Cells (organelles, structures, diffusion/osmosis, stem cells)
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Define a eukaryote
a cell containing a nucleus/membrane bound organelles
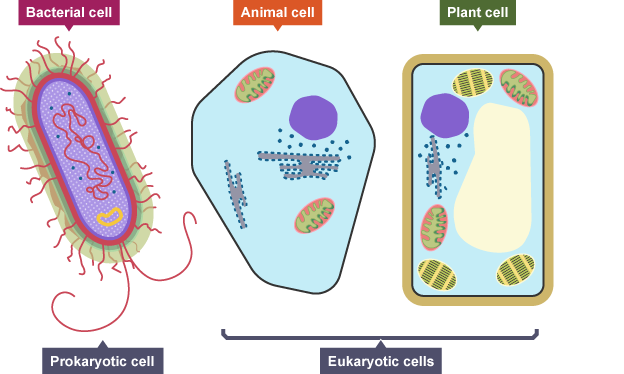
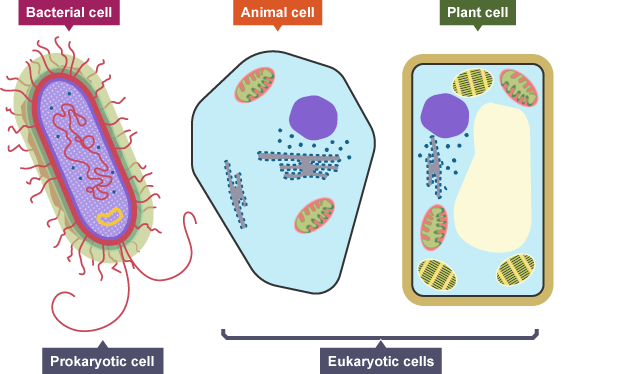
Only which one type of cell has membrane bound organelles?
Eukaryotic
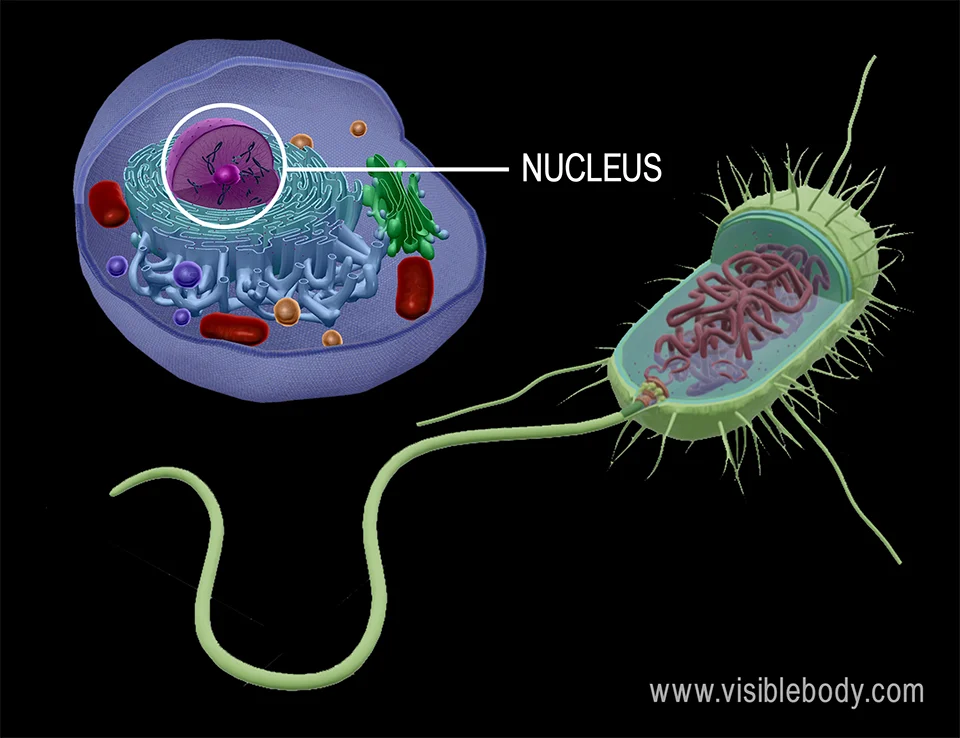
Define a prokaryote
a cell without a nucleus/membrane bound organelle
Function of a nucleus (is in eukaryotes only)
storing genetic material/DNA
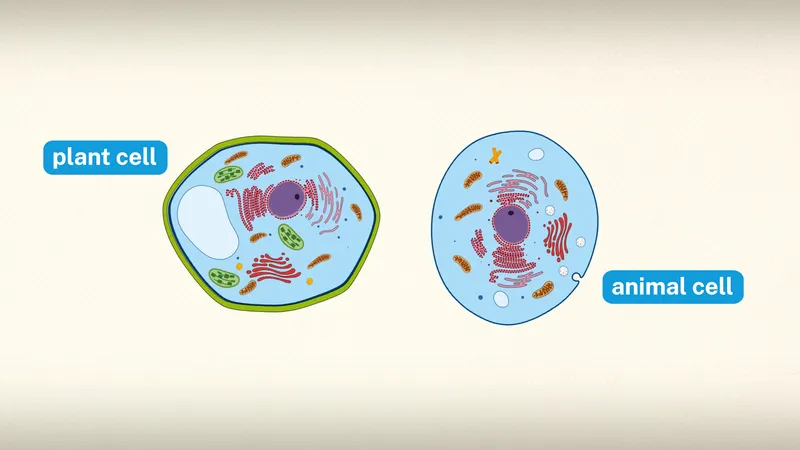
Function of cell wall (is in plant cells and some prokaryotes only)
