CMS II Final: Endo
1/292
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
293 Terms
which conditions are caused by the anterior pituitary?
1. pituitary adenoma
2. hypopituitarism
3. growth hormone deficiency
4. acromegaly and gigantism
5. cushing dz
6. nelson syndrome
which conditions are caused by the posterior pituitary?
1. diabetes insipidus
2. SIADH
3. sheehan syndrome
are pituitary adenomas malignant or benign?
benign
what is the difference between a microadenoma and a macroadenoma?
microadenoma = pituitary tumor <10 mm
macroadenoma = pituitary tumor >10 mm
which type of pituitary adenoma secretes GH?
somatotroph
which type of pituitary adenoma secretes prolactin?
prolactinoma
which type of pituitary adenoma secretes ACTH?
corticotroph
which type of pituitary adenoma secretes FSH/LH?
gonadotroph
bitemporal hemianopsia is a symptom of what?
pituitary adenoma
also:
- HA
- N/V
- altered consciousness
- seizures

what s/sx may a man with hyperprolactinemia experience?
ED
decreased libido
gynecomastia
hypogonaidms
infertility
which drugs may cause hyperprolactinemia?
verapamil
amphetamines
cimetidine
estrogen
opioids
nicotine
cocaine
what are the pathologic causes of hyperprolactinemia?
1. chronic chest wall stimulation (post mastectomy, herpes zoster, chest acupuncture, nipple rings)
2. cirrhosis
3. renal failure
4. hypothyroidism
5. MS
6. spinal cord lesion
7. SLE
what is the treatment of choice for hyperprolactinemia?
therapy with dopaminergic drug → cabergoline or bromocriptine
deficiency of which hormone can cause infertility, delayed puberty, decreased libido?
gonadotropin deficiency → hypogonadism, decreased body hair, amenorrhea, and ED also caused
deficiency of which hormone can cause decreased cortisol secretion, weakness, and fatigue?
ACTH deficiency → also causes increased skin pigmentation, loss of appetite, weight loss and hypotension
deficiency of which hormone can cause moderate central obesity, increased systolic BP, and growth retardation?
GH deficiency → also causes increased LDL cholesterol, small heart
what are complications of anterior hypopituitarism?
- visual impairment
- hypoadrenalism/adrenal crisis
- fevers, shock, coma, death
what is the first line tx for anterior hypopituitarism?
replace the hormone → growth hormone, prednisone/hydrocortisone, synthroid
what must all pts with hormone deficiencies wear?
medical alert
what do pts with ACTH deficiency need during major physical stress?
more cortisone
growth hormone is stimulated by _______________ and inhibited by __________
GHRH; somatostatin
both are produced by the hypothalamus
short stature and delayed puberty/dentition is associated with deficiency of which hormone?
GH
what s/sx are associated with adult GHD?
- reduced bone mineral density and increased risk of osteoporotic bone fx
- impaired cardiac fxn
- central obesity
- increased insulin sensitivity
- reduced exercise capacity
- emotional disturbance
what are the possible causes of adult GHD?
hx of pituitary tumors that may have been treated with surgery or radiation or may have hx of head trauma
growth hormone level < ___ at birth is highly suggestive of GHD
20 ng/ml
what is the standard test for dx of GHD in adults?
ITT (insulin tolerance test)
what other lab findings may be seen in adults with GHD?
increased lipids, HDL low
what are the complications of GHD?
- premature CV disease
- osteoporosis
- psych disturbance
- insulin resistance
- obesity and its comorbidities
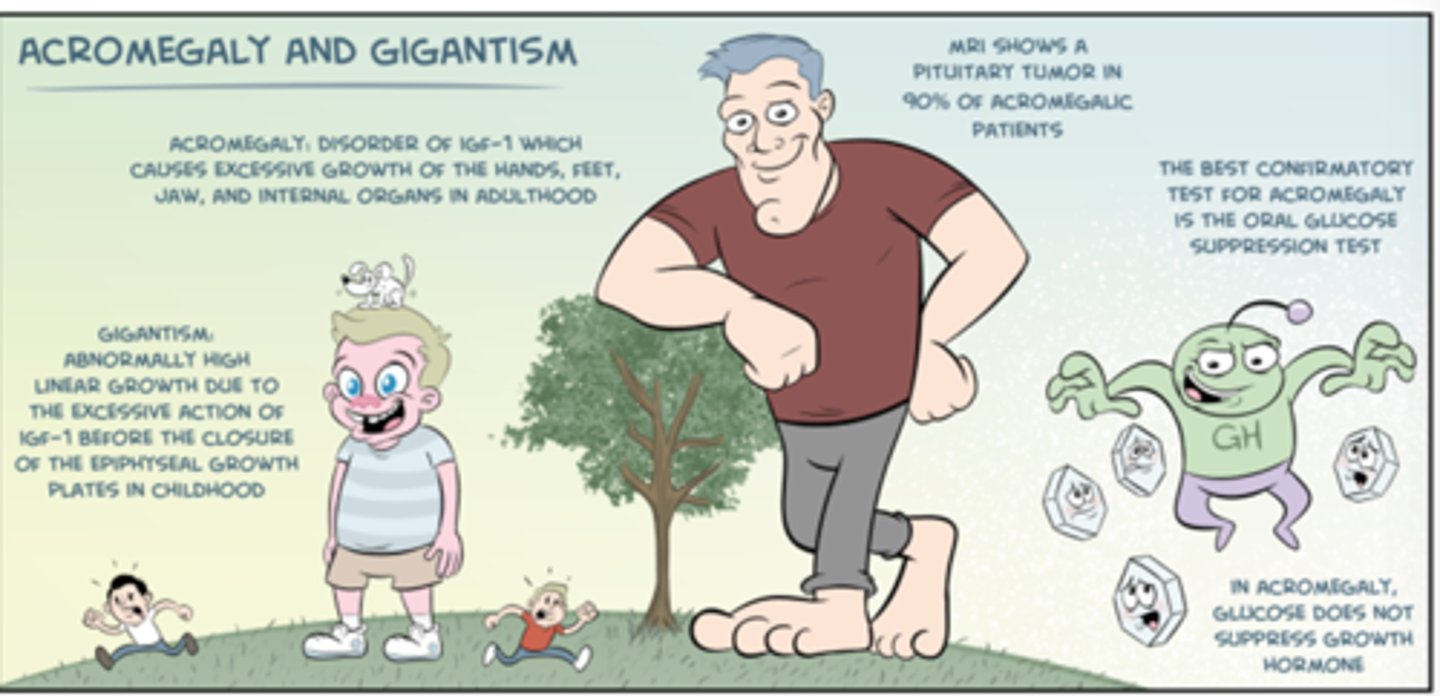
what is the difference between gigantism and acromegaly?
gigantism = abnormally high linear growth d/t excessive action of IGF-1 while the epiphyseal growth plates are open during childhood
acromegaly = same disorder of IGF-1 excess when it occurs AFTER the growth plate fuses
what are the MC cause of death in acromegaly and gigantism?
