A and P: Mink Dissection Practical
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
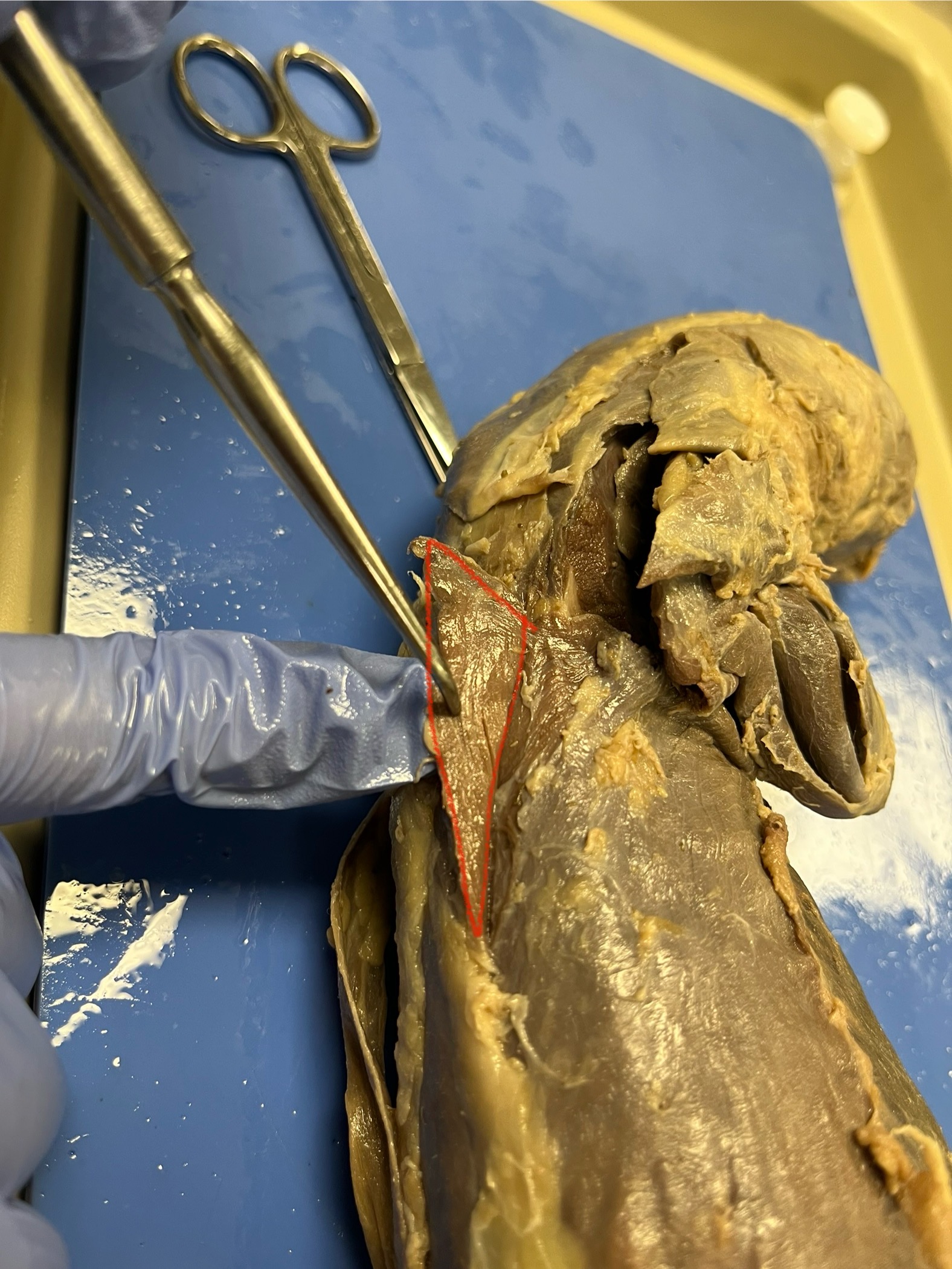
Spinotrapezius
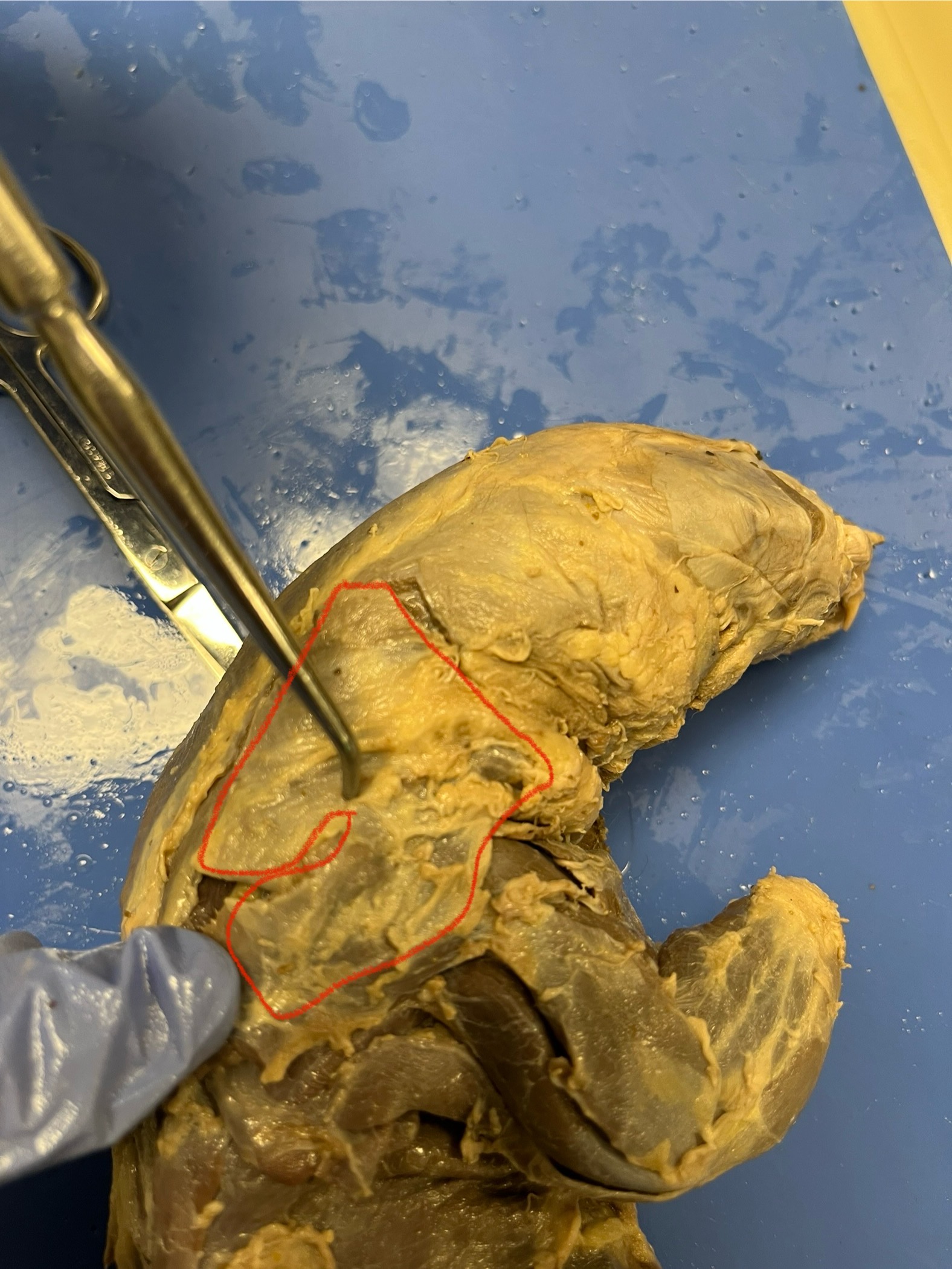
Acromiotrapezius
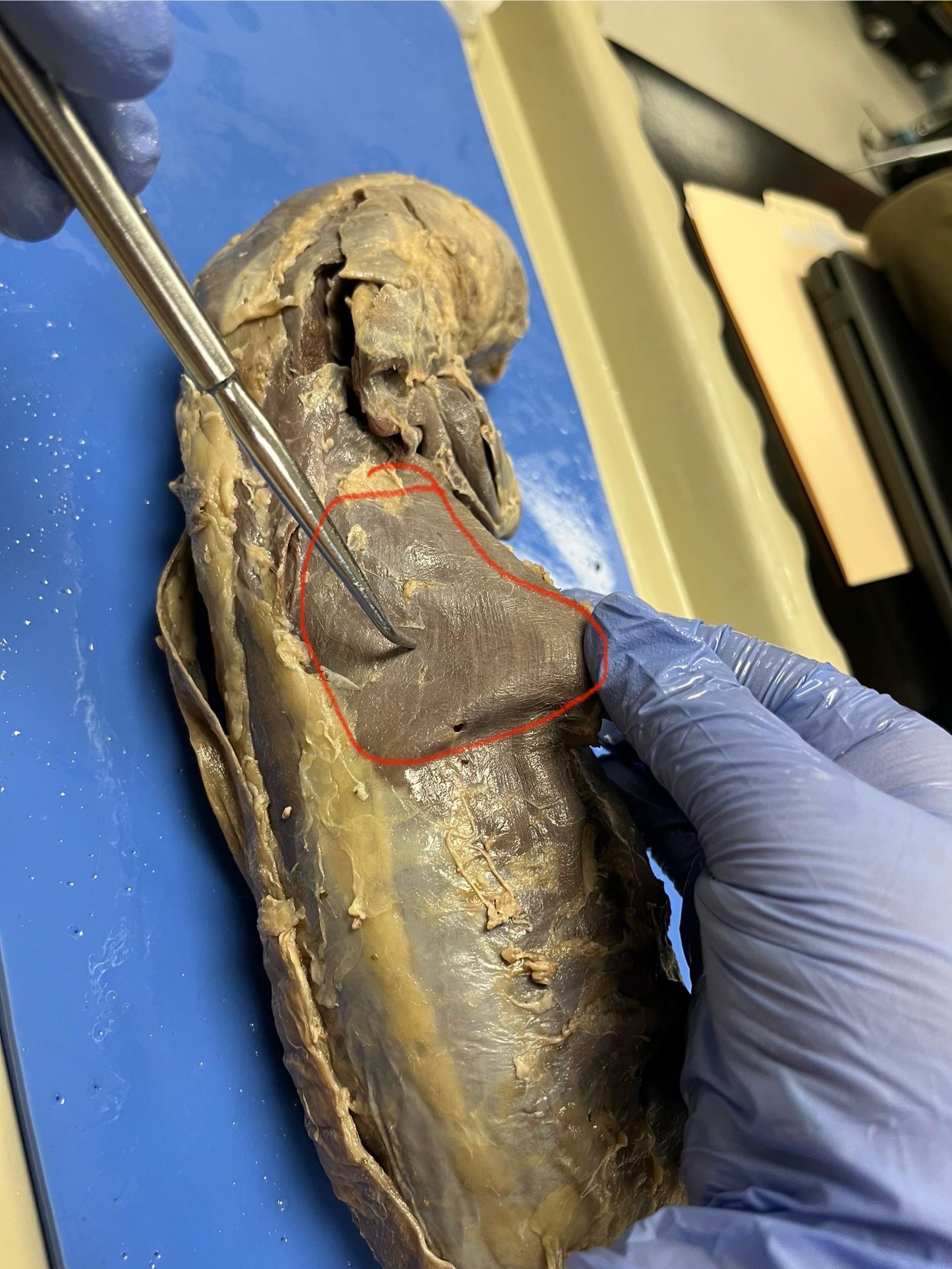
Latissimus Dorsi
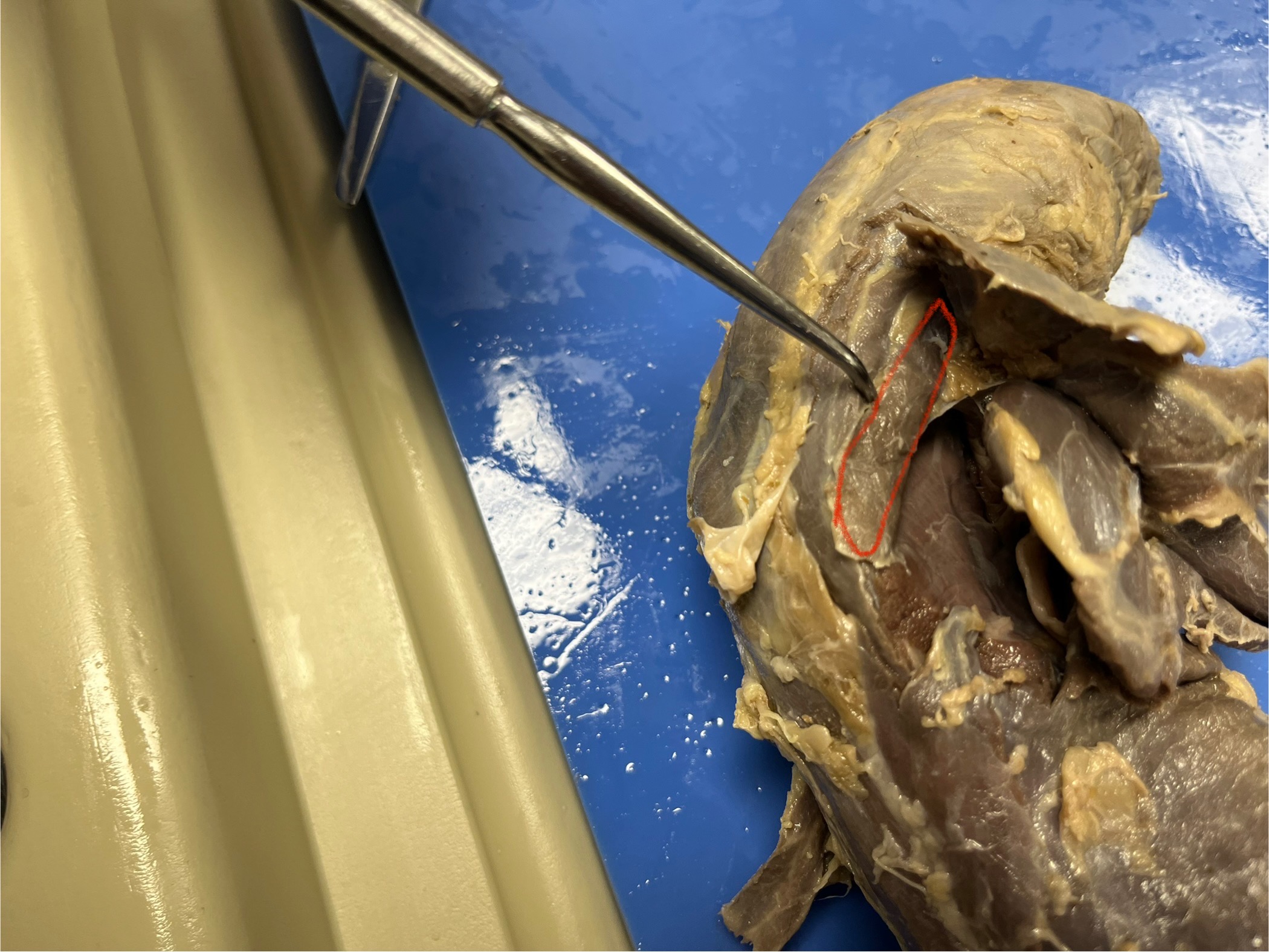
Rhomboideus
Infraspinatus
Supraspinatus
Teres Major
Pectoralis Minor
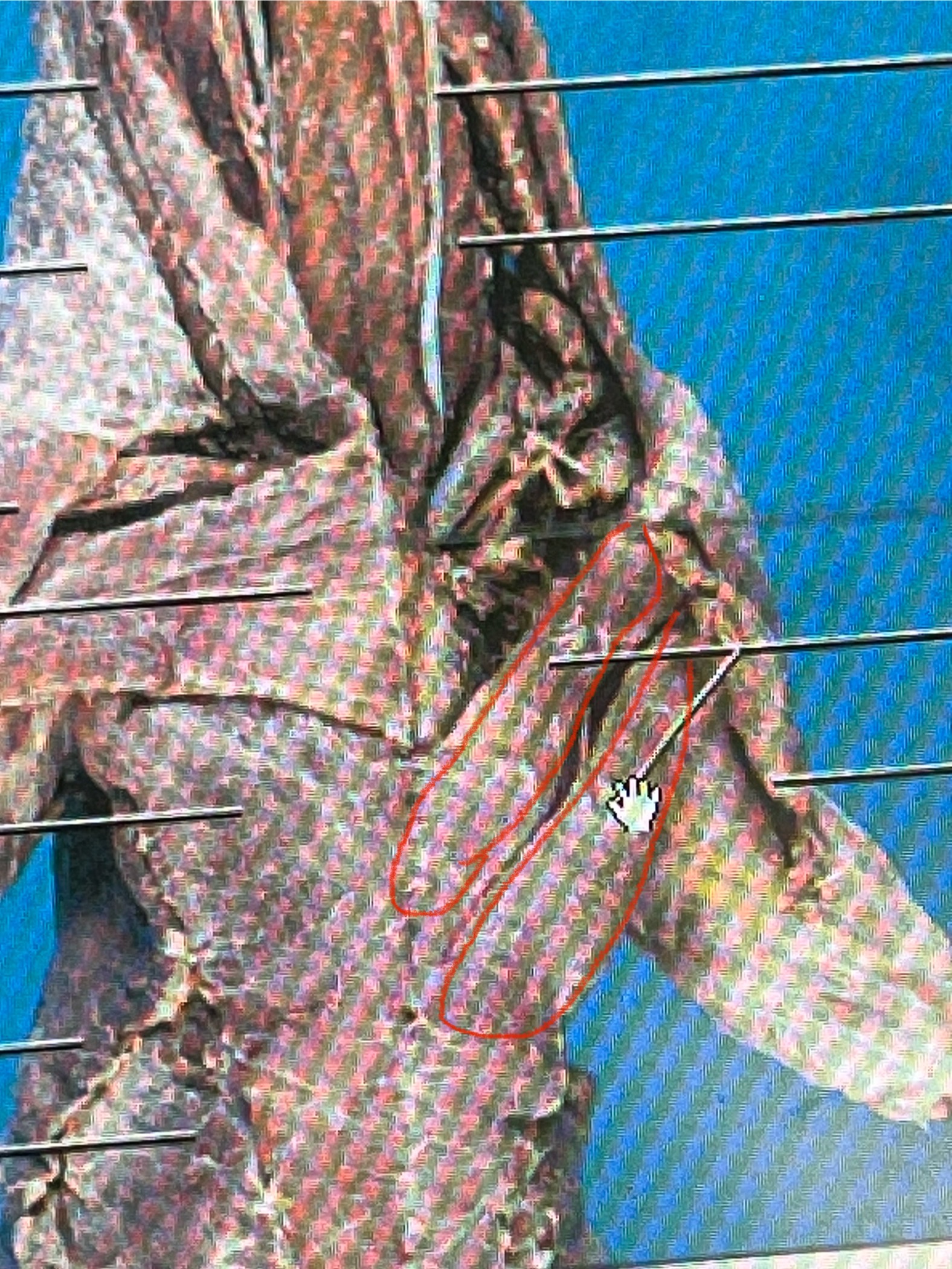
Pectoralis Major

External Obliques
