Unit 4 - Imperfect Competition Guide
[[4.1 - Introduction to Imperfectly Competitive Markets[[
- Firms are able to make an increased profit in the long run if there is less competition since firms are considered to be price makers. There are stricter @@barriers to entry@@ in imperfect competition (Governmental, economies of scale, geography, and so on)
- Common barriers to entry: control of scarce resources, legal barriers, high startup costs
| Perfect Competition | Monopolistic Competition | Monopoly | Oligopoly | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| # of firms | Many | Many | 1 | Few |
| Type of product | Standard | Differentiated | Unique | Standard or different |
| Price control | None | Little | Yes | Some |
| Barriers to entry | None | None (few) | High | High |
[[4.2 - Monopolies[[
@@Monopoly@@: market structure where there is only one firm producing a product
- Only producer of a good, has no close substitutes
- On the graph, there is a downward sloping demand curve
Quantity is produced : at MR = MC
- Price is : MR=MC, up to demand
Supply curve : where MC > AVC
- Allocatively efficient due to them producing at MR=MC
- Productively inefficient because they don’t produce at the minimum of the ATC
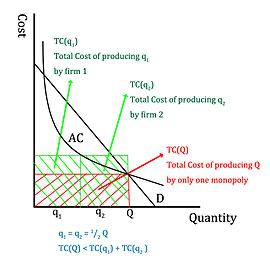
Natural monopoly: has large fixed costs, and long economies of scale, has downward sloping ATC curve
Natural monopoly production point : MR=MC
Government will correct by forcing them to set price : at ATC=D
[[4.3 - Price Discrimination[[
Price discrimination occurs in specific industries as consumers pay a different price for the same good.
- To be able to price discriminate, you need market power
Imperfect price discrimination : charging consumers different prices based on the buyer’s willingness to pay
Perfect price discrimination : charges all consumers the maximum they are willing to pay, no deadweight loss, produce at P=MC
Example : resellers, coupons, bulk buying (costco), etc.
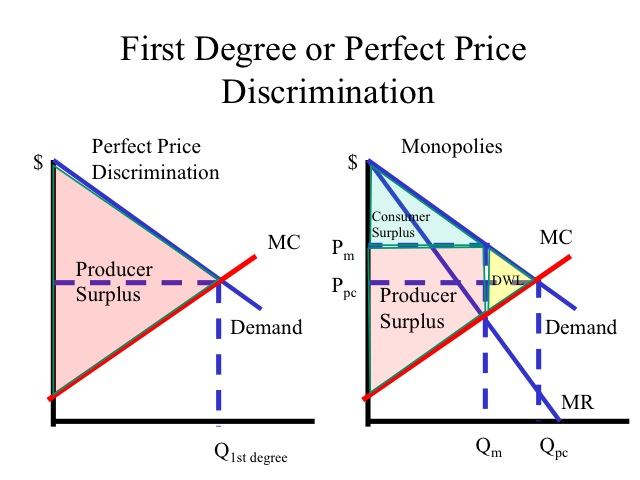
In price discrimination, there is no deadweight loss and no consumer surplus as well, only producer surplus.
[[4.4 - Monopolistic Competition[[
@@Monopolistic competition:@@ is another term for imperfect competition, and occurs when many companies offer competing products which are similar but not perfect substitutes.
