BISC306 Final Exam (Contains Cardio 1&2, Resp, Renal/WAB, & GI)
1/243
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
244 Terms
Which of the following changes would most increase the resistance to blood flow in a blood vessel?
A. Doubling the diameter of the vessel
B. Halving the length of the vessel
C. Halving the diameter of the vessel
D. Doubling the length of the vessel
E. Decreasing the hematocrit from 50% to 40%
C. Halving the diameter of the vessel
Consider the equation F = dP/R. It describes the flow (F) of fluid in a tube in which there is a pressure difference (dP) between the two ends (X & Y) and a resistance (R) to flow. The equation indicates that
A. the flow of fluid in a tube depends upon the absolute pressure at the beginning of the tube
B. the flow of fluid from point X to point Y in a tube depends upon the difference in pressure between X and Y
C. the greater the resistance to flow in a tube, the greater the flow for any given pressure difference
D. both A and B are correct
E. Both B and C are correct
B. the flow of fluid from point X to point Y in a tube depends upon the difference in pressure between X and Y
Which of the following statements regarding the cardiac cycle is correct?
A. The atrioventricular valves are open during mid-to-late diastole
B. The aortic valve is open during isovolumetric ventricular contraction
C. The first heart sound is the closing of the semilunar valves
D. During isovolumetric ventricular relaxation, blood flows from the atria into the ventricles
E. The volume of blood leaving the left side of the heart is greater than that leaving the right side
A. The atrioventricular valves are open during mid-to-late diastole
The aortic valve
A. Prevents the backflow of blood into the aorta during ventricular diastole
B. Prevents the backflow of blood into the aorta during ventricular ejection
C. Prevents the backflow of blood into the left ventricle during ventricular ejection
D. Prevents the backflow of blood into the left ventricle during ventricular diastole
D. Prevents the backflow of blood into the left ventricle during ventricular diastole
Normally, the hydrostatic pressure difference between capillary fluid and interstitial fluid favors movement of fluid _______ the capillary. The osmotic pressure difference between capillary fluid and interstitial fluid favors movement of fluid _________ the capillary.
A. into; into
B. Into; out of
C. out of; out of
D. out of; into
D. out of; into
Ventricular contraction
A. begins during the first part of the P wave
B. begins just after the T wave
C. begins just after the Q of QRS
D. begins during the latter part of the P wave
E. none of the above
C. begins just after the Q of QRS
Cardiac muscle cannot undergo tetanus because its absolute refractory period lasts almost as long as the muscle twitch.
A. True
B. False
A. True
Cardiac output is equal to
A. the difference between the end-diastolic volume and the end-systolic volume
B. The product of heart rate and stroke volume
C. the difference between the stroke volume at rest and the stroke volume during exercise
D. the stroke volume less the end-systolic volume
E. the product of heart rate and blood pressure
B. The product of heart rate and stroke volume
If the membranes of the cardiac muscle cells in the SA node become more permeable to potassium ions,
A. the heart rate will increase
B. the heart rate will decrease
C. the membrane will depolarize
D. the stroke volume will increase
E. the intracellular concentration of Ca2+ ion will increase
B. the heart rate will decrease
In which situation would the stroke volume be the greatest?
A. when calcium channel blockers are present
B. when the force of contraction is decreased
C. when venous return is decreased
D. when the difference between the end-diastolic volume and the end-systolic volume is small
E. when venous return is increased
E. when venous return is increased
Put these phases of the cardiac cycle in the correct order.
1. opening of the semilunar valves
2. isovolumic contraction
3. beginning of atrial systole
4. closure of the AV valves
5. completion of ventricular filling
6. beginning of ventricular systole
7. ventricular relaxation
8. ventricular ejection
C. 3, 5, 6, 4, 2, 1, 8, 7
The difference between the systolic and diastolic pressure is called the
A. systemic pressure
B. mean arterial pressure
C. pulse presssure
D. blood pressure
E. circulatory pressure
C. pulse presssure
Which of the following is greater?
A. blood pressure when sympathetic stimulation to the heart increases
B. blood pressure when parasympathetic stimulation to the heart increases
A. blood pressure when sympathetic stimulation to the heart increases
If action potential propagation through the bundle of His were blocked, which of the following events would you expect to occur?
