Psychological Disorders
5.0(1)Studied by 23 people
0%Unit 8 Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1UdGDK35QRG1xsqKngwEqMfw_yua0TNaTpOz_o0XQAwM/edit
Last updated 11:40 PM on 4/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
1
New cards
psychological disorders
a syndrome that causes significant disturbance in behavior, emotion, and cognition
2
New cards
1) harm others
2) be maladaptive (disrupt efficient functioning)
3) make self/others uncomfortable/distressed
2) be maladaptive (disrupt efficient functioning)
3) make self/others uncomfortable/distressed
What is clinically dysfunctional behavior or thought?
3
New cards
Culture-bound syndromes
syndromes that are generally limited to specific societies or culture areas and are localized, folk, diagnostic categories that frame coherent meanings for certain repetitive, patterned, and troubling sets of experiences and observations
4
New cards
Szaz
this person believed
* mental illness = metaphor for problems in living
* criticizes psychiatry and argues against the concept of mental illness
* mental illness = metaphor for problems in living
* criticizes psychiatry and argues against the concept of mental illness
5
New cards
Rosenhan’s Experiment
“pseudopatients” told mental institutions symptoms and were admitted and diagnosed with **serious** disorders
* No staff identified them as fake patients
\
= proved diagnoses unreliable and supported deinstitutionalization
* No staff identified them as fake patients
\
= proved diagnoses unreliable and supported deinstitutionalization
6
New cards
Deinstitutionalization
shifting care from long-stay psychiatric hospitals to community-based mental health services
7
New cards
Psychoanalytic/Psychodynamic Approach
a theory to explain disorders
= unconscious conflicts with others or with societal expectations lead to disordered behavior
= unconscious conflicts with others or with societal expectations lead to disordered behavior
8
New cards
Learning (Behavioral) Approach
a theory to explain disorders
= dysfunctional behaviors are the result of classical/operant conditioning gone wrong
or
the result of observational learning: watching others get rewarded for dysfunctional behaviors
= dysfunctional behaviors are the result of classical/operant conditioning gone wrong
or
the result of observational learning: watching others get rewarded for dysfunctional behaviors
9
New cards
Biological Approach
a theory to explain disorders
= psychological disorders are the result of
* hormone/neurotransmitter imbalances
* genetic abnormalities
* brain damage
= psychological disorders are the result of
* hormone/neurotransmitter imbalances
* genetic abnormalities
* brain damage
10
New cards
Biopsychosocial Model
a theory to explain disorders that includes:
* cognitive approach
* humanist approach
* family systems approach
* biological approach
* cognitive approach
* humanist approach
* family systems approach
* biological approach
11
New cards
Cognitive Approach
a theory that’s part of the Biopsychosocial Model to explain disorders
= maladaptive thinking → dysfunctional behavior
\
* individuals interpret their experience incorrectly
= maladaptive thinking → dysfunctional behavior
\
* individuals interpret their experience incorrectly
12
New cards
Humanist Approach
a theory that’s part of the Biopsychosocial Model to explain disorders
= faulty/interrupted development process social/emotional immaturity → disfunction
\
→ So, the goal of a humanistic therapy = to promote social/emotional maturity and growth
= faulty/interrupted development process social/emotional immaturity → disfunction
\
→ So, the goal of a humanistic therapy = to promote social/emotional maturity and growth
13
New cards
Family Systems Approach
a theory that’s part of the Biopsychosocial Model to explain disorders
= familial behaviors, thinking, expectations, environment of household → dysfunctional behavior
= familial behaviors, thinking, expectations, environment of household → dysfunctional behavior
14
New cards
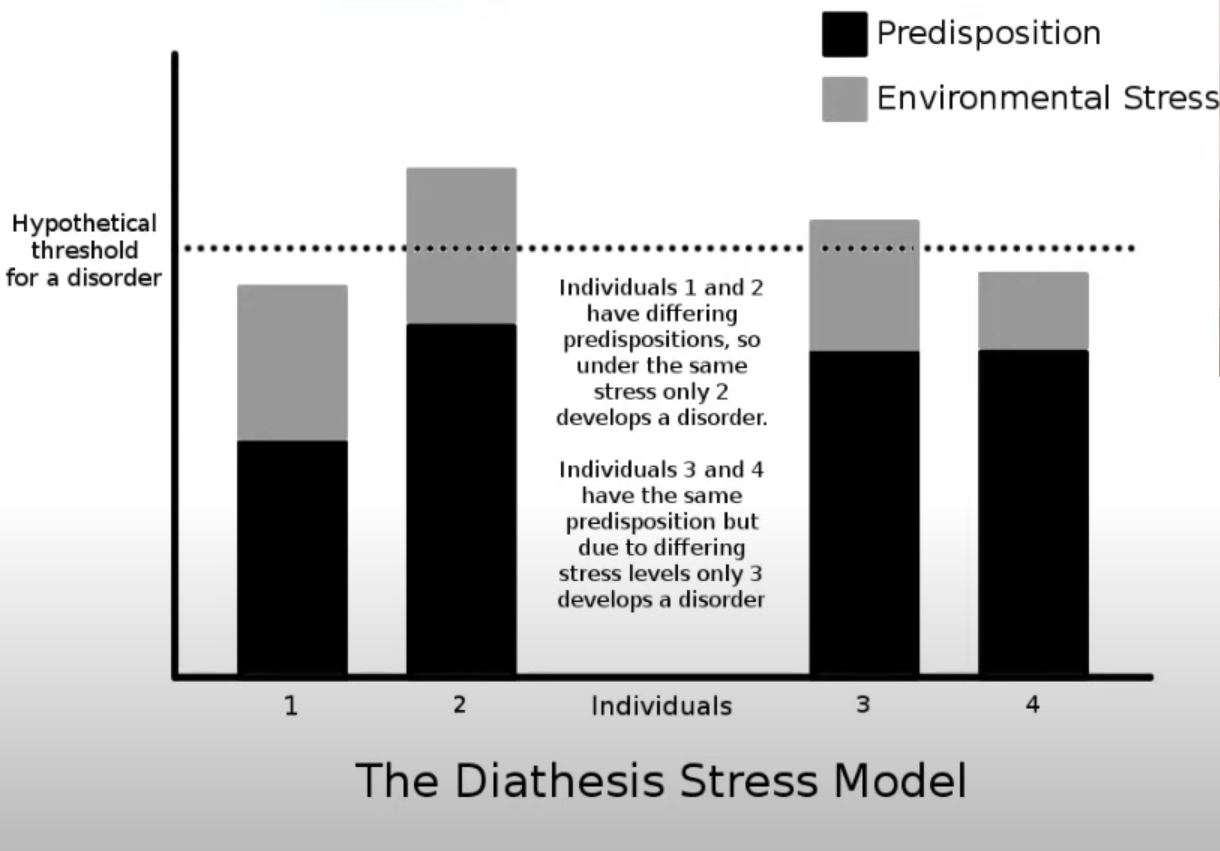
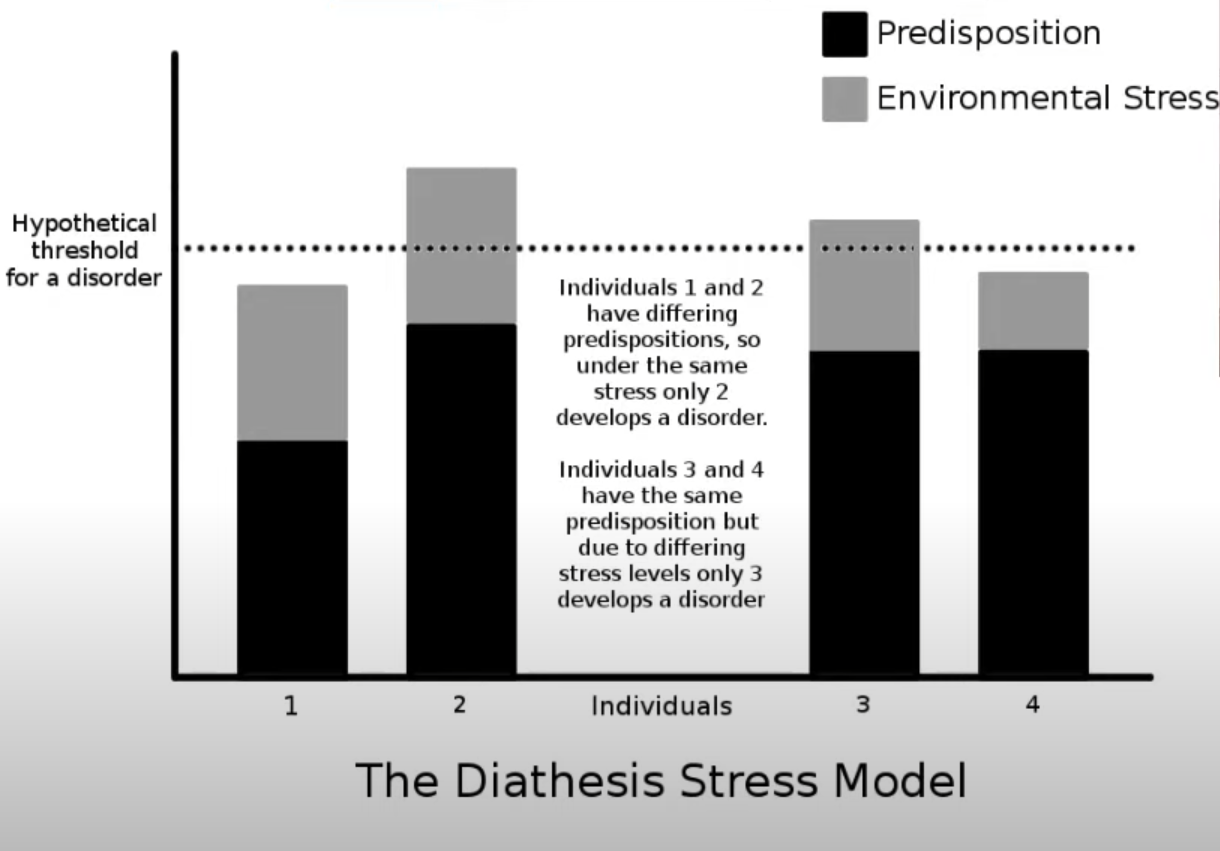
Diathesis-Stress Model
= an individual may have a genetic predisposition for stress (nature) but an environmental trigger (nurture) is also needed for the disorder to appear
\
both Genetic Predisposition + Environment = disorder
BUT ALSO
how high or low ability to cope with stress is another factor of how likely you are to develop it
\
both Genetic Predisposition + Environment = disorder
BUT ALSO
how high or low ability to cope with stress is another factor of how likely you are to develop it
15
New cards
Comorbidity
= the simultaneous presence of 1+ disorders in an individual
16
New cards
Psychopathology
= the study of causes, progression, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of disorders
17
New cards
Concordance
the probability of one person having the trait if the other does depending on their relationship
18
New cards
Prevalence
= the total # of both new and old cases in a population
given as a %
given as a %
19
New cards
Incidence
= rate of NEW occurrences of a condition in a population
20
New cards
DSM-5
= a __**diagnosis**__ handbook
\
%%+ provides common language of symptoms%%
%%+ establishes consistent reliability for diagnosis%%
\
==- DOES NOT include treatment of any disorder==
\
%%+ provides common language of symptoms%%
%%+ establishes consistent reliability for diagnosis%%
\
==- DOES NOT include treatment of any disorder==
21
New cards
Patient Confidentiality
= therapists must not reveal info about their patients unless they believe patient is an immediate threat to self or others
22
New cards
Intellectual Disability
Neurodevelopmental Disorder #1
**= limits to a person’s ability to learn at an expected level and function**
\
1. symptoms
* **sit up, crawl, or walk later than other children**
* **learn to talk later, or have trouble speaking**
* **find it hard to remember things**
* **have trouble understanding social rules**
* **have trouble seeing the results of their actions**
* **have trouble solving problems**
\
2. **onset: during childhood or adolescence**
**prevalence: Approximately 1 – 3 % of the global population has an intellectual disability**
\
3. causes/explanations for the disorder
* **Genetic conditions. Sometimes an intellectual disability is caused by abnormal genes inherited from parents, errors when genes combine, or other reasons. ...**
* **Complications during pregnancy. ...**
* **Problems during birth. ...**
* **Diseases or toxic exposure**
\
4. prognosis
* **require support for life.**
* **the more severe the cognitive disability/physical problems the person has, the shorter the life expectancy**
**= limits to a person’s ability to learn at an expected level and function**
\
