MSK ILS Practical 1
1/170
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
171 Terms
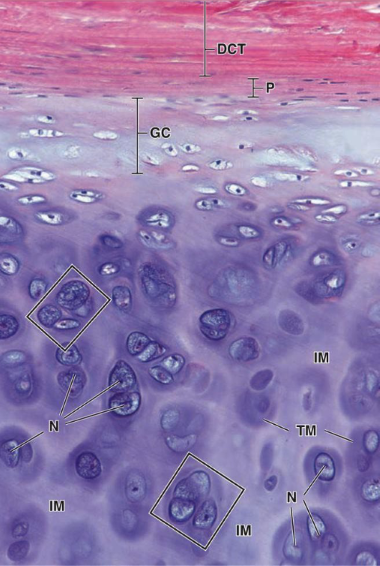
hyaline cartilage location
epiphyseal plates, synovial joints, costal cartilage, nasal cavity, trachea
hyaline cartilage function
resist compression
cushion, smooth, low friction for joints
structural support in pulm system
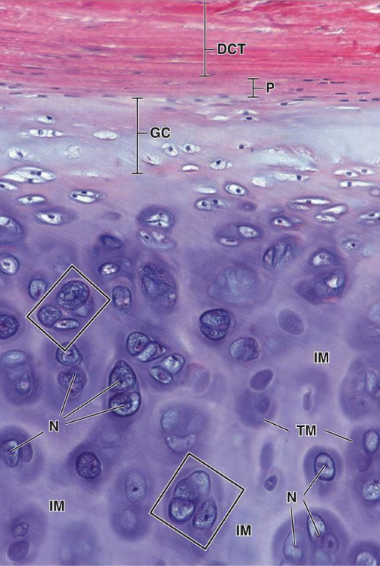
hyaline cartilage main cell types + cartilage?
chondroblast + chondrocytes
T2 collagen
isogenous groups
clusters of chondrocytes from mitosis, in the IM
elastic cartilage location
external ear, eustachian tube, epiglottis
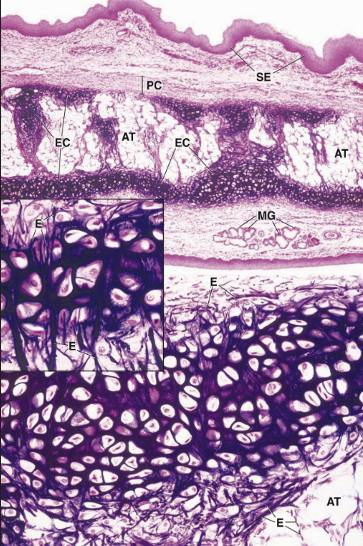
elastic cartilage function
flexible support for soft tissue
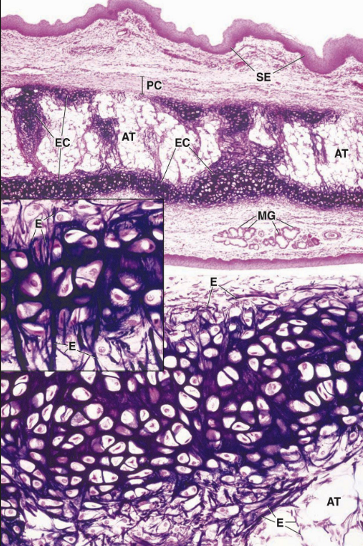
elastic cartilage cell types + cartilage?
