Positive Psychology: Positive Cognitive States and Processes
Fixed vs Growth Mindset:
- Fixed Mindset: intelligence is ^^static^^
- Leads to a desire to look smart
- Growth Mindset: intelligence ^^can be developed^^
- Leads to a desire to learn
- Tyranny of Now: cheat on a test, run from difficulty, find someone who has it worse
- Discover the Power of Yet
- ^^Process^^ the error by learning deeply from it
- ^^Reward the use of effort, strategy and process^^ instead of results alone
- Every time students are pushed out of their comfort zones, neurons form stronger connections that can make one smarter, wiser.
- Basic human abilities can be cultivated and nurtured.
Mindfulness, Flow, and Spirituality: In Search of Optimal Experiences
Life Pursuits
- Intentional, moment-to-moment searches for optimal experiences give us joy and fulfillment.
- Mindless pursuit of less than meaningful goals or unchallenging ones leaves people bored and empty.
Many walk through life unaware of the significance of our lives and its relation to our experiences and emotional selves.
Daniel Kahnenman
- There are about 20,000 moments in 3 seconds in a 16-hour day, so this is what life consists of a sequence of moments.
- Each moment is very rich in experience. There is a goal, a mental content, a physical state and even an emotional arousal.
- Many things are happening.
- And then you can ask, “What happens to these moments?”
Mindfulness
- State of active, open attention to the present. This state is described as observing one’s thoughts and feelings without judgment.
- Awareness + Acceptance
- Flexible state of mind
- Here and now
- Context and perspective
- Active search for novelty > mindlessness involves zoning out to everyday life.
This requires us to
- Overcome mind wandering to reduce uncertainty in everyday life
- Override the tendency to engage in automatic behavior
- Engage less frequently in evaluations of self, others and situations.
Openness to novelty and sensitivity to context and perspective.
Cultivating awareness of everyday happenings and physiological and psychological sensations.
Qualities
- Non judging
- Non striving
- Acceptance
- Patience
- Trust
- Openness
- Letting go
- Gentleness
- Generosity
- Empathy
- Gratitude
- Loving
- Kindness
Living with Mindfulness
- Being mindful of emotions
- Being mindful of eating
- Mindful stretching exercises
- Mindful breathing and sitting
Benefits of Mindfulness
- Successful treatment of chronic pain and anxiety
- Stress-reduction
- Affiliative trust towards others (mindful parenting)
- Change in perspectives and outlook
- Increased cultural sensitivity
Mindful Brain and Rejection
- Part of the human experience is being rejected
- Mindful individuals report less distress during reaction because they don’t attempt to suppress the experience in the first place
- Mindfully accepting, rather than suppressing goes a long way towards healing from social injuries.
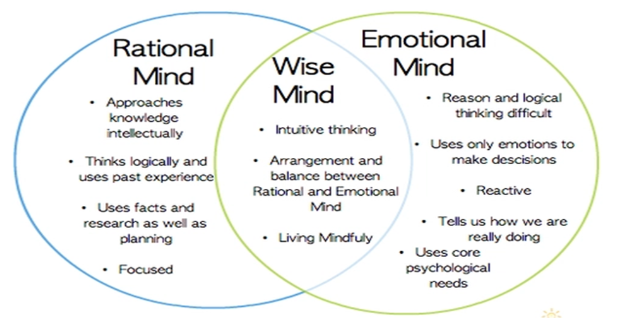

Flow and Mindfulness
Mindfulness and flow involve deep concentration, flow involves goal-directed behavior
Mindfulness channels concentration toward the present moment, flow channels concentration toward skill and goal achievement which includes past and future and assessment of these thoughts
Flow
- A person can make himself happy or miserable, regardless of what is actually happening outside just by changing the content of consciousness
- State which a person involved perceived that nothing else matters
- ^^Intense concentration^^, no attention for problems or anything else
- Where one loses oneself in the process, time gets distorted
- ^^“Can do” attitude^^
- Happiness is something that individuals can conjure themselves
- Happiness was a function of our degree of engagement with whatever we choose to do
- Start doing more of what you love
- ^^Optimal state of engagement^^
- A person perceives challenges to action as neither underutilizing nor overwhelming his or her existing skills.
- Has clear attainable goals and immediate feedback about progress
Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi
- Intrigued by the stories about artists who “^^lost themselves in their work^^”
- Similar activities that causes this single-mindedness state
- State of “full-capacity” living that is believed to be directly linked to optimal development and functioning.
Finding your Flow
- Why do people pursue particular goals with great fervor in the absence of rewards?
- Conditions of flow appear remarkably similar across work settings, play settings and cultures, which include:
- Perceived challenges and opportunities for actions that stretch
- Clear proximal goals and immediate feedback about progress.
What happens during flow?
- Intense and focused concentration on what one is doing at the present moment
- Merging of action and happiness
- Loss of reflective self-consciousness
- A sense that one can control one’s actions.
- Time has passed faster than normal
- Experience that activity as intrinsically rewarding, end goal just an excuse for the process.
Benefits of Flow
- Mastery of skills
- Flow in workspaces
- Optimal experiences
- Flow influencing the environment and the individual
- Work becomes “serious play”
Autotelic Personality
- Cluster of traits exhibited by a person who enjoys life and generally does things for his/her own sake rather than in order to achieve something later.
Concept of Flow
- Optimal experiences and its role in development
- Focus, attention and the self
- Flow, complexity and development
- Measuring Flow and Autotelic Personality
- Consequences of Flow
- Nature and Dynamics of Flow
- Obstacles and Facilitators of Flow
- Autotelic Families
- Interventions and Programs to Foster Flow
Spirituality: In Search of the Sacred
- Thoughts, feelings and behaviors that fuel and arise from the search for the Sacred.
- Spiritual strivings, which include personal goals associated with the ultimate concerns of purpose, ethics and recognition of the transcendent.
- Although specific content of spiritual beliefs varies, all cultures have a concept of an ultimate, transcendent, sacred and divine force.
- Belief in God
- Value of Prayer
- Religion
- Aid in human functioning
- Mental health
- Marriage and Family Life
- Stress and Grief