A. there would be a slowing of the rate of contraction of the ventricles
B. the atria would contract more frequently than the ventricles
C. the atria would be unable to contract
D. the ventricles would go into fibrillation
E. both A and B
E. both A and B
Large doses of certain stimulants can lead to dangerous increases in heart rates. Such a stimulant is a
A. positive chronotropic agent
B. negative chronotropic agent
C. positive inotropic agent
D. negative inotropic agent
A. positive chronotropic agent
An autorhythmic heart cell is one in which
A. action potentials fire spontaneoulsy.
B. action potentials are stimulated by internal stores of acetylcholine.
C. action potentials always occur at exactly the same frequency.
D. all filaments contract and relax with a high degree of synchrony.
E. action potentials are initiated by the autonomic nervous system.
A. action potentials fire spontaneously.
The force per unit area that blood places on the inside wall of a blood vessel:
A. is called the pulse
B. is called the blood pressure
C. increases the further the vessel is from the heart
D. is greater during diastole
B. is called the blood pressure
Which of the following is not one of the three main factors influencing stroke volume?
A. afterload
B. chronotropic agents
C. inotropic agents
D. venous return
B. chronotropic agents
Which heart chambers would contain deoxygenated blood?
A. left atrium and right atrium
B. left ventricle and right ventricle
C. right atrium and right ventricle
D. left atrium and left ventricle
E. right atrium and left ventricle
C. right atrium and right ventricle
Which region of the ECG reflects the plateau phase of ventricular muscle cells' action potentials?
A. P-T segment
B. S-T segment
C. Q-R segment
D. P-R interval
E. T-P interval
B. S-T segment
As blood moves from the arterial end to the venous end of a capillary, net filtration pressure:
A. increases, as blood hydrostatic pressure rises
B. increases, as blood colloid osmotic pressure rises
C. decreases, as blood hydrostatic pressure decreases
D. decreases, as blood colloid osmotic pressure decreases
E. remains the same, as rises in blood osmotic pressure are offset by declines in tissue osmotic pressure
C. decreases, as blood hydrostatic pressure decreases
Atherosclerosis (fat build-up in artery walls, which narrows the arteries) involves a:
A. sustained increase in blood flow that leads to decreases in venous resistance to keep blood pressure constant
B. sustained increase in resistance that leads to increases in arterial pressure to maintain adequate blood flow
C. sustained decrease in resistance that leads to decreases in arterial pressure to maintain adequate blood flow
D. sustained decrease in blood flow that leads to increases in arterial diameter to lower resistance and raise pressure
E. sustained increase in blood pressure that leads to compensatory vasodilation
B. sustained increase in resistance that leads to increases in arterial pressure to maintain adequate blood flow
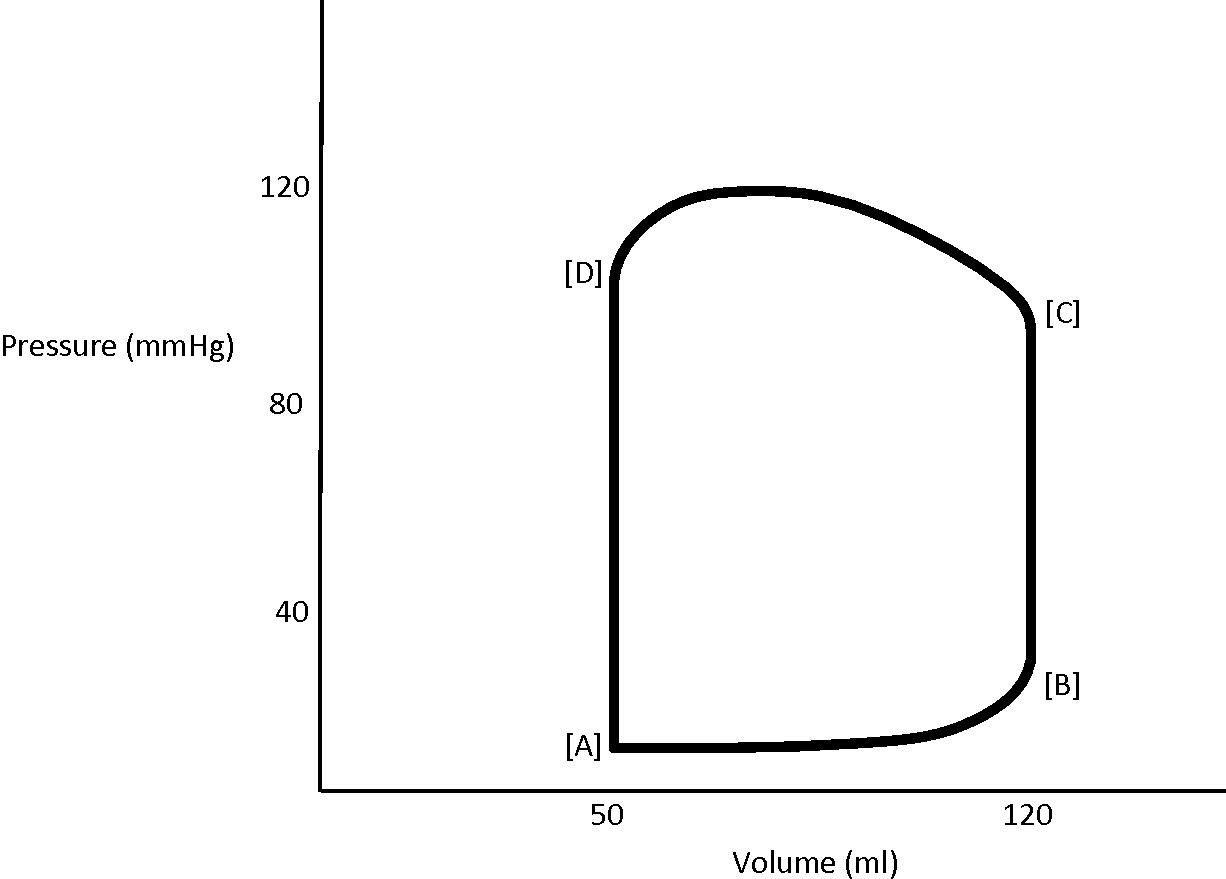
The period of isovolumic (isovulumetric) contraction is indicated by ______ on the diagram.
A. the A-B interval
B. the B-C interval
C. the C-D interval
D. the A-D interval
B. the B-C interval
Which of the following is not primarily a function of blood plasma
A. Transport of hormones
B. Being in osmotic balance with red blood cells
C. Having plasma proteins that exert an osmotic pressure favoring fluid absorption into the capillaries