chondroblast + chondrocytes
T2 collagen
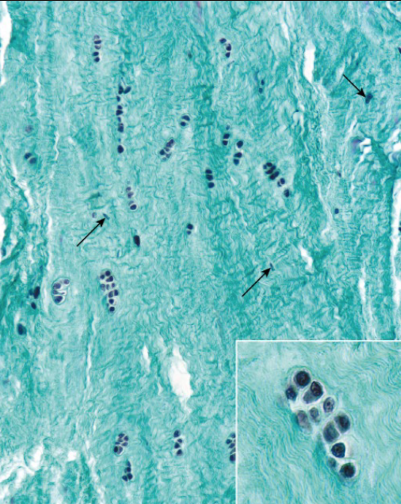
fibrous cartilage location
IV disc, pubic symphysis, sternoclavicular joint, TMJ, menisci
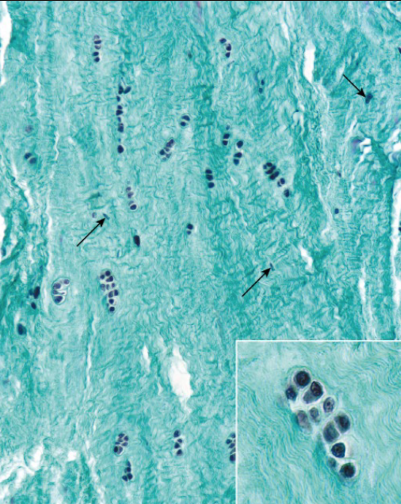
fibrous cartilage function
resist deformation under stress
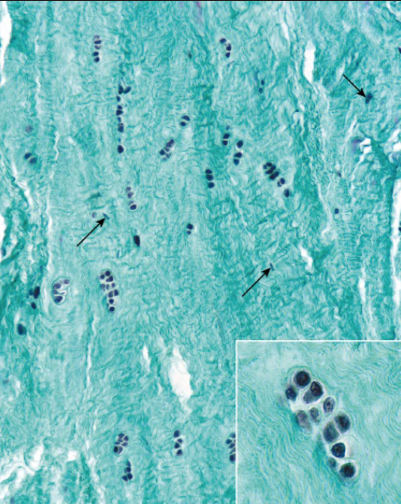
fibrous cartilage major cell type + cartilage?
fibroblasts (produce T1) + chondrocytes
T1 + T2 collagen
which types of cartilage have perichondrium?
hyaline + elastic
which types of cartilage have calcification?
hyaline: endochondral bone formation + aging
fibrous: bone repair
chondrocytes function?
mature cells in lacunae
maintain matrix
chondroblasts function?
in perichondrium
produce matrix
interstitial growth of tissue
growth from within
via chondrocyte
articular cartilage + epiphyseal plate
appositional tissue growth
growth from ends
via chondroblast in perichondrium
what does intramembranous ossification form and how?
flat bones (cranial vault, maxilla/mandible, clavicle)
uses mesenchymal cells —> osteoblasts
what does endochondral ossification form and how?
skull base, vertebrae, long bones , pelvis
begins at hyaline —> 1 ossification center (diaphysis) —> 2 ossification center (epiphysis)
zones of ossification
resting chondrocyte
proliferating chondrocyte
hypertrophic chondrocyte
calcified chondrocyte
Real Pros Have Coke
achondroplasia
overactive FGR3 —> excessive proliferation
short stature
appositional bone growth
thickening via adding to periosteal
interstitial bone growth
lengthening from epiphyseal plate
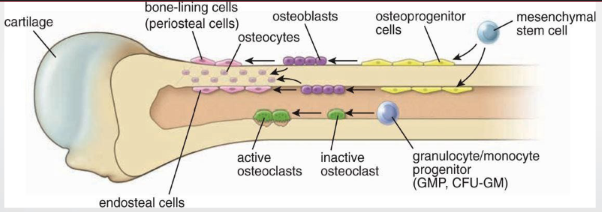
periosteum bone layer
fibrous outer layer
sharpey fibers (T1)
from mesenchymal cells
endosteal bone layer
connective tissue w/o fibers
from mesenchymal cells —> cytes —> blasts
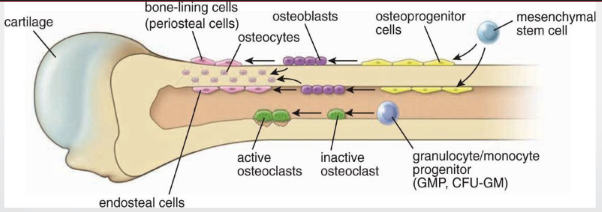
osteoprogenitor cells
like fibroblasts
from mesenchymal cells
diff into osteoblasts
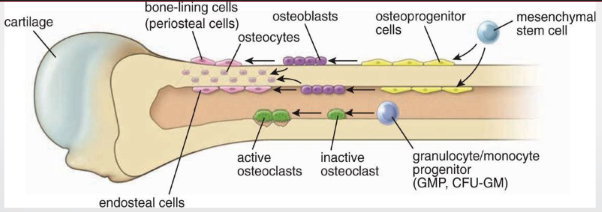
osteoblasts
come from osteoprogenitor cells
provide osteoid (bone matrix)
contain T1, proteoglycans, glycoprotein
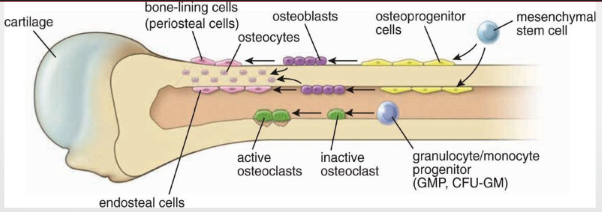
osteocytes
from osteoblasts —> mature in bone cell (lacunae)
formation + maintenance of bone
heterochromatin, RER, golgi
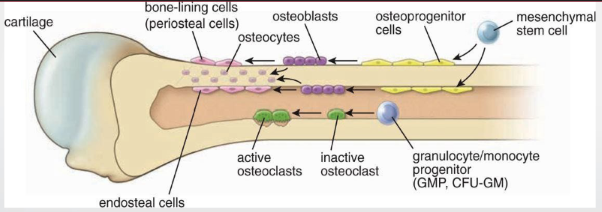
osteoclasts
multinucleated phagocytic cells —> mononucleated progenitor
resorb + remodel
howship lacunae: resorption bay
what does the Ca2+ and phosphate in bone stored in?
