Chapter 6 - Motivation concepts
Defining motivation
- @@Motivation@@: processes that account for an individual’s intensity, direction and persistence and effort towards attaining a goal.
Early theories of motivation
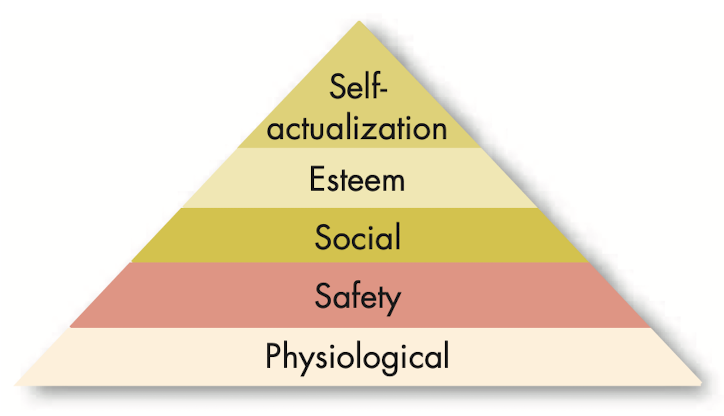
@@Hierarchy of needs theory@@: hierarchy of five needs - psychological, safety, social, esteem and self-actualization in which, as each need is substantially satisfied, the next need becomes dominant.
- Lower-order needs: needs satisfied extremely such as psychological and safety needs.
- Self-actualization: drive to become what a person is capable of becoming.
- Higher-order needs: needs satisfied internally such as social, esteem and self-actualization needs.
@@Theory X@@: assumption that employees dislike work, are lazy, dislike responsibility and must be coerced to perform.
@@Theory Y@@: assumption that employees like work, are creative, seek responsibility and can exercise self-direction.
@@Two-factor theory@@: theory that relates intrinsic factors to job satisfaction and associates extrinsic factors with dissatisfaction. Also called motivation-hygiene theory.
- Hygiene factors: factors such as company policy and administration, supervision and salary that when adequate in a job, placate workers. When these factors are adequate, people will not be dissatisfied.
@@McClelland’s theory of needs@@: theory which states that achievement, power and affiliation are three important needs that help explain motivation.
- Need for achievement (nAch): drive to excel, to achieve in relation to a set of standards. and to strive to succeed.
- Need for power (nPow): need to make others behave in a way in which they would not have behaved otherwise.
- Need for affiliation (nAff): desire for friendly and close interpersonal relationships.
Contemporary theories of motivation
@@Self-determination theory@@: theory of motivation that is concerned with the beneficial effects of intrinsic motivation and the harmful effects of extrinsic motivation.
- Cognitive evaluation theory: version of self-determination theory which holds that allocating extrinsic rewards for behavior that had been previously intrinsically rewarding tends to decrease the overall level of motivation if the rewards are seen as controlling.
- Self-concordance: degree to which peoples reasons for pursuing goals are consistent with their interests and core values.
- Job engagement: investment of employees physical, cognitive and emotional energies into job performance.
@@Goal-setting theory@@: theory which says that specific and difficult goals, with feedback, lead to higher performance.
- Promotion focus: self-regulation strategy that involves striving for goals through advancement and accomplishment.
- Prevention focus: self-regulation strategy that involves striving for goals by fulfilling duties and obligations.
- Management by objectives (MBO): program that encompasses specific goals, participatively set, for an explicit time period, with feedback on goal progress.
@@Self-efficacy theory@@: individual’s belief that he/she is capable of performing a task.
@@Reinforcement theory@@: theory that says that behavior is a function of its consequences.
