Circuits Signals
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
EKG amplituede
10 uV to 5mV
EKG Frequency
0.05Hz to 150Hz, generally 100Hz so sample at 200Hz
EEG Amplitude
10 to 200 uV (microvolts)
EEG frequency
0.5-30Hz, so sample at around 60
EMG amplitude
0 to 10mV
EMG frequency
0-500Hz for surface (sample at 1000Hz)
0-1000Hz for indwelling
Nerve potentials amplitude
50 to 100mV
Nerve potentials frequency
0.05-500Hz
Analog
A continuous electrical or physical signal that varies over time where its value can be any point within a range
Digital
A signal of discrete values taken at fixed timed points
Frequency content analog
Different frequencies and their corresponding amplitudes that make up the analog signal
Bandwidth
Analog signal’s total range of frequencies
Background electrical frequency
50Hz for Europe, 60Hz for US
Nyquist theorem
To reconstruct a continuous signal from its sampled digital form, sampling rate must be at least twice the highest frequency component of the original signal.
Aliasing
A distortion that occurs when an analog signal is sampled at too low of a rate
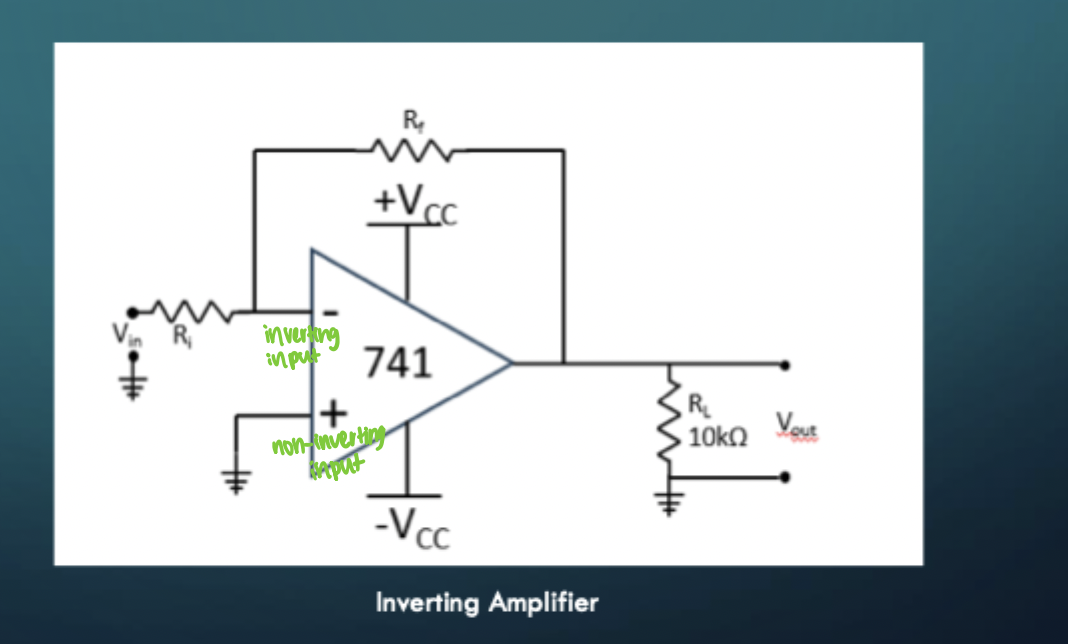
Inverting Amp
A = -Rf/Ri
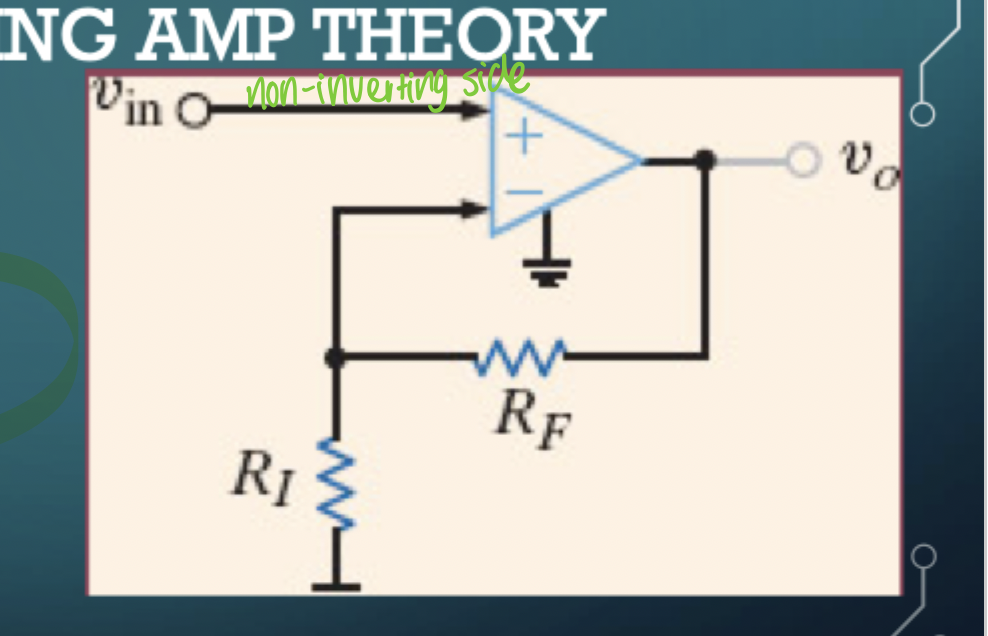
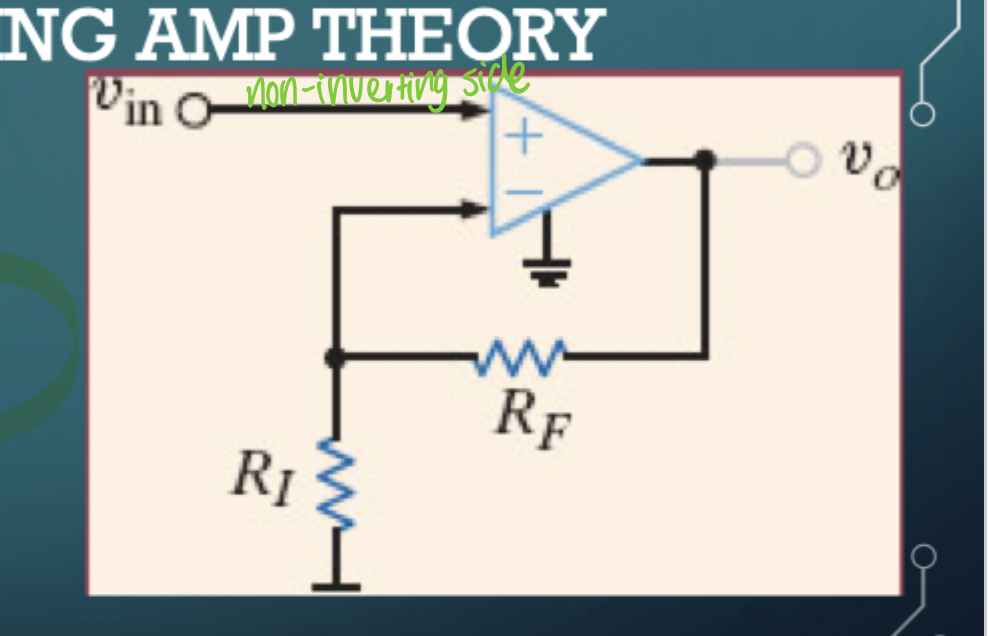
Non-inverting amp
A = 1 + Rf/Ri
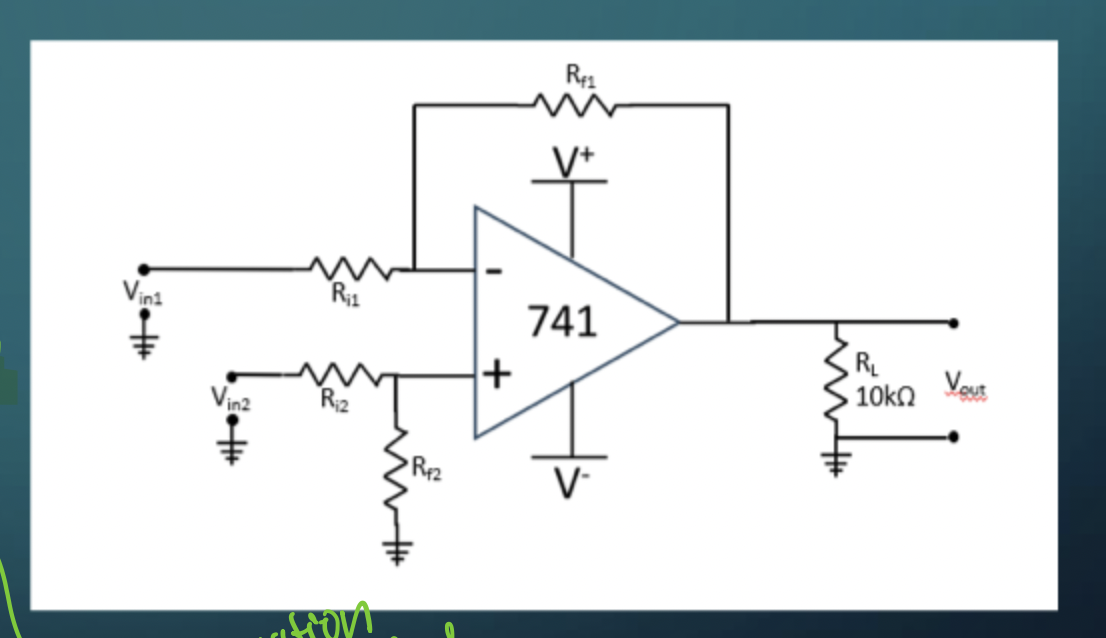
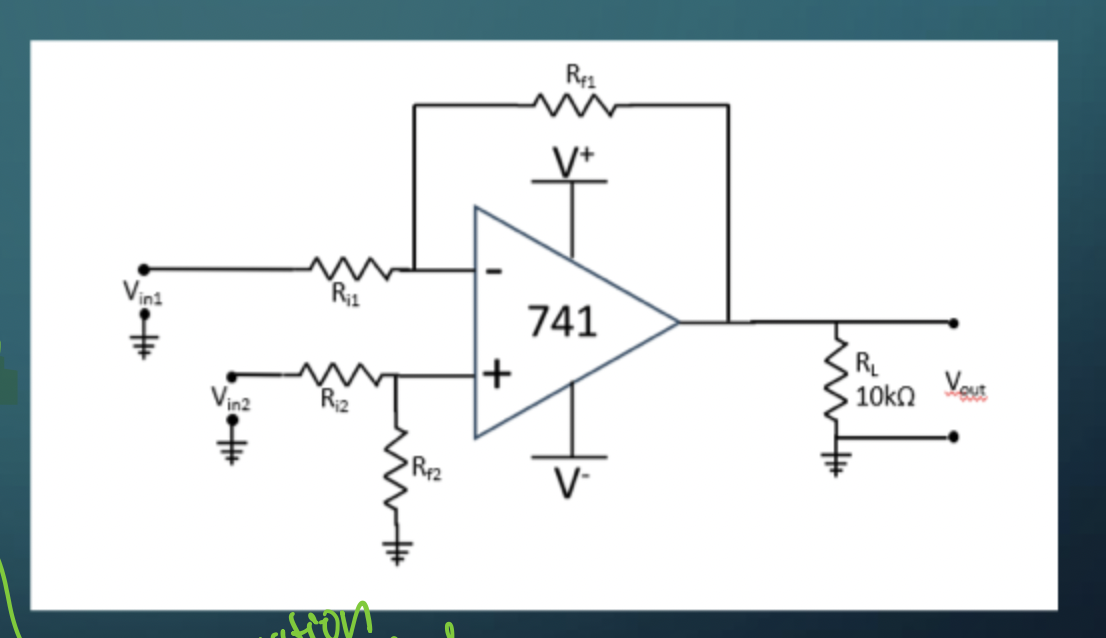
Differential Amplifier
Vout = (Rf/Ri) (Vin2 - Vin1)