PD E3 - Trauma
1/68
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
What is the first hour of trauma, from the time of injury until definitive care, in which a major portion occurs in prehospital transport & care?
Golden hour
What is the time you realistically have once the patient arrives inside the hospital, in which you perform thorough primary care& secondary survey, resuscitation & end with definitive care?
Platinum half hour
What is the first step of trauma assessment?
Ability to recognize acutely ill patient → breathing difficulties, clutching chest/ throat, slurred speech, confusion, LOC, sweating for no reason, uncharacteristic skin color
Which survey consists of 2 parts, CPR & VS assessment, to check for life threatening conditions and is performed in ≤ 30 s?
Primary survey
Which survey checks for conditions that COULD become life-threatening by rapid interview, rechecking vital signs, and a focused PE?
Secondary survey
What are the ABCDEs of primary survey?
Airway w/ C spine control
Breathing
Circulation w/ hemorrhage control
Disability: neuro status / deformity
Exposure / environment control
What should you assume when performing primary survey?
Patient is in cardiopulmonary arrest until proven otherwise
What are immediate life threatening injuries or conditions that must be treated immediately?
Inadequate airway protection, airway obstruction, tension / open PTX, flail chest w/ hypoxia, massive hemothorax, cardiac tamponade, severe hypothermia, severe shock from hemorrhage unresponsive to fluid resuscitation
What conditions should you exclude first or rapidly correct when assessing breathing?
Tension / open PTX, flail chest, massive hemothorax
How should you evaluate cardiac function in adults?
Carotid pulse
How should you evaluate cardiac function in infants?
Palpate precordium
How do you assess blood volume and cardiac output?
LOC, skin color, pulse
What should you do for bleeding control?
Direct pressure, pressure point, elevation, tourniquet
What are signs of circulatory compromise?
Distended or collapsed neck veins, chest wall or cervical wounds with external or possible internal bleeding, abrasions, contusions, deformities, lacerations
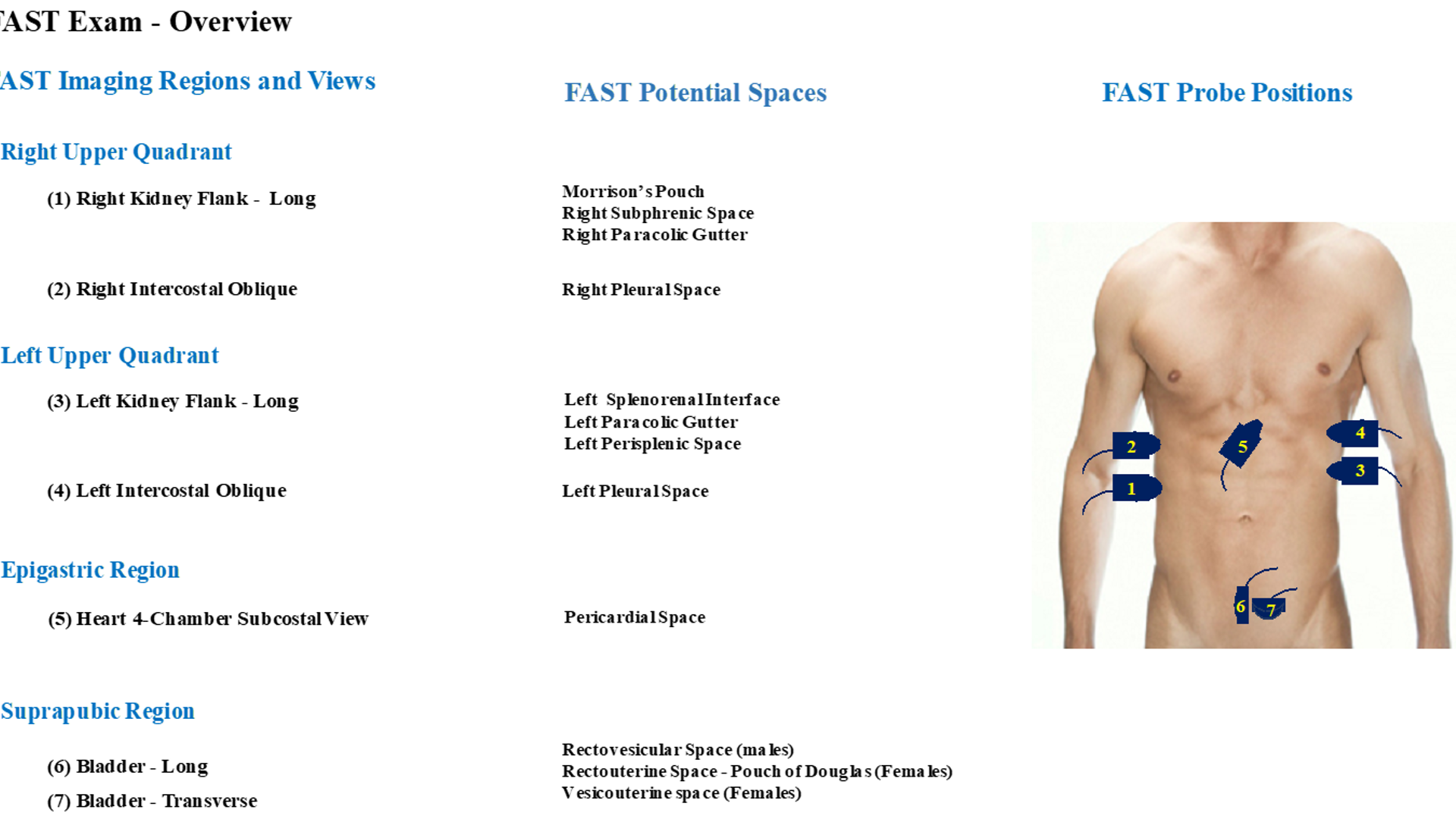
What is a FAST exam?