D. Providing clotting factors that are ready to be activated
E. Transport of oxygen
E
The left ventricle has a thicker wall than the right ventricle because the left ventricle has to pump blood against a higher pressure
A. True
B. False
A
The pacemaker of the heart is normally what structure
A. Sinoatrial node
B. Atrioventricular node
C. Mitral valve
D. Bundle of His
E. Left ventricle
A
The plateau of the action potential in cardiac ventricular cells results from the opening of voltage-gated long-lasting ________channels in the plasma membrane of the cell
A. Na+
B. K+
C. Ca2+
D. Cl-
E. Glucose
C
Which of the following would be most likely to be determined with a patient's ECG recording
A. A heart murmur
B. Stroke volume
C. Cardiac output
D. Blockage of conduction of electrical signals between the atria and the ventricles
E. A leaky atrioventricular valve
D
Which of the following statements about the cardiac cycle is true
A. The duration of systole is greater than that of diastole in a subject at rest
B. During isovolumetric ventricular relaxation, blood flows from the atria into the ventricles
C. Closure of the atrioventricular valves occurs at the onset of ventricular systole
D. The QRS complex occurs at approximately the same time as the closure of the semilunar valves
E. The first valves to go from closed to open after the atrial kick are the atrioventricular valves
C
Which best defines the cardiac output
A. The end-diastolic volume minus the end-systolic volume
B. The output of the aortic arch baroreceptors
C. The volume of blood in the arterial tree at any moment in time
D. The stroke volume divided by the heat rate
E. The product of the heart rate and the volume ejected from the ventricle during a cardiac cycle
E
Which is true regarding regulation of heart rate
A. Stimulation of parasympathetic nerves to the heart causes a slowing of heart rate
B. Stimulation of sympathetic nerves to the heart causes an increase in heart rate
C. A person whose heart lacks autonomic innervation has a faster heart rate at rest than a person with a normal innervated heart
D. The slope of diastolic depolarization in SA node cell action potentials determines the heart rate
E. All of the choices are true
E
According to the Frank-Starling mechanism of the heart
A. The left ventricle ejects a larger volume of blood with each systole than the right ventricle
B. The intrinsic rate of the heart's pacemaker is 100 beats/min
C. Cardiac output increases with increased heart rate
D. Stroke volume increases with increased venous return
E. Both ventricles contract simultaneously
D
If the arterial blood pressure in the brain is suddenly decreased, the flow through arterioles in the brain will immediately fall and then which of these will occur next
A. Brain arterioles will constrict to accelerate blood flow through the brain capillaries
B. Brain arterioles will dilate due to a decrease in levels of CO2
C. Blood flow will remain at the new, lower level due to reactive hyperemia
D. Blood flow will rise to levels above normal due to excess O2 levels
E. Blood flow will return toward its original level due to flow autoregulation
E
Normally, the hydrostatic pressure difference between capillary fluid and interstitial fluid favors movement of fluid ________ a tissue capillary. The protein osmotic pressure difference between capillary fluid and interstitial fluid normally favors movement of fluid ________ a tissue capillary.
