E1 Ortho- Cervical
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
How many vertebrae are in the cervical spine?
7
How many pairs of nerves are in the cervical spine?
8
What is the name of C1?
Atlas
What is the name of C2?
Axis
C5 motor function
Deltoid & Biceps
C5 reflex
Biceps reflex
Review branches of the brachial plexus
:)
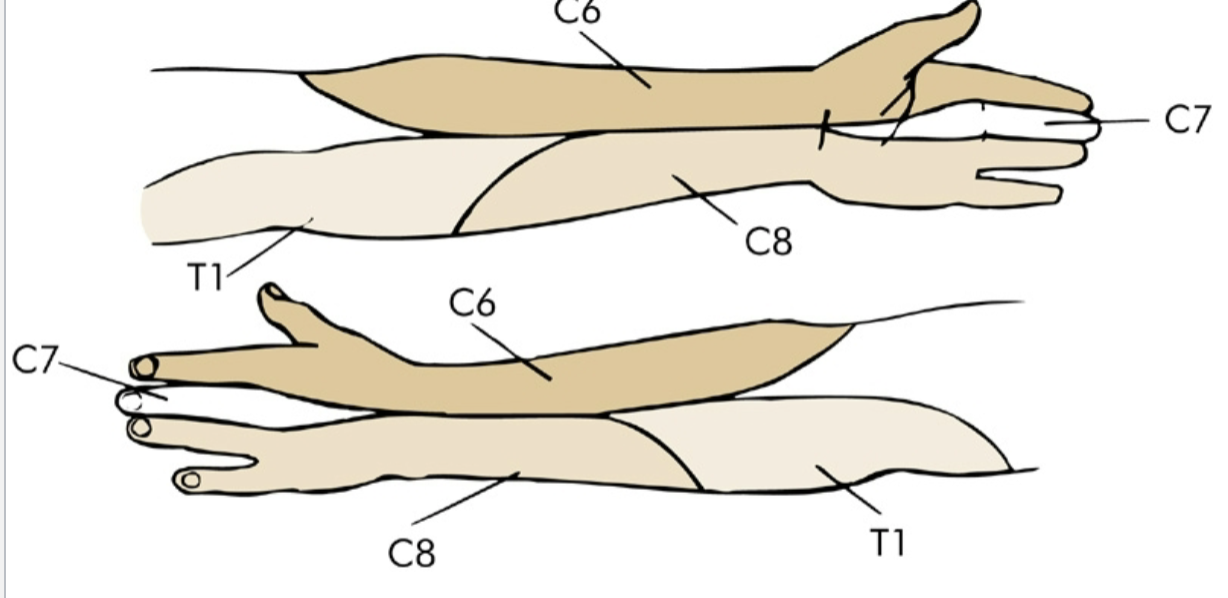
Review
dermatomes
C5 sensation
Lateral arm
C5 motor
deltoid, biceps
C5 reflex
biceps reflex
C6 motor
Biceps & Wrist extensors
C6 reflex
Brachioradialis reflex
C6 sensation
Lateral forearm and 1st digit (thumb)
C7 motor function
Triceps, Wrist flexors, Finger extensors
C7 reflex
Triceps reflex
C7 sensation
3rd digit (middle finger)
C8 motor function
Interossei mms, finger flexors
C8 sensation
Medial forearm & 5th digit (pinky)
C4 sensory
Trapezius
T1 motor
Interossei mm (abduction & adduction fingers)
T1 sensation
medial arm
special tests- cervical
slide 20; also videos you can watch
Spurling test (cervical)
axial load → lat. flex and rotate neck
radiating pain indicates nerve root compression
Distraction test (cervical)
upward distracting force
relief of sx indicates foraminal compression of nerve root
Kernig test (cervical)
supine: flex hip/knee then extend knee
pain in/radiating to legs indicates meningeal irritation or infxn
Brudzinski test (cervical)
Supine: flex neck, hip flex
pain reduction w/ knee knee flexion indicates meningeal irritation
Lhermitte’s test (cervical)
Supine: hyperflexion of C-spine
shocking sensation down spinal cord = myelopathy or MS
How do you test for Hoffman reflex?
