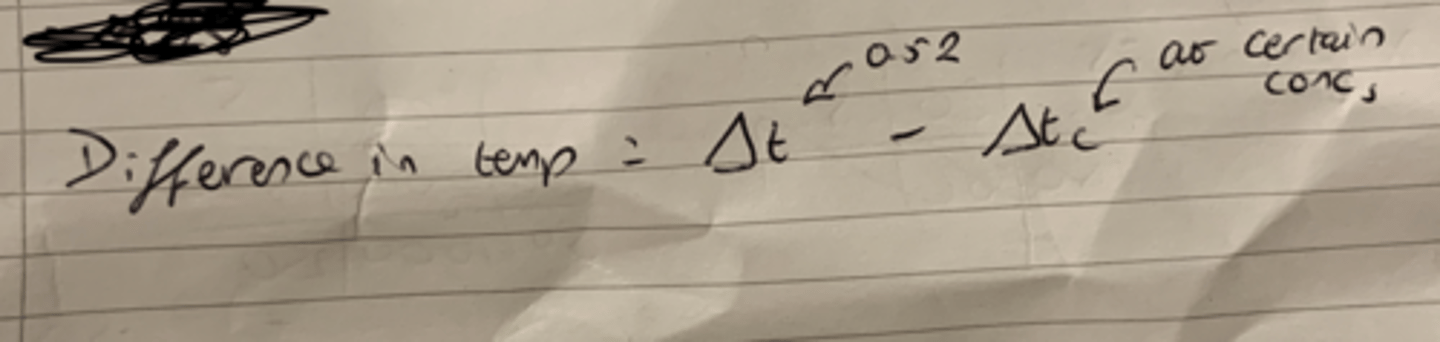
Equation that links pOH and pH.
pOH + pH = 14
Equation that links Ka, Kb and Kw.
Kw = Ka x Kb