hydroxyapatite crystals
what composes the osteon?
lamellae + haversian canal
what does haversian canals hold?
contain BV, nerves, loose CT
canaliculi
projections from osteocytes
comm. via gap junction
share nutrients
volkmann’s canal
connect haversian canals
perpendicular to diaphysis
nutrient arteries
supply spongy bone + marrow
periosteal arteries
supply compact bone
periosteal nerve
carry pain fibers (i.e fracture)
bone repair mechanism
hematoma —> fibrocartilaginous callus —> bone callus —> bone remodel
osteoporosis
dec bone density
unbalanced osteoclast > osteoblast
osteomyelitis
inflammation of bone + marrow via pathogens
S. aureus MRSA
osteophytes
bone spurs via mechanical damage or aging
Heberden or Bouchard nodes
paget’s
older male, loss of hearing
inc osteoclast + osteoblast
bones large but weak
osteomalacia
vit D deficiency —> adult rickets (bow leg, stiffness, weakness)
osteopetrosis
hereditary
dec osteoclastic —> inc bone mass
fibrous joint characteristics + types
fibrous tissues
coronal suture
syndesmosis: dentoalveolar + interosseous
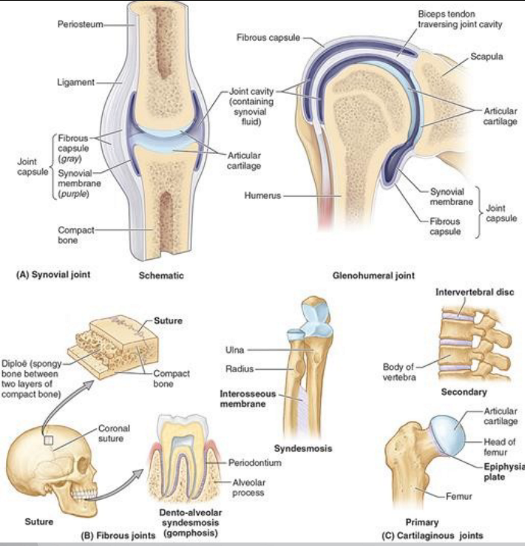
primary cartilaginous joint
synchondroses: hyaline, limited movement
e.g epiphyseal plate
secondary cartilaginous joint
fibrocartilage
slight movement
symphyses: IV disc
synovial joint characteristics
joint capsule —> outer fibrous + inner synovial
reinforced by extrinsic + intrinsic ligaments
synovial: plane joint
uniaxial gliding
metacarpals + cuneiforms
AC joint
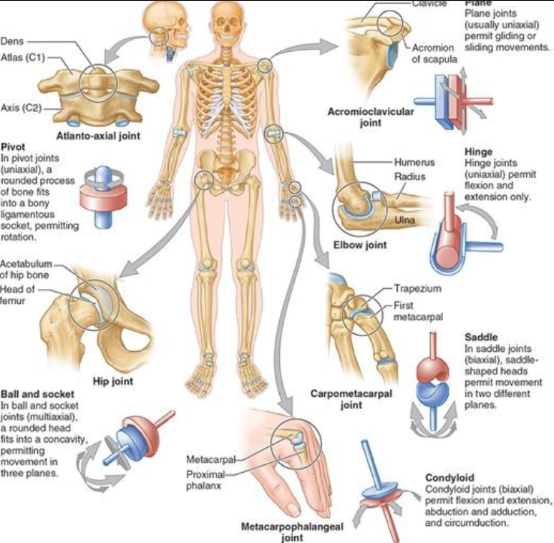
synovial: hinge joint
uniaxial flexion + extension only
joint capsule
elbow, interphalangeal, ankle
synovial: saddle joint
biaxial abduction/adduction + flexion/extension