CV and resp. complications → normalization of IGF-1 levels is associated with return to normal life expectancy
what are the physical signs of acromegaly and gigantism?
- excessive growth of hands, feet, jaw, and internal organs
-soft, doughy (?), sweaty handshake
- tall
- impotence
-HTN
- OSA
- tooth spacing increase
- goiter
- deep voice
- tumor mass may cause HA, visual changes d/t optic nerve compression, and hypopituitarism
serum levels of IGF-1 are consistently _________ in pts with acromegaly and used to monitor treatment success
elevated
what is the standard criteria for dx of GH excess (acromegaly and gigantism)?
inability to suppress serum GH during glucose-tolerance test (GTT)
→ failure to suppress serum GH levels to <5 within 3hrs is dx of pituitary GH excess
what medications can be used to tx acromegaly and gigantism?
dopamine agonists → bromocriptine, cabergoline → bind to pituitary D2 receptors and suppress GH secretion
octreotide (sandostatin) → suppresses serum GH in pts with acromegaly and normalizes circulating IGF-1
what are possible causes of Cushing's syndrome?
1. exogenous glucocorticoids (MC)
2. endogenous glucocorticoid overproduction
3. ectopic ACTH (secreted by oat cell or SCLC or carcinoid tumors)
why do ectopic sources of ACTH continue to make ACTH despite elevated levels of cortisol?
they don't have cortisol receptors for the negative feedback
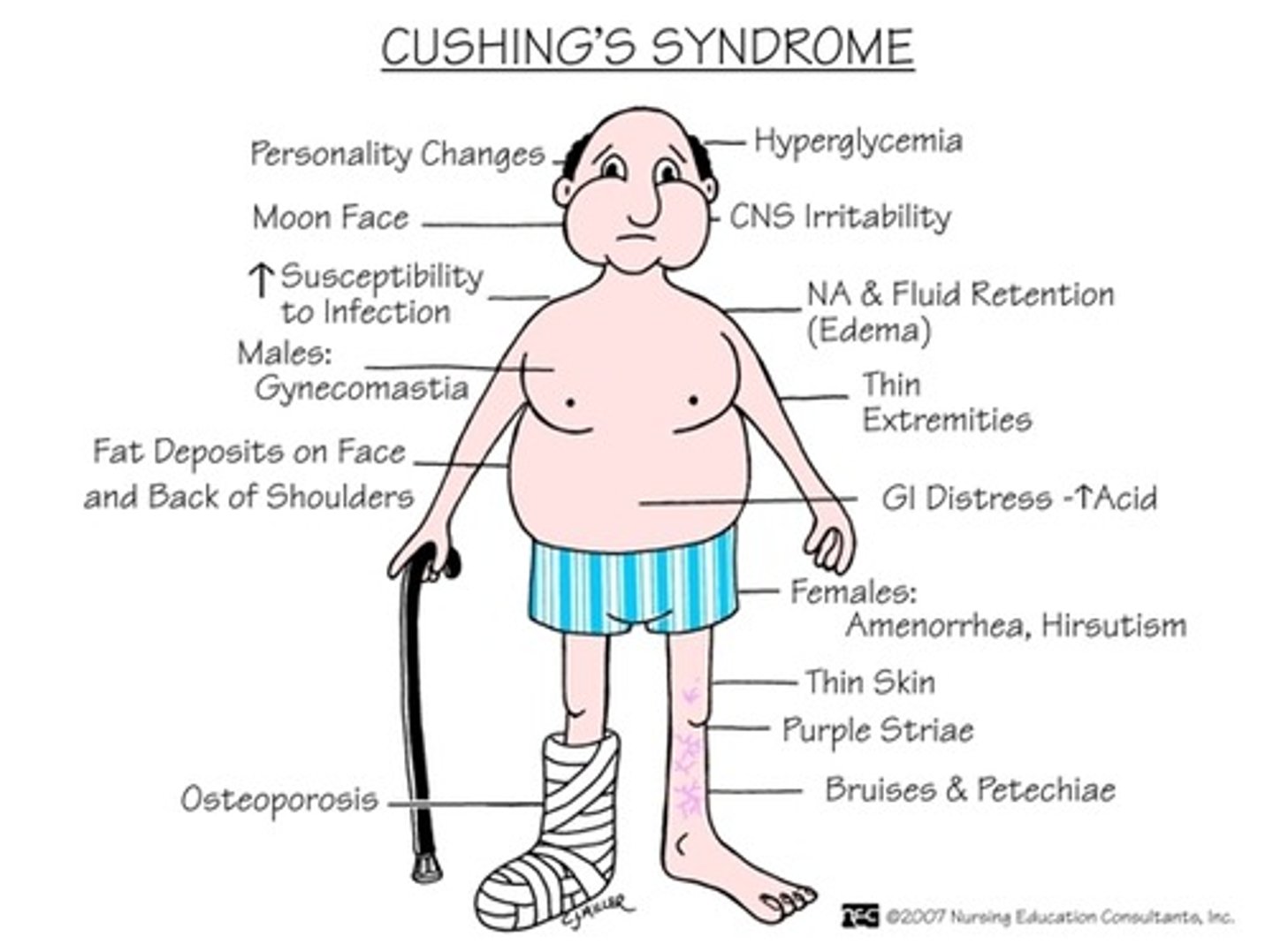
what are the s/sx of cushing syndrome?
- weight gain → moon face, buffalo hump, central obesity
- skin changes → purple stretch marks, easy bruising, skin thinning, lanugo facial hair
- progressive proximal muscle weakness
- menstrual irregularities
- psych probs
- HTN and edema (from inc. aldosterone)
- osteoporotic fx and kyphosis/height loss
- poor wound healing
what abnormal lab findings may be seen in cushing syndrome?
ACTH → elevated
cortisol → elevated
glucose → elevated
also: leukocytosis, lymphocytopenia, hypokalemia, glycosuria
what are the results of the dexamethasone suppression test in a normal patient?
suppression of pituitary production of cortisol
what are the results of the dexamethasone suppression test in a pt with a pituitary adenoma?
low doses → no suppression
high doses → cortisol suppression
what are the results of the dexamethasone suppression test in a pt with an ectopic source of cortisol/ACTH?
low dose → no suppression
high dose → no suppression
what findings from the urinary free cortisol test exclude the dx of endogenous cushing syndrome?
3 urine free cortisol levels in the normal range
what are the complications of cushing syndrome?