1. symptoms
* **sit up, crawl, or walk later than other children**
* **learn to talk later, or have trouble speaking**
* **find it hard to remember things**
* **have trouble understanding social rules**
* **have trouble seeing the results of their actions**
* **have trouble solving problems**
\
2. **onset: during childhood or adolescence**
**prevalence: Approximately 1 – 3 % of the global population has an intellectual disability**
\
3. causes/explanations for the disorder
* **Genetic conditions. Sometimes an intellectual disability is caused by abnormal genes inherited from parents, errors when genes combine, or other reasons. ...**
* **Complications during pregnancy. ...**
* **Problems during birth. ...**
* **Diseases or toxic exposure**
\
4. prognosis
* **require support for life.**
* **the more severe the cognitive disability/physical problems the person has, the shorter the life expectancy**
23
New cards
adaptive functioning
= **how well a person handles common demands in life and how independent they are compared to others of a similar age and background**
24
New cards
Autism Spectrum disorder
Neurodevelopmental Disorder #2
= any one of a group of disorders characterized by difficulties with social communication and social interaction and restricted and repetitive patterns in behaviors, interests, and activities
\
## 1. symptoms
the symptoms of people with ASD will fall on a continuum, with some individuals showing mild symptoms and others having much more severe symptoms. This spectrum allows clinicians to account for the variations in symptoms and behaviors from person to person
* **language development**
(doesn't speak or has delayed speech
* **social development**
(responding inappropriately in conversations,
misreading nonverbal interactions,
having difficulty building friendships appropriate to their age)
* **cognitive development**
(doesn’t express emotions or seem to understand others’ emotions,
unusually sensitive to light, sound, or touch,
indifferent to pain or temperature)
* **need for routines**
## 2. onset and prevalence
* onset: preschool years
* prevalence: 2.3%
\
## 3. causes/explanations for the disorder
* genetics
## 4. prognosis
* no cure for autism spectrum disorder,
* intensive, early treatment can make a big difference
## 5. any differences by demographic group?
* boys 4 times more likely to be diagnosed than girls
* families who have one child with autism spectrum disorder have an increased risk of having another child with the disorder.
* children with certain medical conditions have a higher than normal risk of autism spectrum disorder or autism-like symptoms.
* babies born before 26 weeks of gestation may have a greater risk of autism spectrum disorder
= any one of a group of disorders characterized by difficulties with social communication and social interaction and restricted and repetitive patterns in behaviors, interests, and activities
\
## 1. symptoms
the symptoms of people with ASD will fall on a continuum, with some individuals showing mild symptoms and others having much more severe symptoms. This spectrum allows clinicians to account for the variations in symptoms and behaviors from person to person
* **language development**
(doesn't speak or has delayed speech
* **social development**
(responding inappropriately in conversations,
misreading nonverbal interactions,
having difficulty building friendships appropriate to their age)
* **cognitive development**
(doesn’t express emotions or seem to understand others’ emotions,
unusually sensitive to light, sound, or touch,
indifferent to pain or temperature)
* **need for routines**
## 2. onset and prevalence
* onset: preschool years
* prevalence: 2.3%
\
## 3. causes/explanations for the disorder
* genetics
## 4. prognosis
* no cure for autism spectrum disorder,
* intensive, early treatment can make a big difference
## 5. any differences by demographic group?
* boys 4 times more likely to be diagnosed than girls
* families who have one child with autism spectrum disorder have an increased risk of having another child with the disorder.
* children with certain medical conditions have a higher than normal risk of autism spectrum disorder or autism-like symptoms.
* babies born before 26 weeks of gestation may have a greater risk of autism spectrum disorder
25
New cards
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity disorder
Neurodevelopmental Disorder #3
= pattern of inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity that interferes with functioning or development
* Needs to move; feels restless
* Can't sit through meetings, meals, movies
* Extremely impatient
* Finishes people's sentences; draws rapid conclusions (Blurts out answers before questions have been completely asked)
\
\
* **symptoms start before age 12**
* **4.4% of US adults have ADHD**
\
\
genes and environmental factors likely plays a role in the development of the condition
\
\
* **ADHD does not fade at a specific age**
* **no cure for ADHD**
= pattern of inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity that interferes with functioning or development
* Needs to move; feels restless
* Can't sit through meetings, meals, movies
* Extremely impatient
* Finishes people's sentences; draws rapid conclusions (Blurts out answers before questions have been completely asked)
\
\
* **symptoms start before age 12**
* **4.4% of US adults have ADHD**
\
\
genes and environmental factors likely plays a role in the development of the condition
\
\
* **ADHD does not fade at a specific age**
* **no cure for ADHD**
26
New cards
Tourette’s Syndrome
Neurodevelopmental Disorder #4
= individuals have sudden, rapid, recurrent, non-rhythmic, stereotyped motor movements or vocalizations
these movements/vocalizations called “tics”
= individuals have sudden, rapid, recurrent, non-rhythmic, stereotyped motor movements or vocalizations
these movements/vocalizations called “tics”
27
New cards
Neurodevelopmental disorders
broad category of disorders which are defined by delayed or impaired speech, language, motor condition, and visuo-spatial skills
28
New cards
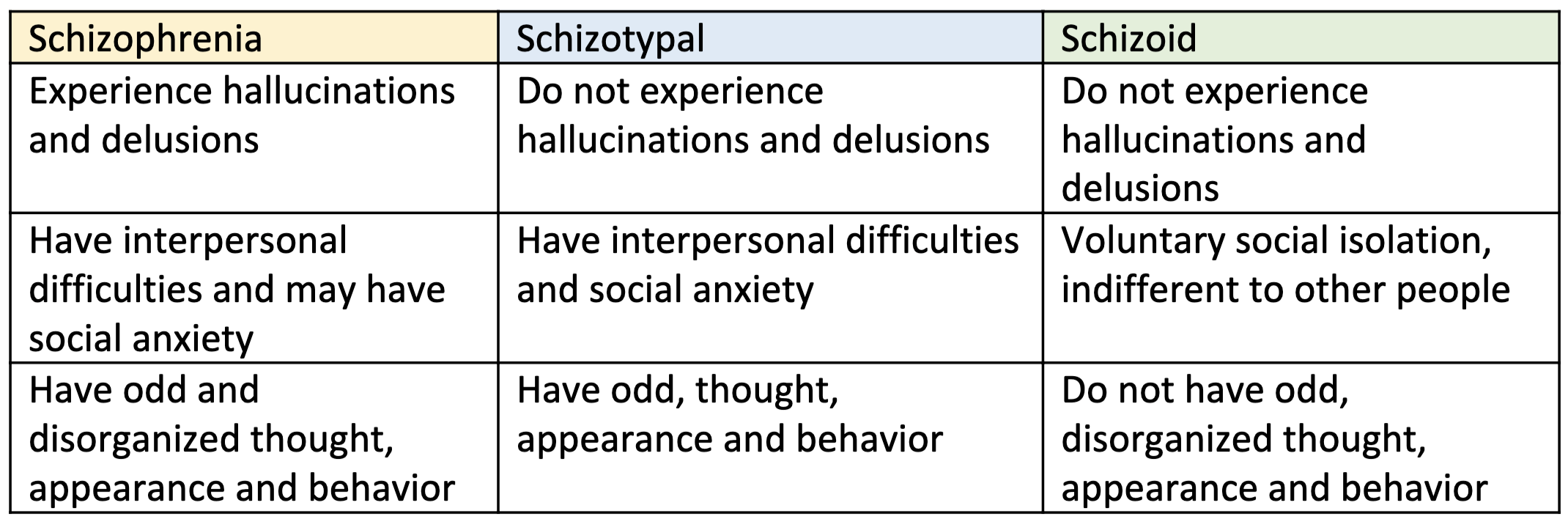
Schizophrenia
= a break from reality
\
between ages 16 and 30
0\.32% of people worldwide
\
Men often get symptoms earlier than women
\
3. causes
**genetics**: mutations, odds of developing is x10 greater if parent/sibling has it
**brain structure:** changes in prefrontal (working memory) and medial (declarative memory) temporal lobe regions
**brain chemistry**: neurotransmitters imbalance: too much dopamine and serotonin.
**viral infection:** x2 risk
**neural pruning:** An over excessive pruning of in regions responsible for functions affected by schizophrenia, like planning and cognition