maintains and supports the structure of a cell and allows it to cope with osmotic pressure (the minimum pressure applied to a solution to stop the flow of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane).
green outline is cell wall of plant cell in comparison to animal cell
Function of cytoplasm (is in all cells)
where chemical reactions happen and organelles operate in
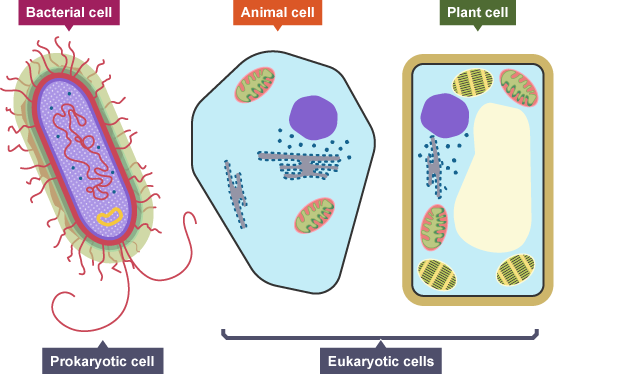
Function of cell membrane (is in all cells)
controls what enters or exits the cell (protective purposes)
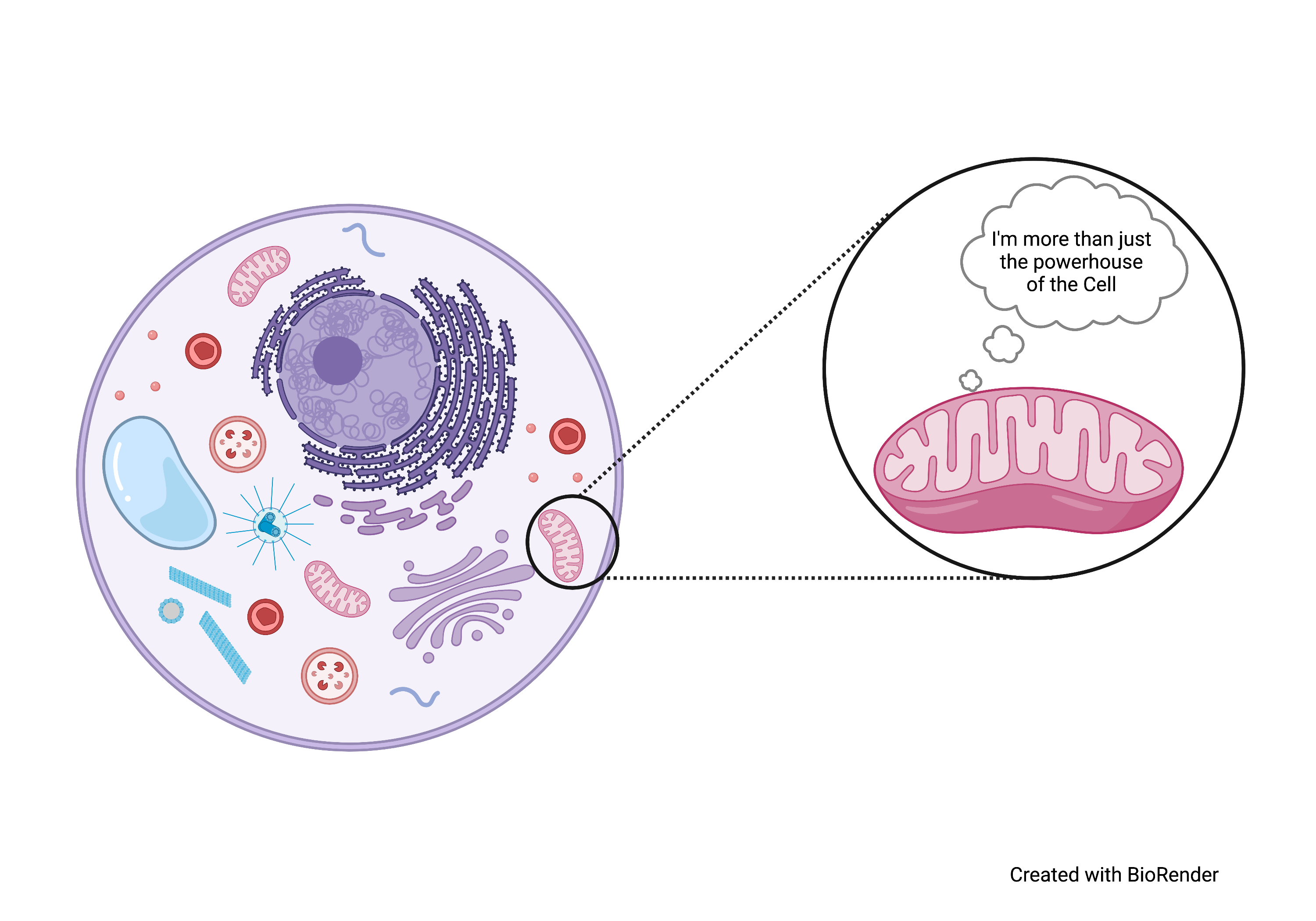
Function of mitochondria (is in eukaryotes only)
releases energy for cell to function; site of respiration- fuels various cellular purposes
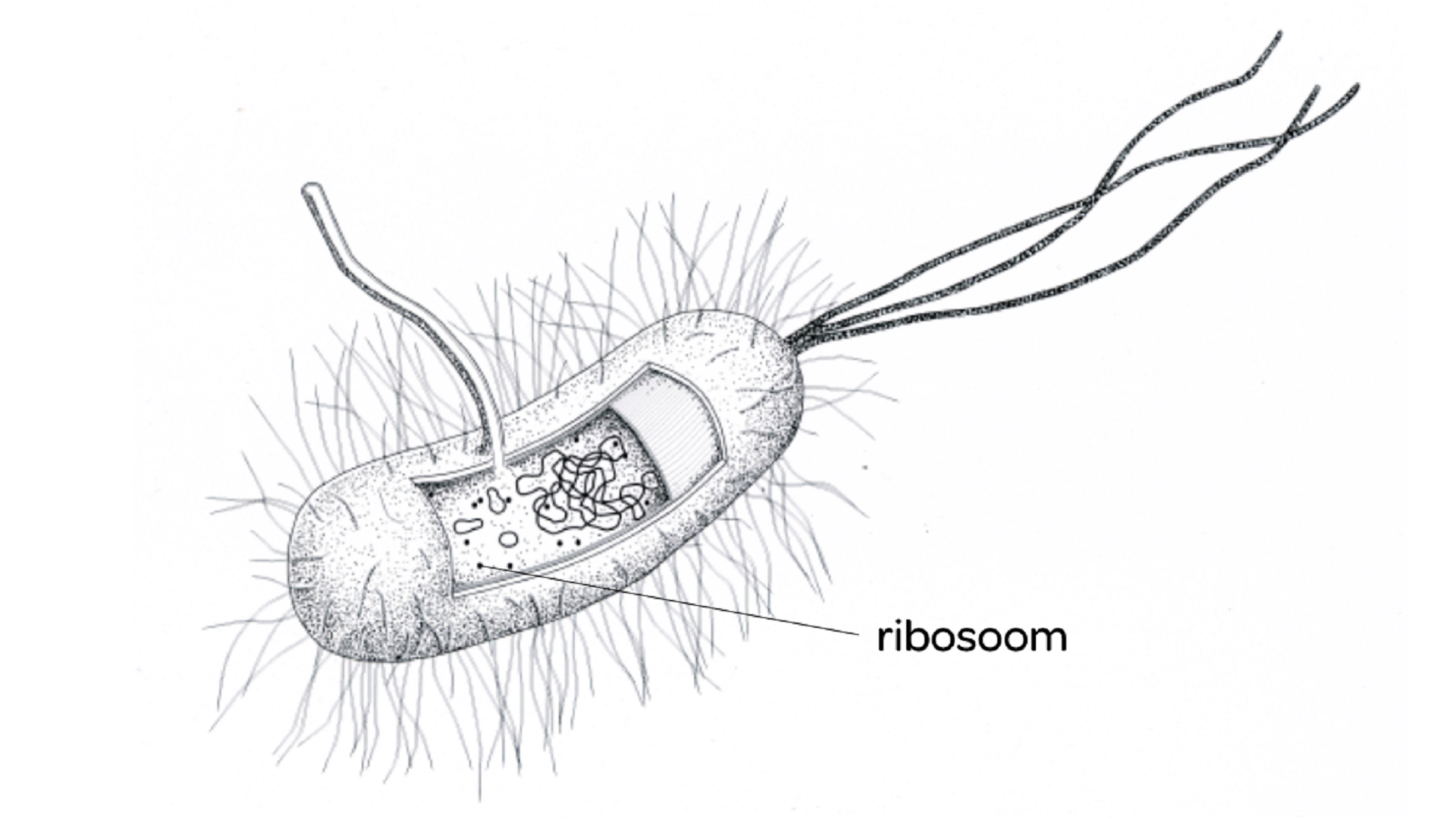
Function of ribosomes (is in all cells)
conduct protein synthesis
P.S: ribosoom is ribosome in Dutch…