HTN
DM
increased infection
osteoporisis
what is the cause of Nelson's syndrome?
pituitary tumor that grows AFTER bilateral adrenalectomy
what causes hyperpigmentation seen in Nelson's syndrome?
increased MSH → POMC is a precursor for both MSH and ACTH so when ACTH increases, POMC increases and causes MSH to also increase
what are the s/sx of Nelson's syndrome?
very high ACTH
hyperpigmentation
HA from pituitary tumor
visual field loss
what is the treatment for Nelson's syndrome?
surgery if adenoma
glucocorticoids (hydrocortisone) bc no adrenal glands
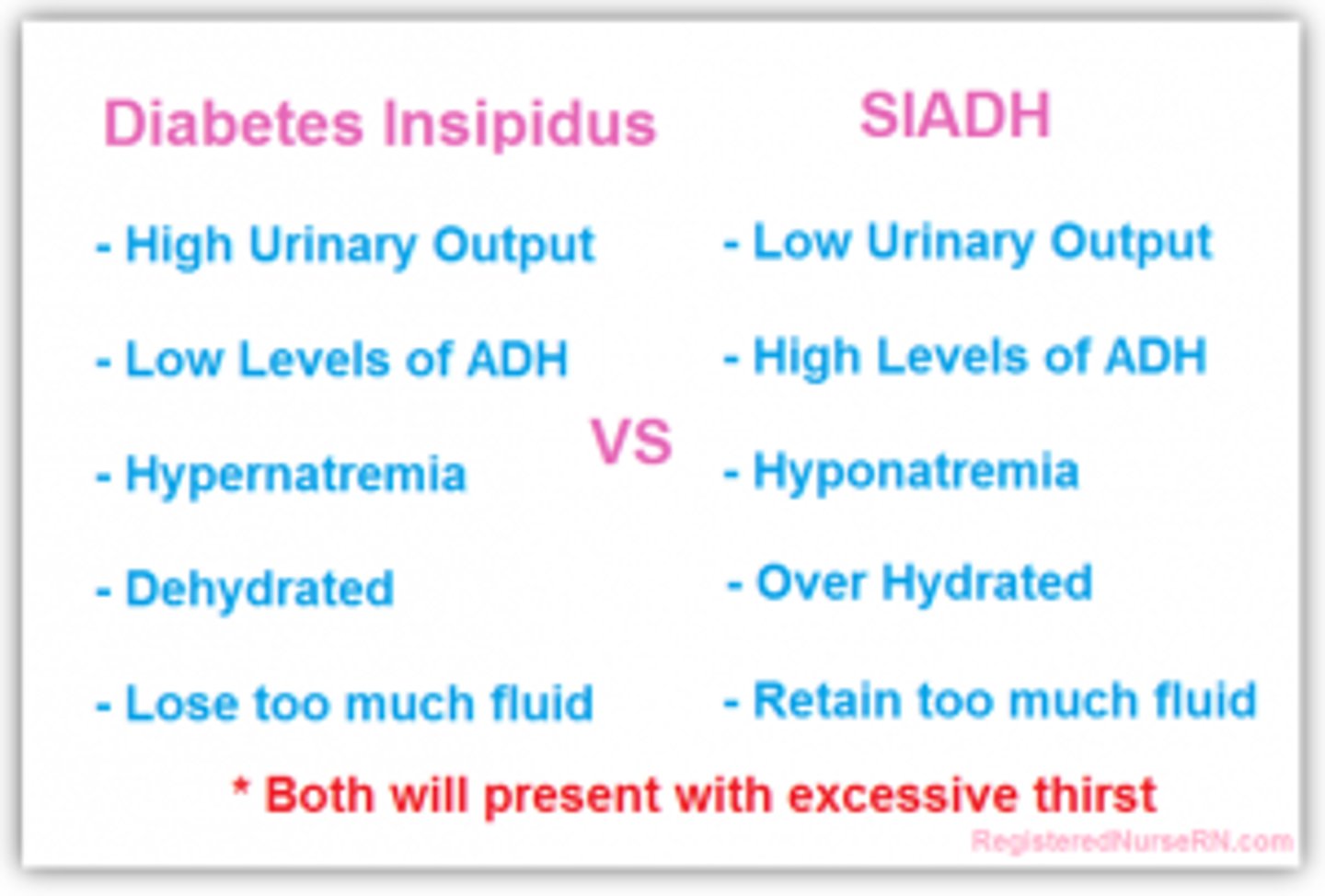
what causes SIADH?
increased ADH → increased blood volume → increased BP
what causes diabetes insipidus (DI)?
decreased ADH → increased water elimination → increased urinary output
what is the difference between central and nephrogenic DI?
central = brain isn't making ADH → low serum ADH
nephrogenic = kidneys aren't responding to ADH → normal serum ADH
what are the main symptoms of DI?
polyuria
polydipsia
nocturia
also
- HA
- visual disturbances
what test is diagnostic for DI?
water deprivation test
what water deprivation test results indicate central DI? nephrogenic?
central = minimal ADH levels and activity; the urine doesn't become concentrated BUT in response to exogenous ADH, urine osmolality increases by >50%
nephrogenic = normal/elevated serum ADH; kidneys fail to respond to exogenous ADH
what are the hallmark lab findings of DI?
urine specific gravity of 1.005 or less
urine osmolality <200
increased plasma osmolality
what is the first line tx for central DI?
desmopressin (DDAVP)
vasopressin is second line
which dx is defined by hyponatremia and hypo-osmolality resulting from inappropriate, continued secretion of ADH despite normal/increased plasma volume?
SIADH → results in impaired water excretion
MC cause of euvolemic hyponatremia in hospitalized pts
what causes hyponatremia in SIADH?
excessive WATER not d/t deficiency of sodium
basically so diluted that the concentration of sodium is low
what PE findings would you expect in a pt with SIADH?