Focused assessment sonography in trauma
In the management of shock, what should you assume when in doubt?
Hypovolemia (but consider other causes)
When is recombinant factor VIIa used in the treatment of bleeding?
All other measures have failed; stops blood loss, reduces blood requirement & improves clotting parameters
What quick neuro assessment should be done?
*AVPU
Alert
Verbal response
Pain response
Unresponsive
In the Glasgow coma scale (GCS), what is the most accurate predictor of future outcomes?
Initial “post resuscitation” score (primary concern is if pt can maintain airway)
*≤ 8 at 6 hrs → 50% will die
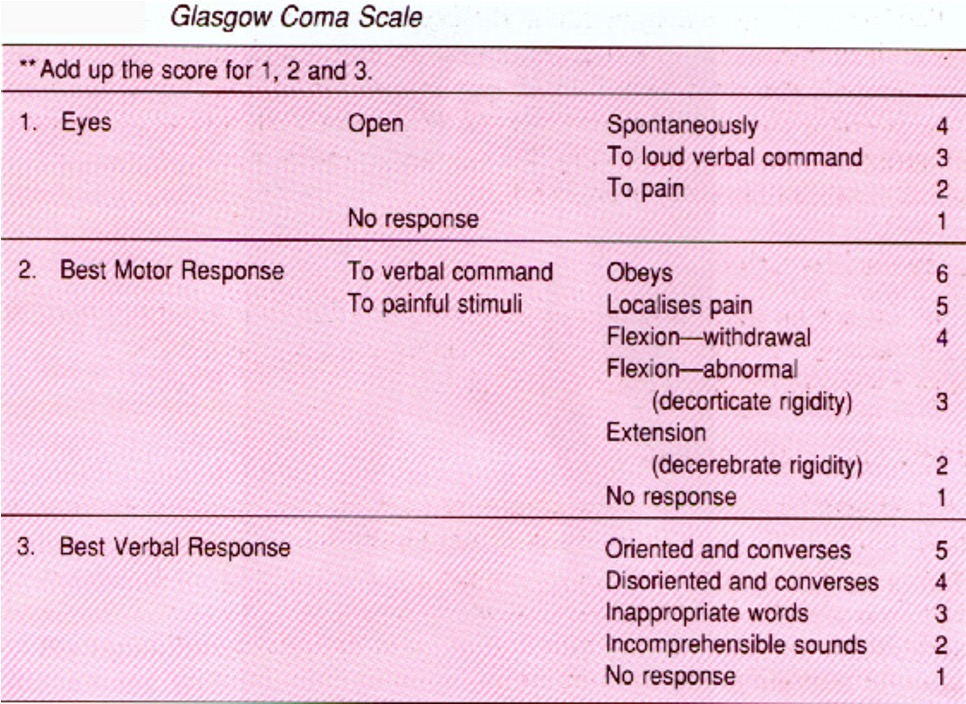
What are the scores for the eye category on GCS?
4 pts: open spontaneously
3 pts: open to loud verbal command
2 pts: open to pain
1 pt: no response
What are the scores for the best motor response category on GCS?
6 pts: obeys verbal command
5 pts: localizes to pain
4 pts: flexion - withdrawal to pain
3 pts: flexion - abnormal to pain (decorticate)
2 pts; extension to pain (decerebrate)
1 pt: no response
What are the scores the best verbal response category on GCS?