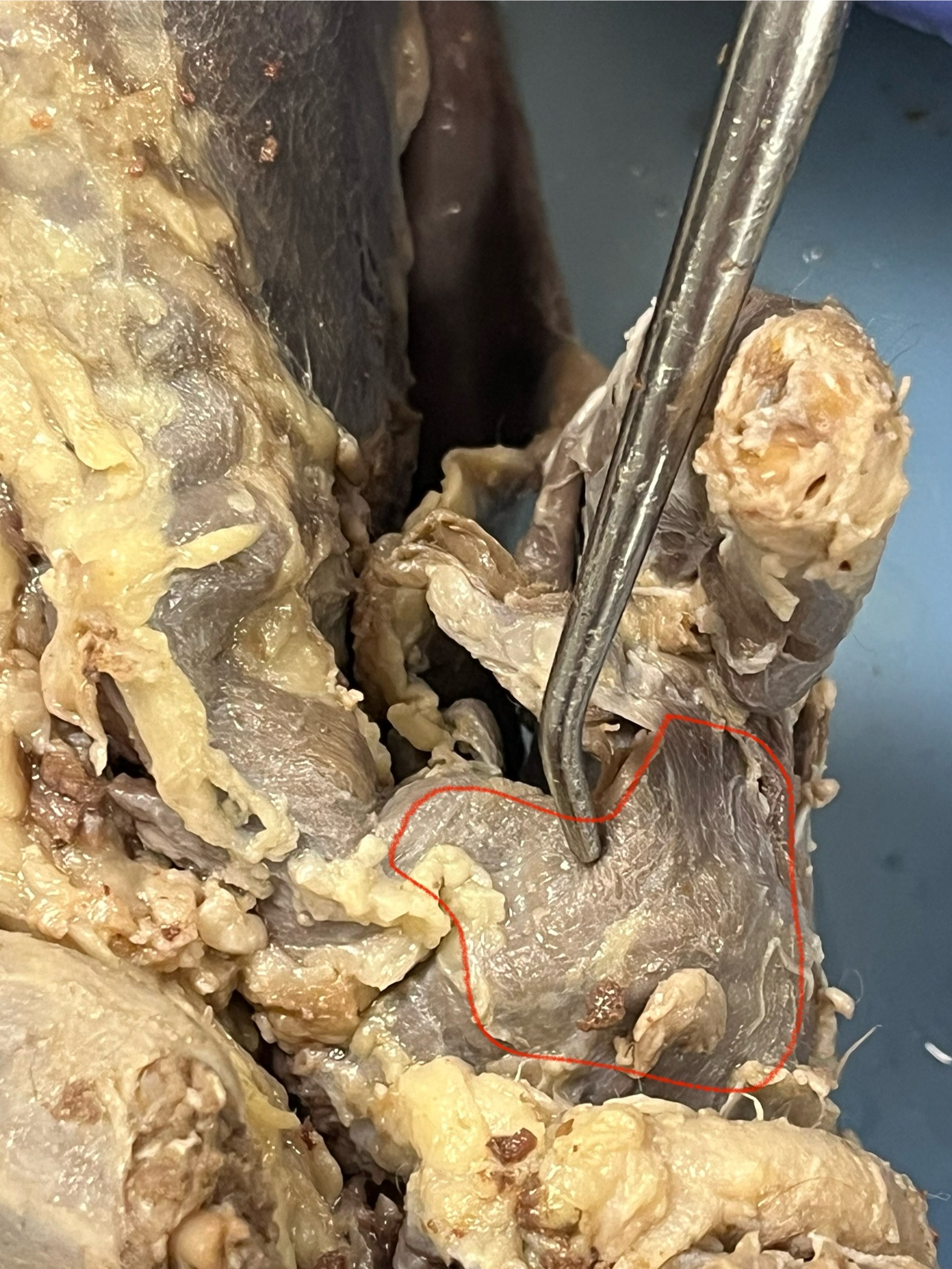
Internal Obliques
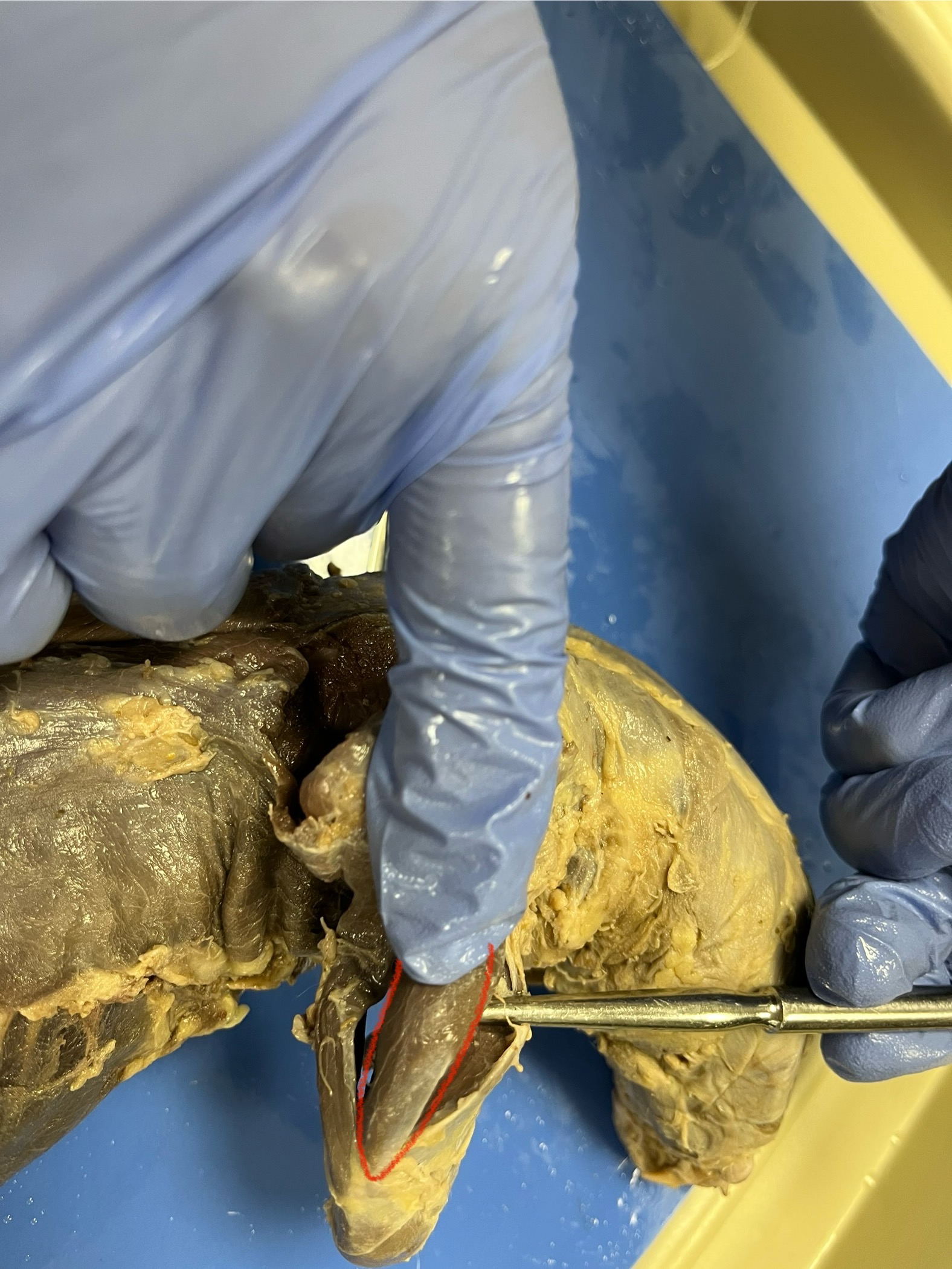
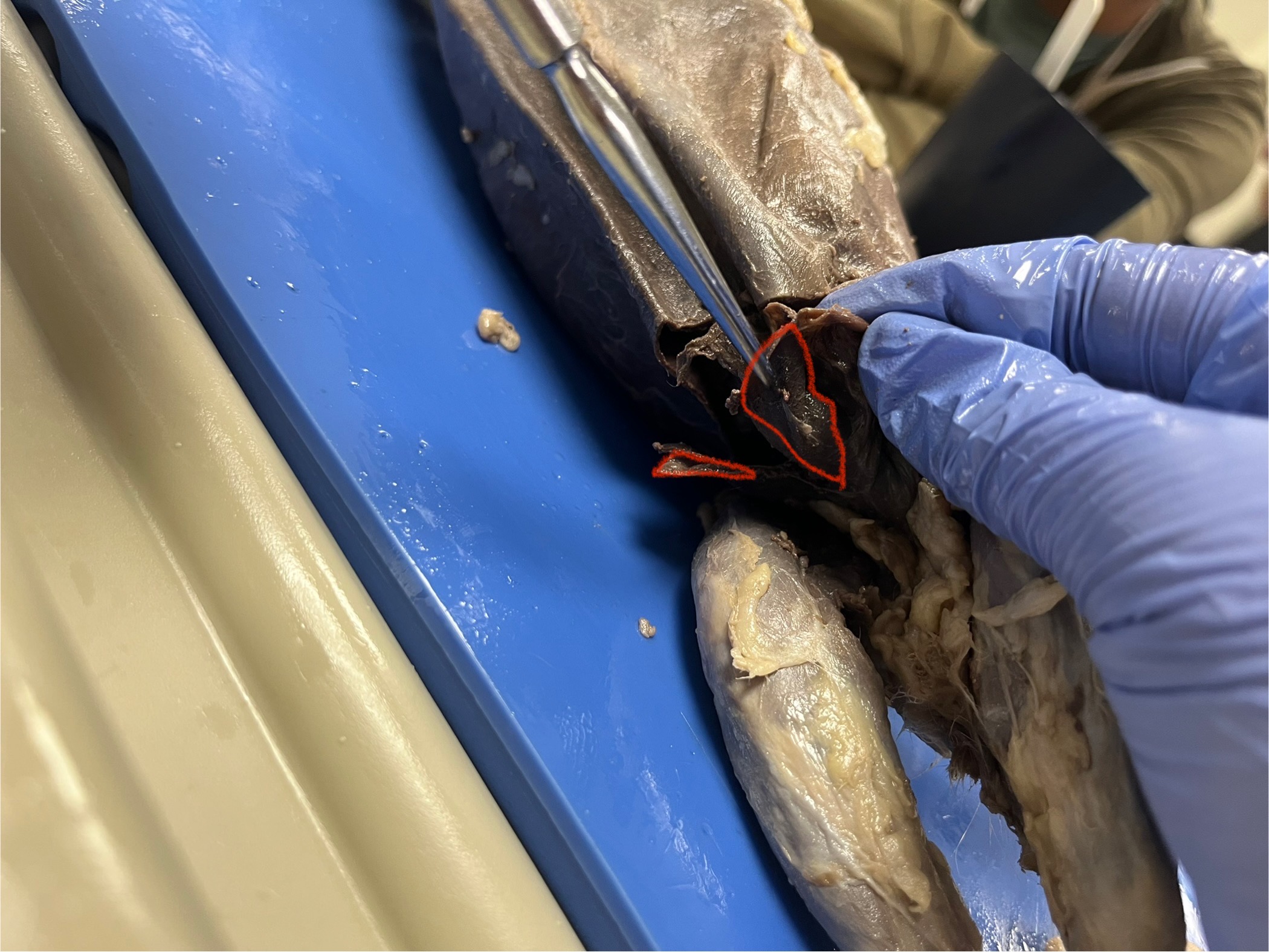
Triceps Brachii (Long Head)
Triceps Brachii (Lateral Head)
Triceps Brachii (Medial Head)
Palmaris Longus
Epitrochlearis
Sartorius
Gracilis
Gluteus Maximus
Gluteus Medius
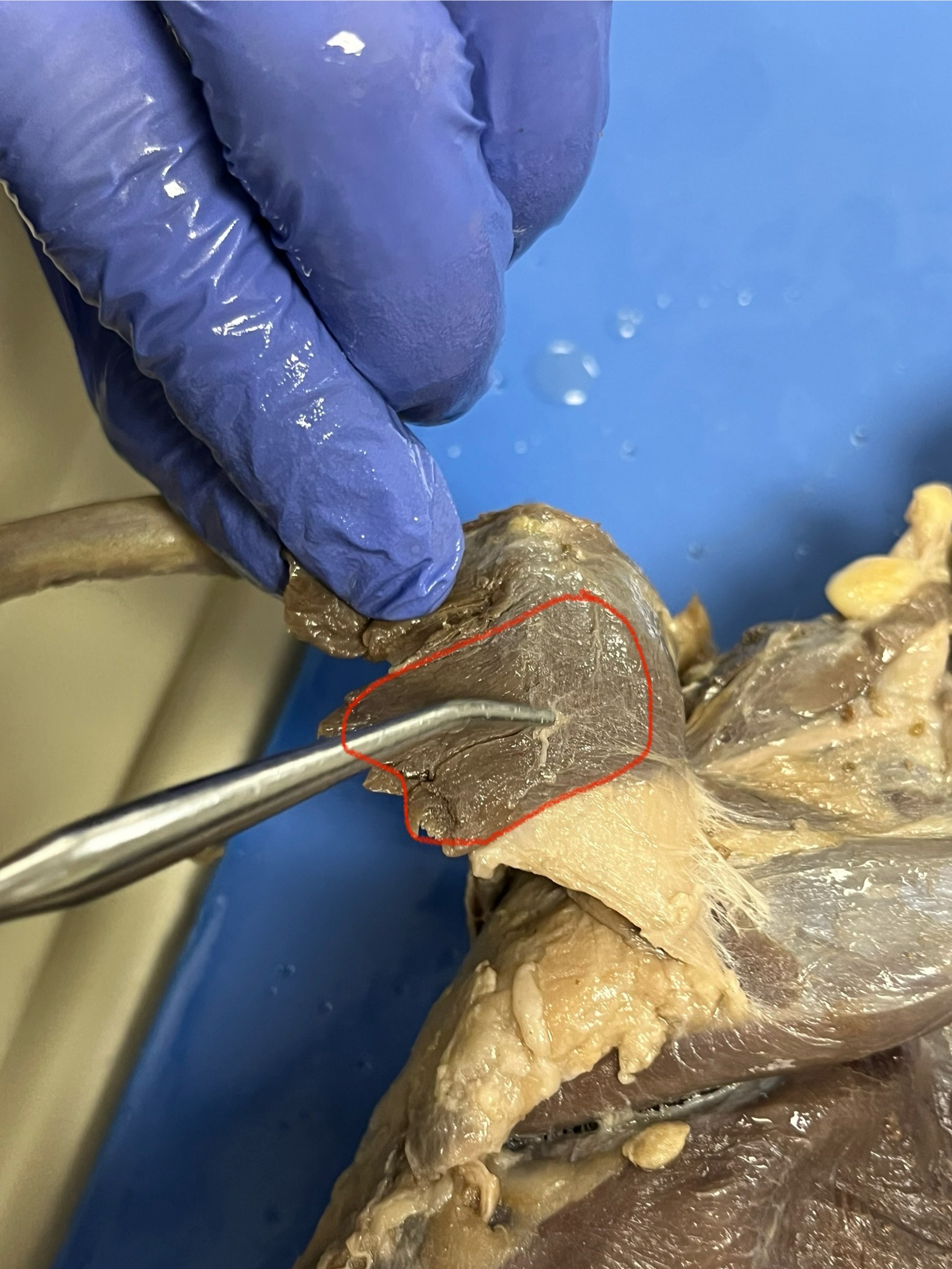
Biceps Femoris
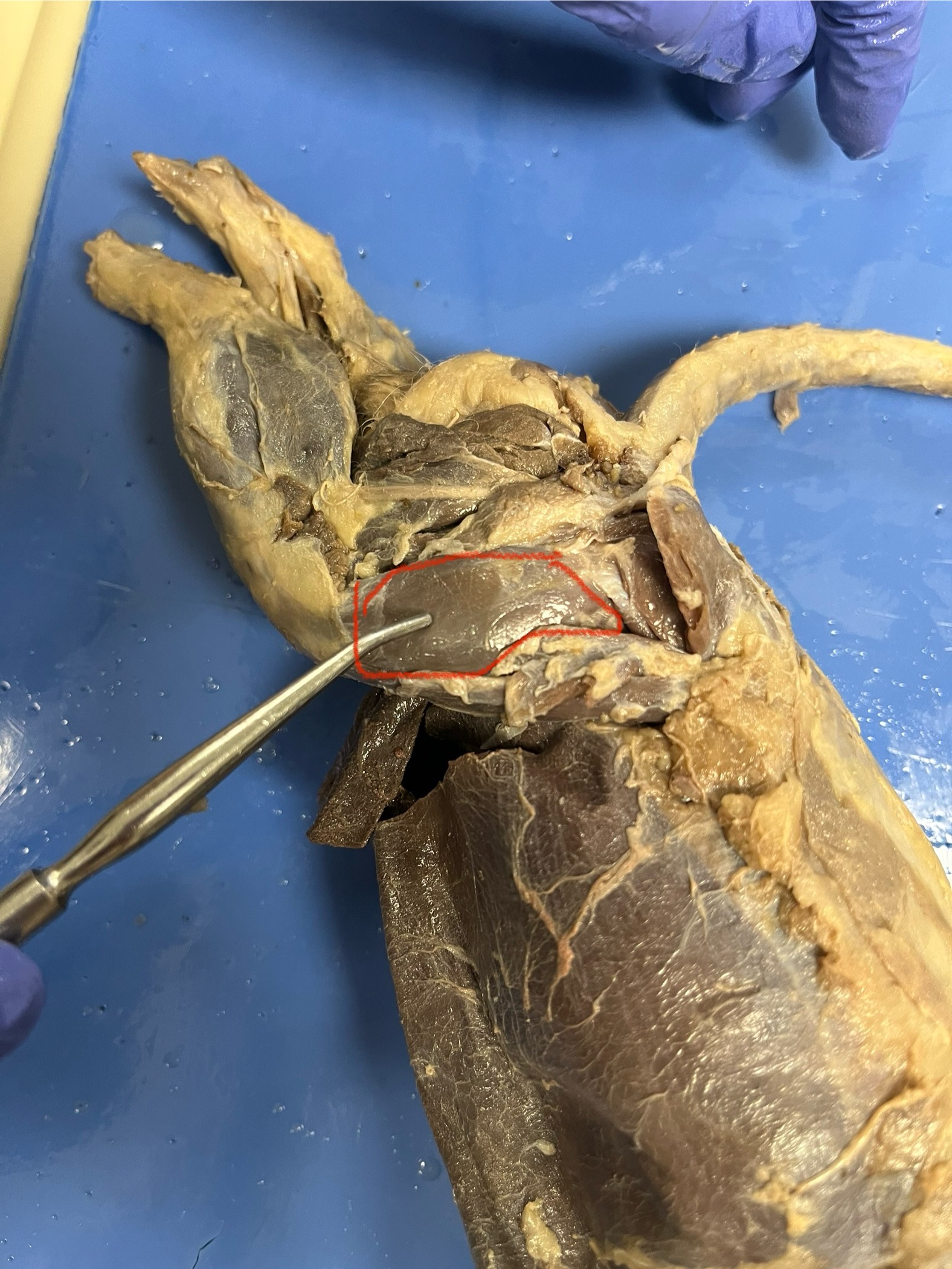
Vastus Lateralis
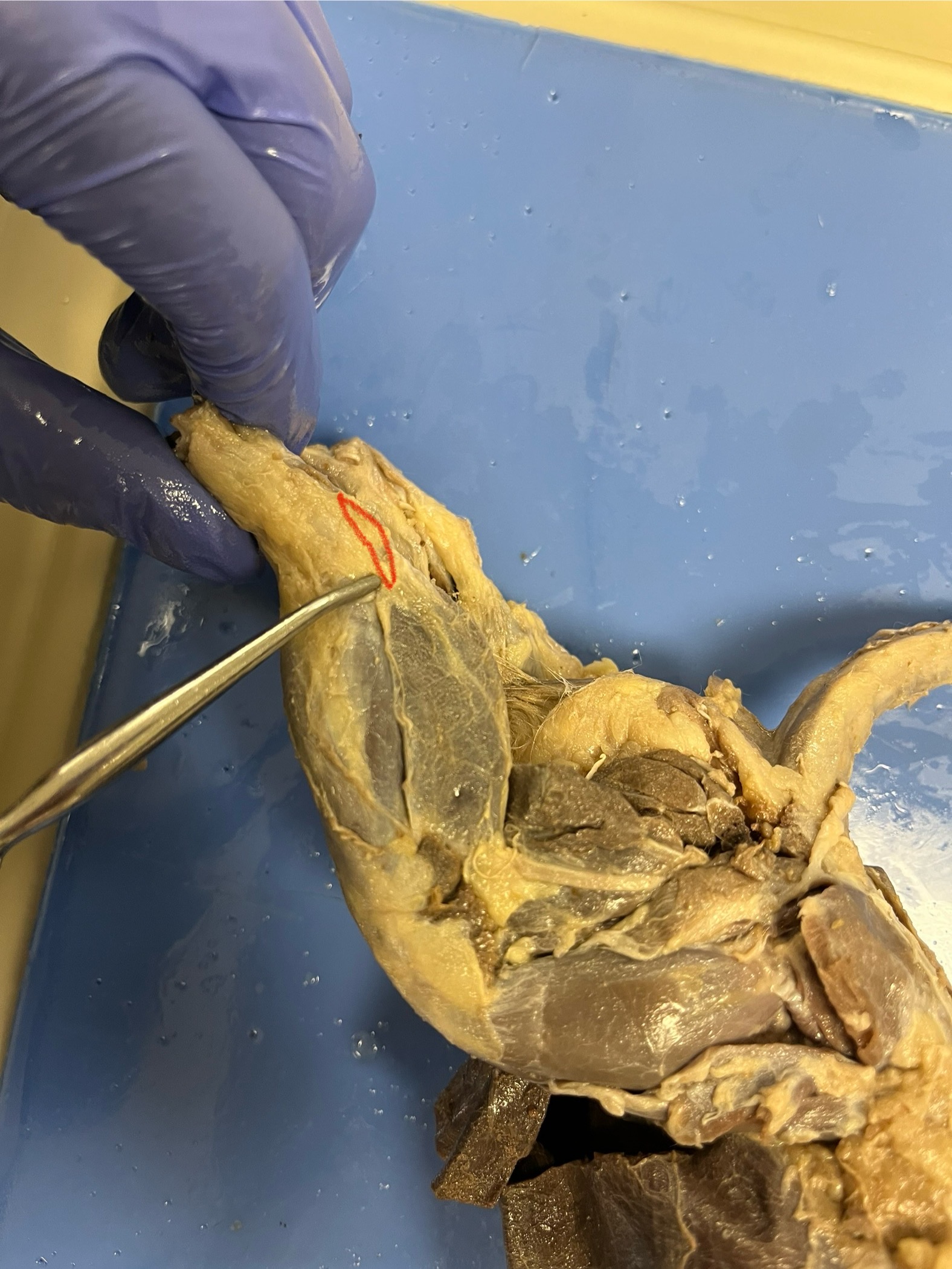
Achilles Tendon