- confusion, disorientation, delirium
- generalized muscle weakness, myoclonus, tremor, asterixis, hyporeflexia, ataxia, dysarthria, Cheyne-stokes respiration, pathologic reflexes
- generalized seizures, coma
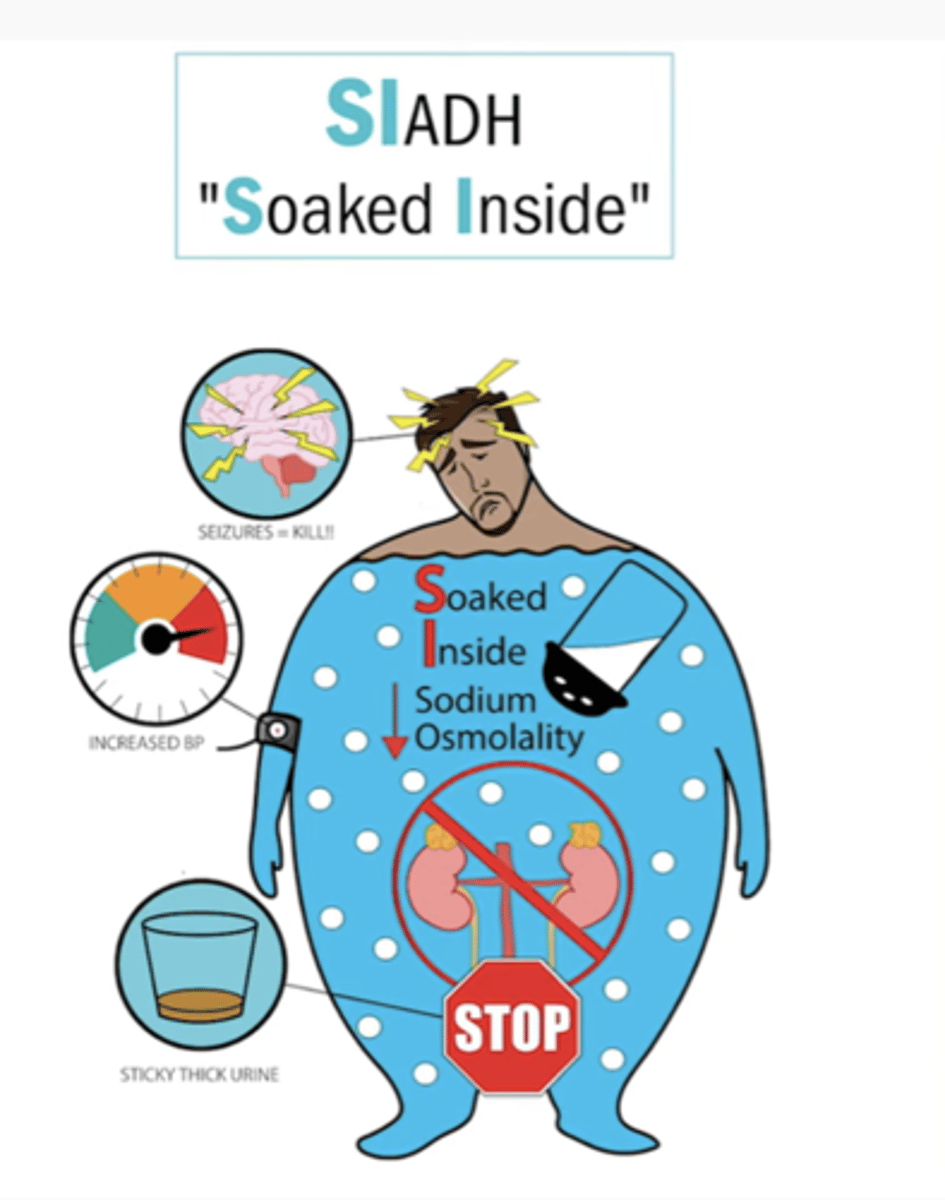
how is hyponatremia corrected in SIADH?
fluid restriction and vasopressin-2 receptor antagonists (or loop diuretics)
neuro sx = replace sodium
what is the risk when correcting hyponatremia in SIADH?
central pontine myelinolysis (CPM)
raise Na+ by 0.5-1 mEq/hr
what are the complications of SIADH?
cerebral edema
noncardiogenic pulm edema
CPM
what is an infarction of the pituitary gland secondary to hemorrhage during childbirth?
Sheehan syndrome → risk in preg women with type 1 DM
what is the MC presentation of sheehan syndrome?
breast involution and failure to lactate from prolactin deficiency
followed by failure of menses to resume
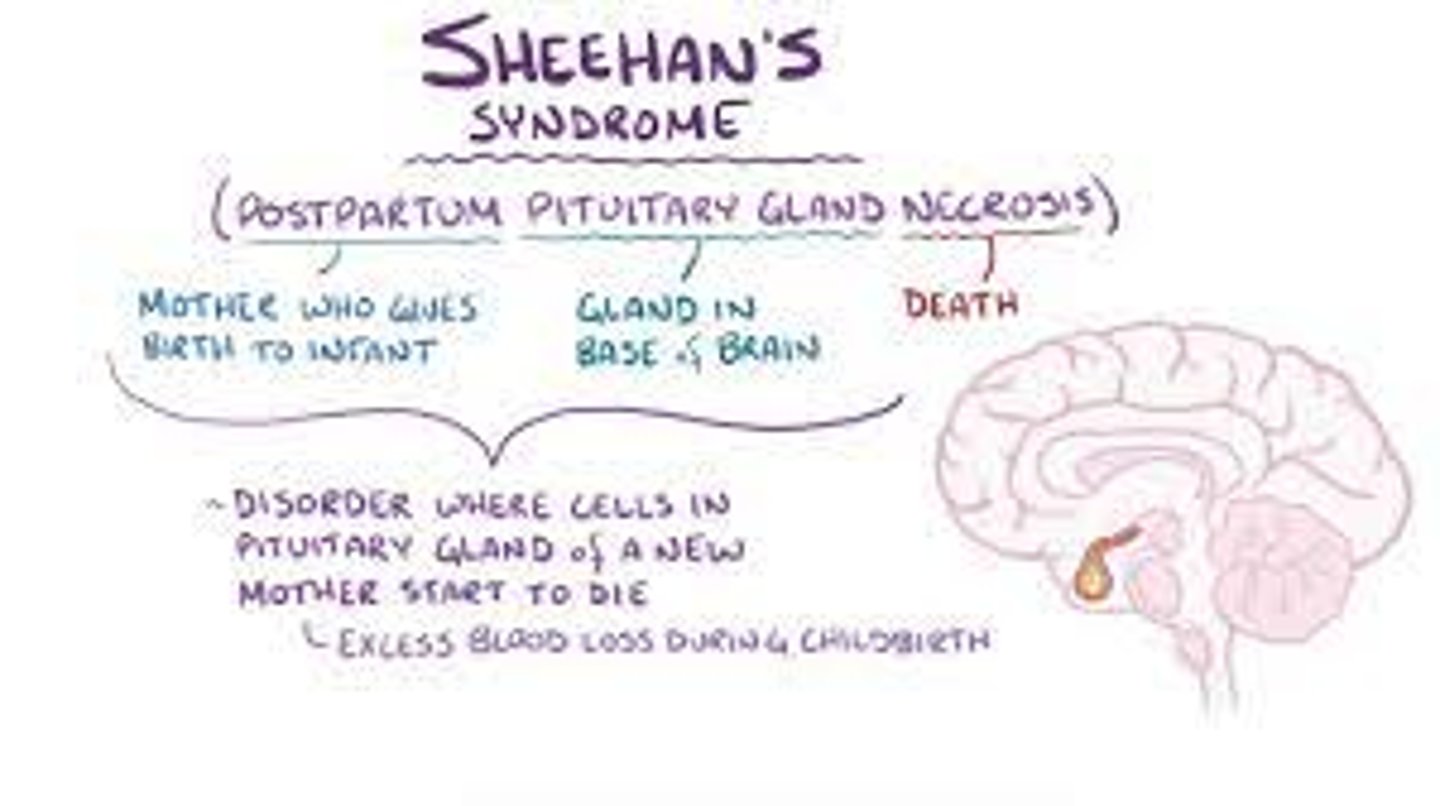
what do labs in Sheehan syndrome show?