\
* **Environmental/Diathesis-Stress model**
genetic predisposition + environment STRESS **→ schizophrenia**
\
4. prognosis
* lifelong treatment
\
between ages 16 and 30
0\.32% of people worldwide
\
Men often get symptoms earlier than women
\
3. causes
**genetics**: mutations, odds of developing is x10 greater if parent/sibling has it
**brain structure:** changes in prefrontal (working memory) and medial (declarative memory) temporal lobe regions
**brain chemistry**: neurotransmitters imbalance: too much dopamine and serotonin.
**viral infection:** x2 risk
**neural pruning:** An over excessive pruning of in regions responsible for functions affected by schizophrenia, like planning and cognition
\
* **Environmental/Diathesis-Stress model**
genetic predisposition + environment STRESS **→ schizophrenia**
\
4. prognosis
* lifelong treatment
29
New cards
Schizotypal Personality Disorder
= mental health condition marked by a consistent pattern of intense discomfort with close relationships and social interactions
unlike schizophrenia, _____ disorder does not include hallucinations and delusions
and people with _____ disorder usually can be made aware of the difference between their distorted ideas and reality
unlike schizophrenia, _____ disorder does not include hallucinations and delusions
and people with _____ disorder usually can be made aware of the difference between their distorted ideas and reality
30
New cards
Positive Symptoms of Schizophrenia
* Hallucinations
* Delusions
* Disorganized speech/behavior
* Delusions
* Disorganized speech/behavior
31
New cards
Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia
* **Flattened Affect** = suppressed emotional/facial expression
* Reduced Speech
* Loss of interest in activities
* Reduced Speech
* Loss of interest in activities
32
New cards
Delusions
= false beliefs that are not based in reality
\
ex. you think that you're being harmed or harassed
\
ex. you think another person is in love with you
\
\
ex. you think that you're being harmed or harassed
\
ex. you think another person is in love with you
\
33
New cards
Hallucinations
= seeing or hearing things that don't exist
34
New cards
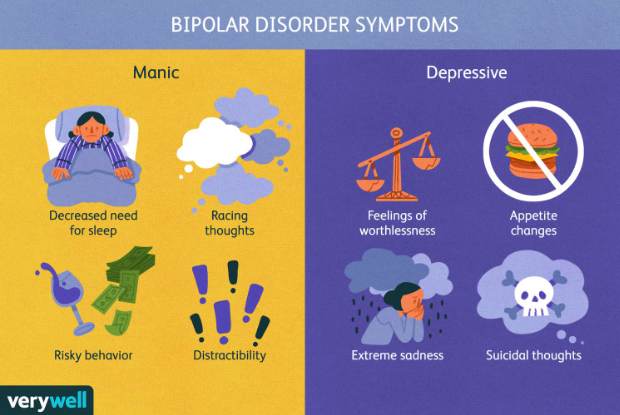
Bipolar Disorder
= a mental health condition marked by large shifts in mood from mania to depression
\
* **onset average: 25 years old**
2\.8% of US adults
3. causes
heritable component
Stressful events might include grief over a death in the family, trauma, loss of a job, the birth of a child or moving into a new home
\
4. prognosis
* 50% of patients experience a second episode within two years of the first episode. Poor prognosis is associated with: Substance dependency
**Bipolar disorder may worsen with age or over time if the condition is left untreated**. As time goes on, a person may experience episodes that are more severe and more frequent than when symptoms first appeared
\
* **onset average: 25 years old**
2\.8% of US adults
3. causes
heritable component
Stressful events might include grief over a death in the family, trauma, loss of a job, the birth of a child or moving into a new home
\
4. prognosis
* 50% of patients experience a second episode within two years of the first episode. Poor prognosis is associated with: Substance dependency
**Bipolar disorder may worsen with age or over time if the condition is left untreated**. As time goes on, a person may experience episodes that are more severe and more frequent than when symptoms first appeared
35
New cards
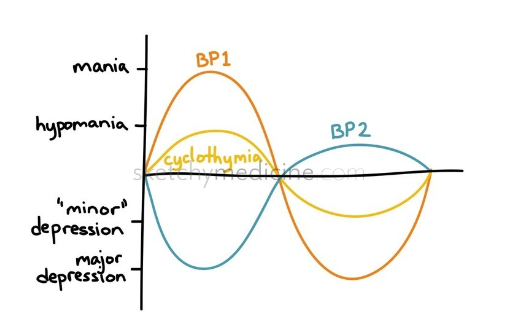
BP 1 vs. BP 2
BP 1 = episodes of depression, hypomania, and mania
BP 2 = episodes of depression and hypomania (less severe than mania)
BP 2 = episodes of depression and hypomania (less severe than mania)
36
New cards
Cyclothymic disorder
= a milder form of bipolar disorder involving many "mood swings," with hypomania and depressive symptoms that occur frequently. People with cyclothymia experience emotional ups and downs but with less severe symptoms than bipolar I or II disorder.
37
New cards
Major Depressive disorder
A depressive Disorder
**= a common and serious medical illness that negatively affects how you feel, the way you think and how you act.**
\
\
1\. symptoms
* mood/emotional symptoms
* **feelings of sadness**
* **a loss of interest in activities you once enjoyed**
* **Angry outbursts, irritability or frustration, even over small matters**
* cognitive symptoms
* **Difficulty thinking, concentrating or making decisions**
* **Thoughts of death or suicide**
* behavioral symptoms
* **Increase in purposeless physical activity (e.g., inability to sit still, pacing, handwringing) or slowed movements or speech (these actions must be severe enough to be observable by others)**
* **Changes in appetite — weight loss or gain unrelated to dieting**
2\. onset and prevalence
* **onset: Depression can occur at any time, but on average, first appears during the late teens to mid-20s**
* **prevalence: one in six people (16.6%) will experience depression at some time in their life.**
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* Biological
* **There is a high degree of heritability (approximately 40%) when first-degree relatives (parents/children/siblings) have depression.**
* **People with depression appear to have physical changes in their brains. The significance of these changes is still uncertain, but may eventually help pinpoint cause**
* __**Brain chemistry.**__ **Neurotransmitters are naturally occurring brain chemicals that likely play a role in depression. Recent research indicates that changes in the function and effect of these neurotransmitters and how they interact with neurocircuits involved in maintaining mood stability may play a significant role in depression and its treatment**
* __**Hormones**__**. Changes in the body's balance of hormones may be involved in causing or triggering depression**
\
* Learning/Environmental
* **Synthetic Chemicals From Foods. ...**
* **Natural Disasters. ...**
* **Trauma. ...**
* **Substance Abuse. ...**
* **Chronic Illness and Injuries. ...**
* **Grief**
* Cognitive
* people's thoughts, inferences, attitudes, and interpretations, and the way in which they attend to and recall events, can increase their risk for the development and recurrence of depressive episodes
4\. prognosis
* Depression is among the most treatable of mental disorders. Between 80% and 90% percent of people with depression eventually respond well to treatment. Almost all patients gain some relief from their symptoms
* **antidepressants** might be prescribed to help modify one’s brain chemistry.
* Psychotherapy, or “talk therapy,” is sometimes used alone for treatment of mild depression; for moderate to severe depression, psychotherapy is often used along with antidepressant medications.
5\. any differences by demographic group?
\
* **Women are more likely than men to experience depression. Some studies show that one-third of women will experience a major depressive episode in their lifetime.**
**= a common and serious medical illness that negatively affects how you feel, the way you think and how you act.**
\
\
1\. symptoms
* mood/emotional symptoms
* **feelings of sadness**
* **a loss of interest in activities you once enjoyed**
* **Angry outbursts, irritability or frustration, even over small matters**
* cognitive symptoms
* **Difficulty thinking, concentrating or making decisions**
* **Thoughts of death or suicide**
* behavioral symptoms
* **Increase in purposeless physical activity (e.g., inability to sit still, pacing, handwringing) or slowed movements or speech (these actions must be severe enough to be observable by others)**
* **Changes in appetite — weight loss or gain unrelated to dieting**
2\. onset and prevalence
* **onset: Depression can occur at any time, but on average, first appears during the late teens to mid-20s**
* **prevalence: one in six people (16.6%) will experience depression at some time in their life.**
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* Biological
* **There is a high degree of heritability (approximately 40%) when first-degree relatives (parents/children/siblings) have depression.**
* **People with depression appear to have physical changes in their brains. The significance of these changes is still uncertain, but may eventually help pinpoint cause**
* __**Brain chemistry.**__ **Neurotransmitters are naturally occurring brain chemicals that likely play a role in depression. Recent research indicates that changes in the function and effect of these neurotransmitters and how they interact with neurocircuits involved in maintaining mood stability may play a significant role in depression and its treatment**
* __**Hormones**__**. Changes in the body's balance of hormones may be involved in causing or triggering depression**
\
* Learning/Environmental
* **Synthetic Chemicals From Foods. ...**
* **Natural Disasters. ...**
* **Trauma. ...**
* **Substance Abuse. ...**
* **Chronic Illness and Injuries. ...**
* **Grief**
* Cognitive
* people's thoughts, inferences, attitudes, and interpretations, and the way in which they attend to and recall events, can increase their risk for the development and recurrence of depressive episodes
4\. prognosis
* Depression is among the most treatable of mental disorders. Between 80% and 90% percent of people with depression eventually respond well to treatment. Almost all patients gain some relief from their symptoms
* **antidepressants** might be prescribed to help modify one’s brain chemistry.
* Psychotherapy, or “talk therapy,” is sometimes used alone for treatment of mild depression; for moderate to severe depression, psychotherapy is often used along with antidepressant medications.
5\. any differences by demographic group?
\
* **Women are more likely than men to experience depression. Some studies show that one-third of women will experience a major depressive episode in their lifetime.**
38
New cards
Persistent Depressive disorder (a.k.a. Dysthymia)
A depressive Disorder
= consistent sadness accompanied by eating/sleep disturbance, low energy/self-esteem, and diminished concentration
How is it different from Major Depressive disorder?
\
* Persistent depressive disorder lasts longer but does not include suicidal thoughts/attempts, so it is considered less acute but longer-lasting
= consistent sadness accompanied by eating/sleep disturbance, low energy/self-esteem, and diminished concentration
How is it different from Major Depressive disorder?
\
* Persistent depressive disorder lasts longer but does not include suicidal thoughts/attempts, so it is considered less acute but longer-lasting
39
New cards
Seasonal Affective disorder
A depressive Disorder
= depression with a regular seasonal pattern
\
How is it different from Major Depressive disorder?
\
* noticeable change in an individual’s mood, generally involving depression in cold,dark winter months and a lack of symptoms in the warmer months
* reduced light exposure has an impact on serotonin during fall/winter, seems to be main cause of SAD
* may have other contributing factors bc countries with extreme seasonal patterns (i.e. Norway and Sweden) have low suicide rates/rank high on happiest countries of the world
= depression with a regular seasonal pattern
\
How is it different from Major Depressive disorder?
\
* noticeable change in an individual’s mood, generally involving depression in cold,dark winter months and a lack of symptoms in the warmer months
* reduced light exposure has an impact on serotonin during fall/winter, seems to be main cause of SAD
* may have other contributing factors bc countries with extreme seasonal patterns (i.e. Norway and Sweden) have low suicide rates/rank high on happiest countries of the world
40
New cards
Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder
A depressive Disorder
= chronic and severe irritability and temper tantrums in young children
\
Why was DMDD added to the DSM-5?