pt seated with their relaxed hand cradled in yours, flick the long fingernail
index finger and thumb flexion is a sign of long-tract spinal cord involvement in the neck
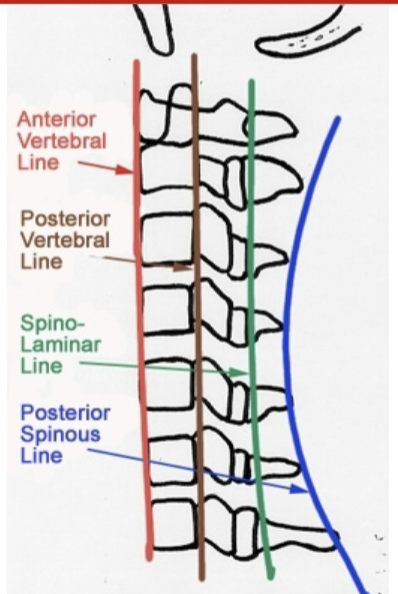
review
life lines of C spine
What is the most important XR for C-spine trauma analysis?
Cross table lat view from C1-T1
What is a Fuchs view XR?
modified Water’s view to demonstrate the odontoid tip
What is a Swimmer’s view XR?
entire cervical spine is imaged, alignment of vertebrae and joints can be assessed and counted easily
What causes cervical headaches (cephalgia)?
neck pain that radiates to the head
What sx of a cervical headache?
usually unilateral, neck tenderness, HA is upon awaking and inc throughout the day, dizziness, weakness, migraine sx
What stretching exercise can be done to improve cervical headaches?
McKenzie exercise (chin tuck)
What RF inc the odds of a herniated cervical disk?
cigarette smoking, frequent heavy lifting, diving
What S/sx are associated w/ herniated cervical disk?
neck/shoulder pain, radiates, numbness, UE weakness/ paresthesia, muscle spasms, dec grip strength; worsens or lasts longer than a strain
What special test can be used to dx a herniated cervical disk?
(+) Spurling’s test
What is the confirmatory test for diagnosis of herniated cervical disk?
MRI or CT with contrast
*consider EMG if radiates
What test is helpful in differentiating radiculopathy from peripheral neuropathy and nerve compression syndromes?
EMG or NCV
What herniated cervical disk would result in pain at the base of neck, shoulder, and/or anterolateral arm?
C4-C5 (C5 root)
What herniated cervical disk would result in pain at the neck, shoulder, medial border of scapula, lateral aspect of arm, and/or radial aspect of forearm?
C5-C6 (C6 root)
What herniated cervical disk would result in pain at the neck, shoulder, medial border of scapula, lateral aspect of arm, and dorsum of forearm?
C6-C7 (C7 root)
What herniated cervical disk would result in numbness of deltoid region?
C4-C5 (C5 root)
What herniated cervical disk would result in numbness of dorsolateral aspect of thumb and index finger?
C5-C6 (C6 root)
What herniated cervical disk would result in numbness of index, long fingers, and/or dorsum of hand?
C6-C7 (C7 root)
What herniated cervical disk would result in motor weakness of deltoid and/or biceps?
C4-C5 (C5 root)
What herniated cervical disk would result in motor weakness of biceps and/or wrist extensors?
C5-C6 (C6 root)
What herniated cervical disk would result in motor weakness of triceps and/or finger extensors?
C6-C7 (C7 root)
What herniated cervical disk would result in a biceps reflex change?
C4-C5 (C5 root)
What herniated cervical disk would result in a biceps & brachioradialis reflex change?
C5-C6 (C6 root)
What herniated cervical disk would result in a triceps reflex change?
C6-C7 (C7 root)
What is the tx for a herniated cervical disk?
spontaneous resolution in 2-8 wks, anti-inflammatory meds, muscle relaxants
AVOID -narcotics, cervical manipulation
What are signs of cervical stenosis?
chronic neck pain, pain worsens w/ upright activity, dec ROM, HA, radicular pain in UE
Hoffman reflex, clonus, hyperreflexia, Babinski
Where do degenerative findings most commonly occur in the cervical spine?
C5-C6 & C6-C7 disk spaces
What testing is helpful to dx cervical spondylosis?
CT: evaluate canal narrowing
MRI: evaluate cord/root compression
What is Cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM)?
Narrowing of the spinal canal that leads to spinal cord compression in the cervical spine
What demographic is most affected by cervical spondylotic myelopathy?
males over 55 yo
What effect does Cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM) have on gait and reflexes?
Ataxia and hyperreflexia
What special tests help dx cervical spondylotic myelopathy?
(+) Hoffman and Babinski
(+) Lhermitte’s
R/O: vertebral artery test, spurling’s test
What tests help dx cervical spondylotic myelopathy?