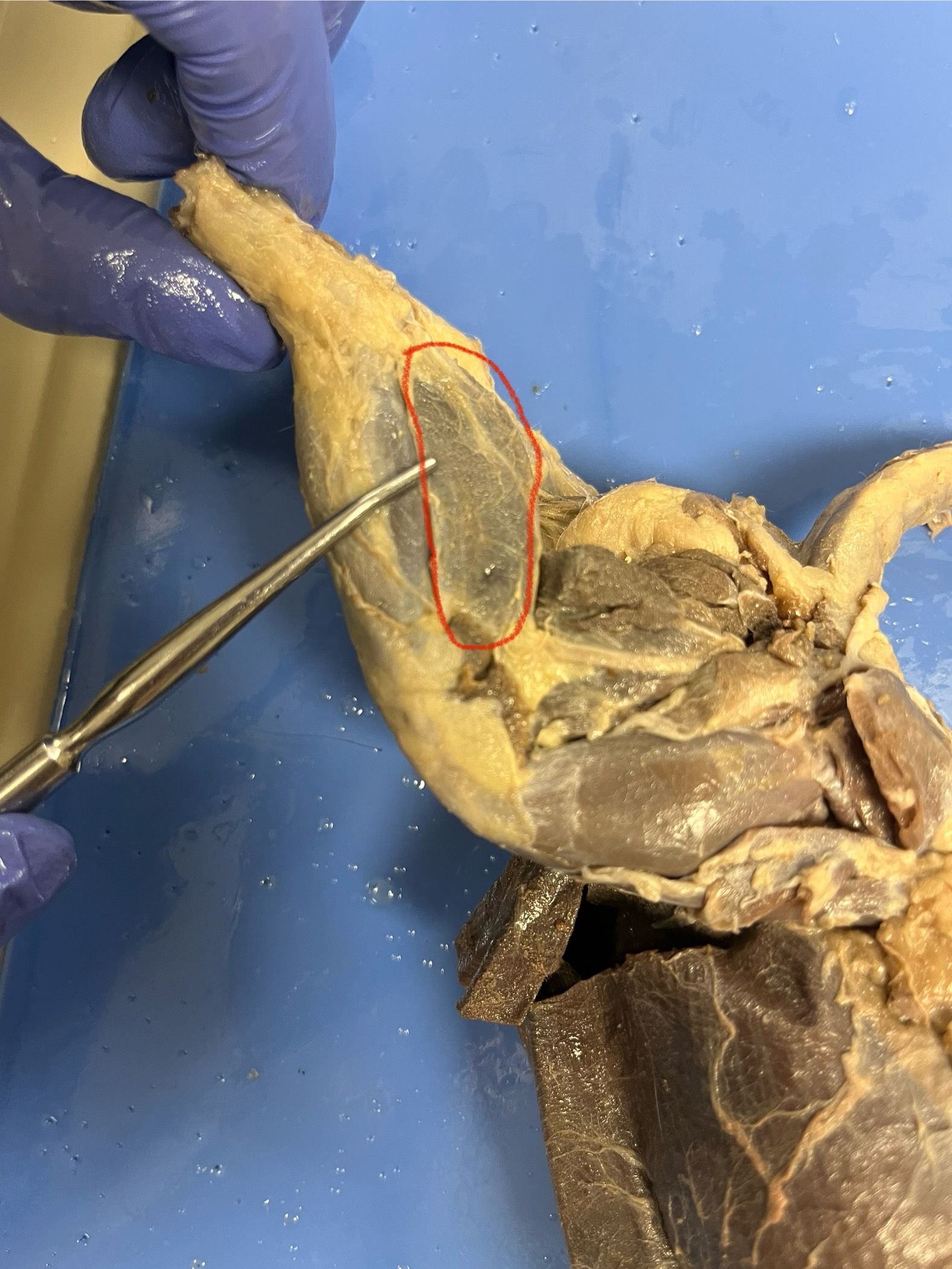
Gastrocnemius
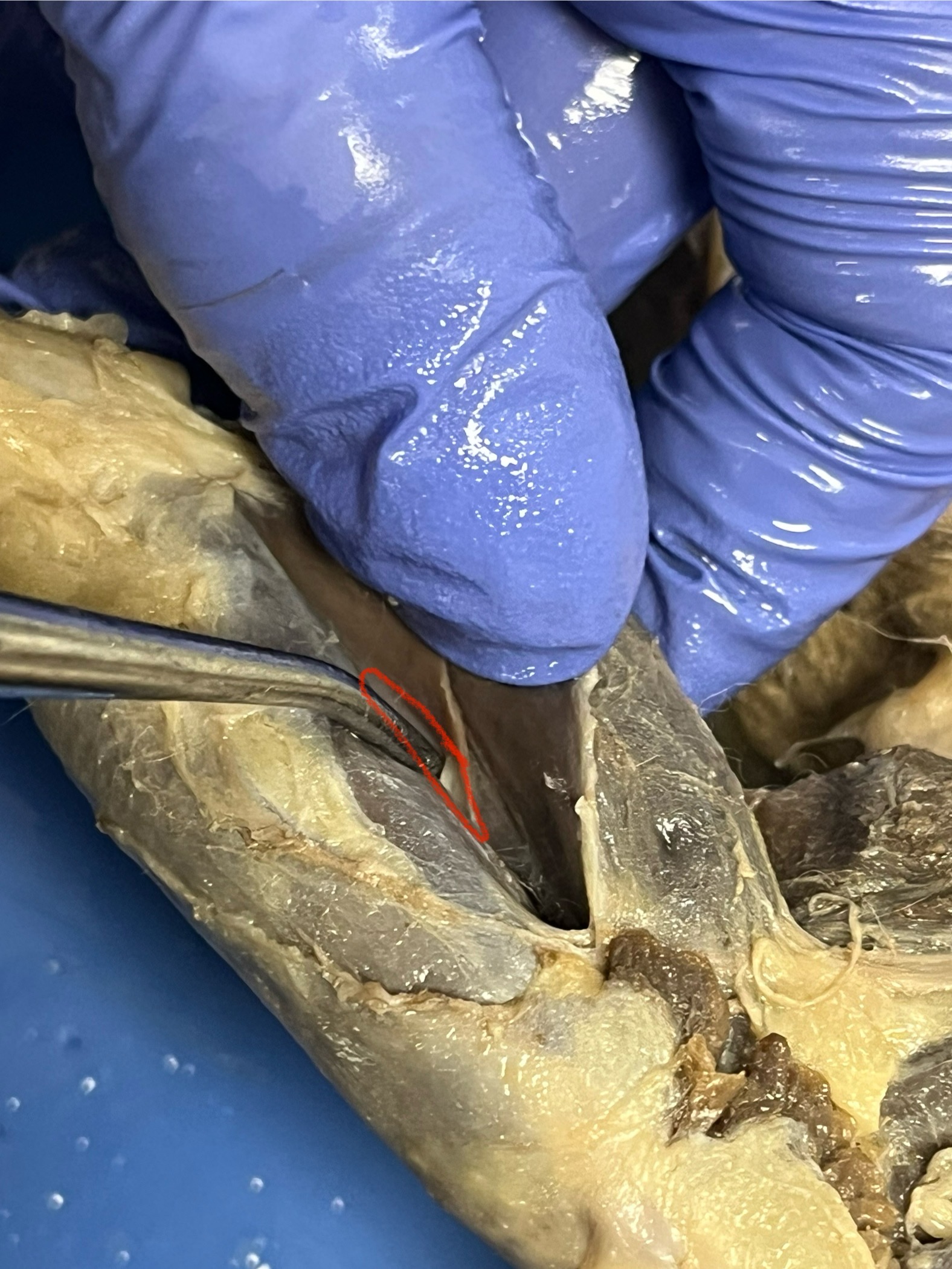
Soleus
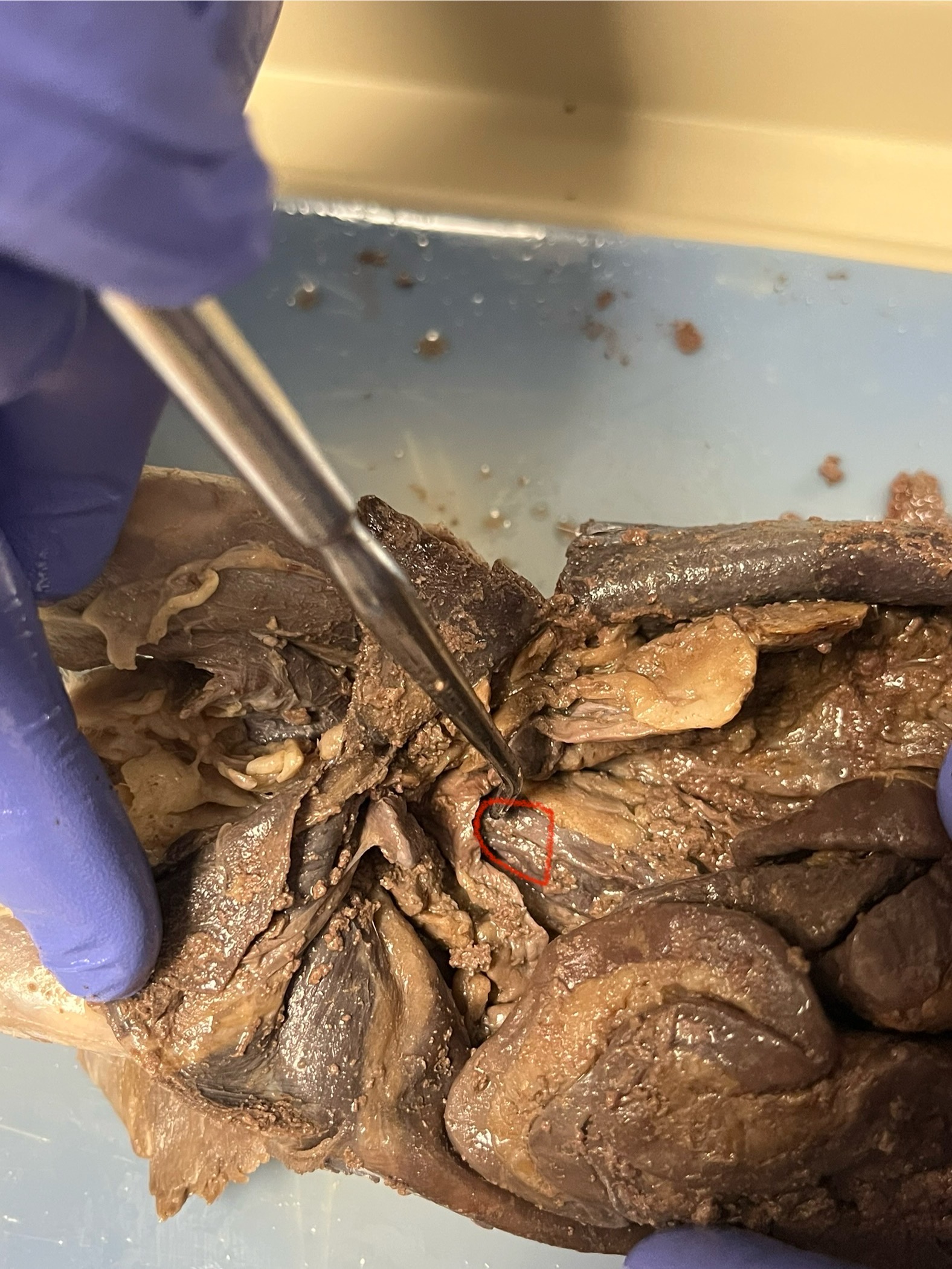
Rectum

Large Intestine
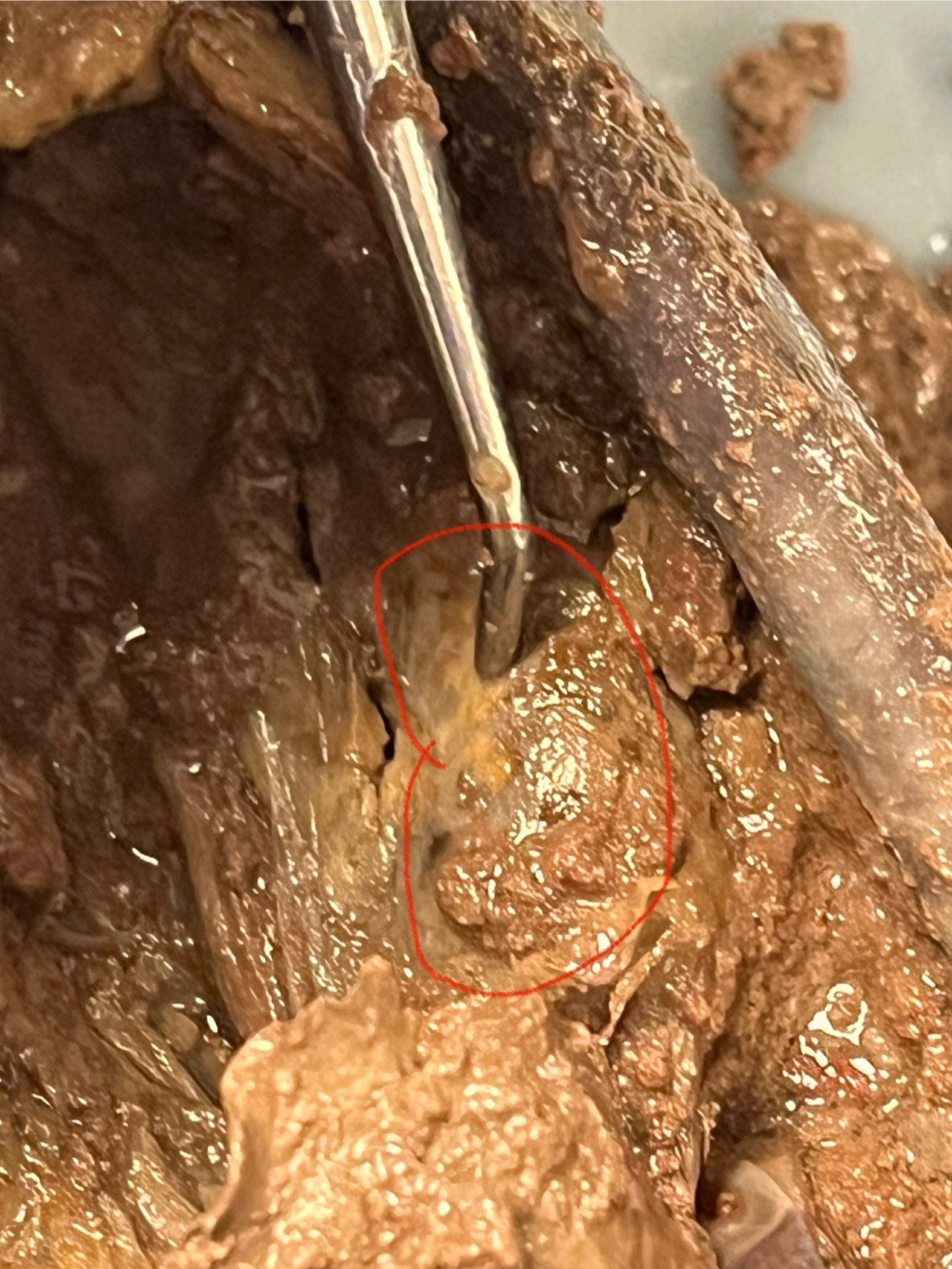
Kidney
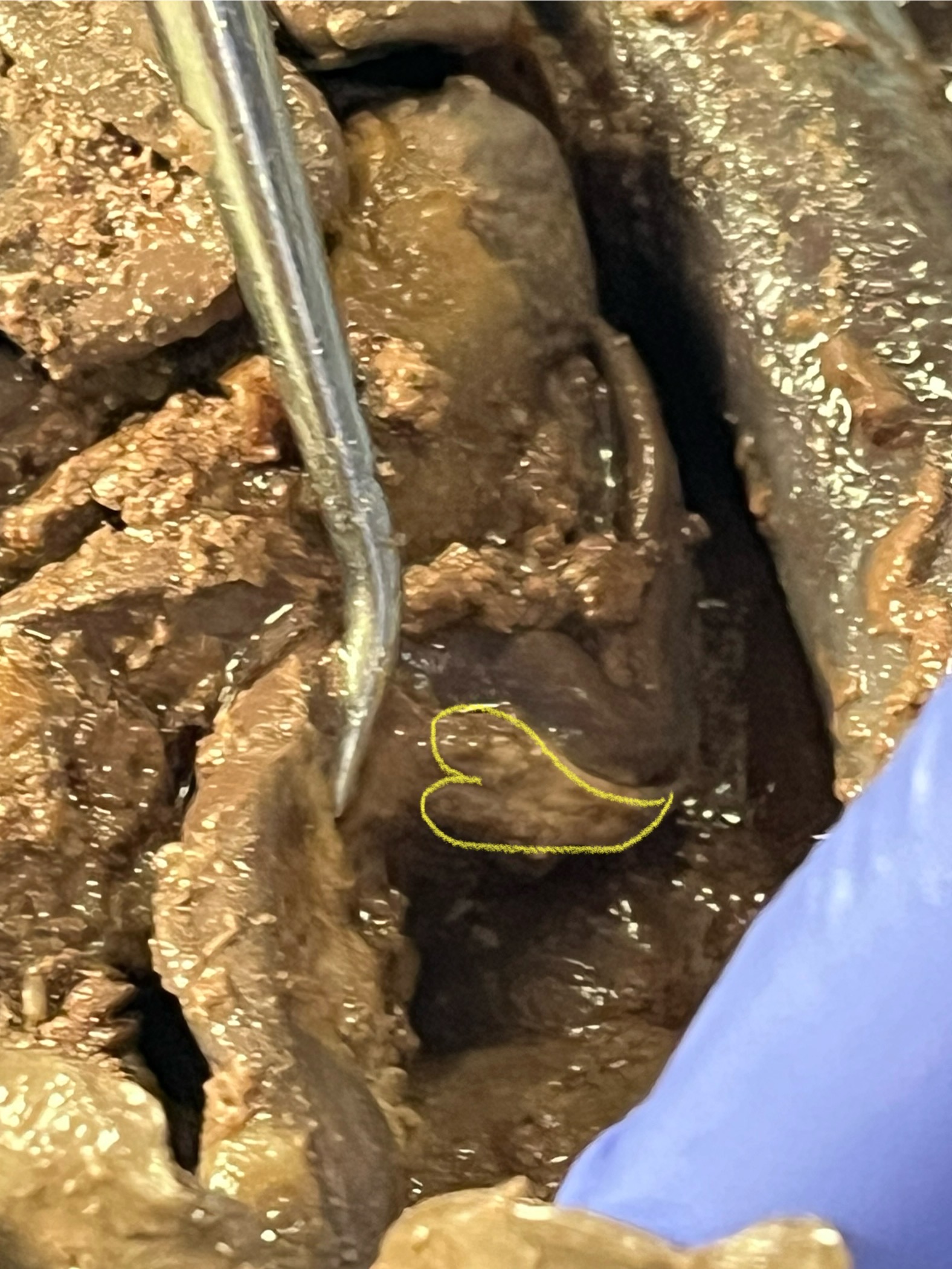
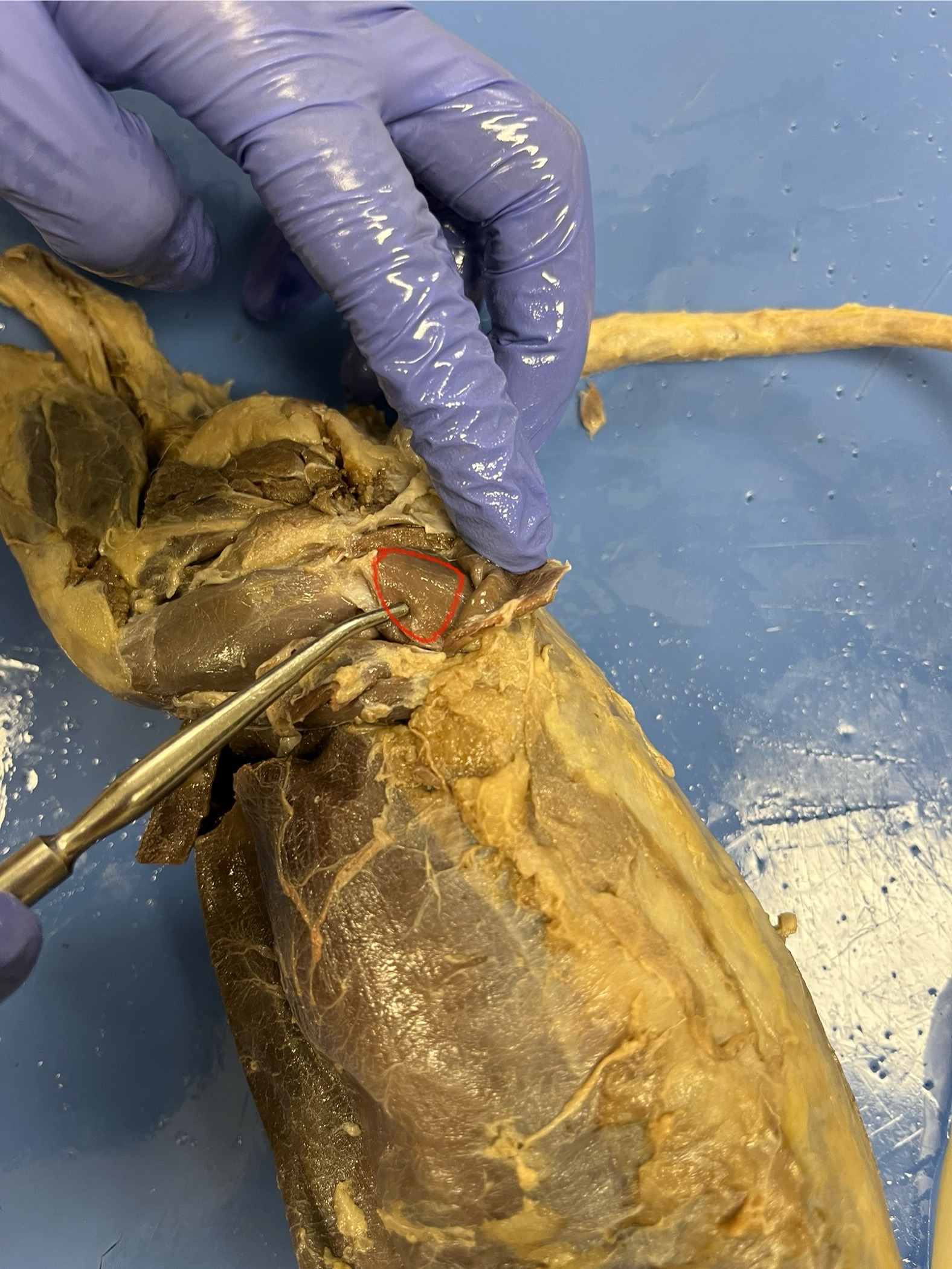
Pancreas
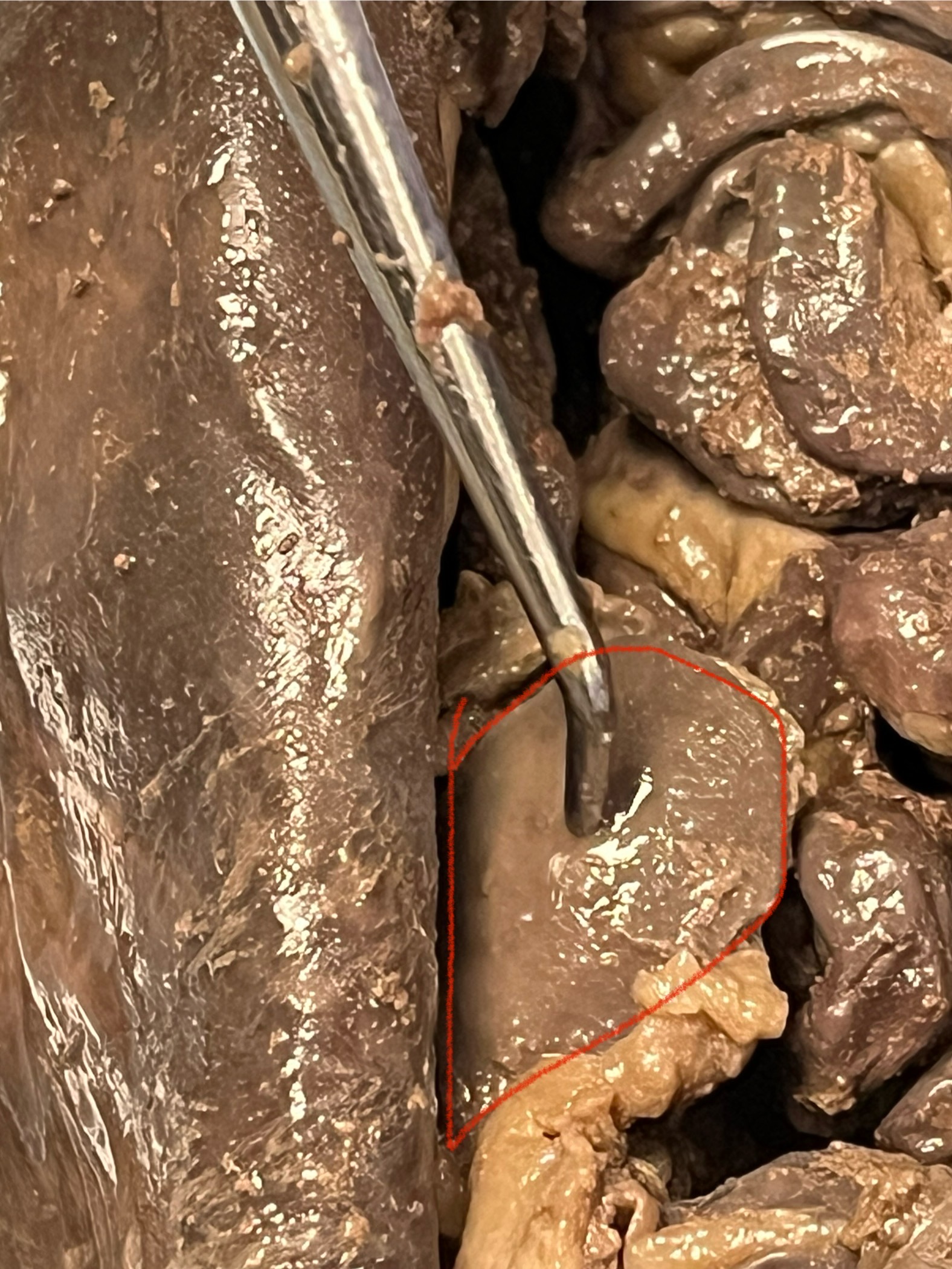
Spleen
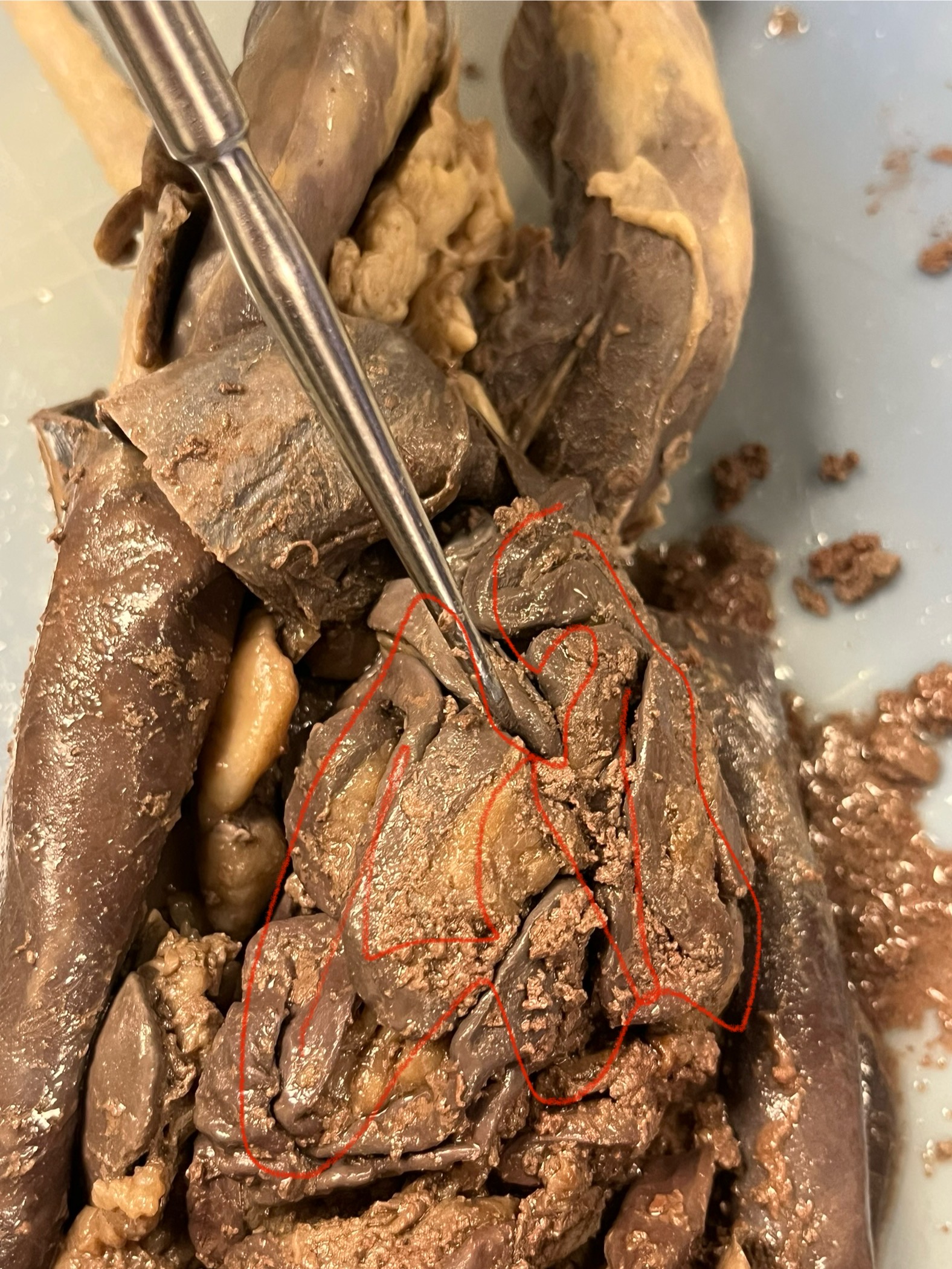
Small Intestine
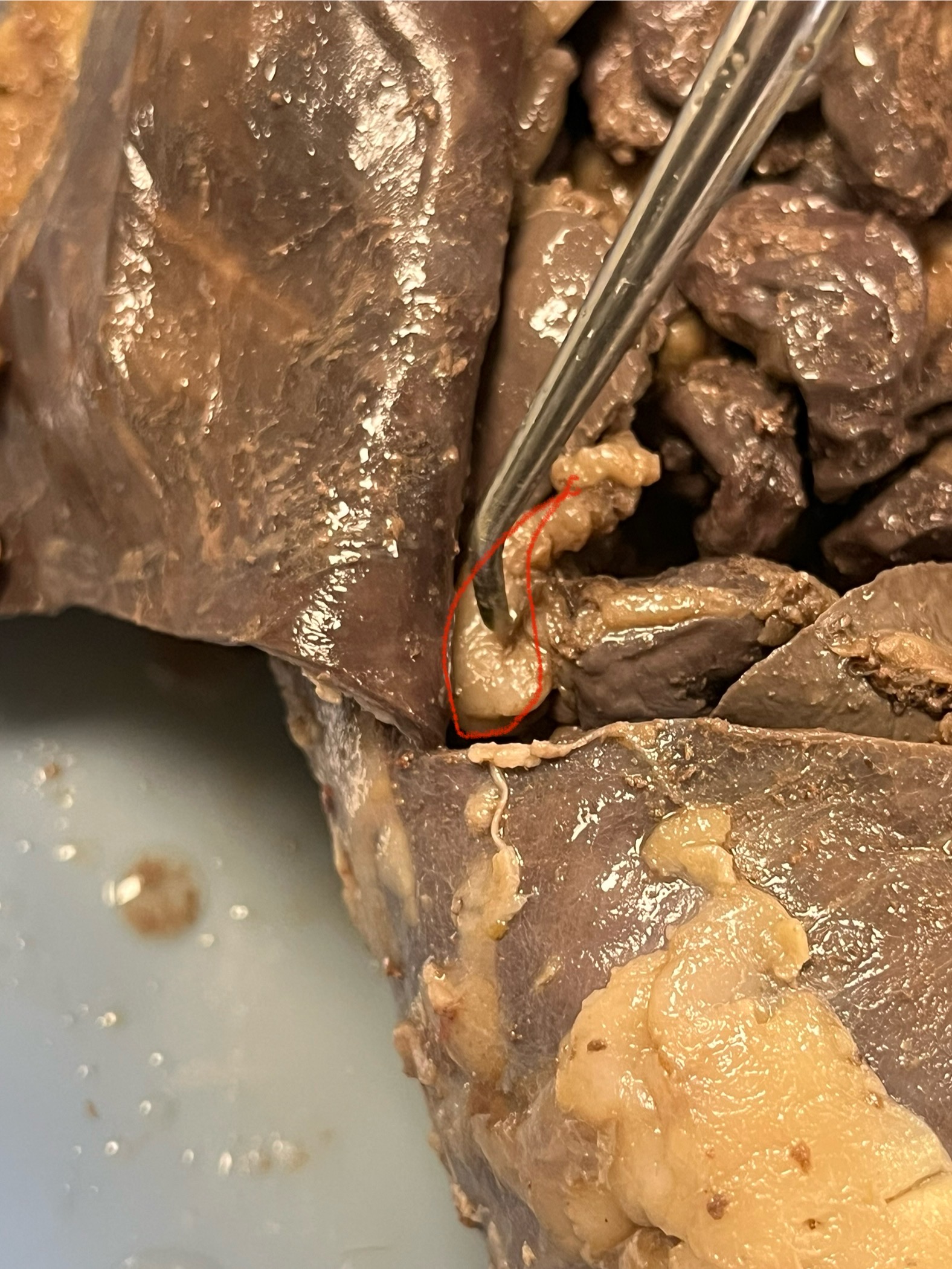
Stomach