Define protein synthesis and explain its cruciality
the process of making protein for the cell, important to carry out chemical reactions
Organelles plant cells contain but animal don’t
vacuole, chloroplasts, cell wall
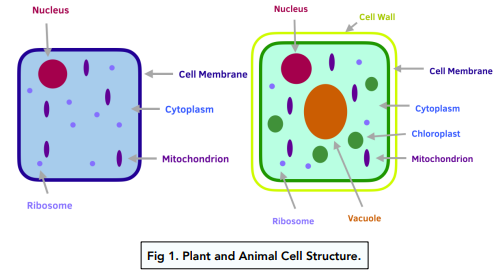
Organelles only prokaryotes contain
plasmids and nucleoid (DNA)
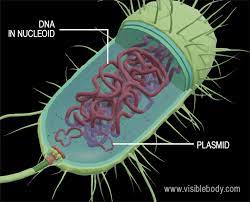
Function of vacuole (is in plant cells only)
a fluid-filled sac that stores water and cell sap
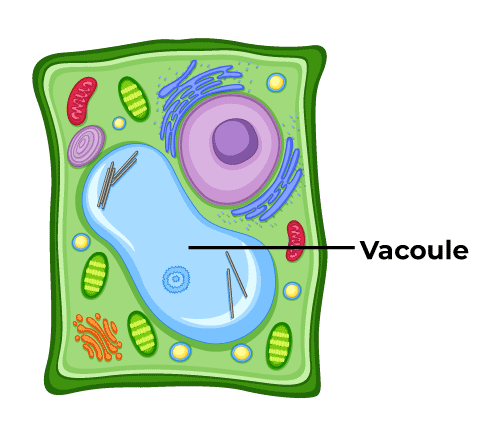
Function of chloroplasts (is only in plant cells)
Organelles containing chlorophyll that conduct photosynthesis, where light energy is converted into glucose and used to produce carbohydrates
Function of plasmids (only present in prokaryotes)