A. Into; into
B. Into; out of
C. Out of; out of
D. Out of; into
D
Which of the following statements concerning the capillaries is false
A. Increasing capillary hydrostatic pressure decreases the likelihood that filtration will occur
B. Velocity of blood flow is slower in the capillaries than in the arteries
C. It is possible for a capillary to filter fluid at its arterial end and absorb fluid at its venous end
D. Large capillary pores are more likely to be found in liver capillaries than in brain capillaries
E. Large proteins that escape capillaries and enter the interstitial fluid are returned to the circulation via the lymphatic system
A
Following hemorrhage, reflexes are triggered that attempt to compensate for the blood loss. As a result of the blood loss and the reflex mechanisms, which of the following will be TRUE, compared to pre-hemorrhage values
A. Both cardiac output and total peripheral resistance will be increased
B. Both cardiac output and total peripheral resistance will be decreased
C. Cardiac output will be increased and total peripheral resistance will be decreased
D. Cardiac output will be decreased and total peripheral resistance will be increased
E. Hematocrit will be increased
D
Which of the following occurs first in hemostasis
A. Activation of the fibrinolytic system
B. Platelet aggregation
C. A clotting cascade that leads to the conversion of fibrinogen to stable fibrin
D. Conversion of prothrombin to thrombin
E. Conversion of plasminogen to plasmin
B
The condition of shock is an example of failure of homeostatic mechanisms to compensate when one or more parts of the reflex control system are damaged
A. True
B. False
A
The valve located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary trunk (artery) is the
a. aortic semilunar valve.
b. pulmonary semilunar valve.
c. tricuspid valve.
d. mitral valve.
e. bicuspid valve.
b
An incompetent pulmonary semilunar valve could result in less blood reaching the
a. lungs.
b. heart muscle.
c. right ventricle.
d. aorta.
e. right atrium.
A
An incompetent mitral valve may cause blood to back up into the
a. aorta.
b. left atrium.
c. left ventricle.
d.coronary circulation.
e. right atrium.
B
When a pacemaker potential in the SA node reaches threshold,
a.the permeability to K+ ions increases.
b. many voltage-gated Ca2+
channels open.
c. voltage-gated Ca2+ channels close.
d. RMP has been restored.
e.permeability of the cell does not change.
b
Which of the following will depolarize immediately after the AV node depolarizes?
a.the AV bundle
b. Purkinje fibers
c. atrial myocardium
d.bundle branches in
the ventricular septum
A
The spontaneous opening of sodium channels marks the beginning of ____ of a myocardial
contractile cell.
a.depolarization
b. repolarization
c.hyperpolarization
d. isopolarization
A
The plateau phase seen during the action potential of a cardiac muscle cell is due to the
a.sodium-potassium pump.
b.opening of sodium channels.
c.continuing to have open calcium channels.
d.closure of chloride channels.
e.closing of calcium channels.
C
Which of the following is mismatched?
a.opening of sodium channels
-depolarization
b.closing of calcium channels
-plateau phase
c.opening of potassium channels
-rapid repolarization
d.opening of calcium channels
-plateau phase
B
Which of the following would result from a reduced function of the sodium channels in the SA
node?
a.depolarization would be delayed
b.the heart rate would decrease
c. repolarization would not occur
d.a shortened plateau phase
e.depolarization would
be delayed and the heart rate would decrease
E
What wave is atrial depolarization?
P wave
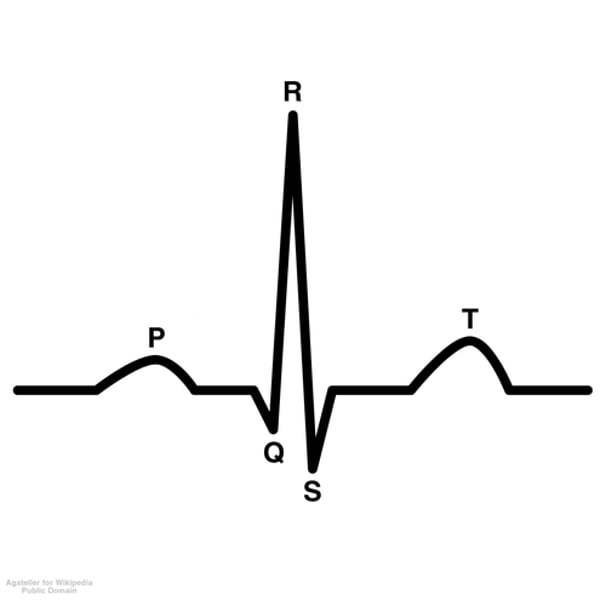
What wave is ventricular repolarization?