* to address concerns about the potential for the over-diagnosis and treatment of bipolar disorder in children
1\. symptoms
* severe, recurrent (≥3 times/week) temper outbursts (verbally and/or behaviorally) that are grossly out of proportion in intensity or duration to the situation, and inconsistent with the developmental level
* the mood between temper outbursts is persistently irritable or angry most of the day, nearly every day, and observable by others
* “hyperarousal” symptoms (insomnia, agitation, distractibility, racing thoughts or flight of ideas, pressured speech, and intrusiveness)
2\. onset and prevalence
* by history or observation, the age at onset is before 10 years
* the diagnosis should not be made for the first time before age 6 years or after 18 years
* affects between 2-5% of children in the US, mostly male
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* A young person’s genetic history is the strongest determining factor that could cause the onset of DMDD. In fact, among children and adolescents who meet criteria for this illness, all typically have a family history of depression, anxiety disorders, or substance use disorders in their backgrounds. Additionally, an irritable personality, which is said to be heritable, is an example of another way that genes can influence the onset of this disorder.
4\. prognosis
* no treatment/cure yet
* More research is needed to determine whether treatment with SSRIs and/or stimulants is effective and safe in treating DMDD/SMD
* Behavioral and other psychotherapeutic interventions also should be considered in treating DMDD/SMD, particularly given their impairment in many social domains
5\. any differences by demographic group?
\
* increased risk if male
* affects mostly school-age children
* increased risk if family history of anxiety, depressive, or substance use disorders
= chronic and severe irritability and temper tantrums in young children
\
Why was DMDD added to the DSM-5?
* to address concerns about the potential for the over-diagnosis and treatment of bipolar disorder in children
1\. symptoms
* severe, recurrent (≥3 times/week) temper outbursts (verbally and/or behaviorally) that are grossly out of proportion in intensity or duration to the situation, and inconsistent with the developmental level
* the mood between temper outbursts is persistently irritable or angry most of the day, nearly every day, and observable by others
* “hyperarousal” symptoms (insomnia, agitation, distractibility, racing thoughts or flight of ideas, pressured speech, and intrusiveness)
2\. onset and prevalence
* by history or observation, the age at onset is before 10 years
* the diagnosis should not be made for the first time before age 6 years or after 18 years
* affects between 2-5% of children in the US, mostly male
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* A young person’s genetic history is the strongest determining factor that could cause the onset of DMDD. In fact, among children and adolescents who meet criteria for this illness, all typically have a family history of depression, anxiety disorders, or substance use disorders in their backgrounds. Additionally, an irritable personality, which is said to be heritable, is an example of another way that genes can influence the onset of this disorder.
4\. prognosis
* no treatment/cure yet
* More research is needed to determine whether treatment with SSRIs and/or stimulants is effective and safe in treating DMDD/SMD
* Behavioral and other psychotherapeutic interventions also should be considered in treating DMDD/SMD, particularly given their impairment in many social domains
5\. any differences by demographic group?
\
* increased risk if male
* affects mostly school-age children
* increased risk if family history of anxiety, depressive, or substance use disorders
41
New cards
Specific Phobia
Anxiety Disorder #1
= A *phobia* is an intense fear of—or aversion to—specific objects or situations. Although it can be realistic to be anxious in some circumstances, the fear people with phobias feel is out of proportion to the actual danger caused by the situation or object
ex. fear of:
* Flying
* Heights
* Specific animals, such as spiders, dogs, or snakes
* Receiving injections
* Blood
\
1\. symptoms
* May have an irrational or excessive worry about encountering the feared object or situation
* Take active steps to avoid the feared object or situation
* Experience immediate intense anxiety upon encountering the feared object or situation
* Endure unavoidable objects and situations with intense anxiety
2\. onset and prevalence
* Onset: can first appear in childhood, usually by age 10, but can occur later in life.
* prevalence: 12.5% of U.S. adults experience specific phobia at some time in their lives
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* Your relatives. If someone in your family has a specific phobia or anxiety, you're more likely to develop it, too.
* Past incidents or traumas. Certain situations might have a lasting effect on how you feel about them. ...
* Learned responses from early life. ...
* Reactions and responses to panic or fear. ...
* Experiencing long-term stress. ...
4\. prognosis
\
* When left untreated, phobias can be lifelong, however, studies show that phobias tend to spontaneously attenuate over time. With the appropriate behavioral techniques and medications, the prognosis is good
= A *phobia* is an intense fear of—or aversion to—specific objects or situations. Although it can be realistic to be anxious in some circumstances, the fear people with phobias feel is out of proportion to the actual danger caused by the situation or object
ex. fear of:
* Flying
* Heights
* Specific animals, such as spiders, dogs, or snakes
* Receiving injections
* Blood
\
1\. symptoms
* May have an irrational or excessive worry about encountering the feared object or situation
* Take active steps to avoid the feared object or situation
* Experience immediate intense anxiety upon encountering the feared object or situation
* Endure unavoidable objects and situations with intense anxiety
2\. onset and prevalence
* Onset: can first appear in childhood, usually by age 10, but can occur later in life.
* prevalence: 12.5% of U.S. adults experience specific phobia at some time in their lives
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* Your relatives. If someone in your family has a specific phobia or anxiety, you're more likely to develop it, too.
* Past incidents or traumas. Certain situations might have a lasting effect on how you feel about them. ...
* Learned responses from early life. ...
* Reactions and responses to panic or fear. ...
* Experiencing long-term stress. ...
4\. prognosis
\
* When left untreated, phobias can be lifelong, however, studies show that phobias tend to spontaneously attenuate over time. With the appropriate behavioral techniques and medications, the prognosis is good
42
New cards
Social Anxiety Disorder
Anxiety Disorder #2
= general intense fear of, or anxiety toward, social or performance situations. They worry that actions or behaviors associated with their anxiety will be negatively evaluated by others, leading them to feel embarrassed
\
= general intense fear of, or anxiety toward, social or performance situations. They worry that actions or behaviors associated with their anxiety will be negatively evaluated by others, leading them to feel embarrassed
\
43
New cards
Panic Disorder
Anxiety Disorder #3
= frequent and unexpected panic attacks.
1\. symptoms
* panic attack = Panic attacks are sudden periods of intense fear, discomfort, or sense of losing control even when there is no clear danger or trigger.
* Not everyone who experiences a panic attack will develop panic disorder
* Pounding or racing heart
* Sweating
* Trembling or tingling
* Chest pain
* Feelings of impending doom
* Feelings of being out of control
2\. onset and prevalence
* onset: Symptoms often begin before age 25 but may occur in the mid-30s.
* prevalence: **estimated 2.7% of U.S. adults had panic disorder in** the past year
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
\
* often occurs when there is no family history
4\. prognosis
* Prognosis can be guarded. The presence of panic disorder without other psychopathology is rare. Most people will have a recurrence of symptoms even after a symptom-free period. Compliance with treatment is a major issue and thus relapse of symptoms is common. Only about 60% of patients achieve remission within 6 months. Triggers for poor outcomes include a chronic illness, high interpersonal sensitivity, unmarried, low social class, and living alone. Besides premature adverse cardiac events, these patients are also at a risk for suicide.
5\. any differences by demographic group?
\
* Panic disorder is twice as common in women as it is in men
= frequent and unexpected panic attacks.
1\. symptoms
* panic attack = Panic attacks are sudden periods of intense fear, discomfort, or sense of losing control even when there is no clear danger or trigger.
* Not everyone who experiences a panic attack will develop panic disorder
* Pounding or racing heart
* Sweating
* Trembling or tingling
* Chest pain
* Feelings of impending doom
* Feelings of being out of control
2\. onset and prevalence
* onset: Symptoms often begin before age 25 but may occur in the mid-30s.
* prevalence: **estimated 2.7% of U.S. adults had panic disorder in** the past year
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
\
* often occurs when there is no family history
4\. prognosis
* Prognosis can be guarded. The presence of panic disorder without other psychopathology is rare. Most people will have a recurrence of symptoms even after a symptom-free period. Compliance with treatment is a major issue and thus relapse of symptoms is common. Only about 60% of patients achieve remission within 6 months. Triggers for poor outcomes include a chronic illness, high interpersonal sensitivity, unmarried, low social class, and living alone. Besides premature adverse cardiac events, these patients are also at a risk for suicide.
5\. any differences by demographic group?
\
* Panic disorder is twice as common in women as it is in men
44
New cards
Agoraphobia
Anxiety Disorder #4
= extreme or irrational fear of entering open or crowded places, of leaving one's own home, or of being in places from which escape is difficult.
\
1\. symptoms
**The physical symptoms of ___ can be similar to those of a panic attack and may include:**
* rapid heartbeat.
* rapid breathing (hyperventilating)
* feeling hot and sweaty.
* feeling sick.
* chest pain.
* difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
* diarrhea.
* trembling
\
2\. onset and prevalence
* onset: can begin in childhood, but usually starts in the late teen or early adult years — usually before age 35
* prevalence: 1.3% of U.S. adult
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* commonly genetically inherited, but there are other reasons someone may develop the disorder:
* experiencing a stressful event, such as bereavement, divorce, or losing your job
* history of mental illnesses:
* depression, anorexia nervosa or bulimia.
* alcohol misuse or drug misuse.
* being in an unhappy relationship
4\. prognosis
* manageable with treatment, which includes medication, cognitive behavioral therapy and lifestyle changes
5\. any differences by demographic group?
\
* Females are diagnosed with ____ more often than males are
= extreme or irrational fear of entering open or crowded places, of leaving one's own home, or of being in places from which escape is difficult.
\
1\. symptoms
**The physical symptoms of ___ can be similar to those of a panic attack and may include:**
* rapid heartbeat.
* rapid breathing (hyperventilating)
* feeling hot and sweaty.
* feeling sick.
* chest pain.
* difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
* diarrhea.
* trembling
\
2\. onset and prevalence
* onset: can begin in childhood, but usually starts in the late teen or early adult years — usually before age 35
* prevalence: 1.3% of U.S. adult
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* commonly genetically inherited, but there are other reasons someone may develop the disorder:
* experiencing a stressful event, such as bereavement, divorce, or losing your job
* history of mental illnesses:
* depression, anorexia nervosa or bulimia.
* alcohol misuse or drug misuse.
* being in an unhappy relationship
4\. prognosis
* manageable with treatment, which includes medication, cognitive behavioral therapy and lifestyle changes
5\. any differences by demographic group?