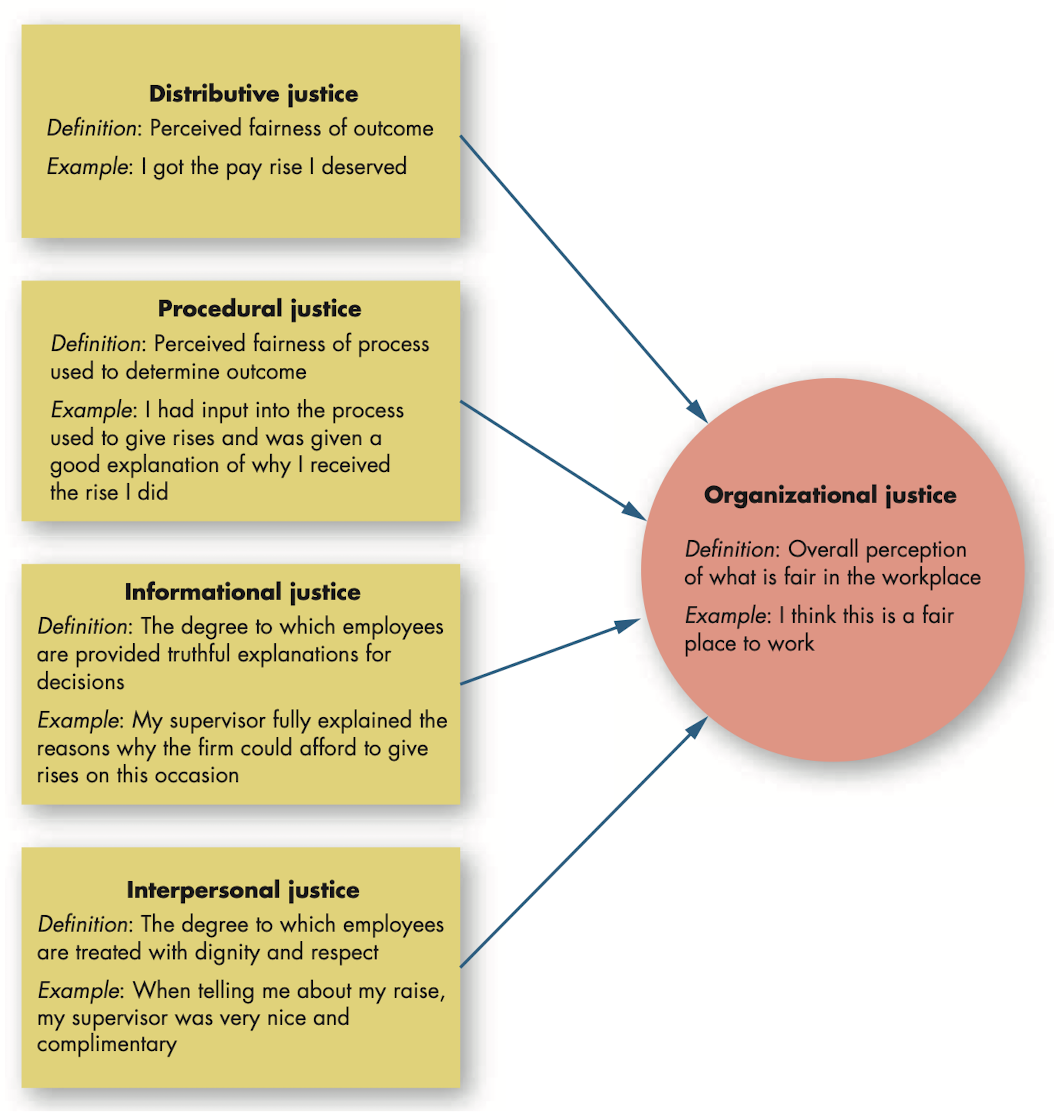
@@Equity theory/organizational justice@@: theory which says that individuals compare their job inputs and outcomes with those of others and then respond to eliminate any inequities.
- Organizational justice: overall perception of what is fair in the workplace, composed of distributive, procedural, informational and interpersonal justice.
- Distributive justice: perceived fairness of the amount and allocation of rewards among individuals.