Characteristics:
Combines features of both a monopoly and perfect competition
Many sellers and differentiated products
Will use advertising to make demand more inelastic + differentiate product
Makes profit in short run, normal profit in long run
Allocatively inefficient (P does not equal MC)
Productively inefficient (does not produce @ minimum of ATC, until long run)
Downwards sloping demand curve
Produce at MR = MC, price is MR = MC up to demand
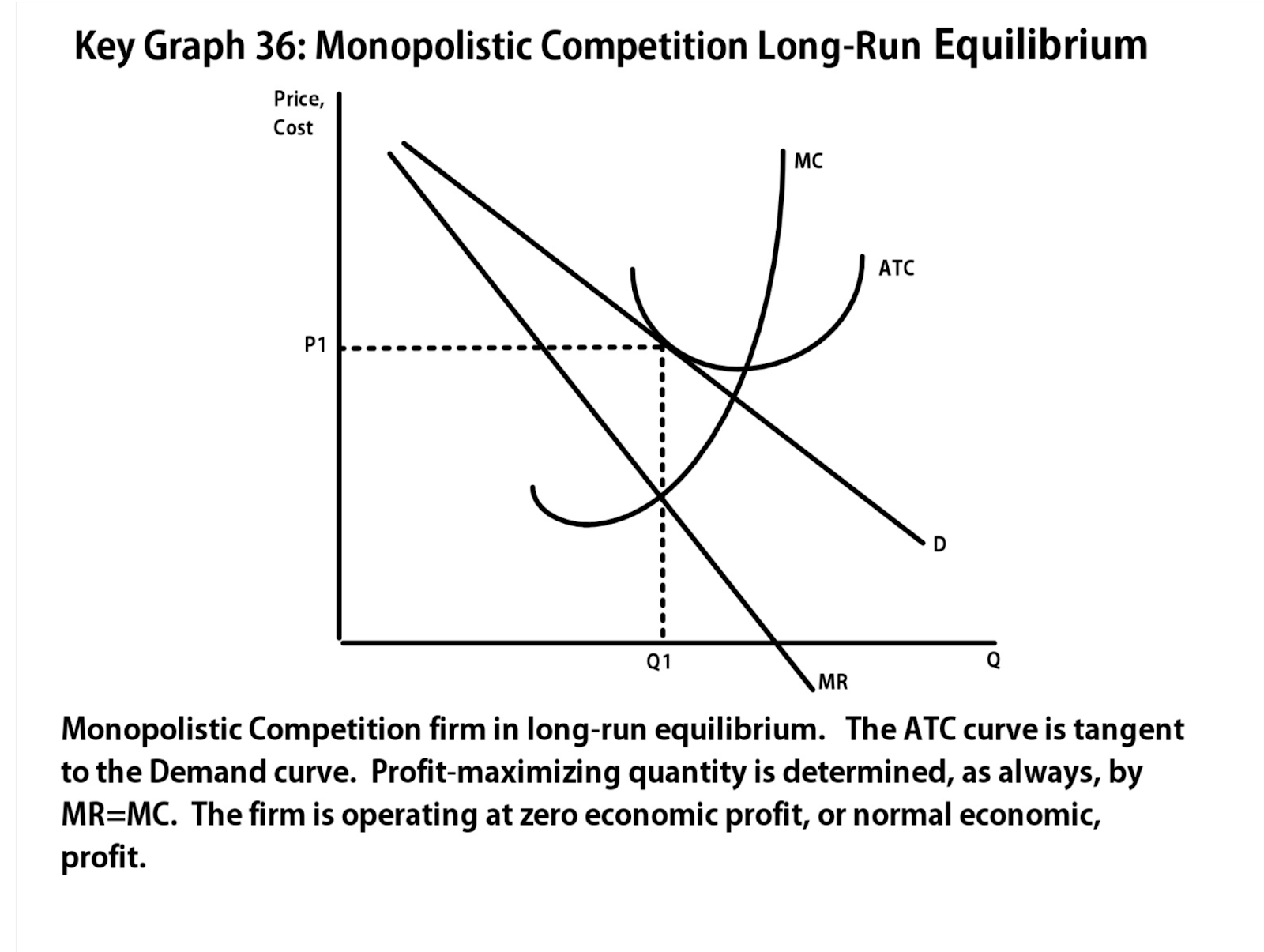
@@Long Run@@
Normal profit in long run
Short run profits will attract new firms to join, which decreases the demand until the demand Curve is tangent to ATC, causing normal profits in long run
In long run, they produce in region where economies of scales exist, because they produce in declining portion of ATC
[[4.5 - Oligopoly and Game theory[[
@@Oligopoly Characteristics@@
- Small number of firms, standard or differentiated product
- Interdependent : all the actions that a firm takes will affect the other firms in the oligopoly (if They ask why the market is an oligopoly, say it’s because they’re interdependent)
- Cartels : a group that agrees to control the price and output of a product (often form in oligopoly)
- Collusion : working together to maximize profit
- Graph is almost identical to monopoly (you will never be asked to draw them)
- Also produce same quantity and price of monopoly
@@Game Theory@@
- Payoff matrix : represents the payoff to each player to show combinations of given strategies
- Dominant strategy : the strategy that has a better payoff regardless of what strategy the opponent chooses
- Nash equilibrium : point where both players can do no better than the other given the choice of their opponent