\
* Females are diagnosed with ____ more often than males are
45
New cards
Generalized Anxiety disorder
Anxiety Disorder #5
= persistent feeling of anxiety or dread that interferes with how you live your life
\
1\. symptoms
* Feeling restless, wound-up, or on-edge
* Being easily fatigued
* Having difficulty concentrating
* Being irritable
* Having headaches, muscle aches, stomachaches, or unexplained pains
* Difficulty controlling feelings of worry
* Having sleep problems, such as difficulty falling or staying asleep
\
2\. onset and prevalence
* onset: begins gradually, often in childhood or adolescence, with symptoms that may worsen during times of stress
* prevalence: 5.7% of U.S. adults experience generalized anxiety disorder at some time in their lives
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
\
4\. prognosis
* prognosis can vary depending on how severe it is. In some cases, GAD is long-term (chronic) and difficult to treat. However, most people experience improvement in their symptoms with medicine and/or talk therapy
5\. any differences by demographic group?
\
* affects more American Indian/Alaskan Native women than women of other races and ethnicities.
* GAD also affects more white women and Hispanic women than Asian or African-American women
= persistent feeling of anxiety or dread that interferes with how you live your life
\
1\. symptoms
* Feeling restless, wound-up, or on-edge
* Being easily fatigued
* Having difficulty concentrating
* Being irritable
* Having headaches, muscle aches, stomachaches, or unexplained pains
* Difficulty controlling feelings of worry
* Having sleep problems, such as difficulty falling or staying asleep
\
2\. onset and prevalence
* onset: begins gradually, often in childhood or adolescence, with symptoms that may worsen during times of stress
* prevalence: 5.7% of U.S. adults experience generalized anxiety disorder at some time in their lives
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
\
4\. prognosis
* prognosis can vary depending on how severe it is. In some cases, GAD is long-term (chronic) and difficult to treat. However, most people experience improvement in their symptoms with medicine and/or talk therapy
5\. any differences by demographic group?
\
* affects more American Indian/Alaskan Native women than women of other races and ethnicities.
* GAD also affects more white women and Hispanic women than Asian or African-American women
46
New cards
Obsessive-Compulsive disorder (OCD)
= person has uncontrollable, reoccurring thoughts ("obsessions") and/or behaviors ("compulsions") that he or she feels the urge to repeat over and over
\
2\. onset and prevalence
* onset: typically begins in adolescence, but may start in early adulthood or childhood. The onset of OCD is typically gradual, but in some cases it may start suddenly
* prevalence: 2% of the world
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* Ongoing anxiety or stress, or being part of a stressful event like a car accident or starting a new job, could trigger OCD or make it worse. Pregnancy or giving birth can sometimes trigger perinatal OCD.
* traumatic experiences such as unexpected exposure to contaminants or various stressful life events often cause the onset of OCD
4\. prognosis
* OCD is often a lifelong condition that can wax and wane.
* People with OCD who __receive appropriate treatment__ often experience increased quality of life and improved social, school and/or work functioning
5\. any differences by demographic group?
\
* Past year prevalence of OCD was higher for females (1.8%) than for males (0.5%)
* African Americans experience OCD at similar rates as the general population (White 2.6% vs. Black 2.3%,; White 1.6% vs. Black 1.6%,,
* but are less likely to receive treatment or experience a remission
\
2\. onset and prevalence
* onset: typically begins in adolescence, but may start in early adulthood or childhood. The onset of OCD is typically gradual, but in some cases it may start suddenly
* prevalence: 2% of the world
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* Ongoing anxiety or stress, or being part of a stressful event like a car accident or starting a new job, could trigger OCD or make it worse. Pregnancy or giving birth can sometimes trigger perinatal OCD.
* traumatic experiences such as unexpected exposure to contaminants or various stressful life events often cause the onset of OCD
4\. prognosis
* OCD is often a lifelong condition that can wax and wane.
* People with OCD who __receive appropriate treatment__ often experience increased quality of life and improved social, school and/or work functioning
5\. any differences by demographic group?
\
* Past year prevalence of OCD was higher for females (1.8%) than for males (0.5%)
* African Americans experience OCD at similar rates as the general population (White 2.6% vs. Black 2.3%,; White 1.6% vs. Black 1.6%,,
* but are less likely to receive treatment or experience a remission
47
New cards
obsessions
= **unwanted, intrusive thoughts, images, or urges that trigger intensely distressing feelings**
\
ex.
\
* Fear of being contaminated by touching objects others have touched
* Doubts that you've locked the door or turned off the stove
* Intense stress when objects aren't orderly or facing a certain way
* Images of driving your car into a crowd of people
\
ex.
\
* Fear of being contaminated by touching objects others have touched
* Doubts that you've locked the door or turned off the stove
* Intense stress when objects aren't orderly or facing a certain way
* Images of driving your car into a crowd of people
48
New cards
compulsions
= behaviors an individual engages in to attempt to get rid of the obsessions and/or decrease distress
\
ex.
\
* Hand-washing until your skin becomes raw
* Checking doors repeatedly to make sure they're locked
* Checking the stove repeatedly to make sure it's off
* Counting in certain patterns
* Silently repeating a prayer, word or phrase
* Arranging your canned goods to face the same way
\
ex.
\
* Hand-washing until your skin becomes raw
* Checking doors repeatedly to make sure they're locked
* Checking the stove repeatedly to make sure it's off
* Counting in certain patterns
* Silently repeating a prayer, word or phrase
* Arranging your canned goods to face the same way
49
New cards
Hoarding disorder
symptoms
* Inability to get rid of possessions.
* Experiencing extreme stress when attempting to throw out items.
* Anxiety about needing items in the future.
* Uncertainty about where to put things.
* Distrust of other people touching possessions.
* Living in unusable spaces due to clutter
2\. onset and prevalence
* typical onset is around age 16
* 2.6%, with higher rates for people over 60 years old and people with other psychiatric diagnoses, especially anxiety and depression.
\
* Inability to get rid of possessions.
* Experiencing extreme stress when attempting to throw out items.
* Anxiety about needing items in the future.
* Uncertainty about where to put things.
* Distrust of other people touching possessions.
* Living in unusable spaces due to clutter
2\. onset and prevalence
* typical onset is around age 16
* 2.6%, with higher rates for people over 60 years old and people with other psychiatric diagnoses, especially anxiety and depression.
\
50
New cards
Body Dysmorphic disorder
= mental health condition in which you can't stop thinking about one or more perceived defects or flaws in your appearance — a flaw that appears minor or can't be seen by others
\
1\. symptoms
* Being extremely preoccupied with a perceived flaw in appearance that to others can't be seen or appears minor
* Strong belief that you have a defect in your appearance that makes you ugly or deformed
* Belief that others take special notice of your appearance in a negative way or mock you
* Engaging in behaviors aimed at fixing or hiding the perceived flaw that are difficult to resist or control, such as frequently checking the mirror, grooming or skin picking
* Attempting to hide perceived flaws with styling, makeup or clothes
* Constantly comparing your appearance with others
* Frequently seeking reassurance about your appearance from others
* Having perfectionist tendencies
* Seeking cosmetic procedures with little satisfaction
* Avoiding social situations
2\. onset and prevalence
* typically begin during adolescence, most commonly by 12-13 years old
* prevalence: affects **1.7% to 2.9% of the general population**
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* Abuse or bullying.
* Low self-esteem.
* Fear of being rejected.
* Perfectionism or comparing yourself with others.
* Genetics.
* Depression, anxiety or OCD.
4\. prognosis
If fully and appropriately treated with both pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy, BDD generally has a good prognosis
5\. any differences by demographic group?
\
* about 40% of people with BDD are men, and about 60% are women
* most often develops in adolescents and teens
\
1\. symptoms
* Being extremely preoccupied with a perceived flaw in appearance that to others can't be seen or appears minor
* Strong belief that you have a defect in your appearance that makes you ugly or deformed
* Belief that others take special notice of your appearance in a negative way or mock you
* Engaging in behaviors aimed at fixing or hiding the perceived flaw that are difficult to resist or control, such as frequently checking the mirror, grooming or skin picking
* Attempting to hide perceived flaws with styling, makeup or clothes
* Constantly comparing your appearance with others
* Frequently seeking reassurance about your appearance from others
* Having perfectionist tendencies
* Seeking cosmetic procedures with little satisfaction
* Avoiding social situations
2\. onset and prevalence
* typically begin during adolescence, most commonly by 12-13 years old
* prevalence: affects **1.7% to 2.9% of the general population**
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* Abuse or bullying.
* Low self-esteem.
* Fear of being rejected.
* Perfectionism or comparing yourself with others.
* Genetics.
* Depression, anxiety or OCD.
4\. prognosis
If fully and appropriately treated with both pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy, BDD generally has a good prognosis
5\. any differences by demographic group?
\
* about 40% of people with BDD are men, and about 60% are women
* most often develops in adolescents and teens
51
New cards
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
1\. symptoms
* intrusion symptoms
* experiencing unwanted memories
* nightmares
* flashbacks
* avoidance symptoms
* avoiding the physical place in which the event took place
* avoiding certain people/activities that remind you of it
* negative cognitions and mood
* loss of concentration
* increased frequency of shame, anger, horror, guilt, sadness
* arousal
* restlessness
* irritability
* outbursts of anger
2\. onset and prevalence
* According to the National Center for PTSD, about 7 or 8 out of every 100 people will experience PTSD at some point in their lives.
* Anyone can get PTSD at any age, but typical onset is young and middle adulthood
\
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* caused by experiencing very troubling and potentially deadly situations (natural disaster, sexual violence, injuries, war)
4\. prognosis
For a diagnosis to occur, the symptoms must be present on an ongoing basis for at least one month after the incident.
Treatment can include medication, psychotherapy, or both. Support from family and friends is also crucial for the patients recovery
5\. any differences by demographic group?
\-Women are more likely to develop PTSD than men
\-Black and Hispanic veterans were shown to have more elevated rates of PTSD
\
\- minority groups are often not able to get access to treatment and therefore have higher severity of the disorder
\
* intrusion symptoms
* experiencing unwanted memories
* nightmares
* flashbacks
* avoidance symptoms
* avoiding the physical place in which the event took place
* avoiding certain people/activities that remind you of it
* negative cognitions and mood
* loss of concentration
* increased frequency of shame, anger, horror, guilt, sadness
* arousal
* restlessness
* irritability
* outbursts of anger
2\. onset and prevalence
* According to the National Center for PTSD, about 7 or 8 out of every 100 people will experience PTSD at some point in their lives.
* Anyone can get PTSD at any age, but typical onset is young and middle adulthood
\
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* caused by experiencing very troubling and potentially deadly situations (natural disaster, sexual violence, injuries, war)
4\. prognosis
For a diagnosis to occur, the symptoms must be present on an ongoing basis for at least one month after the incident.
Treatment can include medication, psychotherapy, or both. Support from family and friends is also crucial for the patients recovery
5\. any differences by demographic group?