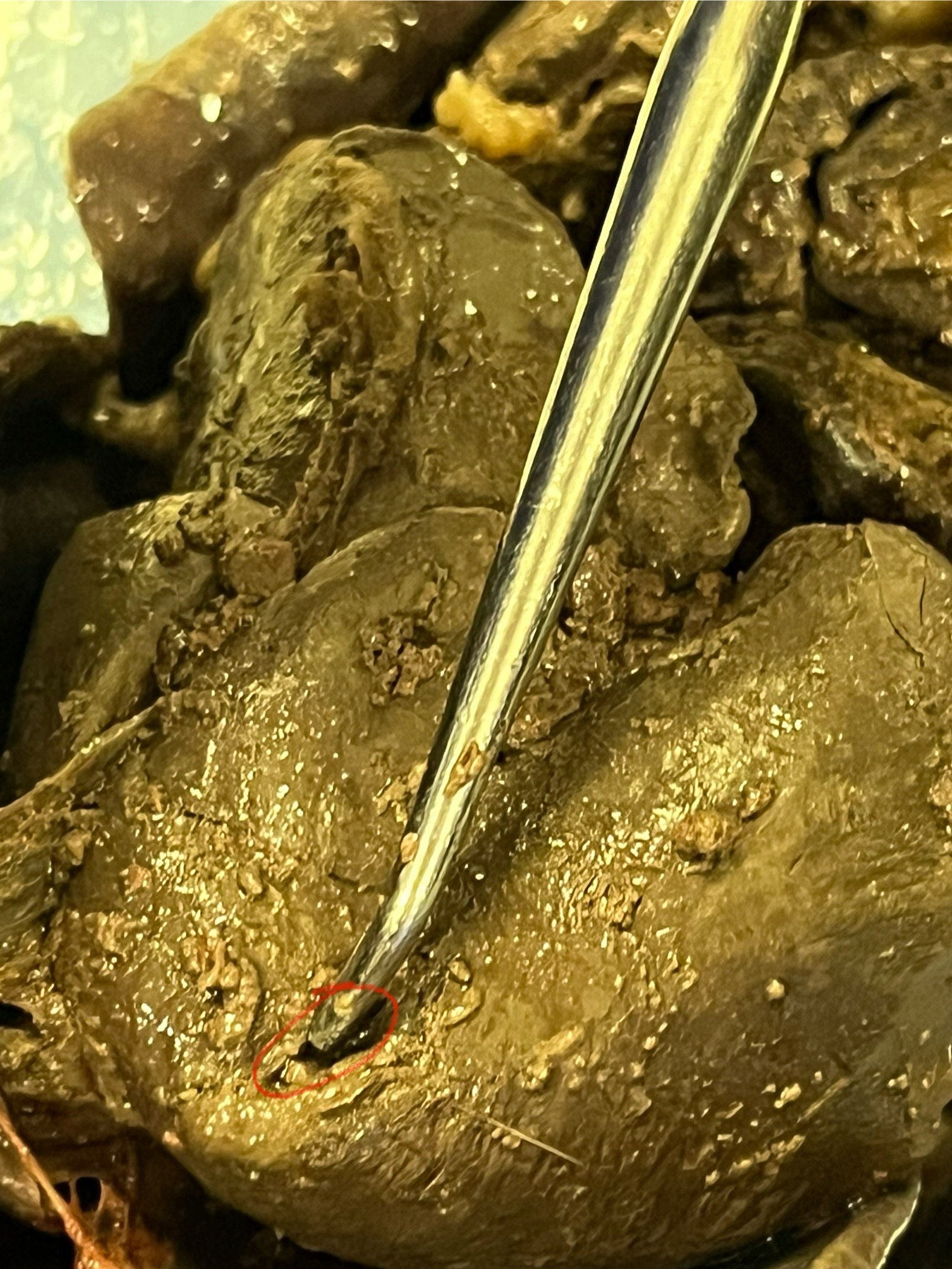
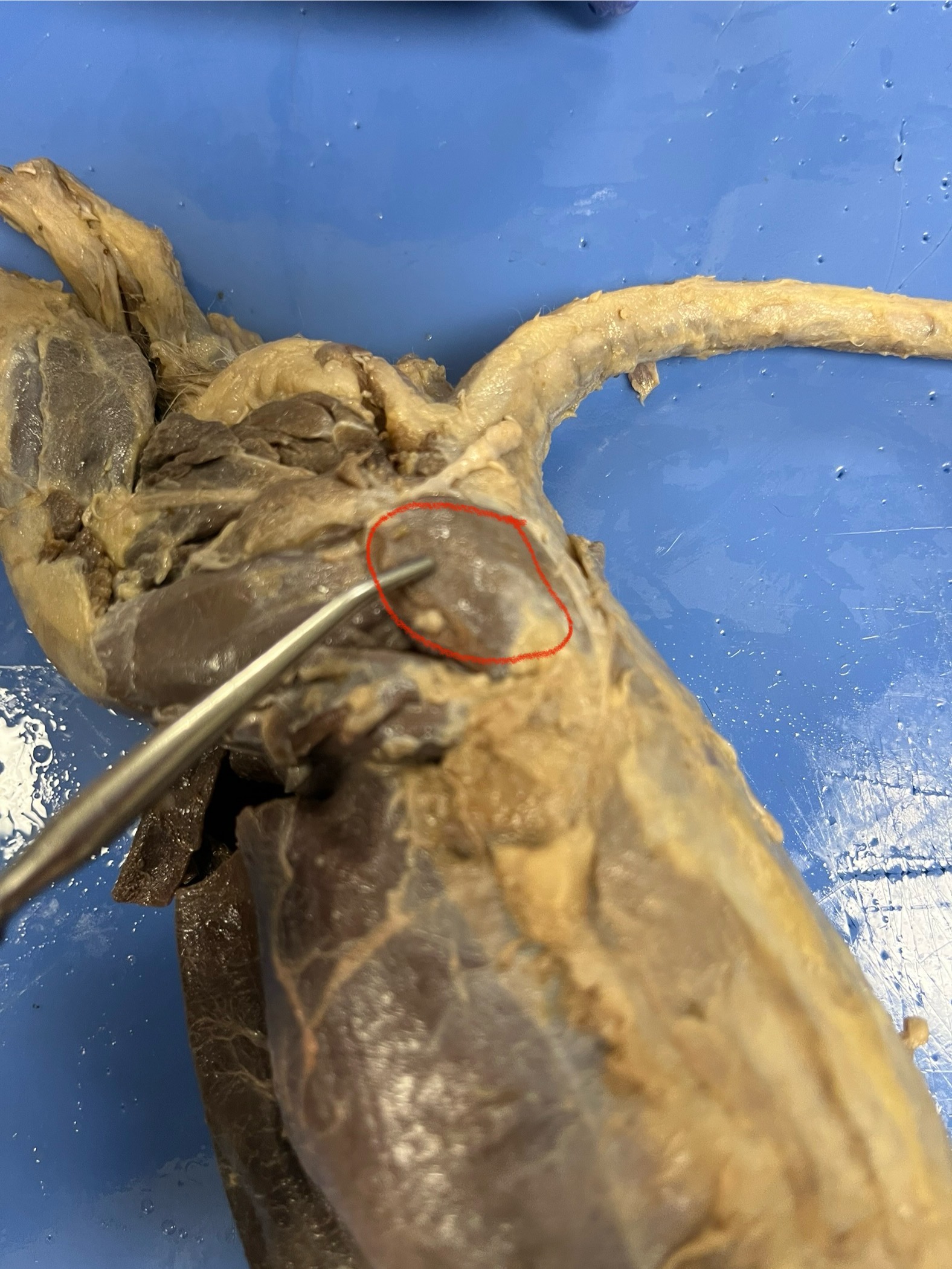
Gallbladder
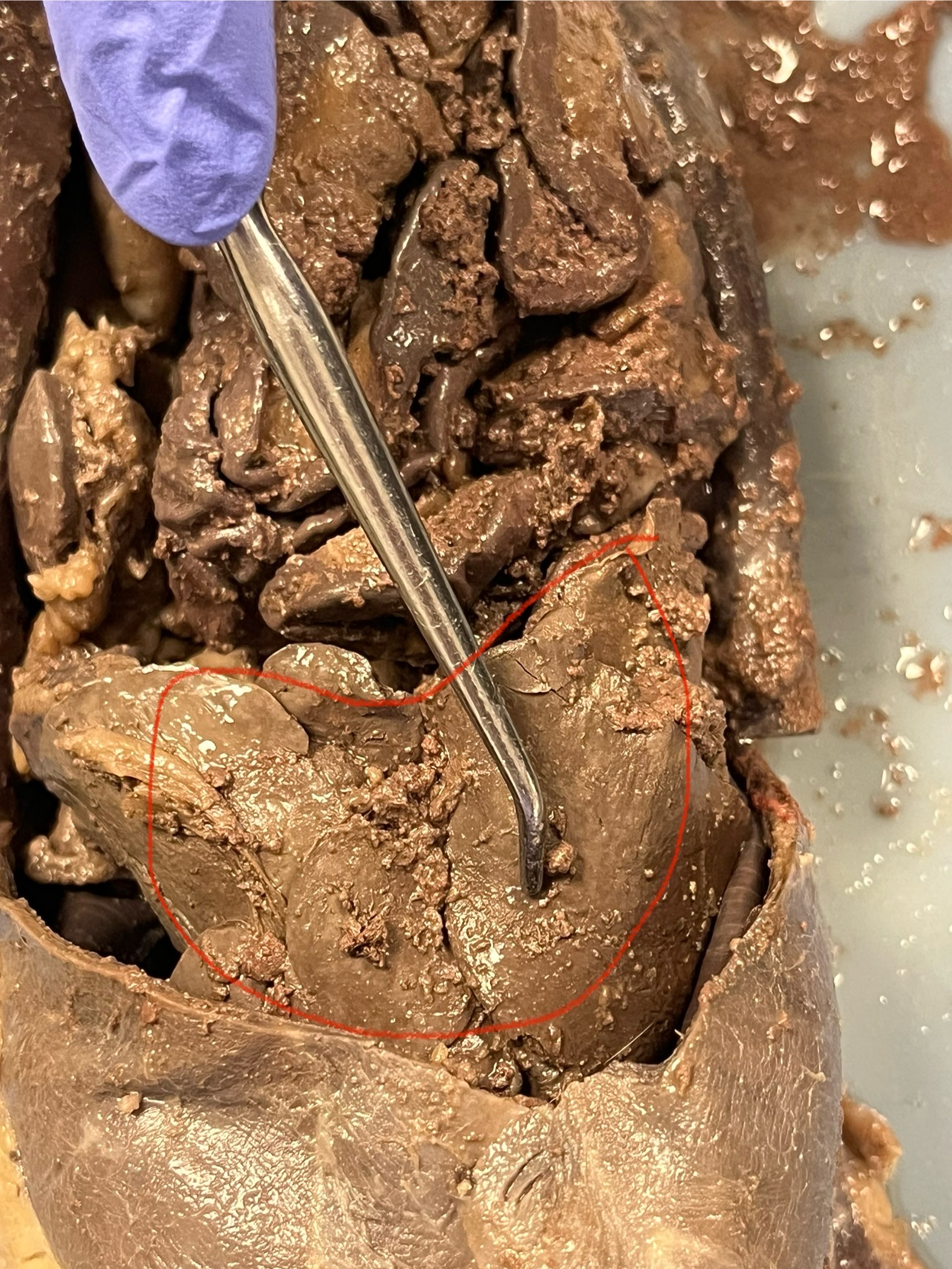
Liver
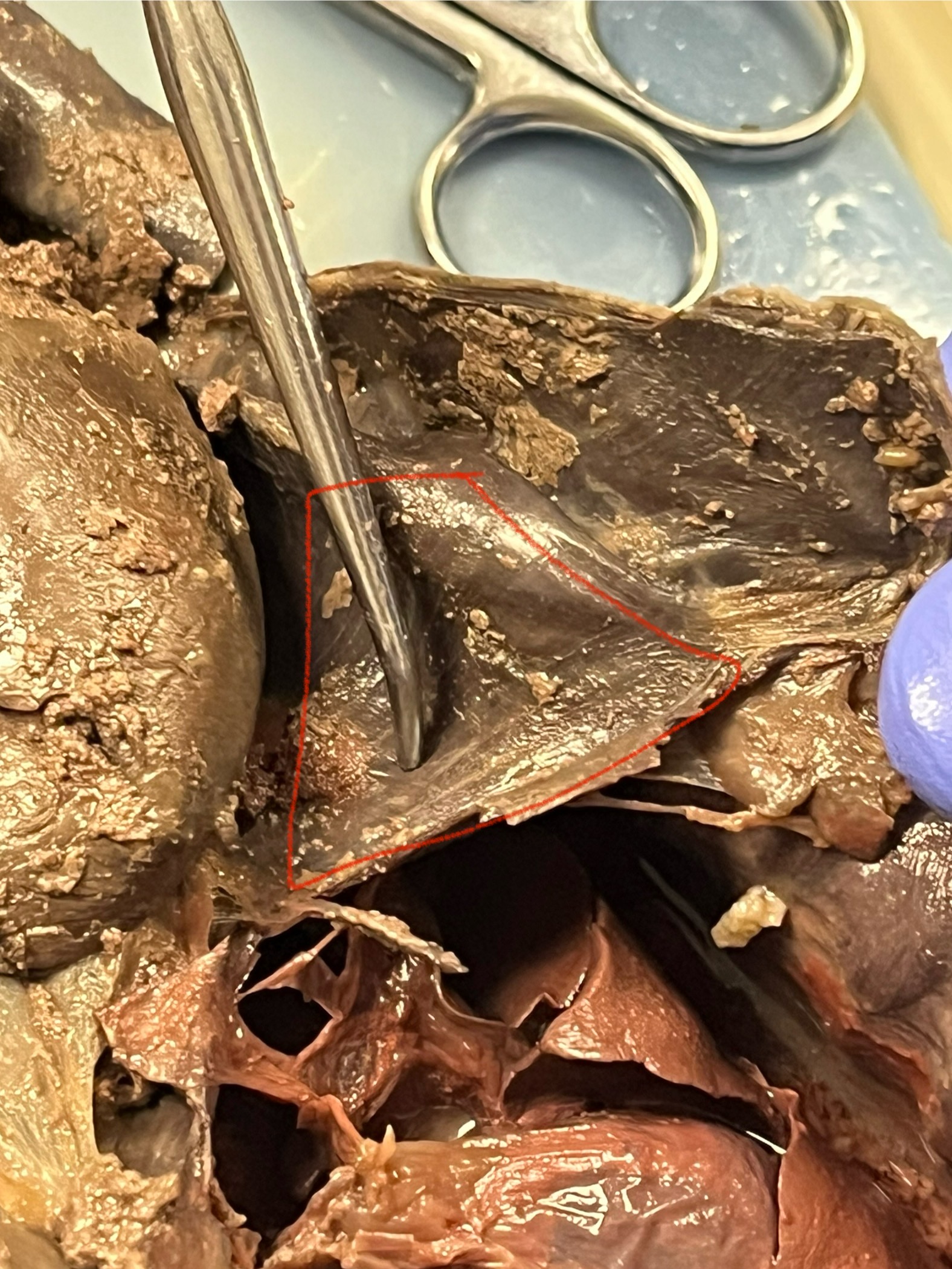
Diaphragm
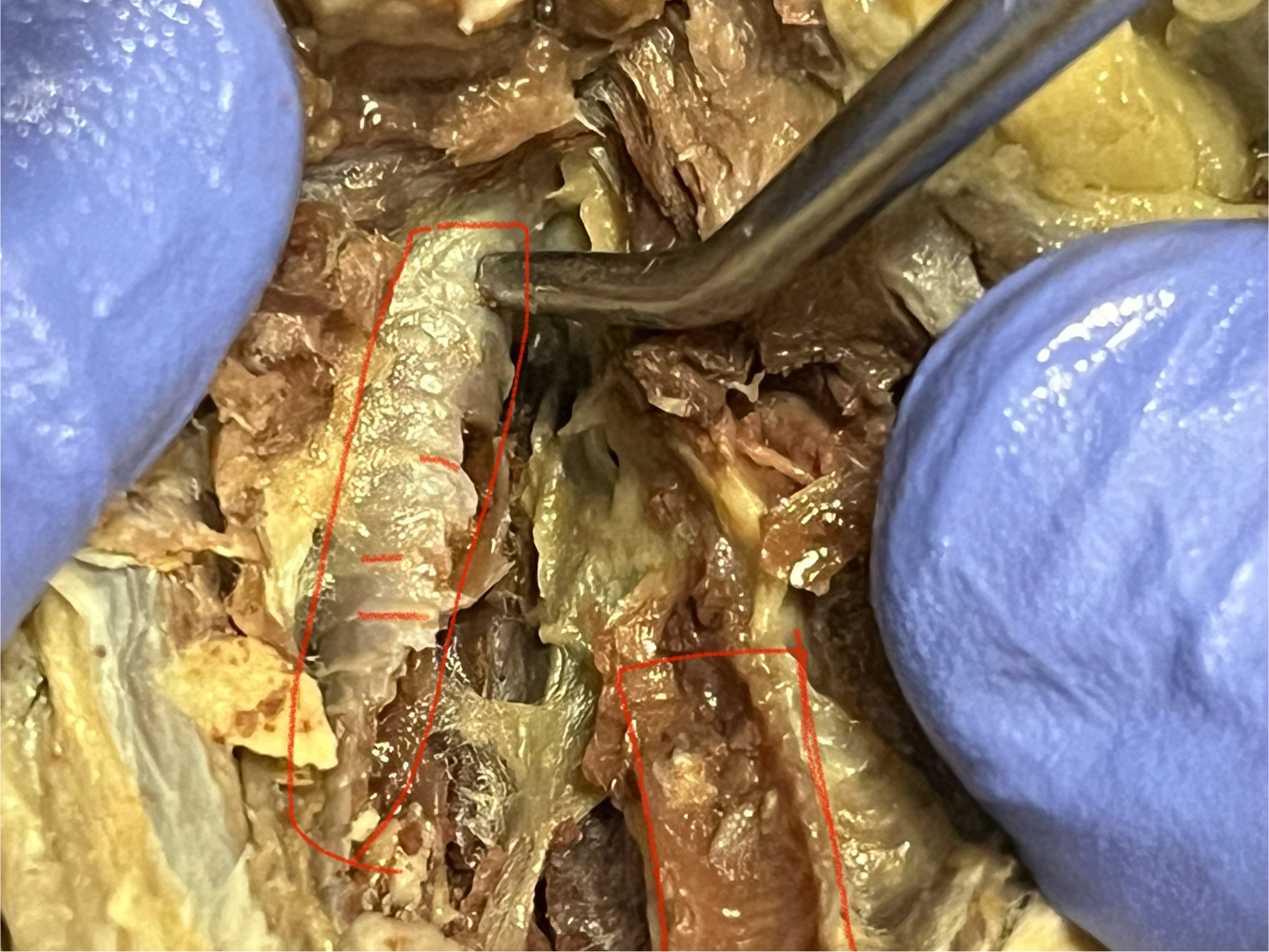
Trachea
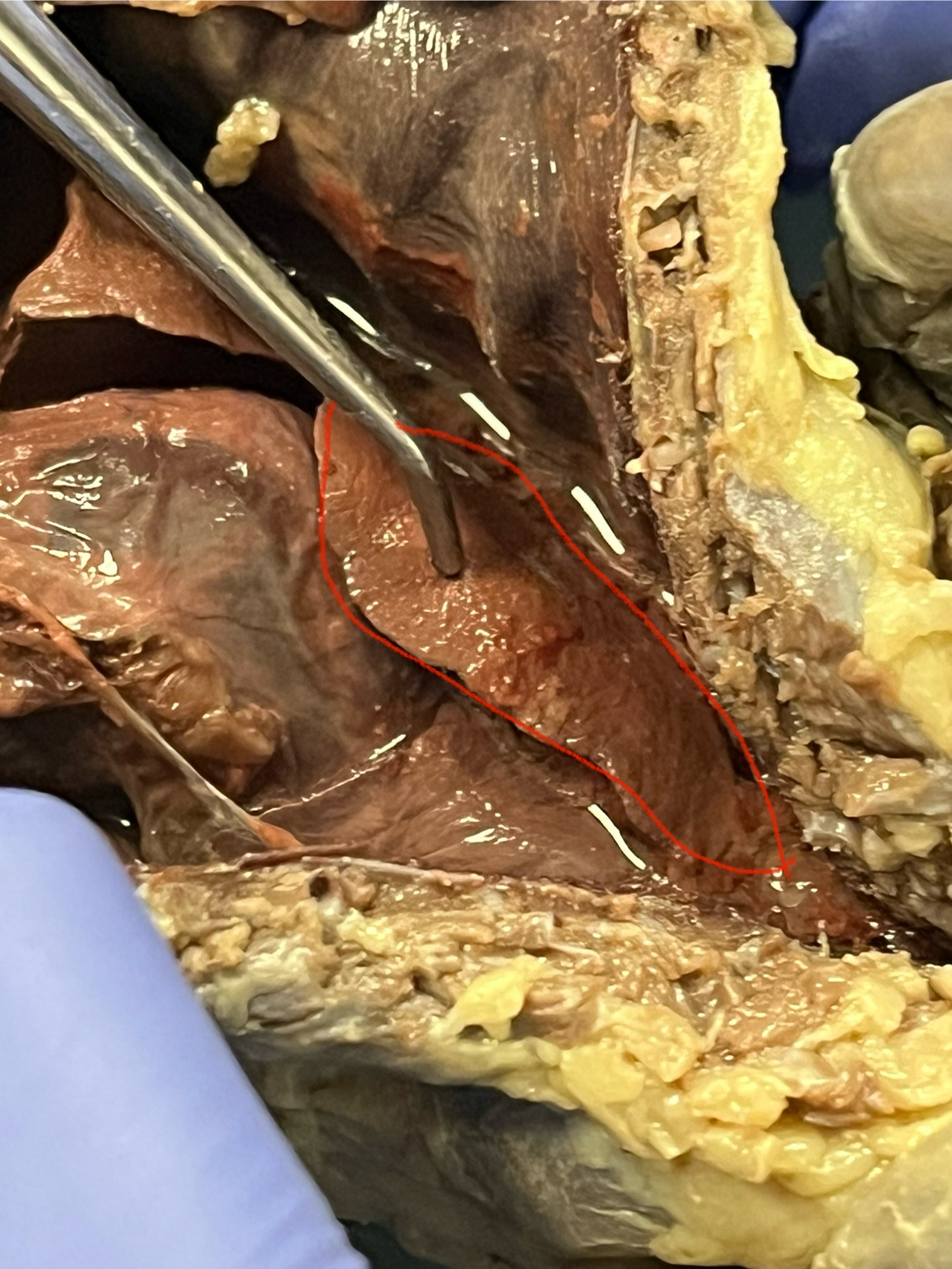
Lung
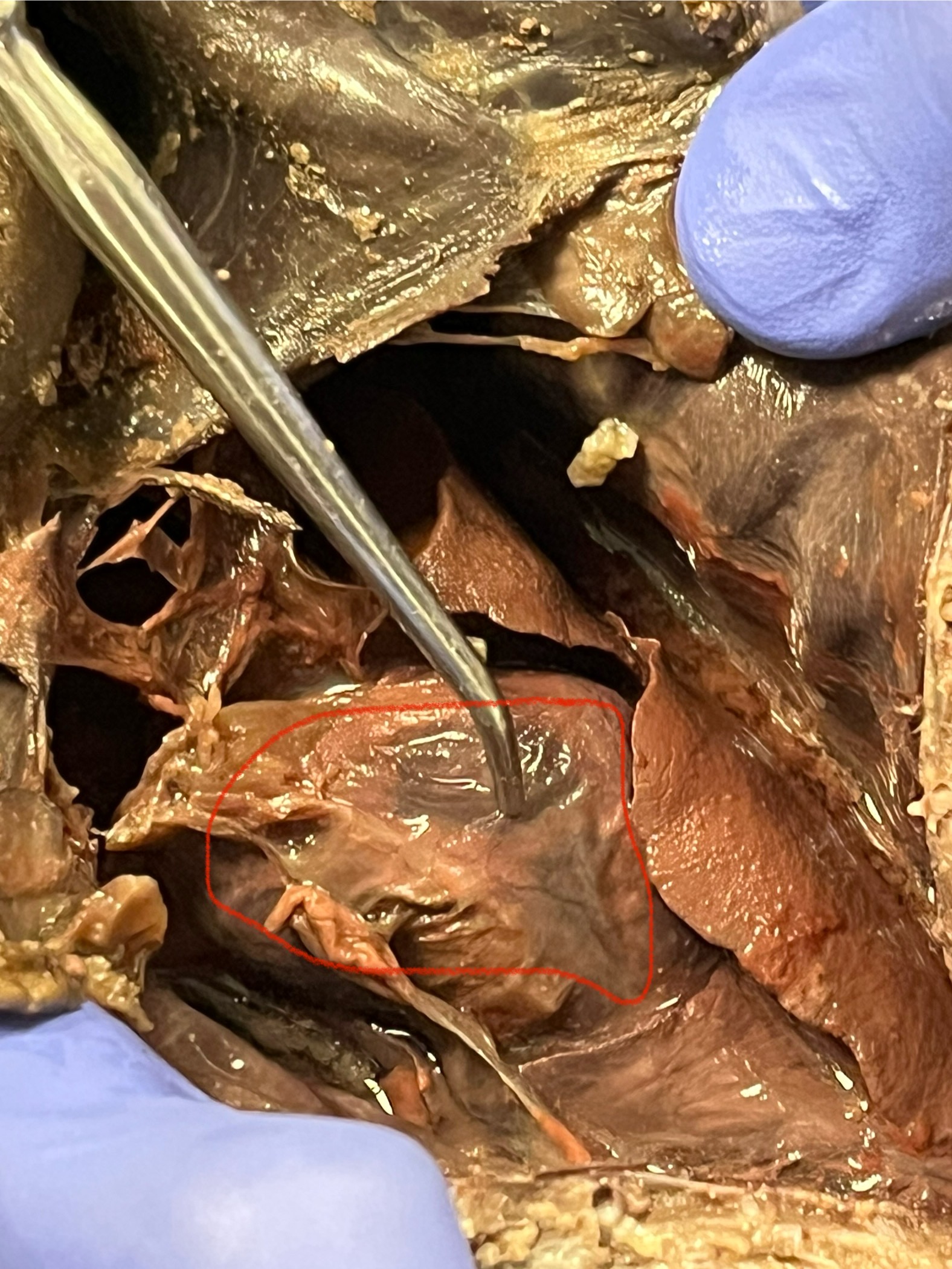
Heart
Esophagus
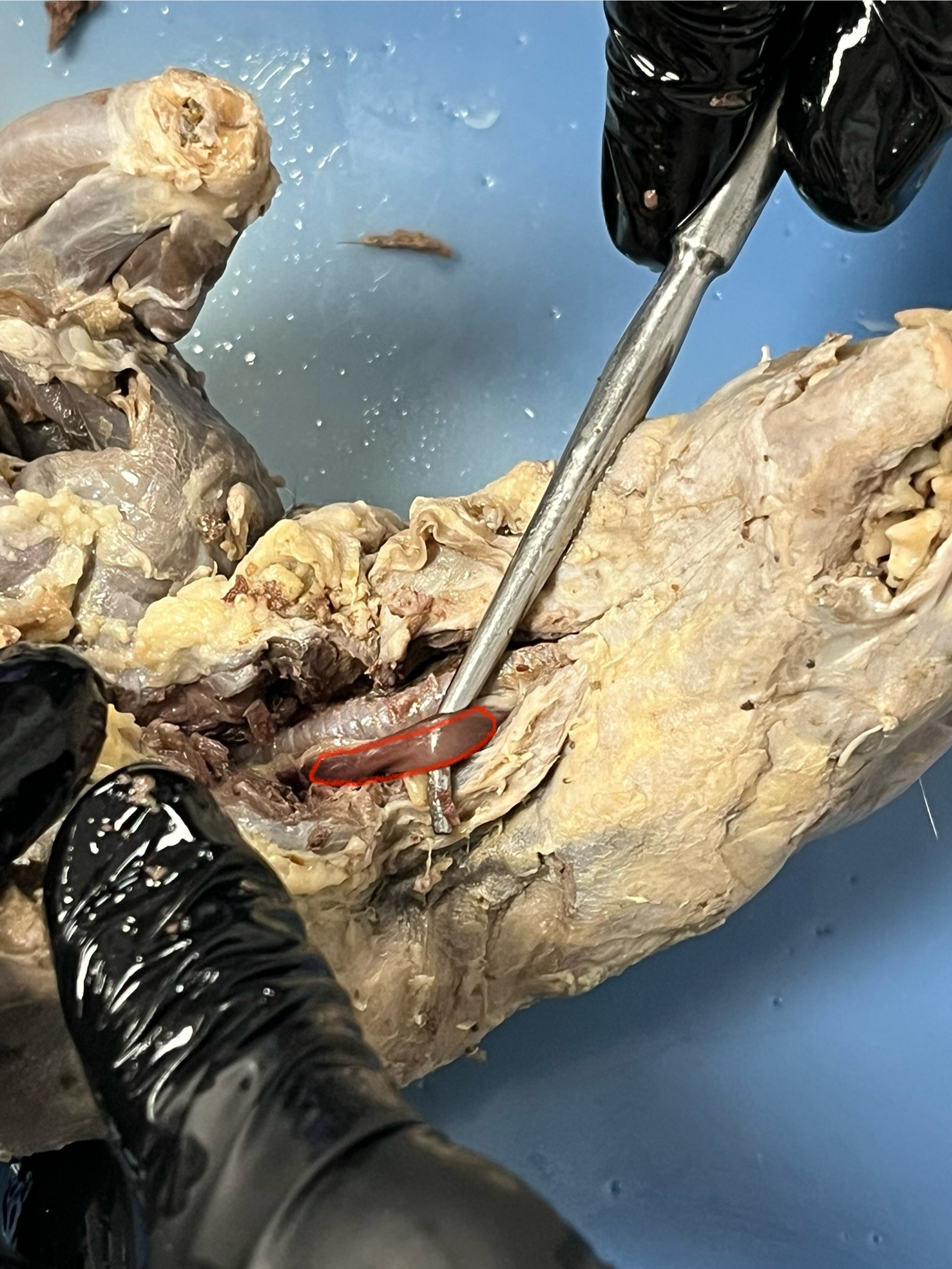
Ovary
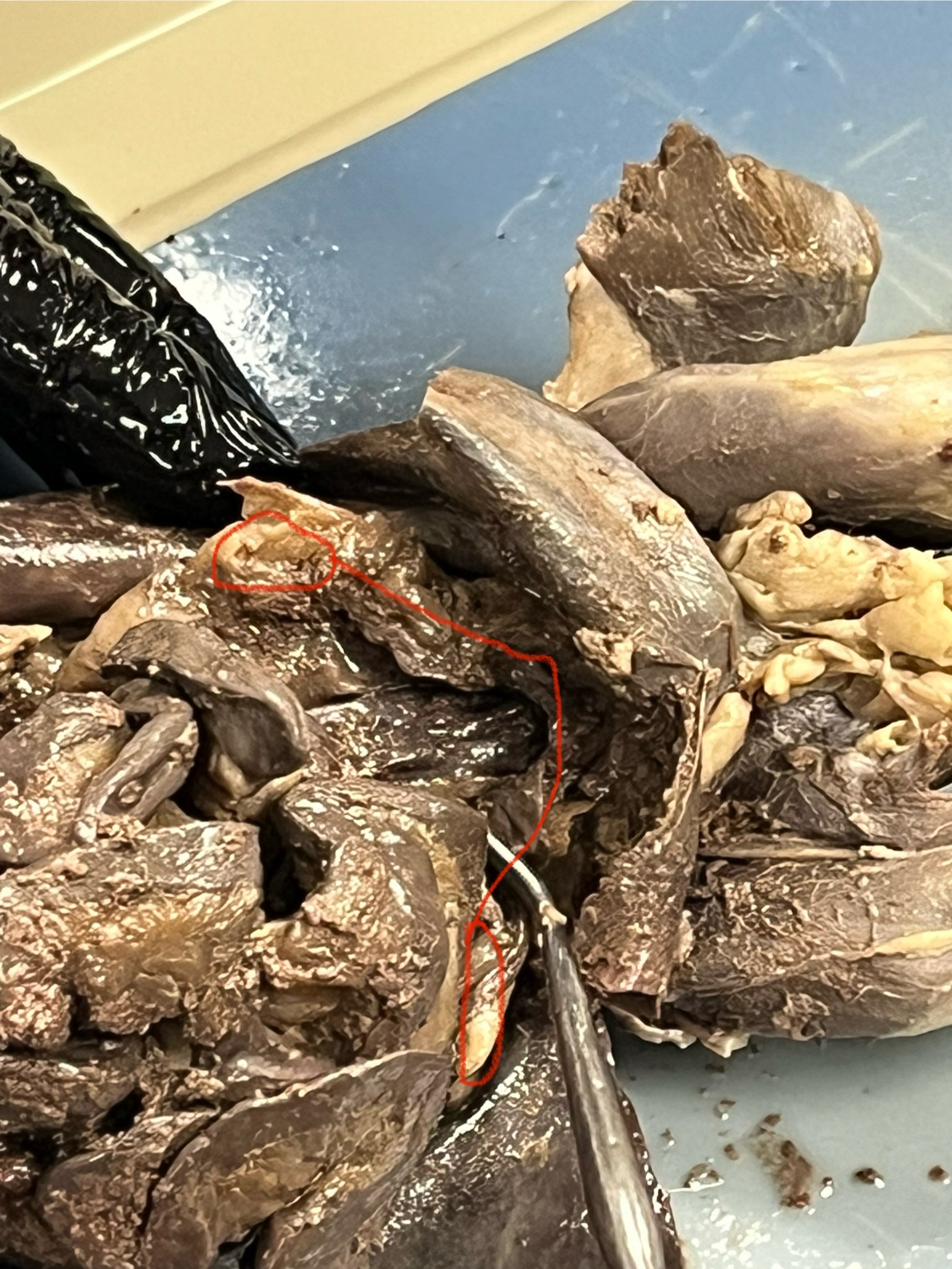

Uterus
