Introduction to Psychology: LGBT Psychology 101
LGBT Psychology
- Being LGBT is about SOGIE
- SOGIE are fundamental dimensions of human life
- Development of SOGIE is part of human development
- Experiencing attraction and forming relationships: Sexual Orientation
- Identity formation: Gender Identity
- Self-expression: Gender Expression
- A branch of psychology that is affirmative of LGBTQ people
- It seeks to challenge prejudice and discrimination against LGBTQ people and the privileging of heterosexuality in psychology and in the broader society
- It seeks to promote LGBTQ concerns as legitimate foci for psychological research and promote non-heterosexist, non-genderist, and inclusive approaches to psychological research and practice
- Scotland - LGBT inclusive curriculum
- Assigned Sex: biological
- Gender Identity: cognitive
- Gender Expression: what other people see
- Sexual Orientation: physically and emotionally attracted
- These are not necessarily linked
Human Development
- Sex
- Physical characteristics of being male or female
- Biological identity
- Gender
- Behavior associated with being male or female
- Social and cultural identity
- Trans
- Men and women whose assigned sex at birth differs from their gender identity
- Trans: migrate
- Individuals who migrate from one side of the gender binary to the other
- Ex. Aiza Seguerra (identified as a man)
- Assigned sex: female
- Gender identity: male
- Gender expression: masculine
- Sexual orientation: heterosexual (because he identifies himself as a male and like women)
- Non-Binary
- People who do not identify within the gender binary
- Other terms include genderqueer, agender, bigender
- Lesbian
- Women attracted to and form romantic relationships with other women
- Refers to one’s sexual orientation
- Ex. Ellen Paige
- Gay
- Men attracted and form romantic relationships with other men
- Refers to one’s sexual orientation
- Ex. Vice Ganda, Matt Bomer
- Bisexual
- Woman or man attracted to man and woman
- Refers to one’s sexual orientation
- Ex. Ezra Miller
- Queer
- Words used for those who defy social norms regarding gender and sexual diversity
- Identifying as “queer” transforms a word that was once judgmentally and hatefully to a postmodern meaning that is empowering, especially for younger people
- Intersex
- A general term use for a variety of conditions in which a person is born with a reproductive or sexual anatomy that doesn’t seem to fit the typical definitions of female or male
- Can manifest at birth, puberty, adulthood
- Hermaphroditism in physiological impossibility
- Asexual
- Individuals who are low on attraction for both sexes
- Could engage in sexual intercourse or relationships
LGB = SO
T = GIE
Psychological Problem
- Low Prevalence: not common
- Dysfunction: impairs daily functioning
- Distress: causes suffering
- “Lesbian, gay, and bisexual orientations are not disorders. Research has found no inherent association between any of these sexual orientations and psychopathology. Both heterosexual behavior and homosexual behavior are normal aspects of human sexuality .. lesbian, hay and bisexual relationships are normal forms of human bonding.” (APA, 2008, p.3)
- Personal effectiveness is not related to sexual orientation or gender identities
- Children of same sex parents are just as likely to be well-adjusted and healthy as children of different-sex parents
Social Psychology
- Scientific investigation of how people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior are influenced by the actual, imagined, or implied presence of others
- Range of topics include conformity, persuasion, influence, obedience, prejudice, discrimination, stereotyping, attitudes, intergroup relations
Social Psychology and LGBT Psychology
Social Identity Theory
- Theory of group membership and intergroup relations based on self-categorization, social comparison, and in terms of ingroup-defining properties
Trans Issues
- Basic understanding the difference between assigned sex at birth and gender identity
- Respect for one’s identity
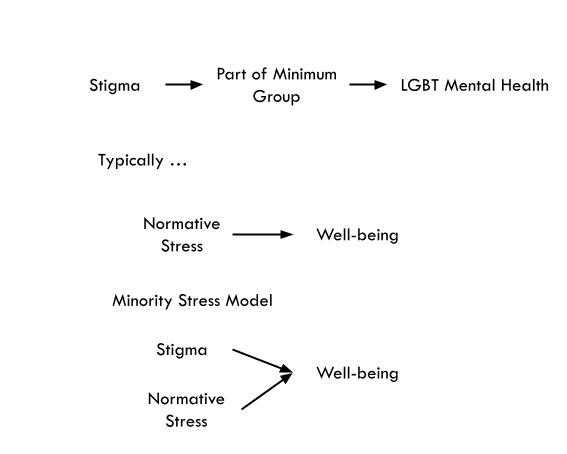
Minority Stress Theory
- Being a part of a stigmatized group negatively impacts well-being
- Sexual and gender minority status, perse, does not lead to poor outcomes
- Experiences of stigma and inequalities are those that reduce well-being for LGBTs
- Social environments with explicit LGBT-alternative policies and LGBT-supportive programs see fewer mental health disparities between LGBTs and non-LGBTs
Affirmative Contexts
- Small stigma