partial hypopituitarism or panhypopituitarism
low free thyroxine, estradiol, cortisol, FSH, TSH, LH, ACTH
what is the tx for Sheehan syndrome?
hormone replacement with glucocorticoids, levothyroxine, sex steroids
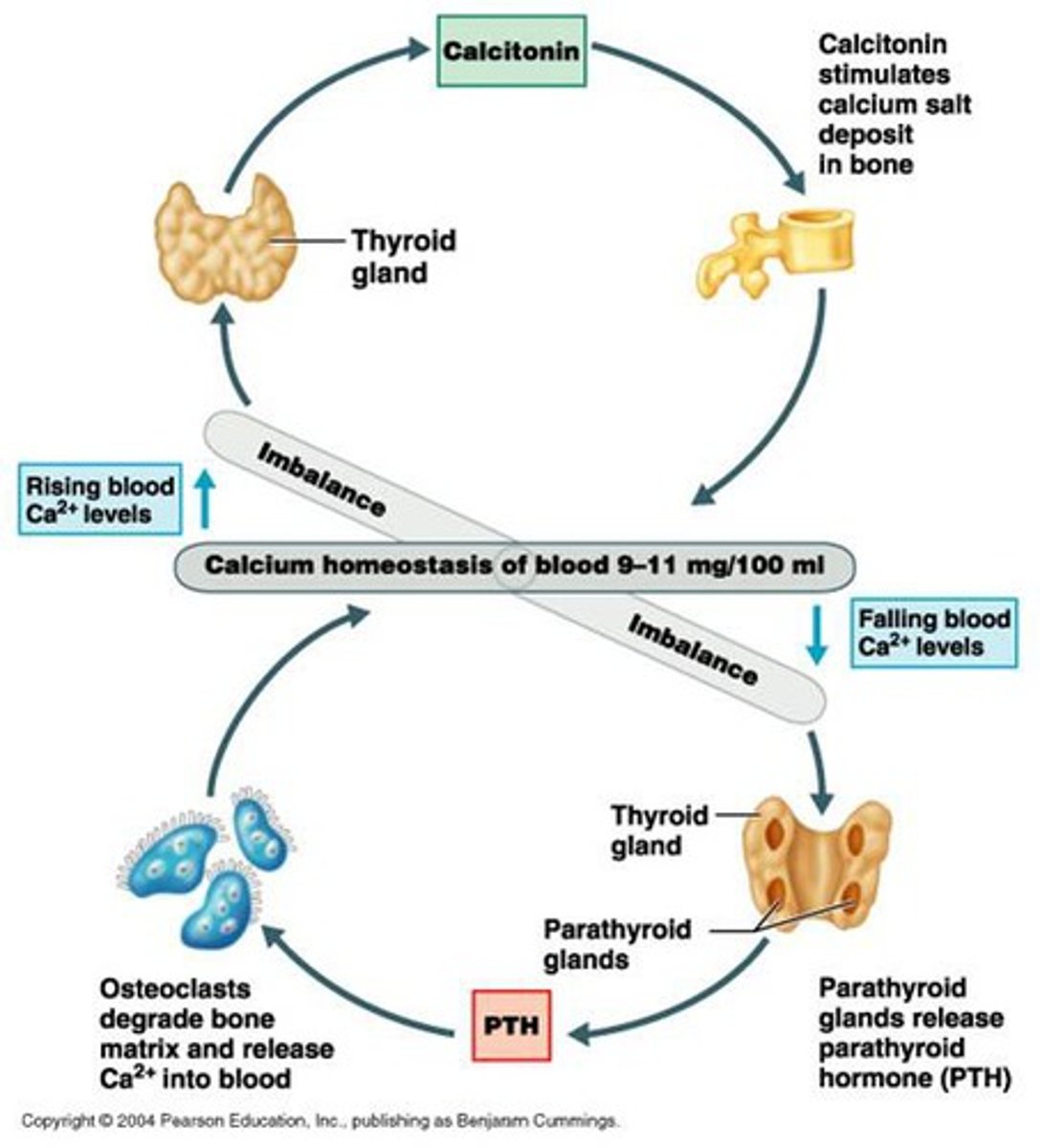
what is the function of PTH?
increase blood calcium levels:
- increases release of calcium and phosphate from bone matrix
- increases calcium reabsorption by kidney
- increases renal production of vit D, which increases intestinal absorption of calcium
primary or secondary hyperparathyroidism: unregulated overproduction of PTH resulting in abnormal calcium homeostasis?
primary → MC caused by adenoma of PT gland
primary or secondary hyperparathyroidism: overproduction of PTH hormone due to chronic abnormal stimulus for its production?
secondary → chronic renal failure and vit D deficiency are MCC
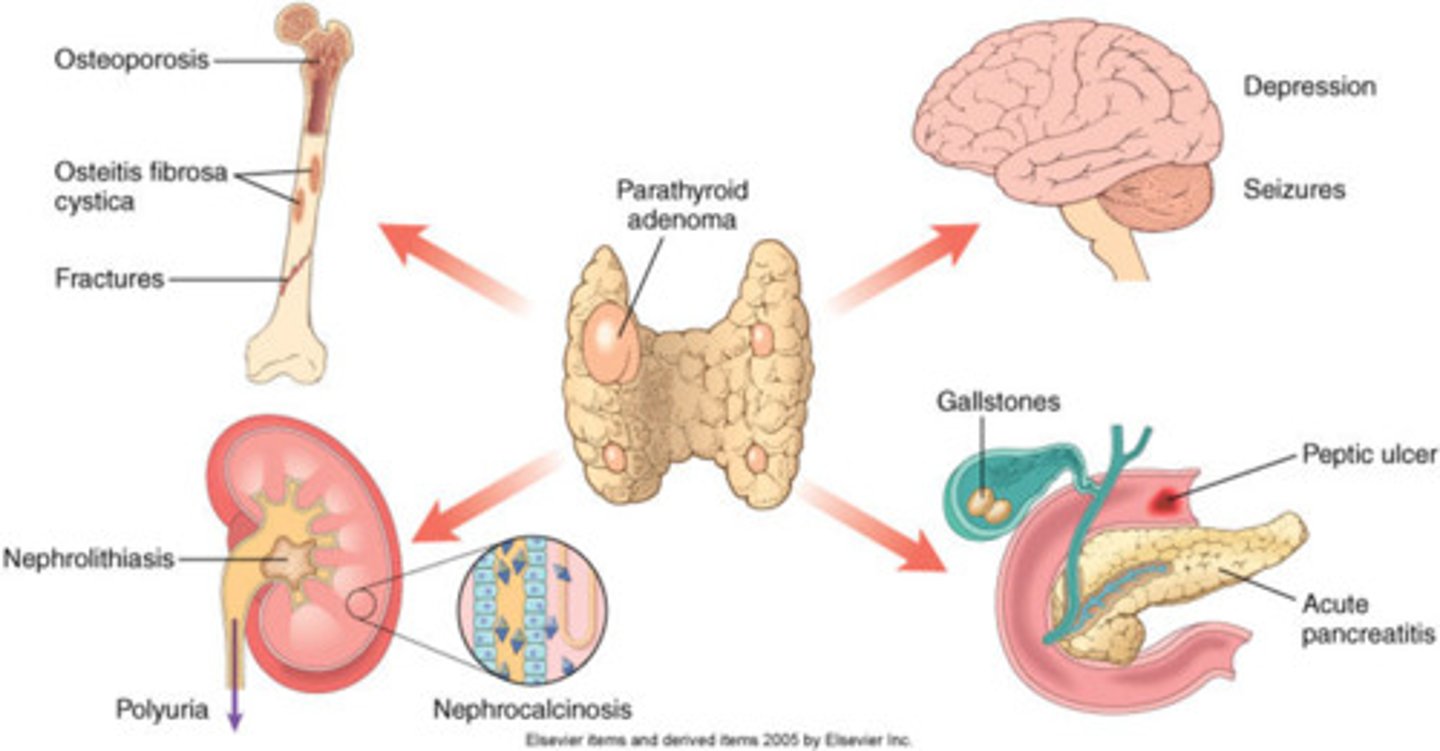
what can the chronic excessive resorption of Ca++ from bone caused by excessive PTH result in?