XR - check alignment
MRI -look for compression
CT myelogram - better detail, show bone spurs, canal size
What is whiplash?
Cervical sprain caused by hyperextension of neck then flexion (MVA); ligamentous injury
What is a cervical strain?
self limiting muscle injury d/t strain from pillows or working at computers; muscle injury
MVA rear-end collision with general neck pain, XR neg, no motor deficits, most likely dx?
Cervical sprain (whiplash)
How does a cervical sprain/strain present?
noradiuclar, nonfocal neck pain, SCM or trapezius pain, worse w/ motion, HA, sleep disturbances; self-limiting, doesn’t radiate
What is a REQUIREMENT of cervical imaging?
All 7 cervical vertebrae must be seen
What is the tx for cervical fxs?
immediate IV steroids (Methylpred), brace c-spine and spine board, cervical collar
What is a Jefferson fracture?
Atlas (C1) burst fracture
What can cause a Jefferson (C1 burst) fracture?
Brick falling from building, football players, diving, compression injuries
What plain films are needed to evaluate a Jefferson fx?
AP, lat, open-mouth views
What causes an Odontoid (C2) fx?
forceful flexion, extension, or rotation; 25% cases assoicated w/ neuro deficit
What is a type 1 Odontoid fx?
rare, avulsion of the alar ligament w/ oblique fx at the tip of the dens
What is a type 2 Odontoid fx?
MC; at the base of the dens
What is a type 3 Odontoid fx?
extends from the dens all the way to the C2 body
What is an Odontoid Fx?
fracture of the dens on C2 (axis) caused by trauma
What is the Predental space?
distance from dens to C1 body; should not be more than 3mm in adults and 5 mm in children
What is the tx for type 1 Odontoid fx?
externally imobilized x 3 mo; repeat imaging
What is the tx for a Type 2 Odontoid fx?
reduction using traction and halo immobilization; elderly tx’d w/ C1-C2 arthrodesis
What is the tx for a Type 3 Odontoid fx?
traction reduction and halo immobilization x 3 months; elderly -C1-12 arthrodesis
What is a Flexion teardrop fx?
large wedge of the anterior aspect of vertebrae d/t forceful flexion
Where does a Clay-shoveler's fracture most commonly occur?
C7
What population is most likely to get a cervical spine dislocation?
M > F, 18-25 yo (inc likelihood of an accident)
What is the tx for a cervical spine dislocation?
emergency consult to ortho & neurosurgeon
cervical HALO
What are atraumatic causes of cervical spine dislocation?
RA, Down’s syndrome
What is a Facet dislocation?
Anterior subluxation of one vertebra on another
*< 50% of the width of a vertebral body = unifacet
*> 50% + widening of interspinous space = bilateral
What causes an Atlanto-occipital dislocation?
hyperextension, distraction, rotational injury w/ excessive force on the ligaments
Who is more likely to experience an Atlanto-occipital dislocation?
children 2x more than adults
What are the consequences of an Atlanto-occipital dislocation?
brainstem dysfunction, cranial nerve deficits, death
When assessing an Atlanto-occipital injury what should you NOT do?
manipulate the neck
What is a Type 1 Atlanto-occipital dislocation?
anterior dislocation and MC
What is a Type 2 Atlanto-occipital dislocation?
pure longitudinal dislocation
What is a Type 3 Atlanto-occipital dislocation?
posterior dislocation
What is a Hangman’s fracture?
spondylolisthesis of the axis d/t bilateral fx of pars; usually result of hyperextension
What is the most common cause of Hangman’s fracture?
MVA
C- spine trauma what do you do?
Backboard, collar, don't move patient
What is the tx for cervical osteoarthritis?
NSAIDS, PT -ROM exercises, ortho/neurosurgery consult
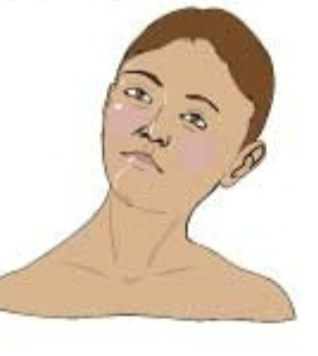
What are sx of Torticollis?
Tilting of the head with chin rotated to the opposite side; head tilts towards affected side
SCM contracture causing pain & dizziness
nystagmus or superior oblique palsy
What is another name for torticollis?
wry neck or “cock robin”
What is Torticollis?
skeletal dysplasia
-spasmodic = muscle or nerve involved