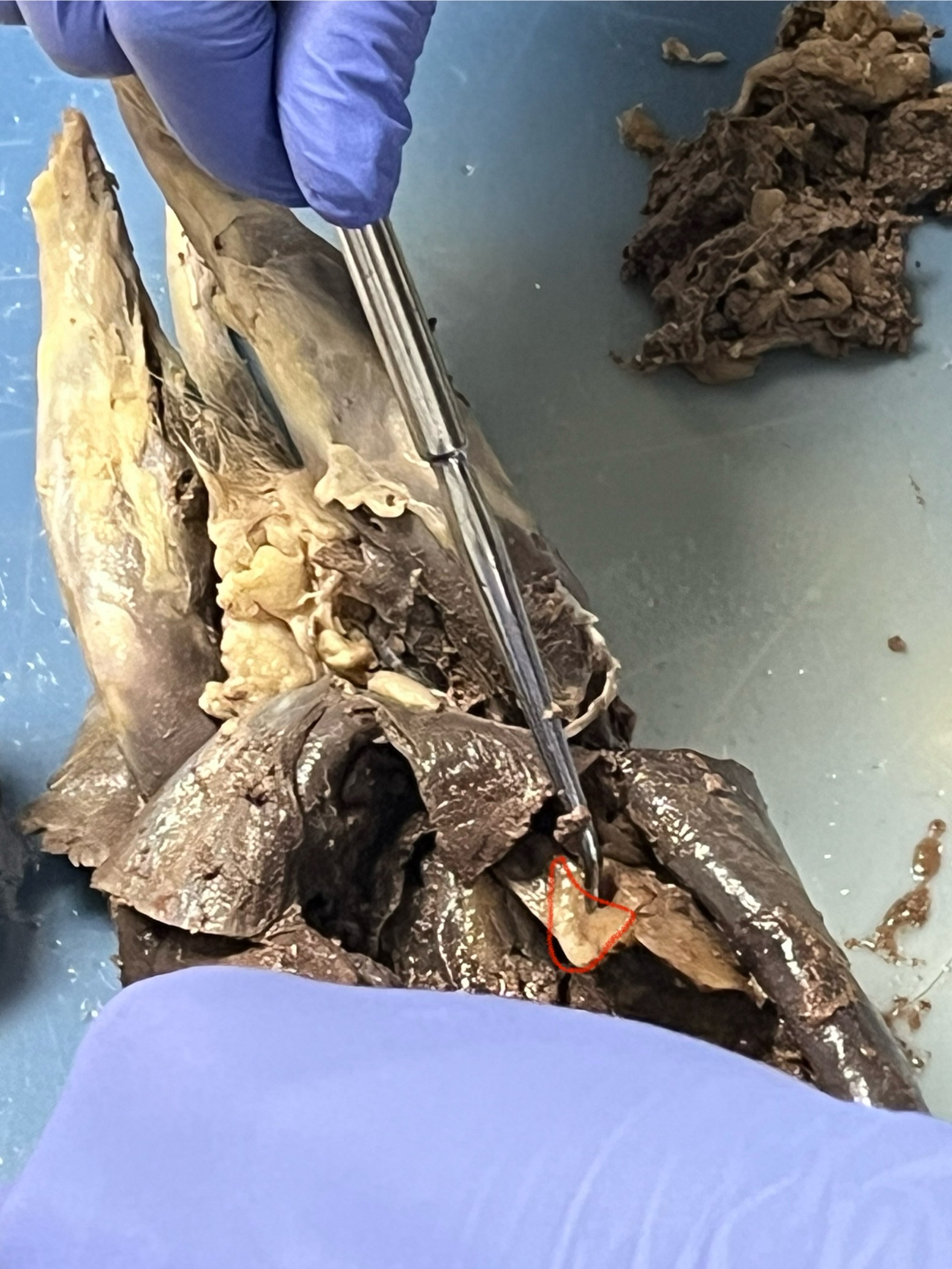
Urinary Bladder
Urethra
Spinotrapeszius
Located along the upper back, stretching from the thoracic spine to the scapula, just behind the acromiotrapezius.
Acromiotrapezius
a broad, flat muscle on the upper back of a mink that holds the scapula in place and lies between the clavotrapezius and spinotrapezius
Latissimus Dorsi
a broad muscle on the mink’s lower back that extends from the spine to the upper arm
Rhomboideus