sternoclavicular
carpometacarpal —> thumb joint
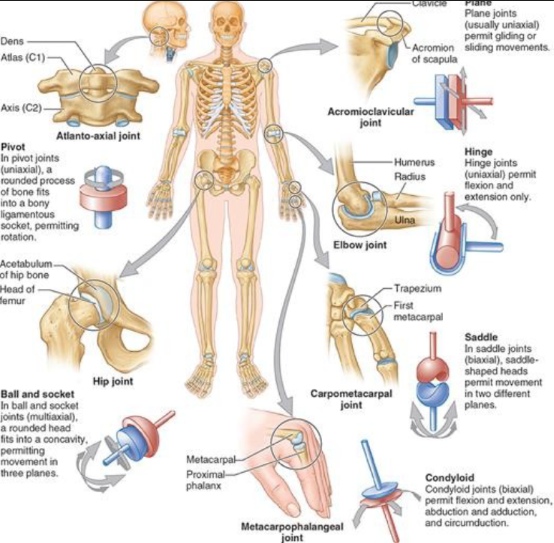
synovial: condyloid joint
biaxial abduction/adduction, flexion/extension, circumduction
metacarpophalangeal joint —> knuckle
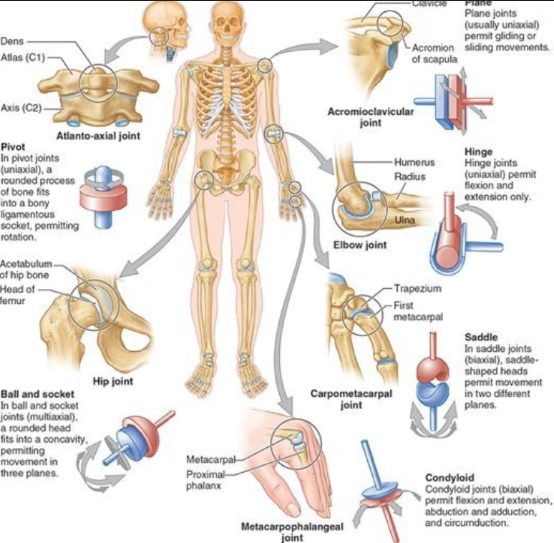
synovial: ball and socket joint
multiaxial, 3 planes
round head in concavity
hip joint
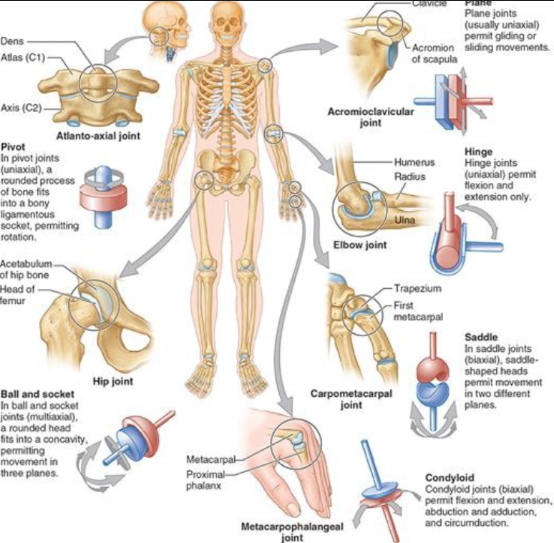
synovial: pivot joint
uniaxial rotation
rounded process in bony socket
atlanto axial joint —> C1 to C2
superficial facia
directly beneath skin
contains fat, BV, lymphatics, cutaneous nerves
deep fascia
covers most of body beneath skin + superficial fascia
invests fascia that covers muscle + nerve bundle
compartment formation
compartment syndrome
inc pressure
cause: fracture, trauma, exertion
symptoms: out of proportion pain, worsens in passive stretch, warm/shiny skin
foot drop
intermuscular septa in arm
separates anterior flexor + posterior extensor
forearm also uses interosseous membrane
compartments of thigh
anterior —> quads, knee extension
medial —> adductors
posterior —> hamstrings, hip extension, knee flexion
compartments of leg
anterior —> dorsiflex foot, extend digits
lateral —> everts foot
posterior —> plantarflex foot, flex digits
bursae
fluid-filled sacs lined by synovial membrane
bursitis
inflammation of bursae —> swelling, dec ROM, septic burst fever
cause: overuse, trauma, infection, arthritis
synovial/ganglionic cyst
benign cyst from joint or tendon sheath
in dorsum of wrist, ankle, foot
popliteal fossa —> baker’s cyst
synovial cyst
comm w/ joint
true synovial lining
ganglionic cyst
NO comm w/ joint
NO synovial lining
what is skin ligament?