- Procedural justice: perceived fairness of the process used to determine the distribution of rewards.
- Informational justice: degree to which employees are provided truthful explanations for decisions.
- Interpersonal justice: degree to which employees are treated with dignity and respect.
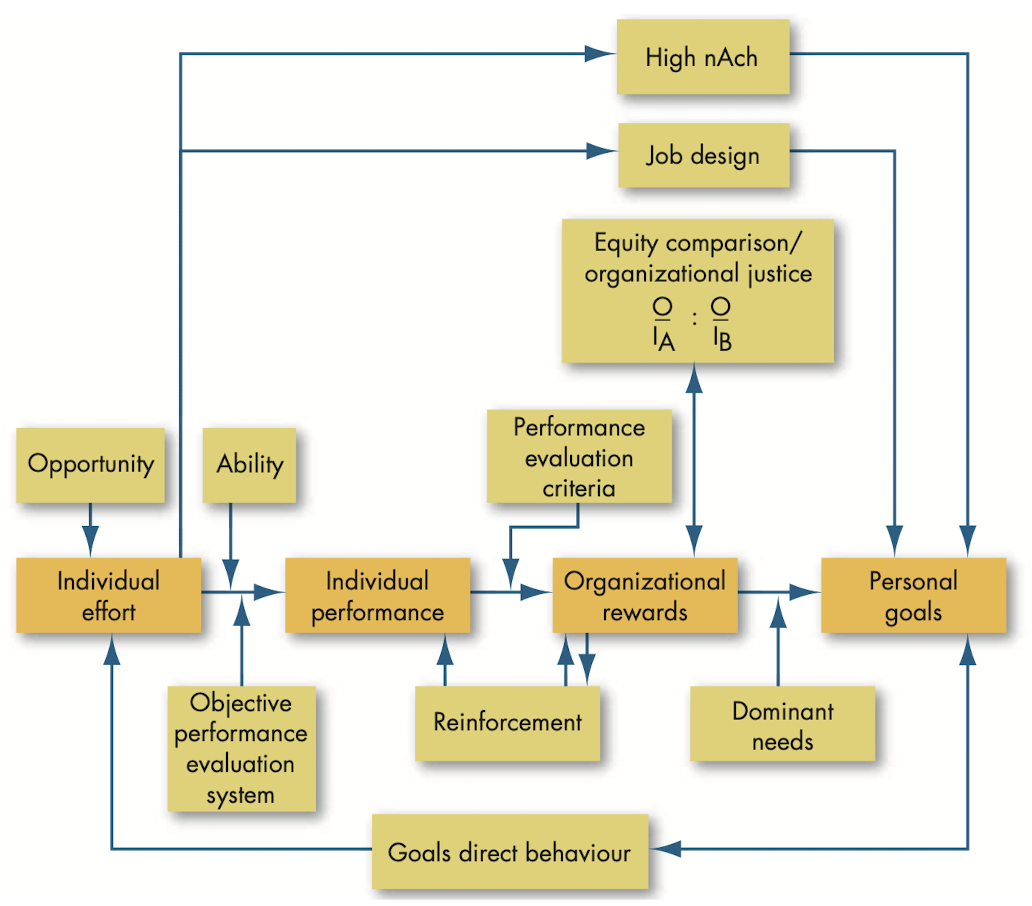
@@Expectancy theory@@: theory which says that the strength of a tendency to act in a certain way depends on the strength of an expectation that the act will be followed by a given outcome and on the attractiveness of that outcome to the individual.
- Effort-performance relationship: probability perceived by the individual that exerting a given amount of effort will lead to performance.
- Performance-reward relationship: degree to which individual believes that performing at a particular level will lead to the attainment of a desired outcome.
- Rewards-personal goals relationship: degree to which organizational rewards satisfy an individual’s personal goals or needs and the attractiveness of those potential rewards for the individual.
Integrating contemporary theories of motivation