lies deep in the upper back of a mink, running from the spine to the medial edge of the scapula
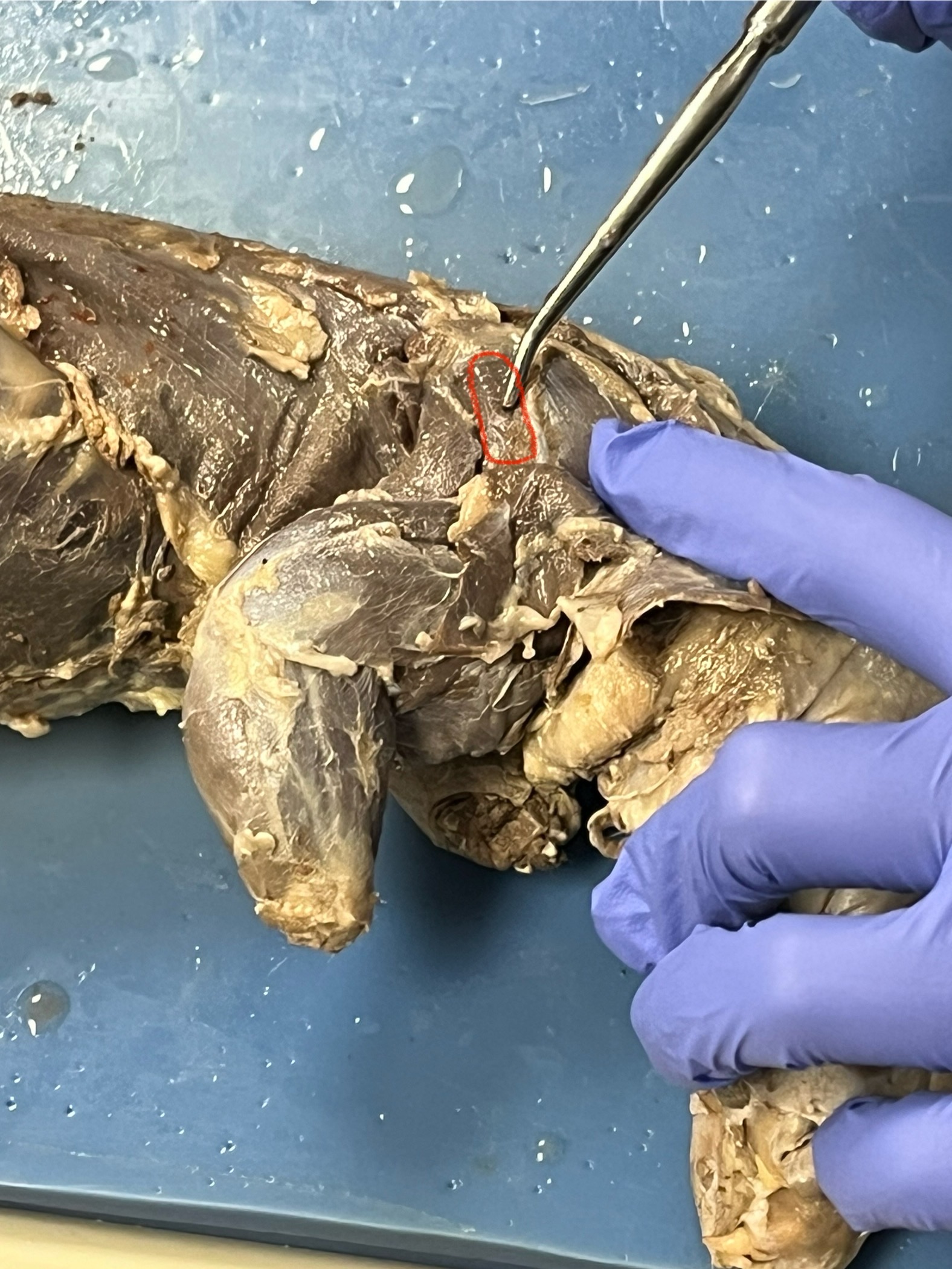
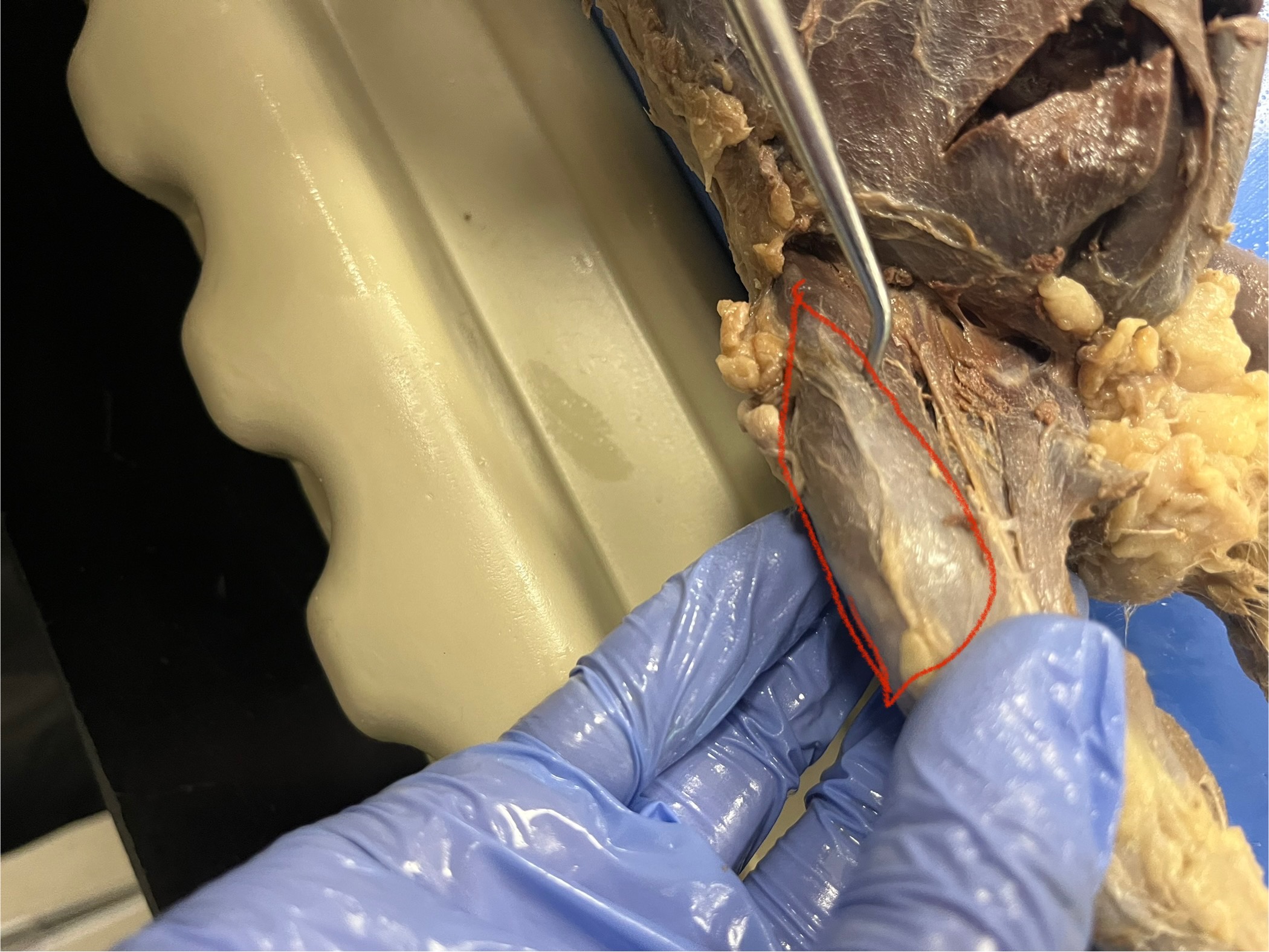
Infraspinatus
a small muscle located on the lateral surface of the scapula, just below the spine of the scapula, and attaches to the humerus
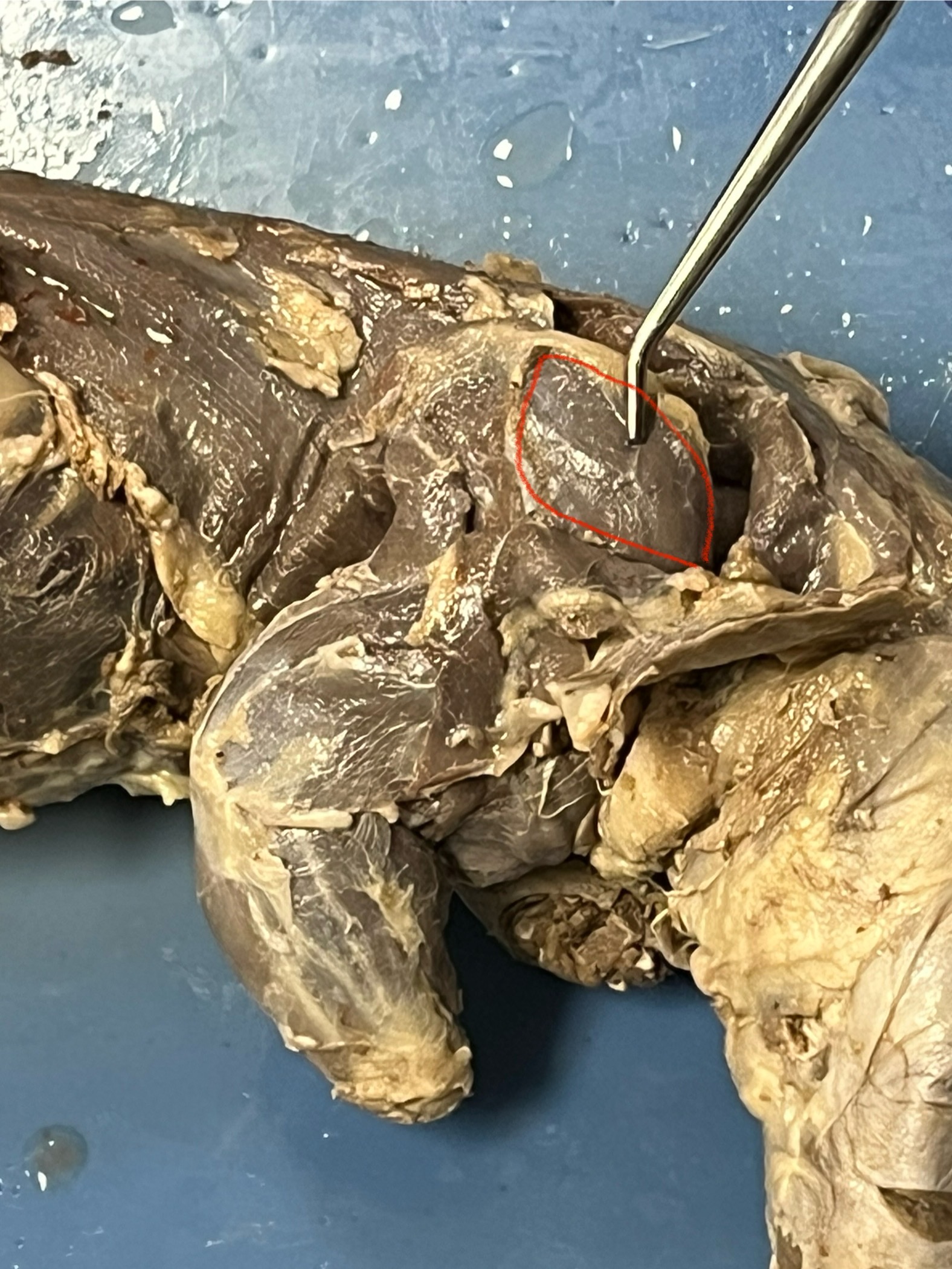
Supraspinatus
located on the dorsal side of the scapula, just above the spine of the scapula, and extends to the humerus.