T wave
Which of the following is greater?
a.blood pressure when sympathetic stimulation to the heart increases
b.blood pressure when parasympathetic stimulation to the heart increases
A
Atherosclerosis (fat build-up in artery walls, which narrows the arteries) involves:
a: a.sustained increase in blood flow that leads to decreases in venous resistance
to keep blood pressure constant.
b.sustained increase in resistance that leads to increases in arterial pressure to
maintain adequate blood flow.
c. sustained decrease in resistance that leads to decreases
in arterial pressure to
maintain adequate blood flow.
d. sustained decrease in blood flow that leads to increases in arterial diameter to lower
resistance and raise pressure.
e.sustained increase in blood pressure that leads to compensatory vasodilation.
b
which of the following is the same in the action potential of a neuron and autorhythmic myocardium?
ions responsible for repolarization (falling phase)
- Potassium ions
During isovolumetric contraction
small amount of extracellular calcium enters the cell through L-type calcium channels during the plateau phase of action potential
- Ca 2+ binds to the ryanodine receptors on the SR and triggers fast Ca 2+ channels
The QRS complex represents the
depolarization of the ventricles
If blood pressure rises what happens to net filtration across the capillary wall?
increases
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) formula
((2*DP)+SP)/3
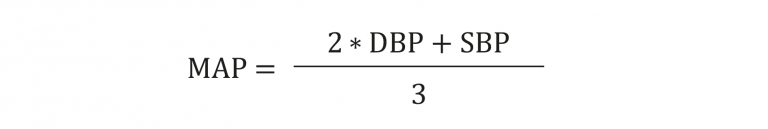
________ are seen as the bottom layer of centrifuged blood
Erythocytes
Formula for net filtration pressure
NFP= (HPb-HPif)- (COPb- COif)
- usually (COPb- COif) is around 0 in normal cases.

Characteristics of Type O Blood
-has anti A antibodies
-has anti B antibodies
-has neither surface antigen A nor B on its erythrocytes
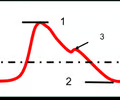
what is the dichrotic notch? How does it impact pressure?
brief rise in aortic pressure caused by backflow of blood rebounding off semilunar valves
What is autoregulation?
the intrinsic ability of an organ or tissue to adjust blood flow according to its needs
What are the effects of the baroreceptor reflex?
Parasympathetic stimulation
- decreased stroke volume
- vasodilation
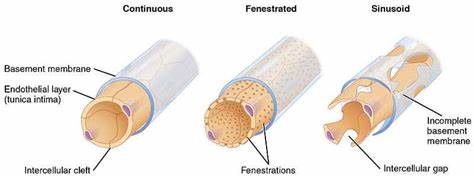
3 types of capillaries
Continuous: Tightest control, most common (muscles, skin). Allow water, oxygen, nutrients, and small waste.
Fenestrated: Leaky with small holes (fenestrations) for faster exchange (intestines, kidneys). Allow larger molecules too.
Sinusoidal (Discontinuous): Leakiest and largest, with big gaps for massive exchange (liver, spleen). Allow even blood cells to pass.
Distinguish between systolic pressure, diastolic pressure, pulse pressure, and mean arterial pressure
Systolic: Peak pressure during heartbeat (higher number).
Diastolic: Pressure when heart relaxes (lower number).
Pulse pressure: Difference between systolic and diastolic (pressure variation).
Mean arterial pressure: Average pressure in arteries (combines systolic and diastolic).
Distinguish between capillary hydrostatic pressure and blood colloid osmotic pressure, explaining the contribution of each to net filtration pressure
Capillary hydrostatic pressure (CHP): Pushes fluid out of capillaries due to blood pressure. Think: water pressure in a hose.
Blood colloid osmotic pressure (BCOP): Pulls fluid in due to proteins in blood that can't easily pass through capillary walls. Imagine a sponge soaking up water.
Net filtration pressure (NFP) determines fluid movement:
NFP = CHP - BCOP
Positive NFP (CHP > BCOP): Fluid filters out (filtration).
Negative NFP (CHP < BCOP): Fluid gets pulled back in (absorption).
Describe how blood flow, blood pressure, and resistance interrelate and the factors the influence them.
Flow: Amount of blood moving through a vessel.
Pressure: Force blood exerts on vessel walls.
Resistance: Opposition blood faces as it flows (like friction).