\-Women are more likely to develop PTSD than men
\-Black and Hispanic veterans were shown to have more elevated rates of PTSD
\
\- minority groups are often not able to get access to treatment and therefore have higher severity of the disorder
\
52
New cards
Acute Stress disorder
= a mental health problem that can occur in __the first month__ after a traumatic event
\
1\. symptoms
* The symptoms of ASD are like PTSD symptoms, but you must have them for longer than one month to have PTSD
2\. onset and prevalence
* Overall, within one month of a trauma, survivors show rates of ASD ranging from 6% to 33%. Rates differ for different types of trauma.
* onset can be at any age
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* Several factors can place you at higher risk for developing ASD after a trauma: having gone through other traumatic events, having had PTSD in the past, having had prior mental health problems, and tending to have symptoms, such as not knowing who or where you are, when confronted with trauma
\
4\. prognosis
\
* If you have ASD, you are very likely to get PTSD. Research has found that over 80% of people with ASD have PTSD six months later. Not everyone with ASD will get PTSD, though.
* Also, those who do not get ASD can still develop PTSD later on. Studies indicate that a small number (4% to 13%) of survivors who do not get ASD in the first month after a trauma will get PTSD in later months or years.
* cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) shown to have positive results
* psychological debriefing (PD) is used to treat it but not backed by research
\
1\. symptoms
* The symptoms of ASD are like PTSD symptoms, but you must have them for longer than one month to have PTSD
2\. onset and prevalence
* Overall, within one month of a trauma, survivors show rates of ASD ranging from 6% to 33%. Rates differ for different types of trauma.
* onset can be at any age
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* Several factors can place you at higher risk for developing ASD after a trauma: having gone through other traumatic events, having had PTSD in the past, having had prior mental health problems, and tending to have symptoms, such as not knowing who or where you are, when confronted with trauma
\
4\. prognosis
\
* If you have ASD, you are very likely to get PTSD. Research has found that over 80% of people with ASD have PTSD six months later. Not everyone with ASD will get PTSD, though.
* Also, those who do not get ASD can still develop PTSD later on. Studies indicate that a small number (4% to 13%) of survivors who do not get ASD in the first month after a trauma will get PTSD in later months or years.
* cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) shown to have positive results
* psychological debriefing (PD) is used to treat it but not backed by research
53
New cards
Developmental Trauma Disorder
= trauma-related disorder specific to children that accounts for the disruptions in development that result from sustained trauma during childhood, which typically occurs in the context of relationships
\
1\. symptoms
* habitual self-harm
* extreme distrust
* verbal or physical aggression toward others
* by school age, may experience impulsivity, aggression, separation anxiety, and intense mood shifts
* problems with sleep, learning, classroom behavior, and relationships with peers
* by adolescence, may turn to addictive behaviors (ex. self-injury or substance use) to cope with emotional turmoil or to feel something when emotionally shut down
2\. onset and prevalence
* onset is during childhood
* prevalence of DSM-5 PTSD and DTD together is approximately 40%
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* interpersonal trauma (either direct or witnessed emotional, physical, or sexual abuse) usually involving a parent or caregiver (can alter a child’s worldview when a relationship that was supposed to be nurturing and protective is the opposite of that)
4\. prognosis
* In the absence of formal diagnostic recognition, the majority of treatment research has been devoted to PTSD, which may not fully capture treatment needs or translate to a more complexly-symptomatic sample of DTD patients
5\. any differences by demographic group?
*(this is data from a specific experiment, because stats are hard to find for something that isn’t officially in the DSM-5 lol*) Regarding a DSM-5 PTSD-adult diagnosis, the distribution among ethnic groups was: 18% Black, 82% Hispanic, 0% White, and 0% Asian. In terms of meeting for the proposed criteria for DTD, the distribution within ethnic groups was: 30% White, 23% Hispanic, 20% among Black, and 0% among Asian.
\
1\. symptoms
* habitual self-harm
* extreme distrust
* verbal or physical aggression toward others
* by school age, may experience impulsivity, aggression, separation anxiety, and intense mood shifts
* problems with sleep, learning, classroom behavior, and relationships with peers
* by adolescence, may turn to addictive behaviors (ex. self-injury or substance use) to cope with emotional turmoil or to feel something when emotionally shut down
2\. onset and prevalence
* onset is during childhood
* prevalence of DSM-5 PTSD and DTD together is approximately 40%
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* interpersonal trauma (either direct or witnessed emotional, physical, or sexual abuse) usually involving a parent or caregiver (can alter a child’s worldview when a relationship that was supposed to be nurturing and protective is the opposite of that)
4\. prognosis
* In the absence of formal diagnostic recognition, the majority of treatment research has been devoted to PTSD, which may not fully capture treatment needs or translate to a more complexly-symptomatic sample of DTD patients
5\. any differences by demographic group?
*(this is data from a specific experiment, because stats are hard to find for something that isn’t officially in the DSM-5 lol*) Regarding a DSM-5 PTSD-adult diagnosis, the distribution among ethnic groups was: 18% Black, 82% Hispanic, 0% White, and 0% Asian. In terms of meeting for the proposed criteria for DTD, the distribution within ethnic groups was: 30% White, 23% Hispanic, 20% among Black, and 0% among Asian.
54
New cards
Dissociative Identity Disorder
= when a person exhibits 2+ distinct personalities
due to conscious awareness separated from previous memories/thoughts
1\. symptoms
* memory loss of certain time periods, events, people, and personal information
* depression, anxiety, suicidal thoughts or behavior
* blurred sense of identity
2\. onset and prevalence
* The typical patient who is diagnosed with DID is a woman, about age 30. A patient’s history typically will reveal onset of dissociative symptoms at ages 5 to 10
* very rare
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* it can be caused by severe and prolonged trauma experienced during childhood, including emotional, physical or sexual abuse.
4\. prognosis
\
* The primary treatment for DID is psychotherapy. Also known as talk therapy or psychosocial therapy, psychotherapy is focused on talking with a mental health professional about your mental health.
due to conscious awareness separated from previous memories/thoughts
1\. symptoms
* memory loss of certain time periods, events, people, and personal information
* depression, anxiety, suicidal thoughts or behavior
* blurred sense of identity
2\. onset and prevalence
* The typical patient who is diagnosed with DID is a woman, about age 30. A patient’s history typically will reveal onset of dissociative symptoms at ages 5 to 10
* very rare
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* it can be caused by severe and prolonged trauma experienced during childhood, including emotional, physical or sexual abuse.
4\. prognosis
\
* The primary treatment for DID is psychotherapy. Also known as talk therapy or psychosocial therapy, psychotherapy is focused on talking with a mental health professional about your mental health.
55
New cards
Dissociative Amnesia
= when a person blocks out specific info, no memory of a specific event
1\. symptoms
* memory loss that's more severe than normal forgetfulness
* can't recall information about yourself or events and people in your life, especially from a traumatic time.
How is it different than retrograde amnesia?
retrograde amnesia is forgetting the events that occurred before a traumatic event, while _________ is forgetting the traumatic event
2\. onset and prevalence
usually sudden
* rare. It affects about 1% of men and people assigned male at birth and 2.6% of women and people assigned female at birth in the general population
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
environment also plays a role. Rates of dissociative amnesia tend to increase after natural disasters and during war
\
4\. prognosis
\
memory eventually returns, sometimes slowly and sometimes suddenly, which makes the overall outlook very good
5\. any differences by demographic group?
\
more common among women than men, usually people who have experienced or witnessed traumatic events, such as physical or sexual abuse, rape, wars, genocide, accidents, natural disasters, or death of a loved one
\
1\. symptoms
* memory loss that's more severe than normal forgetfulness
* can't recall information about yourself or events and people in your life, especially from a traumatic time.
How is it different than retrograde amnesia?
retrograde amnesia is forgetting the events that occurred before a traumatic event, while _________ is forgetting the traumatic event
2\. onset and prevalence
usually sudden
* rare. It affects about 1% of men and people assigned male at birth and 2.6% of women and people assigned female at birth in the general population
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
environment also plays a role. Rates of dissociative amnesia tend to increase after natural disasters and during war
\
4\. prognosis
\
memory eventually returns, sometimes slowly and sometimes suddenly, which makes the overall outlook very good
5\. any differences by demographic group?
\
more common among women than men, usually people who have experienced or witnessed traumatic events, such as physical or sexual abuse, rape, wars, genocide, accidents, natural disasters, or death of a loved one
\
56
New cards
dissociative fugue
a subtype of dissociative amnesia
= when someone temporarily has amnesia and ends up in a location not knowing how they got there with no awareness of their identity
= when someone temporarily has amnesia and ends up in a location not knowing how they got there with no awareness of their identity
57
New cards
Somatic Symptom disorder
= when a person has a significant focus on physical symptoms, such as pain, weakness or shortness of breath, to a level that results in major distress and/or problems functioning. The individual has excessive thoughts, feelings and behaviors relating to the physical symptoms. The physical symptoms may or may not be associated with a diagnosed medical condition, but the person is experiencing symptoms and believes they are sick (that is, not faking the illness).
58
New cards
Illness Anxiety disorder
= an unrealistic fear that they have a serious medical condition or fear that they're at high risk of becoming ill
59
New cards
Conversion disorder
= condition in which a person experiences physical and sensory problems, such as paralysis, numbness, blindness, deafness or seizures, with no underlying neurologic pathology
60
New cards
Factitious disorder
= serious mental disorder in which someone deceives others by appearing sick, by purposely getting sick or by self-injury
61
New cards
Anorexia Nervosa
Eating disorder
= related to starvation
\
1\. symptoms
\
Physical
* Extreme weight loss or not making expected developmental weight gains
* Thin appearance
* Abnormal blood counts
* Fatigue
* Insomnia
* Dizziness or fainting
* Bluish discoloration of the fingers
* Hair that thins, breaks or falls out
Behavioral/Emotional
* Bingeing and self-induced vomiting to get rid of food
* Frequently skipping meals or refusing to eat
* Denial of hunger or making excuses for not eating
\
2\. onset and prevalence
* between 12-25
* 6% of the total population,
* but college-age women are estimated to suffer between 19% and 30%
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* psychological
* unrealistic perception of body weight and an extremely strong fear of gaining weight or becoming fat
* may have obsessive-compulsive personality traits that make it easier to stick to strict diets and forgo food despite being hungry.
* extreme drive for perfectionism, which causes them to think they're never thin enough.
* high levels of anxiety
* Biologically
* may be genetic changes that make some people at higher risk of developing anorexia. Some people may have a genetic tendency toward perfectionism, sensitivity and perseverance — all traits associated with anorexia
* Social/Environmental
* Modern Western culture emphasizes thinness. Success and worth are often equated with being thin. Peer pressure may help fuel the desire to be thin, particularly among young girls.
4\. prognosis
* may result in suffering nerve damage that affects the brain and other parts of the body. As a result, these nervous system conditions can include: Seizures. Disordered thinking
5\. any differences by demographic group?