rings of DNA of genes. Replicates the DNA (copies move between cells so that genetic information can be shared)
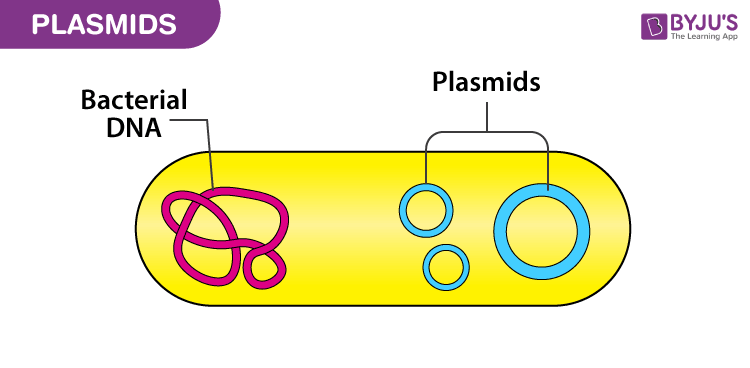
Function of nucleoid (is only in prokaryotes)
storing genetic material/DNA
Name 4 pathogens
bacteria, viruses, fungi and protists
what are microbes?
single celled organisms
what are pathogens
microorganisms/microbes which cause diseases (communicably)
Define a specialized cell
cell with a specific role/job/function
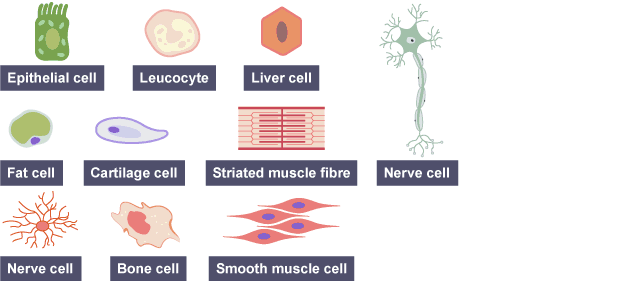
Define cell differentiation
process of a cell becoming specialized; involves development of specific structures of functions. (Once it has been differentiated, it cannot transform into anything else)