osteopenia
in severe cases → may result in osteitis fibrosa cystica
how does hyperparathyroidism cause PUD?
increased calcium → increased gastric acid secretion
what are common sx of hyperparathyroidism?
sx are d/t hypercalcemia!!!!
- muscle weakness
- fatigue
- volume depletion
- N/V
- severe = coma and death!
- neuropsych sx → depression, confusion, subtle deficits
what is a risk factor for hyperparathyroidism?
hx of neck irradiation/surgery
female>male
age>50
what might you see on EKG in a pt with hyperparathyroidism?
shortened QT interval and prolonged PR interval**** and HTN
HYPER P. IS A SHORT QT
due to hypercalcemia!!!!!!!!!
what might labs show in hyperparathyroidism?
- calcium = high
- phosphate = low
- urine phosphate = high
- serum ALP = high (bone dz only)
- vit D = low
- serum PTH = high
- 24 hr urine = increased ca/cr ratio (primary)
what may XR show in hyperparathyroidism?
imaging studies are NOT used to make dx but may show:
- skeletal cysts
- skull mottling (salt and pep)
- osteosclerosis of vertebral bodies
what are the essentials for dx of hyperparathyroidism?
- elevated PTH with elevated calcium = primary dz
- renal stones, polyuria
- HTN, constipation
- fatigue, mental changes
- bone pain, pathologic fx
"bones, stones, abdominal groans, psychic moans, with fatigue overtones"
what is the tx for hyperparathyroidism?
no tx if asx (monitor calcium and creatinine, annual bone density)
- remove diseased gland
- IV saline for acute dehydration
- vit D
- IV bisphosphonates (alendronate)
- calcimimetics (sensipar) decreases PTH secretion
which drug for tx of hyperparathyroidism decreases secretion of PTH?
calcimimetics → cinacalcet hydrochloride (sensipar)
what are the common s/sx of hypoparathyroidism?
neuromuscular instability:
- paresthesias
- hyperirritability
- fatigue/anxiety
- mood swings/personality disturbances
- seizures
- hoarseness
- wheezing and dyspnea
- muscle cramps, diaphoresis, biliary colic
where are pts with hypoparathyroidism more likely to experience muscle cramps?
lower back, legs, and feet
tetany develops if hypocalcemia is severe
which signs demonstrate neuromuscular irritability found in hypoparathyroidism?
Chvostek sign = facial twitching around the mouth induced by gently tapping the ipsilateral facial nerve anterior to ear
Trousseau sign= carpal spasm induced by inflating BP cuff around arm to 20 mmHg above obliteration of radial pulse x3-5 mins; hypocalcemia → contracture
what is the MC cause of hypoparathyroidism?
thyroidectomy
other risk factors:
- neck surgery or trauma
- head and neck cancer
- wilson's disease
- hemochromatosis
cataracts, blurred vision, loss of eyebrow hair, and hyperactive DTRs are common in which dx?
hypoparathyroidism (d/t hypocalcemia)
also:
- brittle nails
- dry scaly skin
- anxiety
- lethargy
- tetany
etc
what labs may be abnormal in hypoparathyroidism?
- calcium and magnesium = low
- alk phos = normal
- serum phosphate = high
- urine ca = low
- CT = calcification of basal ganglia
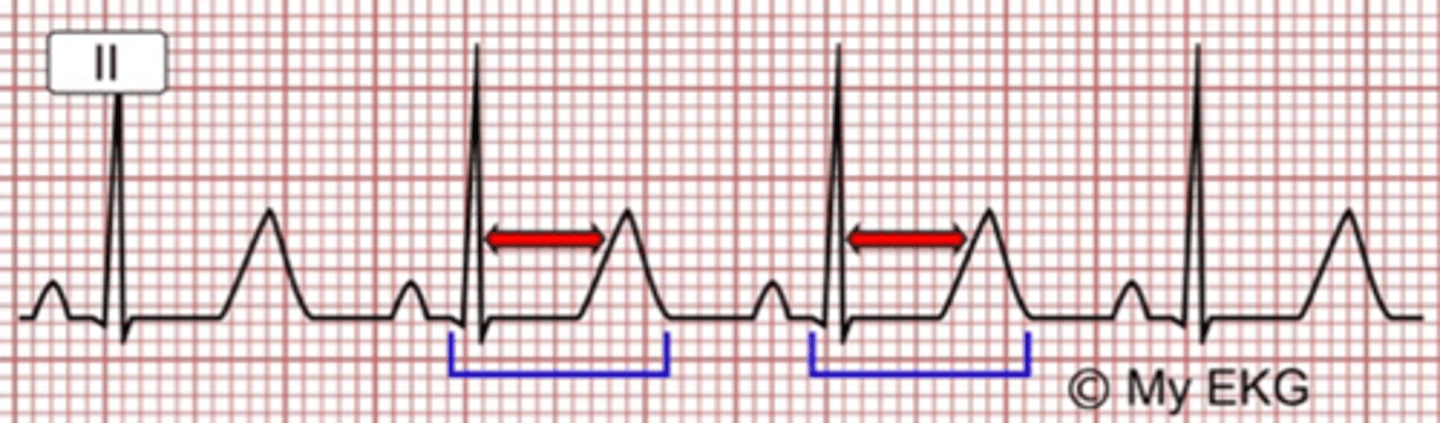
what might you see on EKG in pt with hypoparathyroidism?