\
* three times higher among females (0.9%) than males (0.3%)
= related to starvation
\
1\. symptoms
\
Physical
* Extreme weight loss or not making expected developmental weight gains
* Thin appearance
* Abnormal blood counts
* Fatigue
* Insomnia
* Dizziness or fainting
* Bluish discoloration of the fingers
* Hair that thins, breaks or falls out
Behavioral/Emotional
* Bingeing and self-induced vomiting to get rid of food
* Frequently skipping meals or refusing to eat
* Denial of hunger or making excuses for not eating
\
2\. onset and prevalence
* between 12-25
* 6% of the total population,
* but college-age women are estimated to suffer between 19% and 30%
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* psychological
* unrealistic perception of body weight and an extremely strong fear of gaining weight or becoming fat
* may have obsessive-compulsive personality traits that make it easier to stick to strict diets and forgo food despite being hungry.
* extreme drive for perfectionism, which causes them to think they're never thin enough.
* high levels of anxiety
* Biologically
* may be genetic changes that make some people at higher risk of developing anorexia. Some people may have a genetic tendency toward perfectionism, sensitivity and perseverance — all traits associated with anorexia
* Social/Environmental
* Modern Western culture emphasizes thinness. Success and worth are often equated with being thin. Peer pressure may help fuel the desire to be thin, particularly among young girls.
4\. prognosis
* may result in suffering nerve damage that affects the brain and other parts of the body. As a result, these nervous system conditions can include: Seizures. Disordered thinking
5\. any differences by demographic group?
\
* three times higher among females (0.9%) than males (0.3%)
62
New cards
avoidant restrictive
* Unlike anorexia, (**ARFID) does not involve a fear of weight gain**
**Overall, ARFID means that a person severely avoids or restricts food. However, there are several different ways that ARFID can present, such as:**
\
* **Sensory sensitivity, where people avoid foods of certain types or textures, such as meat, fruits or vegetables**
* **Avoidance of certain foods or food altogether after choking or vomiting**
* **Restriction or avoidance of food due to low appetite or general disinterest in eating**
**Overall, ARFID means that a person severely avoids or restricts food. However, there are several different ways that ARFID can present, such as:**
\
* **Sensory sensitivity, where people avoid foods of certain types or textures, such as meat, fruits or vegetables**
* **Avoidance of certain foods or food altogether after choking or vomiting**
* **Restriction or avoidance of food due to low appetite or general disinterest in eating**
63
New cards
Bulimia Nervosa
= a serious, potentially life-threatening eating disorder. People with bulimia may secretly binge — eating large amounts of food with a loss of control over the eating — and then purge, trying to get rid of the extra calories in an unhealthy way. (purging)
\
1\. symptoms
* Being preoccupied with your body shape and weight
* Living in fear of gaining weight
* Repeated episodes of eating abnormally large amounts of food in one sitting
* Feeling a loss of control during bingeing — like you can't stop eating or can't control what you eat
* Forcing yourself to vomit or exercising too much to keep from gaining weight after bingeing
* Using laxatives, diuretics or enemas after eating when they're not needed
* Fasting, restricting calories or avoiding certain foods between binges
* Using dietary supplements or herbal products excessively for weight loss
* The severity of bulimia is determined by the number of times a week that you purge, usually at least once a week for at least three months.
* Negative self-esteem and problems with relationships and social functioning
* Dehydration, which can lead to major medical problems, such as kidney failure
* Heart problems, such as an irregular heartbeat or heart failure
* Severe tooth decay and gum disease
* Absent or irregular periods in females
* Digestive problems
* Anxiety, depression, personality disorders or bipolar disorder
* Misuse of alcohol or drugs
* Self-injury, suicidal thoughts or suicide
\
2\. onset and prevalence
* Bulimia often begins in the late teens or early adulthood.
* 1.5 percent of the US female population and 0.5 percent of the male population has experienced bulimia in their lifetimes. These percentages translate to 4.7 million females and 1.5 million males.
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* Psychological and emotional problems, such as depression, anxiety disorders or substance use disorders are closely linked with eating disorders.
* In some cases, traumatic events and environmental stress may be contributing factors.
* People who diet are at higher risk of developing eating disorders. Many people with bulimia severely restrict calories between binge episodes, which may trigger an urge to again binge eat and then purge. Other triggers for bingeing can include stress, poor body self-image, food and boredom.
4\. prognosis
* may need several types of treatment, although combining psychotherapy with antidepressants may be the most effective for overcoming the disorder
* cognitive behavioral therapy, family-based treatment, or interpersonal psychotherapy may be used
* Antidepressants may help reduce symptoms when used along with psychotherapy. The only antidepressant specifically approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat bulimia is fluoxetine (Prozac), an SSRI
* Dietitians can design an eating plan to help you achieve healthy eating habits to avoid hunger and cravings and to provide good nutrition
* if symptoms are severe, with serious health complications, you may need treatment in a hospital. Some eating disorder programs may offer day treatment rather than inpatient hospitalization
* Although most people with bulimia do recover, some find that symptoms don't go away entirely
5\. any differences by demographic group?
* Girls and women are more likely to have bulimia than boys and men are.
\
\
\
1\. symptoms
* Being preoccupied with your body shape and weight
* Living in fear of gaining weight
* Repeated episodes of eating abnormally large amounts of food in one sitting
* Feeling a loss of control during bingeing — like you can't stop eating or can't control what you eat
* Forcing yourself to vomit or exercising too much to keep from gaining weight after bingeing
* Using laxatives, diuretics or enemas after eating when they're not needed
* Fasting, restricting calories or avoiding certain foods between binges
* Using dietary supplements or herbal products excessively for weight loss
* The severity of bulimia is determined by the number of times a week that you purge, usually at least once a week for at least three months.
* Negative self-esteem and problems with relationships and social functioning
* Dehydration, which can lead to major medical problems, such as kidney failure
* Heart problems, such as an irregular heartbeat or heart failure
* Severe tooth decay and gum disease
* Absent or irregular periods in females
* Digestive problems
* Anxiety, depression, personality disorders or bipolar disorder
* Misuse of alcohol or drugs
* Self-injury, suicidal thoughts or suicide
\
2\. onset and prevalence
* Bulimia often begins in the late teens or early adulthood.
* 1.5 percent of the US female population and 0.5 percent of the male population has experienced bulimia in their lifetimes. These percentages translate to 4.7 million females and 1.5 million males.
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* Psychological and emotional problems, such as depression, anxiety disorders or substance use disorders are closely linked with eating disorders.
* In some cases, traumatic events and environmental stress may be contributing factors.
* People who diet are at higher risk of developing eating disorders. Many people with bulimia severely restrict calories between binge episodes, which may trigger an urge to again binge eat and then purge. Other triggers for bingeing can include stress, poor body self-image, food and boredom.
4\. prognosis
* may need several types of treatment, although combining psychotherapy with antidepressants may be the most effective for overcoming the disorder
* cognitive behavioral therapy, family-based treatment, or interpersonal psychotherapy may be used
* Antidepressants may help reduce symptoms when used along with psychotherapy. The only antidepressant specifically approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat bulimia is fluoxetine (Prozac), an SSRI
* Dietitians can design an eating plan to help you achieve healthy eating habits to avoid hunger and cravings and to provide good nutrition
* if symptoms are severe, with serious health complications, you may need treatment in a hospital. Some eating disorder programs may offer day treatment rather than inpatient hospitalization
* Although most people with bulimia do recover, some find that symptoms don't go away entirely
5\. any differences by demographic group?
* Girls and women are more likely to have bulimia than boys and men are.
\
\
64
New cards
Binge-Eating disorder
\
= Frequently consuming unusually large amounts of food in one sitting and feeling that eating behavior is out of control
How is Binge-Eating disorder different than Bulimia?
* bulimia is characterized by purging after a binge, while people with binge eating disorder do not purge.
= Frequently consuming unusually large amounts of food in one sitting and feeling that eating behavior is out of control
How is Binge-Eating disorder different than Bulimia?
* bulimia is characterized by purging after a binge, while people with binge eating disorder do not purge.
65
New cards
Conduct disorder
\
= behavioral and emotional problems characterized by a disregard for others
\
1\. symptoms
* Bullying or threatening behavior.
* Physical aggression.
* Cruelty toward people or animals.
* Fire-setting.
2\. onset and prevalence
* before age 10, but commonly develops in adolescence (between ages 10 years to 19 years
* prevalence
* boys: 6% to 16%
* girls: 2% to 9%.
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* abuse, parental rejection or neglect.
* Being diagnosed with other psychiatric disorders
* Biological parents diagnosed with ADHD, alcohol use disorder, depression, bipolar disorder, or schizophrenia.
* Poor nutrition.
* Living in poverty
4\. prognosis
* depends on how early the condition developed and if it was treated. Usually, the disruptive behaviors of conduct stop during early adulthood, but in about one-third of cases, they continue
5\. any differences by demographic group?
\
* more common in children assigned male at birth (AMAB) than children assigned female at birth (AFAB)
= behavioral and emotional problems characterized by a disregard for others
\
1\. symptoms
* Bullying or threatening behavior.
* Physical aggression.
* Cruelty toward people or animals.
* Fire-setting.
2\. onset and prevalence
* before age 10, but commonly develops in adolescence (between ages 10 years to 19 years
* prevalence
* boys: 6% to 16%
* girls: 2% to 9%.
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* abuse, parental rejection or neglect.
* Being diagnosed with other psychiatric disorders
* Biological parents diagnosed with ADHD, alcohol use disorder, depression, bipolar disorder, or schizophrenia.
* Poor nutrition.
* Living in poverty
4\. prognosis
* depends on how early the condition developed and if it was treated. Usually, the disruptive behaviors of conduct stop during early adulthood, but in about one-third of cases, they continue
5\. any differences by demographic group?
\
* more common in children assigned male at birth (AMAB) than children assigned female at birth (AFAB)
66
New cards
Oppositional-Defiant disorder
\
= disorder in a child marked by defiant and disobedient behavior to authority figures
\
1\. symptoms
* irritable mood, argumentative and defiant behavior, aggression, and vindictiveness that last more than six months
2\. onset
* begin before a child is eight years old
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* unknown but likely involves a combination of genetic and environmental factors
4\. prognosis
* therapy
* often improve with age, but more severe forms can evolve into conduct disorder
5\. any differences by demographic group?
2% to 11% of children
more common in boys than in girls
\
= disorder in a child marked by defiant and disobedient behavior to authority figures
\
1\. symptoms
* irritable mood, argumentative and defiant behavior, aggression, and vindictiveness that last more than six months
2\. onset
* begin before a child is eight years old
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* unknown but likely involves a combination of genetic and environmental factors
4\. prognosis
* therapy
* often improve with age, but more severe forms can evolve into conduct disorder
5\. any differences by demographic group?
2% to 11% of children
more common in boys than in girls
\
67
New cards
Substance-related and Addictive disorders
1\. symptoms
* Bloodshot eyes and abnormally sized pupils.