Why don’t red blood cells have a nucleus?
to be able to carry more oxygen
(PS: red blood cells contain proteins called hemoglobin that carry oxygen from your lungs to the rest of your body)
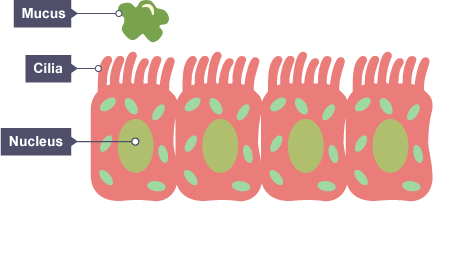
Function of ciliated cells in the human body
move mucus up and out of the airways/trachea
what enzyme does the head of a sperm cell contain? What’s its use?
acrosome helps penetrate egg cell through the membrane
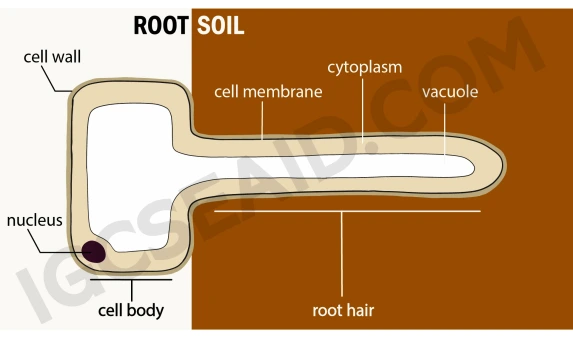
what are root hair cells specialized in? Give an example with one of its physical qualities.
adapted for water absorption:
large surface area(elongated shape)
woody, thin walls for fast water absorption
in an egg cell, what does the cytoplasm contain?