5 pts: oriented and converses
4 pts: disoriented and converses
3 pts: inappropriate words
2 pts: incomprehensible sounds
1 pt: no response
What is a mild GCS score?
13-15
What is a moderate GCS score?
9-12
What is a severe GCS score?
3-8
*less than 8 → intubate
What are 2 important time saving observations in the vital functions assessment?
Check CNS functioning & if skin warm, dry, and normal in color
What should all patients with head or maxillofacial trauma be presumed to have until positively excluded?
C spine injury
What history components are evaluated in the secondary survey?
*AMPLE
Allergies
Meds
PMHx
Last meal
Environment / events preceding the event
*mechanism of injury is critical & EMS are your eyes on seen
When should you have a high index of underlying injury?
Contusion, hematoma, or lacerations noted
When is included on the PE in the secondary survey?
3 main regions: head & neck, torso, extremities
All bones & joints → deformity, open injuries, tenderness, swelling (DOTS)
Screening neuro exam & rectal exam
What should you think if patient reports numbness, weakness or tingling of UE with a neck injury?
C spine injury
What is the MOA of a Jefferson Burts fracture of the atlas?
Axial loading → blow to top of head
What is the MOA of a hangman’s fracture (traumatic spondylolisthesis)?
Anterior displacement of C2 on C3 d/t severe hyperextension (judicial hangings, MVA)
What is the MOA of clay-shovelers fracture?
Flexion
What is the MOA of flexion teardrop fracture?
Flexion
How does a hemothorax sound to percussion?
Dull
How does a tension PTX sound on percussion?
Hyper resonant
What is an open wound that allows air to be sucked in the chest with inspiration?
Sucking chest wound
What is bruising of the cardiac muscle?
*any chest pain following blunt trauma should get an EKG
Myocardial contusion

What condition consists of ≥3 rib fractures in atleast 2 different places that causes the chest wall to become unstable?
Flail chest
What is bruising to the lung?
Pulmonary contusion
What is a collection of blood in the pleural space that usually occurs from bleeding from the major central chest vessels or occasionally an intercostal artery?
Hemothorax
What is an accumulation of air in the pleural space?
PTX
What is increased pressure in the pleural space?
Tension PTX
What is a penetrating injury of the heart that increases pressure on the pericardial space?
Cardiac tamponade
How soon do 90% of patients with an aortic rupture die?
10 minutes
What are causes of blunt abdominal trauma?
MVA- automobile vs pedestrian, falls, industrial or recreational accidents
Which is 5x MC- blunt or penetrating trauma?
Blunt
What are the MC organs injured with blunt trauma?
Liver > spleen
*constantly changes but for his exam the answer is liver
What are the MC organs injured with penetrating trauma?
Small bowl > large bowel > liver
What is the MC injured isolated system in children?
CNS → MCC ≤ 2 is abuse, MCC ≥3 are falls, motor vehicle, bicycle, and pedestrian accidents
What is a better indicator than BP of impending circulatory collapse in children?
*hypotension doesn’t occur until child loses 25-30% BV
HR
What are the scores for verbal category of GCS in children under 4?
5 pts: appropriate words, social smile, fixes & follows
4 pts: cries but consolable
3 pts: persistently irritable
2 pts: restless, agitate
1 pt: none
What are hallmarks of respiratory distress?
Tachypnea, nasal flaring, retractions, stridor, cyanosis, head bobbing, prolonged expiration, grunting
What are crush injuries commonly seen with?
Collapse of buildings in earthquakes, bombing, mine disasters, vehicle & train crashes
What type of injury is often associated with necrosis of muscles and in compartment syndrome where the edema of muscles is contained by the deep fascia?
Crush injuries
What presentation is associated with rhabdomyolysis?
Myalgia, weakness, darkened urine
causes: crush injury, electrical shock, 3rd degree burn, compression d/t prolonged immobilization, venom/snake bite
How is rhabdomyolysis diagnosed?
Definitive → elevated CK (>2-3x mild indicator, >100x normal is very likely)
UA: hemoglobin or myoglobin
What is the treatment for rhabdomyolysis?
Early & aggressive hydration, diuretics (mannitol or furosemide), sodium bicarbonate, renal dialysis if renal failure
What do severe burns require?
Exensive resuscitation first, fluid and blood replacement
What kind of burn?
area is reddened & blanches with pressures
no edema
painful to touch
Superficial / first degree
What kind of burn?