What affects them?
Blood volume: More blood, potentially higher pressure and flow (if resistance stays low).
Heart rate: Faster pumping, potentially higher pressure and flow.
Vessel diameter: Wider vessels = lower resistance, higher flow. Narrowed vessels = higher resistance, lower flow.
Blood thickness: Thicker blood = higher resistance, lower flow.
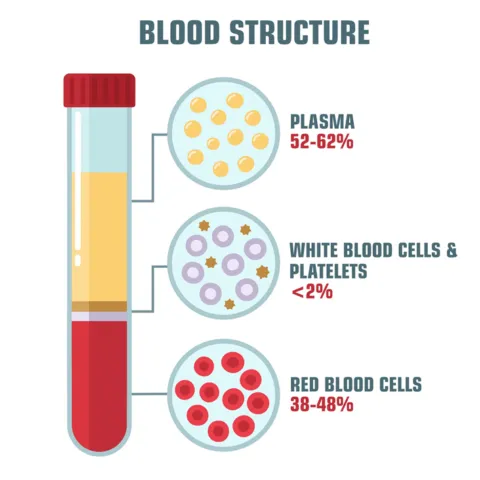
Describe the overall composition of blood, including plasma and cells, and their overall functions.
Plasma (55%)- Straw-colored transport system carrying:
Cells (RBCs, WBCs, platelets)
Nutrients & waste products
Proteins (balance & clotting)
WBC/Platelets (55%)-
WBCs: Defend against infection (tiny amount).
Platelets: Help clot blood to stop bleeding (tiny amount).
RBCS (55%)- Carry oxygen throughout the body using hemoglobin.
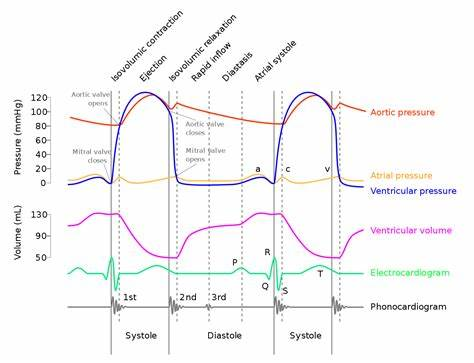
Label Wiggers Diagram IMPORTANT
Which hormone directly stimulates sodium reabsorption in the kidneys?
- angiotensin I
- erythropoietin
- aldosterone
- renin
aldosterone
The volume of air flowing into the alveoli during inhalation/inspiration is increased when there is an increase in (select all that apply)
a. airway resistance
b. airway resistance and the pressure gradient from the atmosphere to the alveoli
c. the pressure gradient from the atmosphere to the alveoli
d. the rate of action potential firing in the motor neurons to the inhalatory/inspiratory muscles
c. the pressure gradient from the atmosphere to the alveoli
d. the rate of action potential firing in the motor neurons to the inhalatory/inspiratory muscles
What does a right shift on the hemoglobin saturation curve mean?
A. It means hemoglobin is being generous and giving up oxygen to the blood
B. It means that hemoglobin is being stingy and hanging on to oxygen, not releasing it to the blood
C. Hemoglobin does not bind oxygen
A. It means hemoglobin is being generous and giving up oxygen to the blood
A patient has a kidney condition that results in the loss of albumin in the urine that exceeds the body's albumin production. The resulting hypoalbuminemia will lead to edema of the extremities. Which of the following is likely to be noted?
A. Increased lymph flow
B. Decreased interstitial fluid hydrostatic pressure
C. Increased in plasma oncotic pressure
D. Increased capillary hydrostatic pressure
A. Increased lymph flow
The word "countercurrent" within "countercurrent multiplier" refers to the opposite direction of flow of _______
(couldn’t find any multiple choice options)
tubular fluid within the ascending & descending limb of the nephron loop
Generally, a very _______ percent of Na+ in the tubular fluid is reabsorbed, and the reabsorption takes place _________.
high, along the entire tubule
Place the regions of the nephron in the correct order for the process of urine formation.
a: Capsular space of glomerulus
b: Nephron loop
c: Collecting duct
d: Distal convoluted tubule
e: Proximal convoluted tubule
a, e, b, d, c
If there is an accumulation of acidic products in the plasma, one would expect
a.an increase in respiration rate.
b.a decrease in respiration rate.
c. no influence on respiration rate
d. an increase in residual volume.
a. an increase in respiration rate.