prolonged QT interval and T wave abnormalities
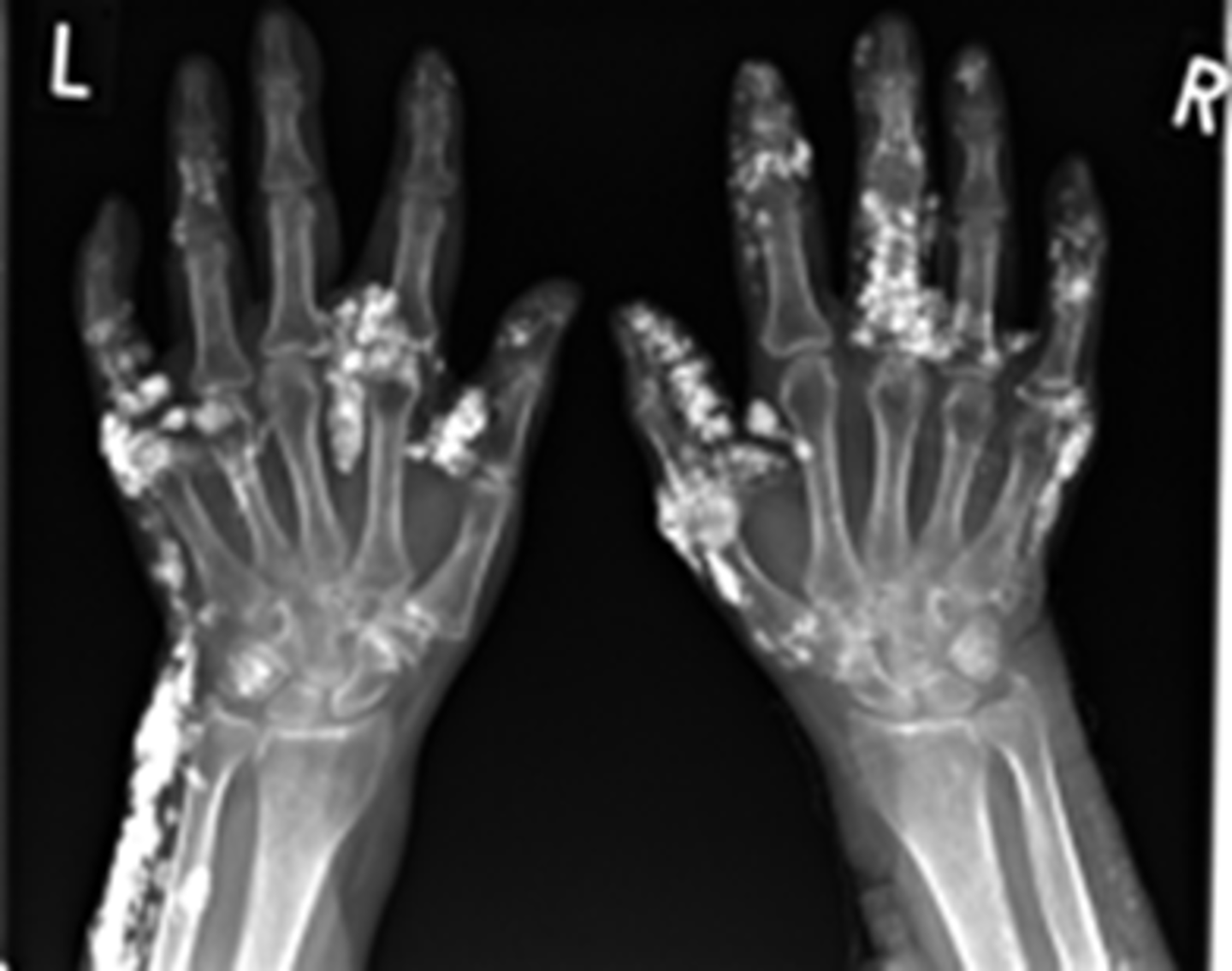
what might you see on XR in pts with hypoparathyroidism?
increased bone density
cutaneous calcifications
what are the essentials of hypoparathyroidism dx?
- tingling lips and hands
- psych changes
- positive Chvostek and Trousseau
- serum Ca and Mg low
what are the mainstays of tx for hypoparathyroidism?
calcium and vitamin D = lifelong tx
pt with primary hypoparathyroidism have a lifelong risk of ____________ ____________
symptomatic tetany
what is the tx for acute tetany?
1. airway management
2. IV calcium gluconate
3. mag sulfate IV
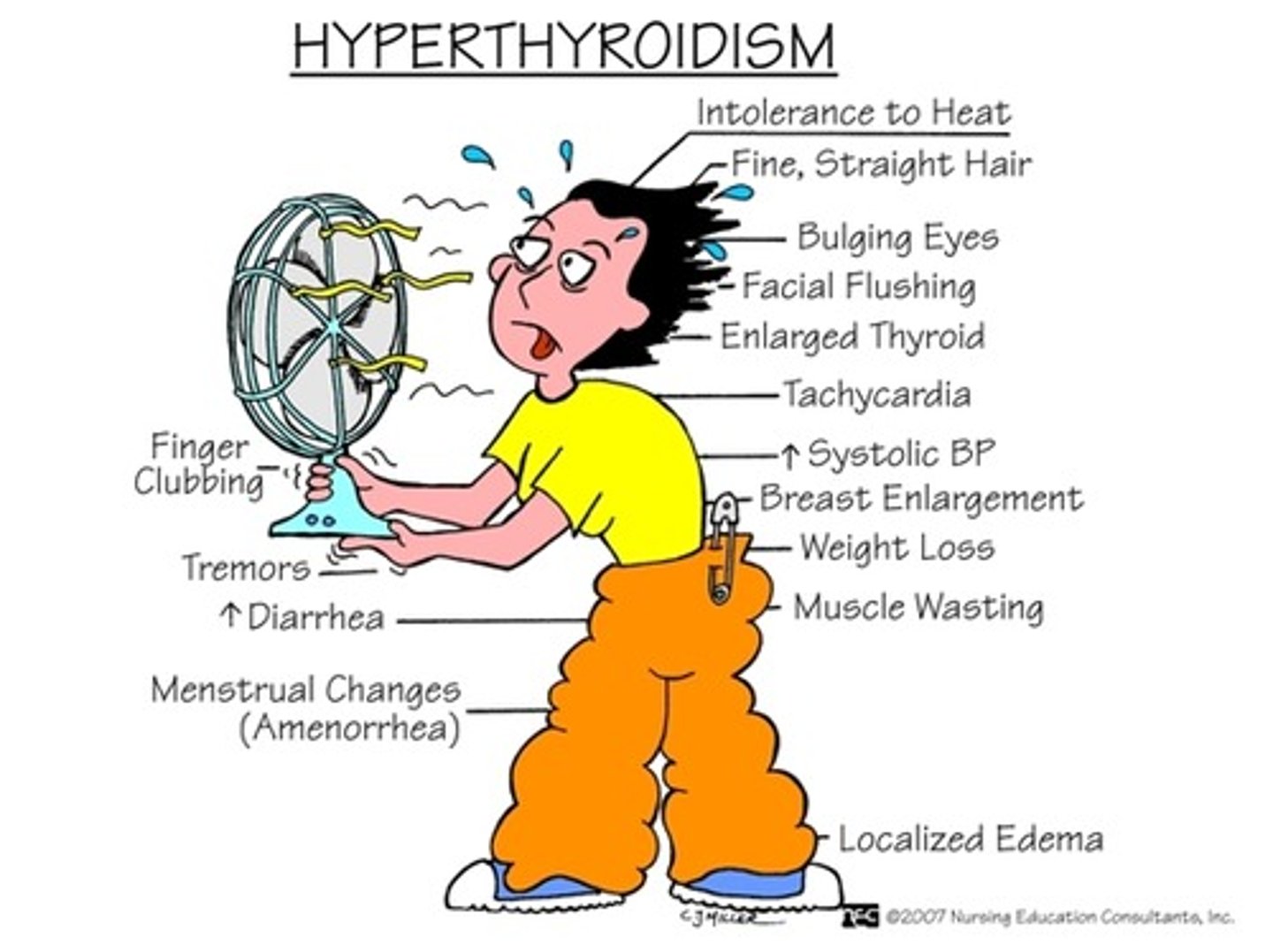
what are the labs for hyperthyroidism?