nutrients for growth
When does the membrane of an egg cell change?
once it has been fertilized by a sperm cell so no more sperms can enter
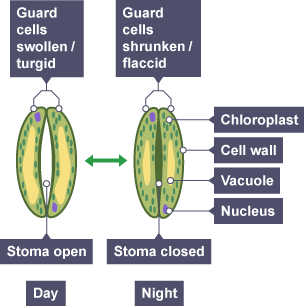
Function of guard cells
allow gas exchange for carbon dioxide and oxygen
in which conditions does a guard cell open and swell? When do they shrink and close?
open in light exposure to photosynthesise. close in an absence of light to prevent water loss(save/store water)
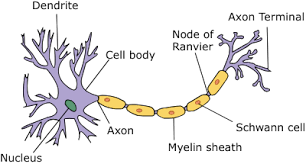
what is a nerve cell covered with?
a fatty myelin sheath for insulation (protects from exterior electric interference) and allows efficient transmission of electric impulses
Define stem cells?
cells that aren’t yet specialized or differentiated
Outline the 3 stem cells
embryonic- found in the early stages of an embryo. Is difficult to obtain
adult- found in the body (typically bone marrow)in limited numbers. Only a limited range of specialized cells can be formed from adult stem cells as they are already partially differentiated.
plant meri-stem cell- found in the tips of roots and shoots. Can differentiate throughout the life of a plant into any type of cell.
Stem cells advantages and disadvantages
advantages:
can be used for research and medical treatment; could treat untreatable diseases
could grow organs for transplant
disadvantages:
ethical issues
some are difficult to access
no success guarantee (particular risk to patients)
expensive research
possible mutation (“over” differentiation)
difficult to harvest and painful
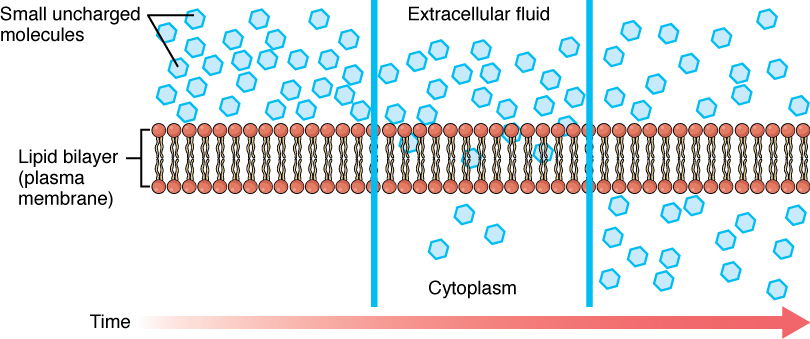
Define diffusion
A passive process(energy unrequired) of particles moving from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
What affects the rate of diffusion? (3)
temperature- the higher the temperature, the more kinetic energy particles have and move with
surface area of membrane- the larger the surface area, the more particles have access to transfer at a time
concentration difference(gradient)- the greater the concentration gradient, the less interferences with the movement of particles
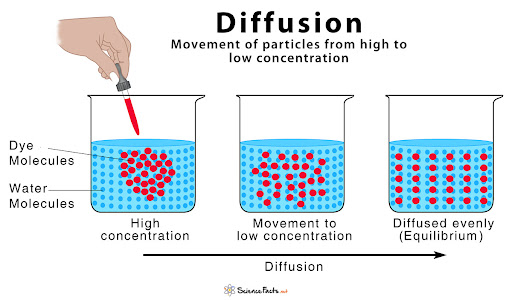
Define osmosis
movement of water molecules from areas of high to low concentration via a partially permeable membrane (permeable only to small water molecules and some solutes but not large solute molecules)
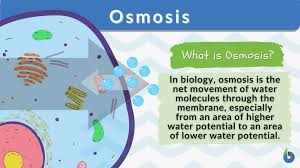
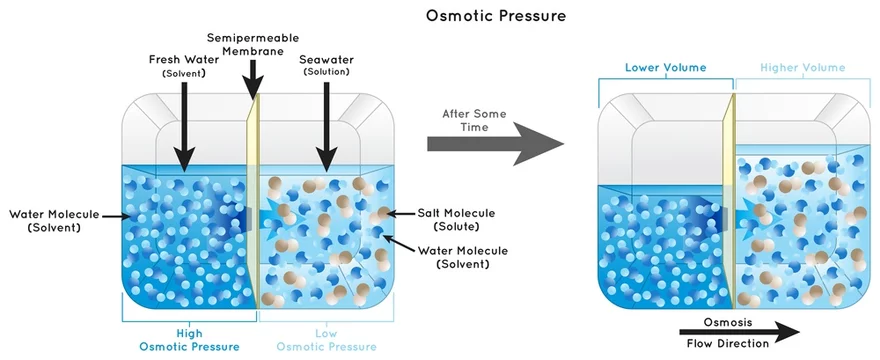
how are diffusion and osmosis different?