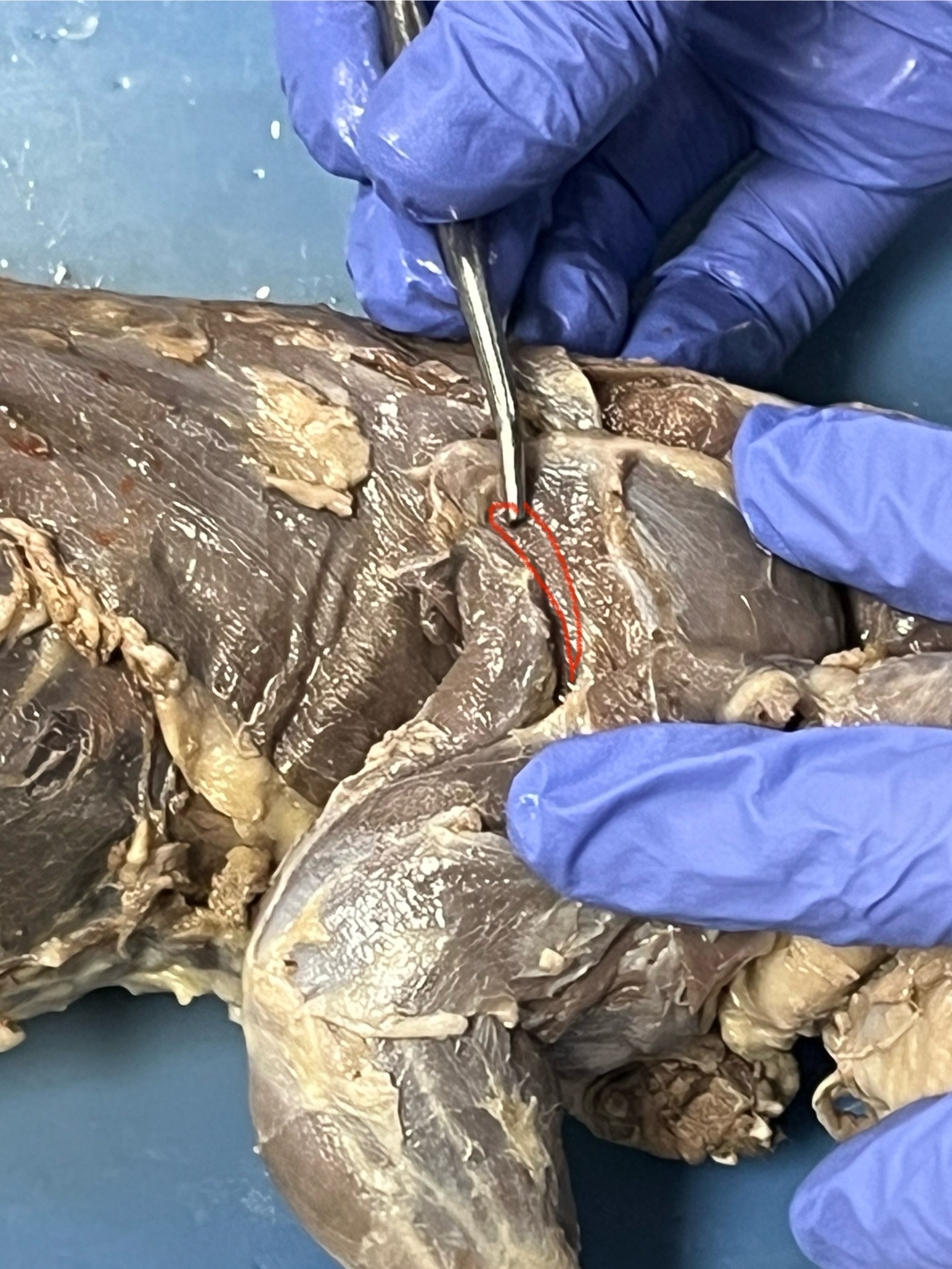
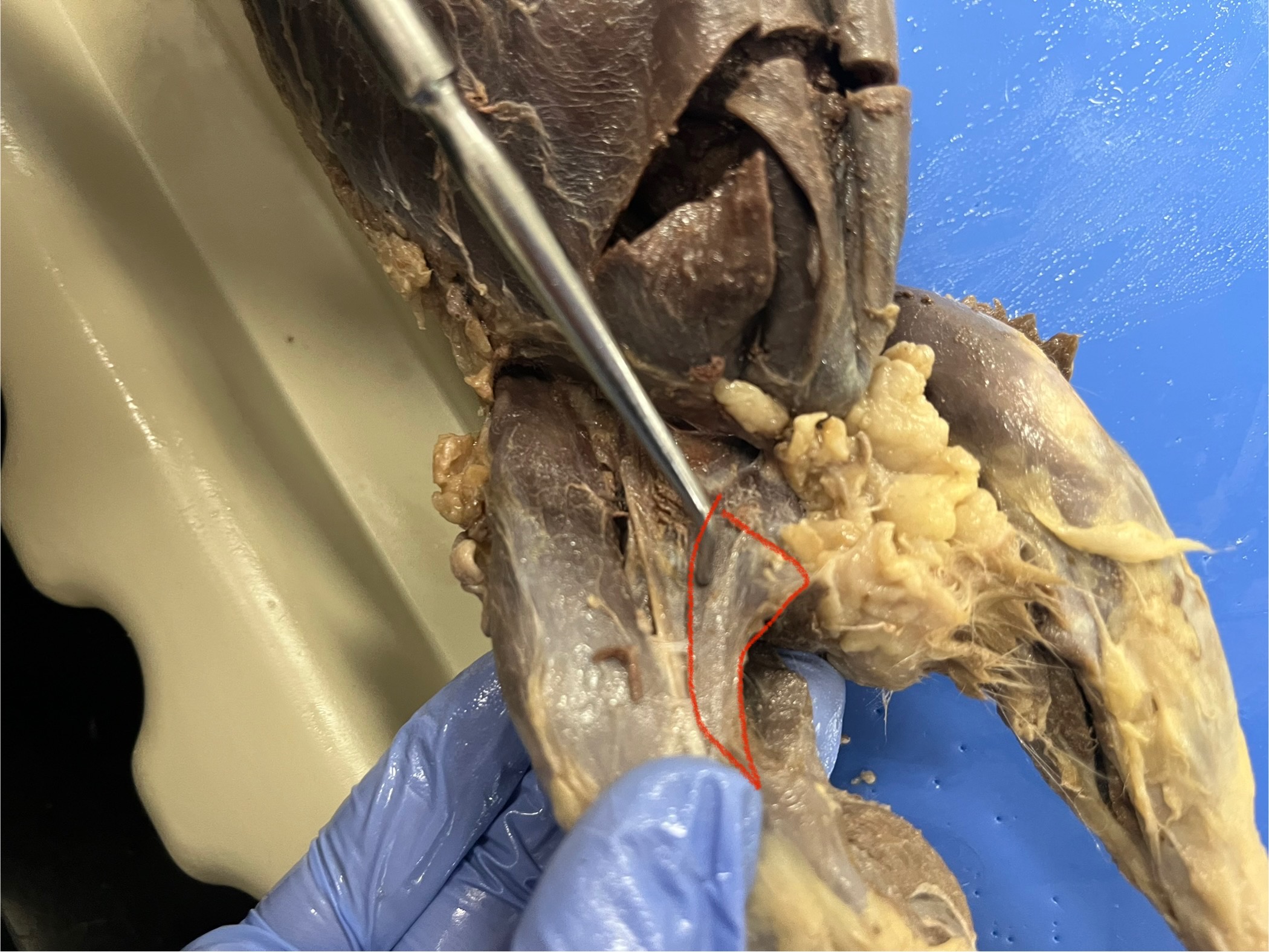
Tere major
a small, thick muscle located on the underside of the scapula, near its posterior (rear) edge, and attaches to the humerus
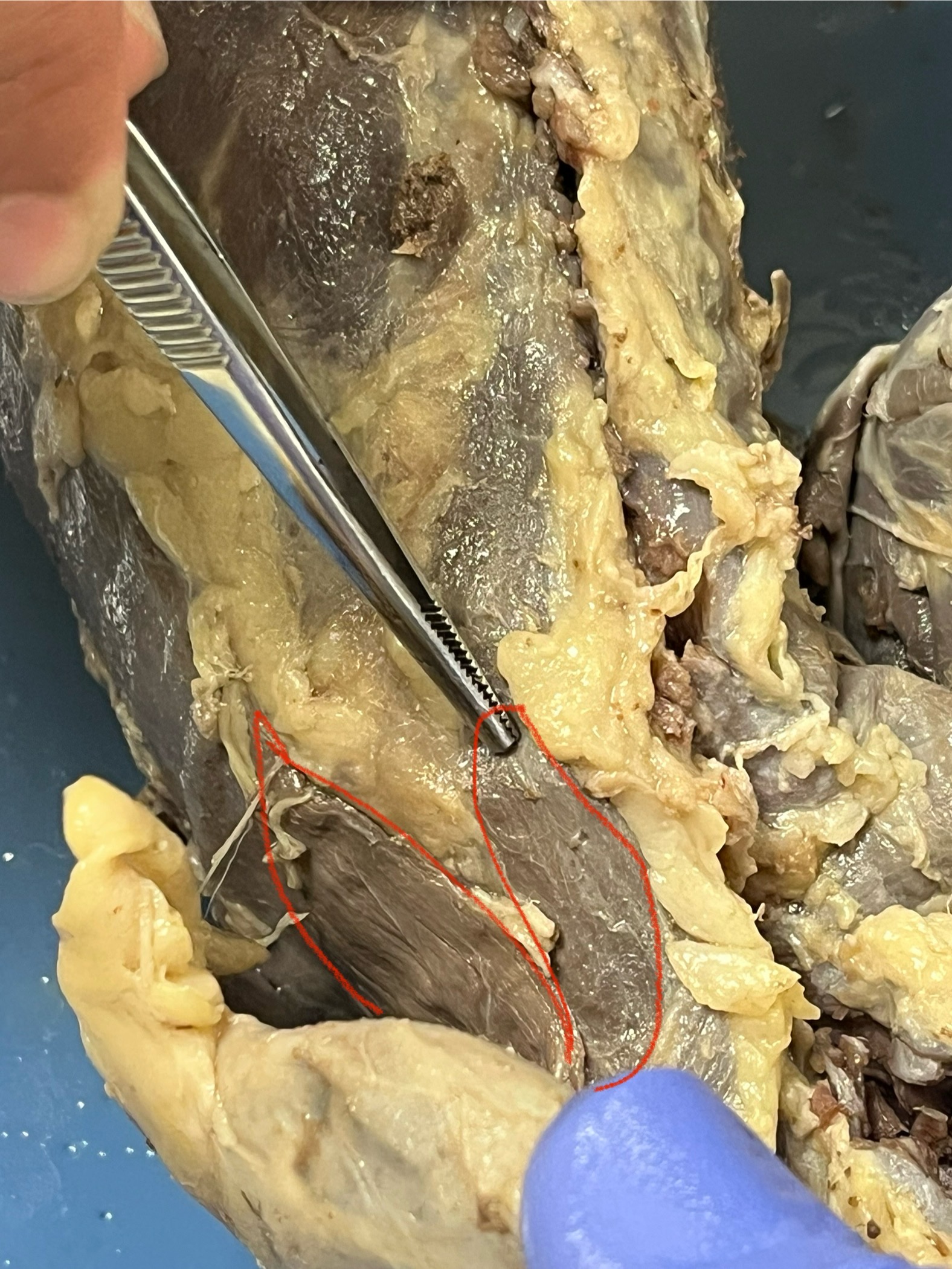
Pectoralis Minor
a thin muscle located beneath the pectoralis major, running from the sternum to the proximal humerus.
Pectoralis Major
a big muscle on the front of the mink’s chest. It connects the breastbone to the upper arm and helps the mink move its front legs.
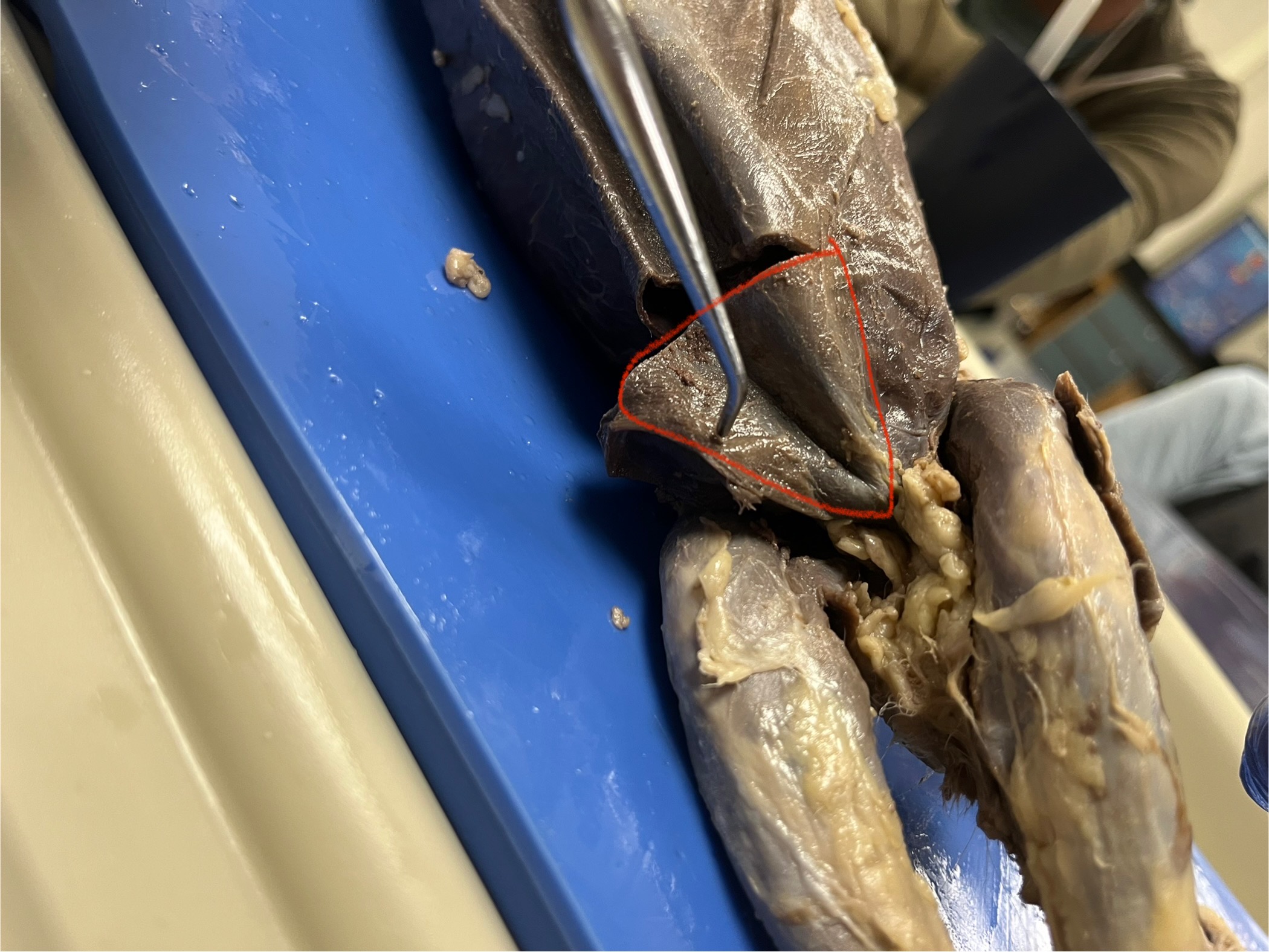
External Obliques
muscles on the sides of the belly. They help twist the body and bend it sideways. In a mink, these muscles wrap around the sides of the torso and support movement and flexibility.
Internal Obliques
muscles located just underneath the external obliques, also on the sides of the belly. They help the body twist and bend sideways, working together with the external obliques to support movement and protect the organs inside the belly. In a mink, they’re inside the sides of the torso, helping with twisting and turning motions.
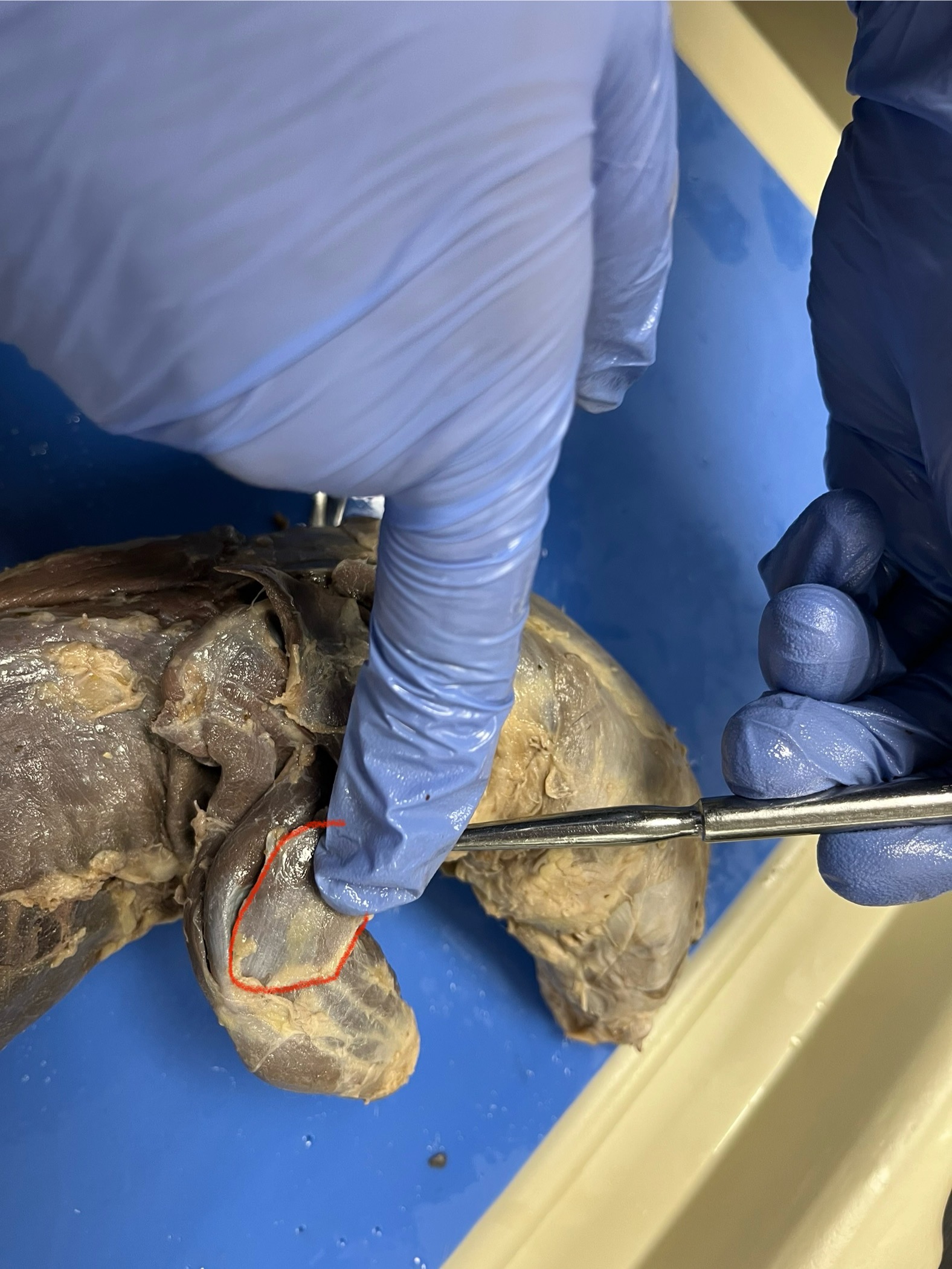
Triceps Brachii (Long Head)
runs from the shoulder blade down the back of the arm to the elbow. It helps straighten the front leg and pull the arm backward, which is important for digging, climbing, and running
Triceps Brachii (Lateral Head)
on the outer side of the upper arm. It helps straighten the front leg by extending the elbow, which is important for pushing, running, and other strong arm movements.