fibrous bands extend into subcut tissues
attach deep dermis to deep fascia
suspensory ligaments —> breasts
aponeurosis
flattened tendon sheath created by muscle that anchors muscle to skeleton
areas that need smoothening
tendinitis
acute irritation from microtears
triggered via overactivity, inflammation
tendinosis
chronic degeneration
due to overuse, minimal inflammation
sprain
ligament
joint stretched beyond limit
joint stability dec+ inflammation increases by grade
strain
muscle
tear of muscle tendon
disability inc + contraction dec by grade
x ray
first line
broken bones, dislocations
dense —> white
CT scan
detailed bone anatomy
complex/occult fracture
MRI
soft tissue, ligament/tendon
marrow edema, tumor
stress fracture
comminuted fracture
shattered into multiple pieces
older/brittle bones
what is the atlanto- occipital joint?
yes nod
lateral mass + occipital bone
ALL
jefferson’s fracture
vertical compression of atlas
displaces lateral masses
what is the atlanto-axial joint?
no nod
Dens + facet for dens
transverse ligament —> rupture dangerous
alar ligament keeps dens in place
hangman’s fracture
pars interarticularis fracture via hyperextension
displaced anteriorly
cervical vertebrae
largest vertebral foramen
bifid process (C3-C6)
transverse foramina —> arteries + veins (NOT C7)
uncus process
thoracic vertebrae
articular facets on transverse process (NOT T11 + T12)
costal facets/demifacets (NOT T10-T11)
ankylosing spondylitis
costovertebral
whiplash
degeneration (bamboo spine)
worsens with deep breathing
which vertebra is most prone to fracture?
T12 —> flexion compression (hard landing)
lumbar vertebrae
triangular vertebral foramen
L1-L2: spinal cord terminates
spondylolysis
L4-L5 pars interarticularis fracture
LBP, central pain, improves with rest
spondylolisthesis
L5 anterior dislocation
spina bifida
L5 and/or S1 neural arches fuse
flexion-distraction (seatbelt)
L2 + L3 post. lig. complex
intense flexion —> in kids
unstable spine, kyphosis
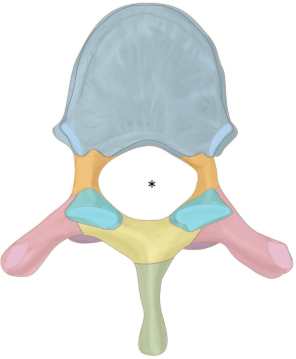
what is orange?
pedicle
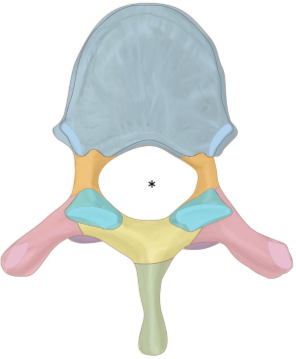
what is teal?
superior articular process
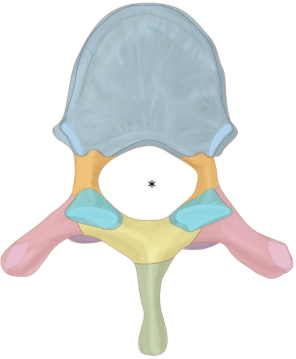
what is yellow?
lamina
ligamentum flavum —> elastin
what is the annulus fibrosus?
surrounds nucleus pulposus
made of fibrocartilage
type 1 collagen
what is the nucleus pulposus?
water + type 2 collagen
herniation
anterior longitudinal ligament (ALL)
connects bodies to IV disc
ONLY ligament that limits extension
posterior longitudinal ligament
mostly IV disc, more internal
prevents post. herniation
pain nerves
zygapophyseal joint
sup + inf articular processes
cervical —> lat flex
L5-S1 —> sit erect
accessory ligament/ligamentum flavum
from lamina above to below
prevent flexion
hypertophied —> push against spinal cord —> stenosis
lower limb weakness/pain
what forms the intervertebral foramen?
sup + inf notches
pedicle —> roof
holds root of spinal nerve
herniated press against L5 or S1 —> sciatica
LBP, radiates down back of thigh
what is in the sacral canal?
cauda equina
superficial (extrinsic) 1st layer
trapezius + latissimus dorsi
action of trapezius?
upper: elevate scapula (shrug)
middle: retract scapula
lower: sup. rotate scapula (parallel bars)