Low TSH, high T3 and T4
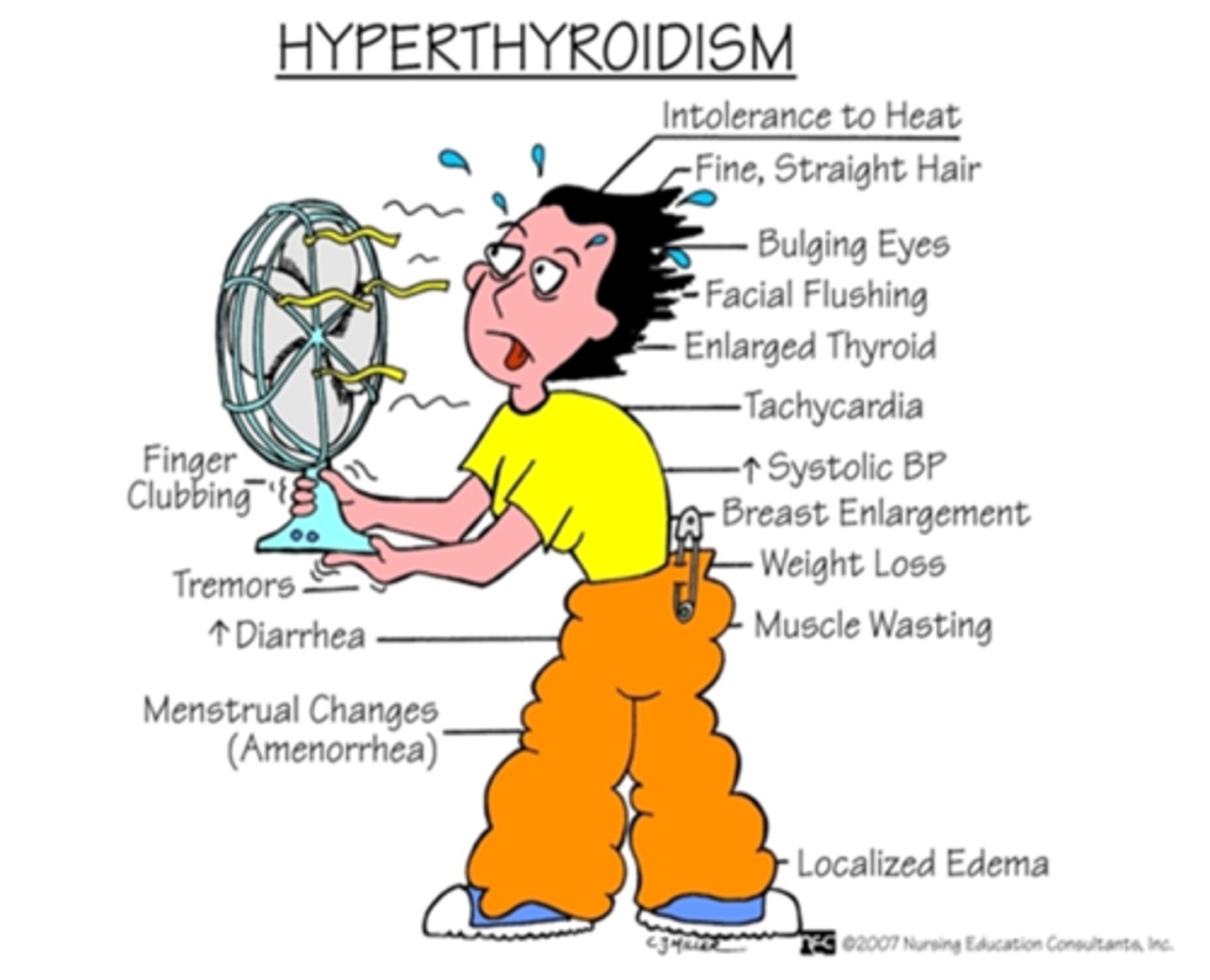
what are the s/sx of hyperthyroidism?
-heat intolerance
-weight loss
-anxiety
-menstrual irregularity
-tremor
-goiter
-exophthalmos
-warm most skin
-lid lag
TSH-R antibody increased indicates which dx?
grave's dz
TPO antibody and anti-thyroglobulin elevation indicates which dx?
hashimoto's dz
which EKG abnormality is common in elderly pts with hyperthyroidism?
a-fib
which drugs may alter thyroid labs?
- estrogen
- heparin
- amiodarone
- phenytoin
- rifampin
- salicylates
what is the tx for hyperthyroidism?
methimazole (DOC)
PTU
what is the drug of choice in 1st trimester of pregnancy for hyperthyroidism and thyroid storm?
PTU → inhibits conversion of T4 to T3
methimazole can be used in 2nd/3rd
what is the definitive tx for hyperthyroidism?
ablation of hyperactive thyroid
what is the MC cause of hyperthyroidism?
Grave's dz → autoimmune disorder of thyroid gland; attacks TSH receptors
TSH-R ab increased