Most carbon dioxide is transported in the blood
a. in the form of bicarbonate ions
b.bound to hemoglobin.
c.dissolved in the plasma.
d. by the leukocytes
e. in the form of carbonic acid
a. in the form of bicarbonate ions
In which of the following sequences does PO2
progressively decrease?
a. body tissue, arterial blood, alveolar air
b. body tissue, alveolar air, arterial
blood
c. blood in aorta, atmospheric air, body tissues
d. atmospheric air, blood in aorta, body tissues
e. body tissue, aorta, alveolar air
d. atmospheric air, blood in aorta, body tissues
During exercise, the oxygen
-hemoglobin dissociation curve
a.shifts to the right.
b.shifts to the left.
c.doesn't shift.
a.shifts to the right.
Mr. Jones has a blood pH of 7.00 and a temperature of 100.5
F. His oxygen-hemoglobin
dissociation curve would
a.shift to the right, causing more O2 to be released to his cells.
b.shift to the left, allowing less O2 to be released to his cells.
c. show no change, allowing the O2 concentration to remain stable.
a.shift to the right, causing more O2 to be released to his cells.
When carbon dioxide levels in the blood increase, the:
a. condition is called hypocapnia.
b. pH of the blood increases.
c. blood becomes more acidic.
d.number of hydrogen ions in the blood decreases.
e.blood becomes more alkaline.
c. blood becomes more acidic.
A patient has severe pneumonia, which has thickened the respiratory membrane. Despite oxygen therapy, he still has rapid respiration and feels as if he is not getting enough air. This is
because:
a. the oxygen increases the stimulation of the carotid and aortic bodies.
b. the oxygen stimulates the respiratory center to increase the respiratory rate.
c. his blood pH increased and stimulated an increase in his respiratory rate.
d. even though he is receiving enough oxygen, carbon dioxide and hydrogen ions accumulate in his blood and cause the respiratory rate to continue to increase.
d.even though he is receiving enough oxygen, carbon dioxide and hydrogen ions accumulate in his blood and cause the respiratory rate to continue to increase.
As the result of an asthmatic attack:
a. ventilation exceeds the ability of blood to pick up oxygen.
b. ventilation is inadequate to oxygenate blood.
c. pulmonary blood flow is reduced while ventilation remains normal.
d. the surface area available for gas exchange increases.
e. bronchioles dilate.
b. ventilation is inadequate to oxygenate blood.
If the total pressure of a mixture of
gases was 760 mm Hg and its composition is 20% oxygen,
0.04% carbon dioxide, 75% nitrogen, and 5% water vapor, then the partial pressure of oxygen would be
a.740 mm Hg.
b.20 mm Hg.
c.148 mm Hg.
d.152 mm Hg.
e.200 mm Hg.
d. 152 mm Hg.
Solving: .2×760=152
During inspiration, contraction of the diaphragm causes the volume of Mr. Jones' thoracic cavity to increase and the pleural pressure to decrease. The pressure in his alveoli (Palv) will:
a. decrease below atmospheric pressure (PB), causing air to move out of his lungs.
b. become greater than atmospheric pressure (PB), causing air to move into his lungs.
c.decrease below atmospheric pressure (PB), causing air to move into his lungs.
d. become greater than atmospheric pressure (PB), causing air to move out of his lungs.
c.decrease below atmospheric pressure (PB), causing air to move into his lungs.
Air moves from High pressure—>Low pressure
Which of the following is part of the upper respiratory tract?
a.lungs
b.pharynx
c.bronchi
d.bronchioles
b. pharynx
all else is part of lower resp. tract
Which of the following is NOT true about oxygen/hemoglobin dissociation in the region directly surrounding exercising muscles?
A. Lactic acid release increases pH shifting the curve to the right
B. Increased heat produced during vigorous activity promotes oxygen dissociation, shifting the curve to the right
C. All of the above answers are correct
D. CO2 increases causing pH to decrease leading to increased oxygen dissociation
A. Lactic acid release increases pH shifting the curve to the right
The erythrocyte (red blood cell) count increases after a while when an individual goes from a low to a high altitude because the ________.
A. Temperature is lower at higher altitudes
B. Concentration of oxygen and/or total atmospheric pressure is lower at high altitudes
C. Concentration of oxygen and/or total atmospheric pressure is higher at higher altitudes
D. Basal metabolic rate is higher at high altitudes
B. Concentration of oxygen and/or total atmospheric pressure is lower at high altitudes
You may have noticed that after a large meal you have had some difficulty breathing. Which explanation is most accurate with regard to this situation?