Dermis & epidermis affected
large thick walled blisters
underlying skin erythematous
Partial thickness / second degree
What kind of burn?
all of skin is destroyed
may have damage to SC tissue & muscle
dry appearance, may be white or charred
requires skin grafting
Full thickness / third degree
What kind of burn?
full thickness burn in which underlying structures (fascia, tendons, and bones) are severe damaged, usually blackened
Fourth degree
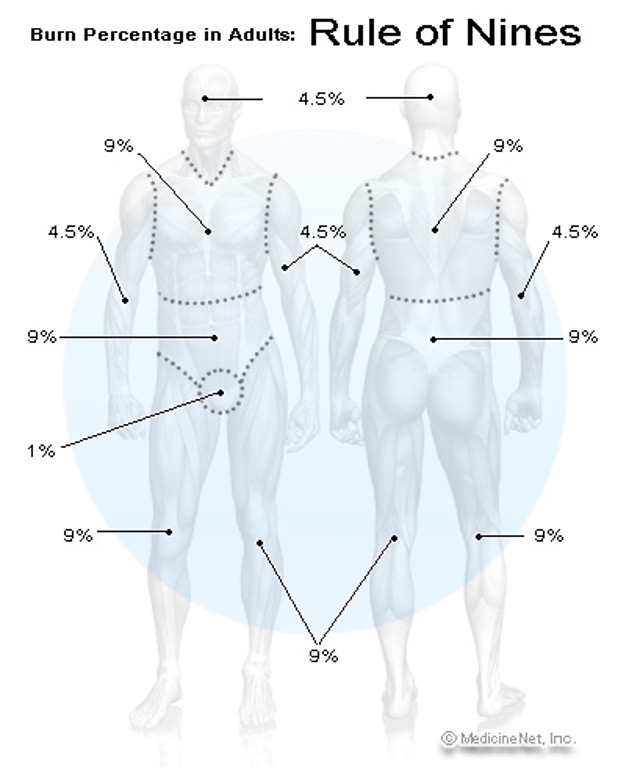
What is the rule of 9s for burns?
1%: each palm, groin
9%: head, front chest, front abdomen, each arm
18%: upper/ mid/ low back & buttocks, each leg (front & back)
What is the most accurate method for estimating burn extent and must be used in the evaluation of all pediatric patients?
Lund-browder chart
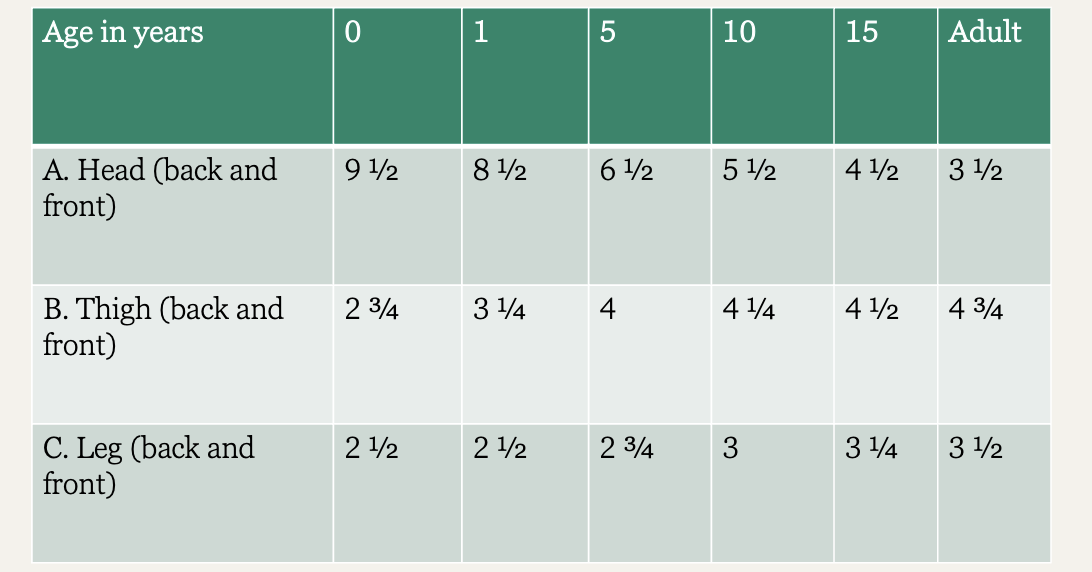
What is the treatment for burns?
Small area → immerse in room temp water to dec heat
Analgesics IV, IM, or SQ (PO not absorbed)
*respiratory status takes priority over treatment of burn
When should a patient be hospitalized for a burn?
Adults > 15%, children > 10%, associated complications, full thickness burns, smoke inhalation, deep burns of hands / face / perineum, circumferential burns of extremities which could cause vascular constriction
After resuscitation and blood transfusion, what should be done for hand trauma?
Every effort to safe thumb & at least 1 finger to allow for functional hand w/ adequate grip