Diffusion is the movement of particles from a high to lower concentration. Osmosis is a type of diffusion but across a partially permeable membrane(from a diluted to a concentrated solution)
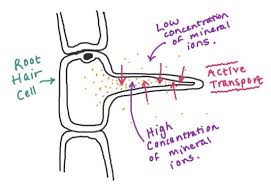
Define active transport
Active transport is the movement of particles from a lower to higher concentration, carried by carrier proteins. It’s an energy-driven process going against a concentration gradient. e.g: root hair cells
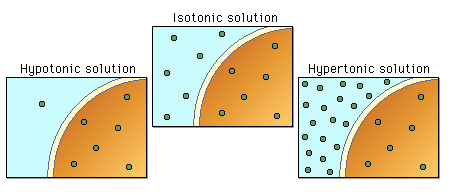
Hypertonic vs Hyotonic
Hypertonic- when solutes in the solution outside of a cell is higher than the internal concentration.
Hypotonic- when the concentration of particles in the inside of a cell is higher than the solutes in the solution outside of it.
(P.S: isotonic is when both concentration of interior and exterior are equal)
Define respiration
release of energy by taking in oxygen and releasing CO2
How does the concentration of sucrose affect the mass of a potato cylinder?
The potato cylinders placed in strong sucrose solutions will lose mass/length as water will have moved from an area of high concentration (inside the potato cells) to an area of lower concentration (outside the potato cells).
Differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms
eukaryotes have a nucleus, prokaryotes don't
prokaryotes have plasmids, eukaryotes don't
eukaryotes are made of cellulose(in plants) or chitin(in fungi) and prokaryotes are made of peptidoglycan/bacteria
Eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles, while prokaryotic cells don’t
eukaryotic organisms can be unicellular or multicellular, whereas prokaryotes are predominantly unicellular
name a protoctist and the disease it causes
Plasmodium, which causes malaria
Describe the pathogen bacteria and refer to a disease
Bacteria are single-celled prokaryotic organisms that can cause diseases such as salmonella
Describe the pathogen fungi and refer to a disease
Fungi is a white, pathogenic growth, it causes diseases such as athlete's foot.
Describe the pathogen virus and refer to a disease
Viruses are infectious agents that can only reproduce inside living cells. An example is HIV Covid.
Describe the pathogen protoctist and refer to a disease
Protoctists are -, like algae, that can cause diseases such as malaria, which is transmitted by the Plasmodium protozoan.
how does the absence of a cell wall affect what happens to a red blood cell in distilled water
How about in a concentrated salt solution
Without a cell wall, red blood cells in distilled water will swell and potentially burst due to osmosis, as water enters the cell.
In a concentrated salt solution, they will shrink as water exits the cell to balance the solute concentration.
A plant virus and its effects
A plant virus, such as Tobacco Mosaic Virus, can cause discoloration plants.
Differences between the structure of bacteria and viruses
bacteria are larger
viruses have a protein coat
viruses have no cell wall or mebrane, bacteria do
bacteria has flagella, viruses don’t
Importance of cell differentiation in the development of an embryo
unspecialized cells develop into specialized cells to produce tissues/organs
why is the choice between adult and embryonic stem cells argued?
embryonic stem cells can make any cell type, in comparison to adult cells which can’t. However, there are ethical issues involved in the use of embryonic cells in particular.