A. Oxygen to the lungs is restricted due to fullness in the stomach.
B. The large quantity of food retards pulmonary blood flow.
C. A full stomach impedes contraction of the diaphragm, limiting inhalation.
D. The food presses on the bronchi making air flow difficult.
E. It's just difficult to fill the lungs since blood-filled oxygen is flowing primarily to the stomach.
C. A full stomach impedes contraction of the diaphragm, limiting inhalation.
Following an automobile accident, a broken rib penetrates into the pleural cavity without piercing through the skin. This leads to a lung collapse. Why does this occur?
A. A decrease in thoracic volume leads to an equality of intrapleural and alveolar pressures
B. Intrapleural pressure is now equal to atmospheric pressure
C. Intrapleural pressure is now equal to the pressure inside of the lung
D. Pleural fluid is now leaking into the thoracic cavity
C. Intrapleural pressure is now equal to the pressure inside of the lung
The reason air flows out of the body during expiration is that during that time:
A. intrapulmonary pressure is greater than atmospheric pressure.
B. atmospheric pressure is greater than intrapulmonary pressure.
C. Intrapleural pressure is greater than atmospheric pressure.
D. Intrapleural pressure is greater than intrapulmonary pressure
A. intrapulmonary pressure is greater than atmospheric pressure.
Which of the following INCORRECTLY describes mechanisms of CO2 transport?
A. As bicarbonate ions in plasma
B. Just over 20% of CO2 is carried in the form of carbaminohemoglobin
C. 7-10% of CO2 is dissolved directly into the plasma
D. Attached to the heme part of hemoglobin
D. Attached to the heme part of hemoglobin
Which of the following provide the greatest surface area for gas exchange?
A. Alveolar ducts
B. Respiratory bronchioles
C. Alveolar sacs
D. Alveoli
D. Alveoli
The symptoms of hyperventilation may be averted by breathing into a paper bag because it ________.
A. Reduces brain perfusion by constricting cerebral blood vessels
B. Helps retain oxygen in the blood
C. Lowers blood pH levels
D. Helps retain carbon dioxide in the blood
D) Helps retain carbon dioxide in the blood
The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the air in the alveoli and blood in the lungs is called:
A. Systemic respiration
B. Cellular respiration
C. Ventilation
D. External respiration
E. Internal respiration
D) External respiration
The amount of air that can be inspired above the tidal volume is called ________.
A. Expiratory capacity
B. Vital capacity
C. Reserve air
D. Inspiratory reserve volume
D. Inspiratory reserve volume
T/F The total dead space in the lungs includes anatomic dead space and any portion of the alveoli that has little or no blood supply.
True, dead space equals anatomical and physiological dead space
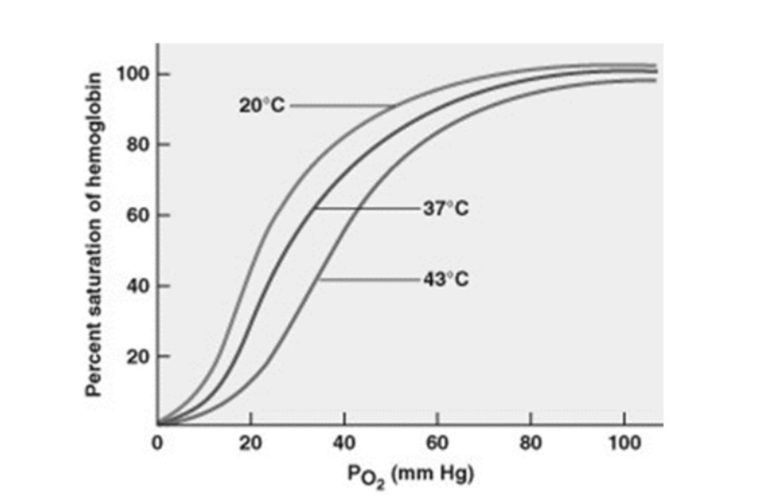
Based on this graph which of the following are true?
A)Greatest delivery of O2 from the blood to the surrounding tissues occurs at 37C, normal body temperature.
B) Fevers are dangerous because less O2 is being released/delivered to body cells.
C) Colder blood temperatures release more O2 from hemoglobin.
D) Hemoglobin has a lower affinity for O2 under higher body temperature conditions.
D) Hemoglobin has a lower affinity for O2 under higher body temperature conditions.
Organize the items listed into the proper sequence of events for gas exchange.
a: O2 is transported to cells by circulatory system.
b: O2 is drawn into the lungs during inhalation.
c: Cells use 02 and generate CO2.
d: CO2 is exhaled.
e: The circulatory system transports CO2 to the lungs.
b, a, c, e, d
Oxygenated hemoglobin releases oxygen more readily when the pH is more basic.
A. True
B. False
B) False