Triceps Brachii (Medial Head)
lies deeper and closer to the bone under the other two heads. It helps straighten the front leg by extending the elbow, working quietly but steadily to support movements like digging and running.
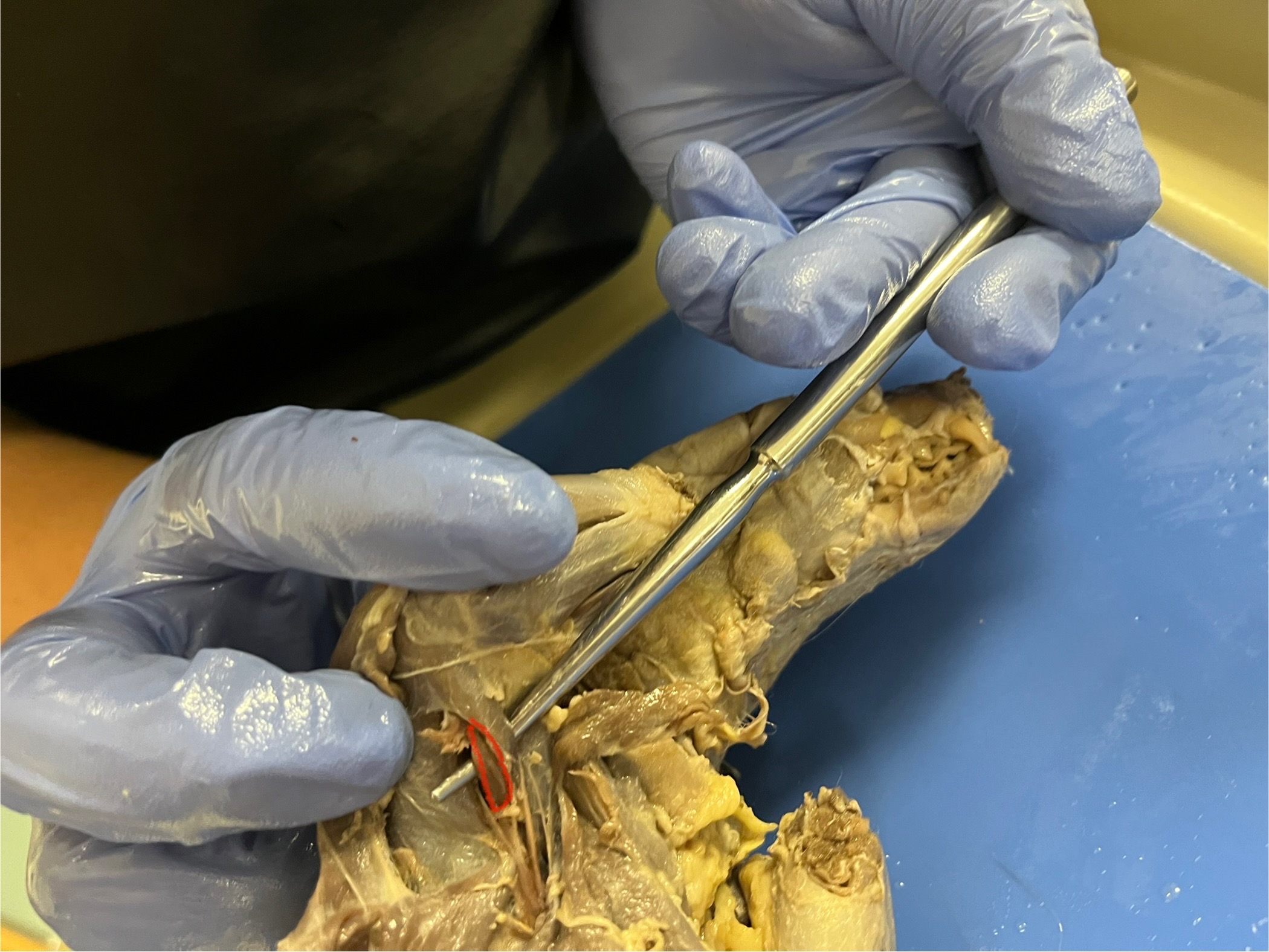
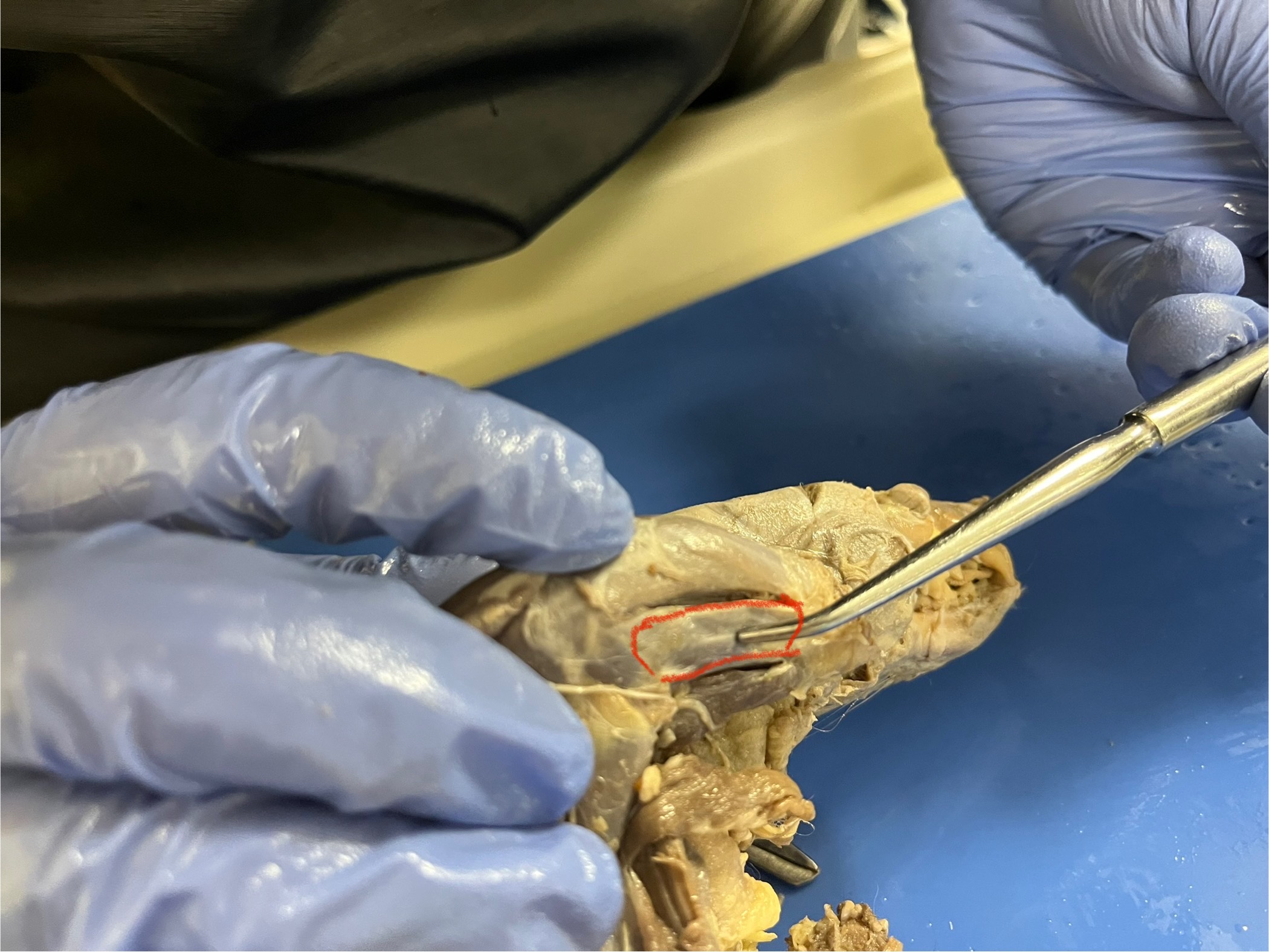
Palmaris Longus
runs from the lower part of the forearm near the elbow down toward the wrist. It helps tighten the skin and tissues in the paw, which can improve grip and control when the mink is climbing or grabbing things.
Epitochlearis
located on the back of the upper arm, near the elbow. It helps extend (straighten) the forearm and assists the triceps muscle during movement. This muscle is important for quick and precise arm actions like climbing or digging.
Sartorius
starts near the hip and stretches diagonally across the thigh to the inside of the knee. It helps the mink bend the leg and rotate it outward, which is useful for walking, climbing, and changing direction quickly.
Gracilis
runs from the pelvis down the inside of the leg to the lower thigh. It helps pull the leg inward (adduction) and also assists in bending the knee, which helps with walking and stabilizing movements.
Gluteus Maximus
found at the back of the hip and helps move the hind leg backward and outward. This muscle is important for powerful movements like running, jumping, and climbing.
Gluteus Medius
located on the side of the hip, just above the gluteus maximus
Biceps Femoris
runs from the pelvis down the back of the leg to the lower leg bones. It helps bend the knee and move the hind leg backward, which is important for running, jumping, and swimming
Vastus Lateralis
a muscle on the outer side of the front thigh.
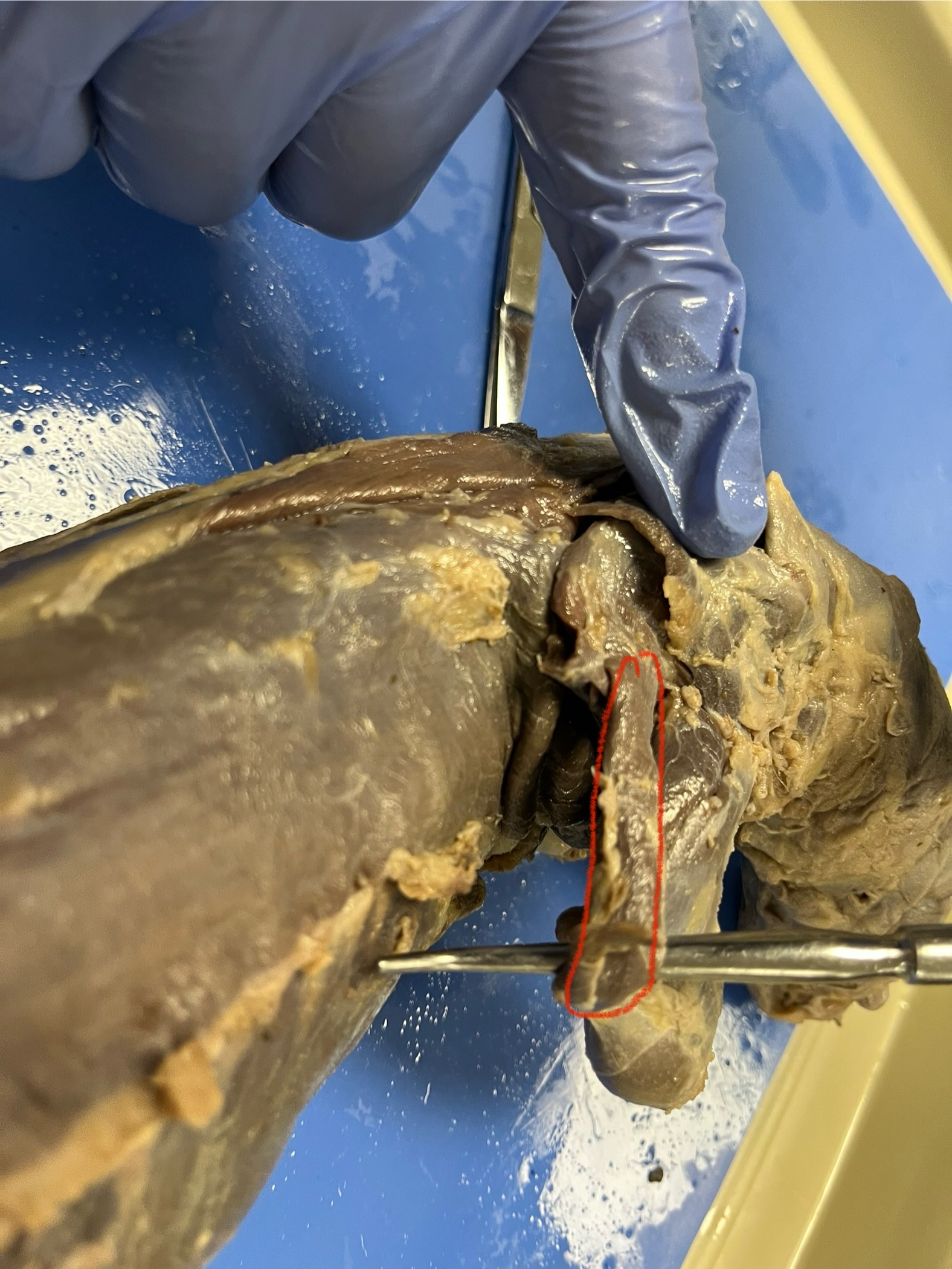
Archilles Tendon
connects the calf muscles to the heel bone and helps push off the ground when the mink runs, jumps, or climbs. It’s essential for powerful and quick movements of the hind leg.
Gastrocnemius
a large calf muscle located at the back of the lower leg.
Soleus
a muscle located underneath the gastrocnemius in the lower leg.
Rectum
located at the end of the digestive tract, inside the lower abdomen, and stores solid waste (feces) before it leaves the body through the anus.
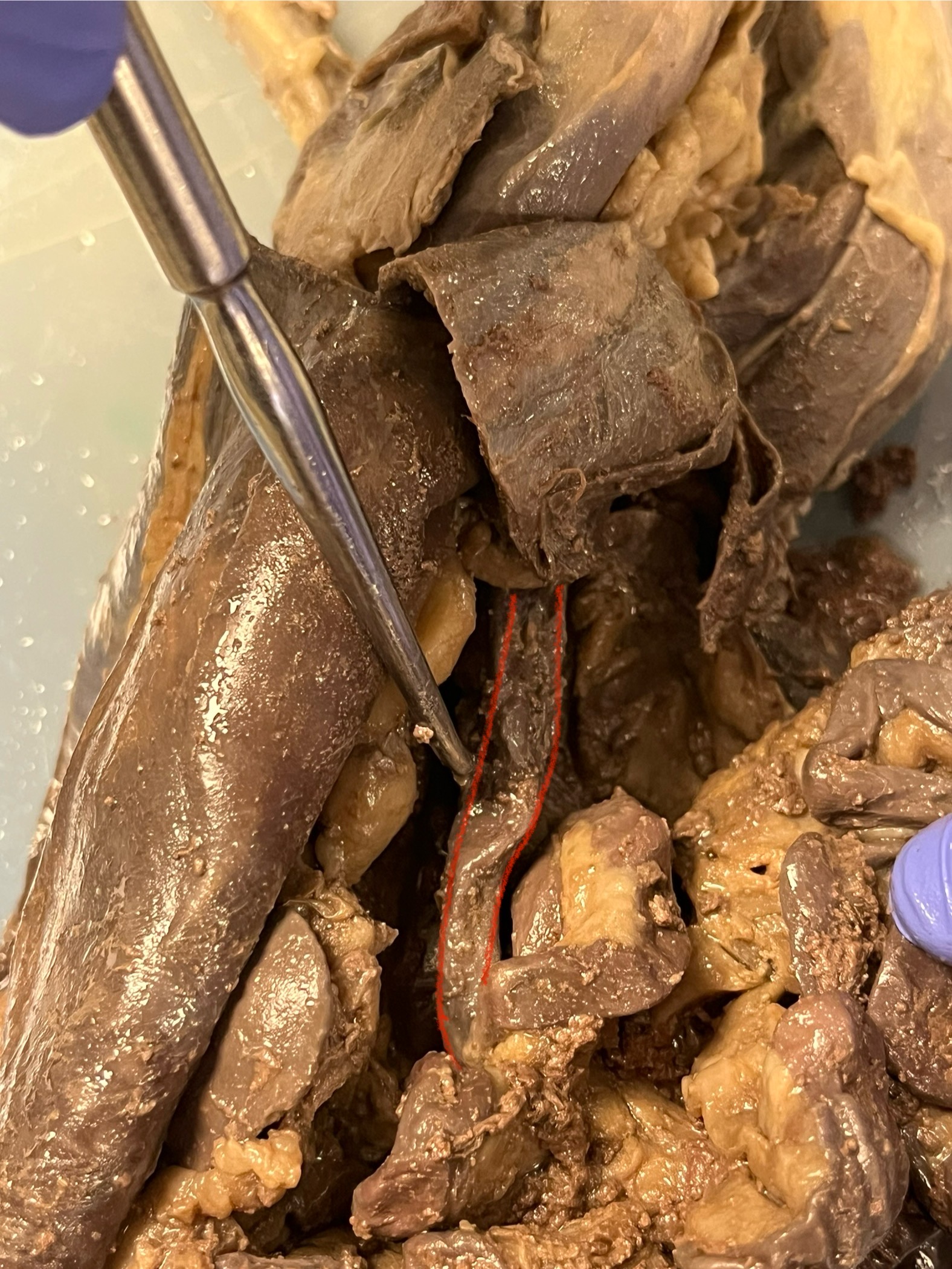
Large Intestine
runs through the lower belly and absorbs water and nutrients from food leftovers, turning them into solid waste before it passes to the rectum for removal.
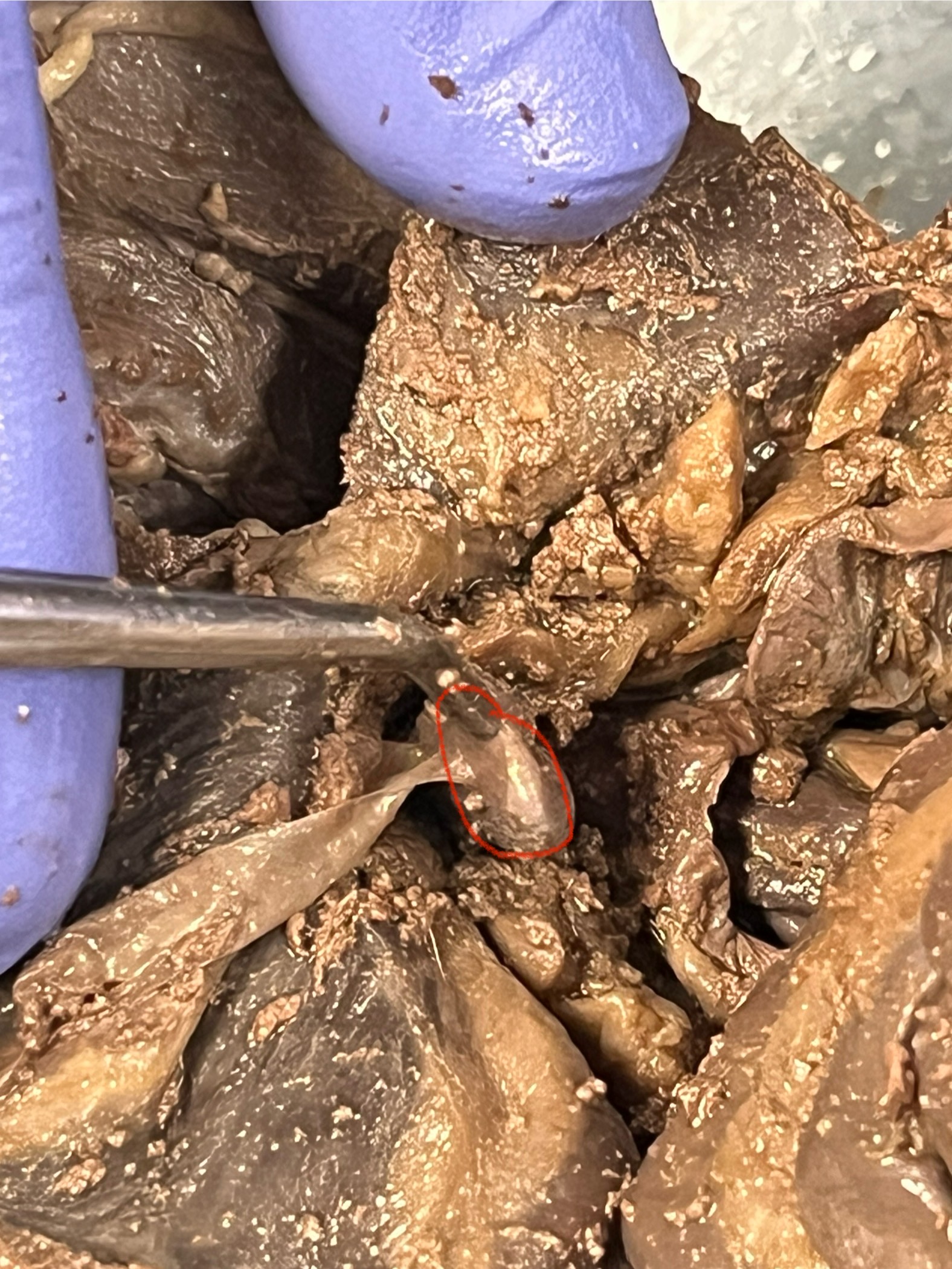
Kidney
two bean-shaped organs located in the lower back area on either side of the spine.