* Sudden weight loss or weight gain.
* Deterioration of physical appearance.
* Unusual smells on breath, body, or clothing.
* Tremors, slurred speech, or impaired coordination
2\. onset and prevalence
* **adolescence or early adulthood**
* **21.9% used illicit drugs in the past year**
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* not known. A person's genes, the action of the drug, peer pressure, emotional distress, anxiety, depression, and environmental stress can all be factors.
4\. prognosis
* Continued consumption can also lead to other medical problems such as: damage to cognitive functions (such as memory, attention, planning)
* Bloodshot eyes and abnormally sized pupils.
* Sudden weight loss or weight gain.
* Deterioration of physical appearance.
* Unusual smells on breath, body, or clothing.
* Tremors, slurred speech, or impaired coordination
2\. onset and prevalence
* **adolescence or early adulthood**
* **21.9% used illicit drugs in the past year**
3\. causes/explanations for the disorder
* not known. A person's genes, the action of the drug, peer pressure, emotional distress, anxiety, depression, and environmental stress can all be factors.
4\. prognosis
* Continued consumption can also lead to other medical problems such as: damage to cognitive functions (such as memory, attention, planning)
68
New cards
Cluster A Personality Disorders
\
= characterized by odd or eccentric behavior.
* major disruptions in relationships because their behavior may be perceived as peculiar, suspicious, or detached
= characterized by odd or eccentric behavior.
* major disruptions in relationships because their behavior may be perceived as peculiar, suspicious, or detached
69
New cards
Paranoid personality disorder
Cluster A Personality Disorder
\
= chronic, pervasive distrust of other people; suspicion of being deceived or exploited by others, including friends, family, and partners.
\
1) symptoms
* Pervasive distrust and suspicion of others and their motives
* Unjustified belief that others are trying to harm or deceive you
* Unjustified suspicion of the loyalty or trustworthiness of others
* Hesitancy to confide in others due to unreasonable fear that others will use the information against you
* Perception of innocent remarks or nonthreatening situations as personal insults or attacks
* Angry or hostile reaction to perceived slights or insults
* Tendency to hold grudges
* Unjustified, recurrent suspicion that spouse or sexual partner is unfaithful
2) prognosis
* The prognosis (outlook) for paranoid personality disorder (PPD) typically depends on whether someone with PPD is willing to accept and commit to treatment. Talk therapy can sometimes reduce paranoia and limit its impact on daily functioning.
* Left untreated, PPD can interfere with a person’s ability to form and maintain relationships, as well as their ability to function socially and in work situations. People with PPD are more likely to stop working earlier in their lives than people without personality disorders.
* In addition, PPD is one of the strongest predictors of aggressive behavior in a hospital setting. PPD is also associated with stalking and excessive litigation (lawsuits).
\
3) any differences by demographic group?
\
* People with PPD are more likely to:
* Live in low-income households.
* Be Black, Native American or Hispanic.
* Be widowed, divorced or separated or never married.
\
= chronic, pervasive distrust of other people; suspicion of being deceived or exploited by others, including friends, family, and partners.
\
1) symptoms
* Pervasive distrust and suspicion of others and their motives
* Unjustified belief that others are trying to harm or deceive you
* Unjustified suspicion of the loyalty or trustworthiness of others
* Hesitancy to confide in others due to unreasonable fear that others will use the information against you
* Perception of innocent remarks or nonthreatening situations as personal insults or attacks
* Angry or hostile reaction to perceived slights or insults
* Tendency to hold grudges
* Unjustified, recurrent suspicion that spouse or sexual partner is unfaithful
2) prognosis
* The prognosis (outlook) for paranoid personality disorder (PPD) typically depends on whether someone with PPD is willing to accept and commit to treatment. Talk therapy can sometimes reduce paranoia and limit its impact on daily functioning.
* Left untreated, PPD can interfere with a person’s ability to form and maintain relationships, as well as their ability to function socially and in work situations. People with PPD are more likely to stop working earlier in their lives than people without personality disorders.
* In addition, PPD is one of the strongest predictors of aggressive behavior in a hospital setting. PPD is also associated with stalking and excessive litigation (lawsuits).
\
3) any differences by demographic group?
\
* People with PPD are more likely to:
* Live in low-income households.
* Be Black, Native American or Hispanic.
* Be widowed, divorced or separated or never married.
70
New cards
Schizoid personality disorder
Cluster A Personality Disorder
= social isolation and indifference toward other people
\
1) symptoms
* often people with it are described as cold or withdrawn
* rarely have close relationships with other people
* may be preoccupied with introspection and fantasy
* Lack of interest in social or personal relationships, preferring to be alone
* Limited range of emotional expression
* Inability to take pleasure in most activities
* Inability to pick up normal social cues
* Appearance of being cold or indifferent to others
* Little or no interest in having sex with another person
2) prognosis
* Schizoid personality disorder is a long-term (chronic) illness that usually does not improve much over time. Social isolation often prevents the person from asking for help or support
3) any differences by demographic group?
\
* affects slightly more men than women
= social isolation and indifference toward other people
\
1) symptoms
* often people with it are described as cold or withdrawn
* rarely have close relationships with other people
* may be preoccupied with introspection and fantasy
* Lack of interest in social or personal relationships, preferring to be alone
* Limited range of emotional expression
* Inability to take pleasure in most activities
* Inability to pick up normal social cues
* Appearance of being cold or indifferent to others
* Little or no interest in having sex with another person
2) prognosis
* Schizoid personality disorder is a long-term (chronic) illness that usually does not improve much over time. Social isolation often prevents the person from asking for help or support
3) any differences by demographic group?
\
* affects slightly more men than women
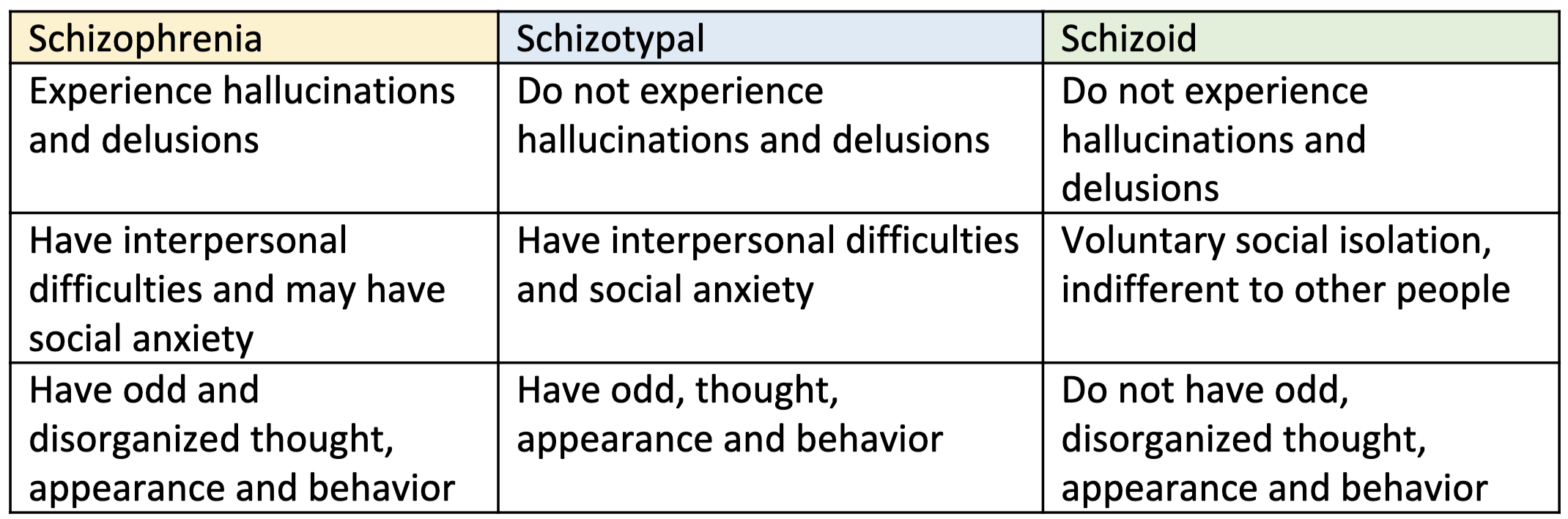
71
New cards
Schizotypal Personality Disorder
Cluster A Personality Disorder
\
= odd speech, behavior, and appearance, as well as strange beliefs and difficulty forming relationships
\
1) symptoms
* Peculiar dress, thinking, beliefs, speech or behavior
* Odd perceptual experiences, such as hearing a voice whisper your name
* Flat emotions or inappropriate emotional responses
* Social anxiety and a lack of or discomfort with close relationships
* Indifferent, inappropriate or suspicious response to others
* "Magical thinking" — believing you can influence people and events with your thoughts
* Belief that certain casual incidents or events have hidden messages meant only for you
2) prognosis
* Schizotypal personality disorder is a chronic condition that requires lifelong treatment. If left untreated, the prognosis (outlook) for schizotypal personality disorder (STPD) is generally poor. It's very common for people with STPD to have other mental health conditions
3) any differences by demographic group?
* Prevalence of STPD is higher among people with lower socioeconomic status, people who are divorced or widowed, and men
How is it different from Schizophrenia?
\
* Both schizotypal personality disorder and schizophrenia may include odd social behaviors and strange beliefs, but a person with schizotypal personality disorder does not experience hallucinations and delusions.
* Distorted thinking is a central feature of schizotypal personality disorder, which is far different from the full psychotic break from reality that occurs with schizophrenia
\
= odd speech, behavior, and appearance, as well as strange beliefs and difficulty forming relationships
\
1) symptoms
* Peculiar dress, thinking, beliefs, speech or behavior
* Odd perceptual experiences, such as hearing a voice whisper your name
* Flat emotions or inappropriate emotional responses
* Social anxiety and a lack of or discomfort with close relationships
* Indifferent, inappropriate or suspicious response to others
* "Magical thinking" — believing you can influence people and events with your thoughts
* Belief that certain casual incidents or events have hidden messages meant only for you
2) prognosis
* Schizotypal personality disorder is a chronic condition that requires lifelong treatment. If left untreated, the prognosis (outlook) for schizotypal personality disorder (STPD) is generally poor. It's very common for people with STPD to have other mental health conditions
3) any differences by demographic group?
* Prevalence of STPD is higher among people with lower socioeconomic status, people who are divorced or widowed, and men
How is it different from Schizophrenia?
\
* Both schizotypal personality disorder and schizophrenia may include odd social behaviors and strange beliefs, but a person with schizotypal personality disorder does not experience hallucinations and delusions.
* Distorted thinking is a central feature of schizotypal personality disorder, which is far different from the full psychotic break from reality that occurs with schizophrenia
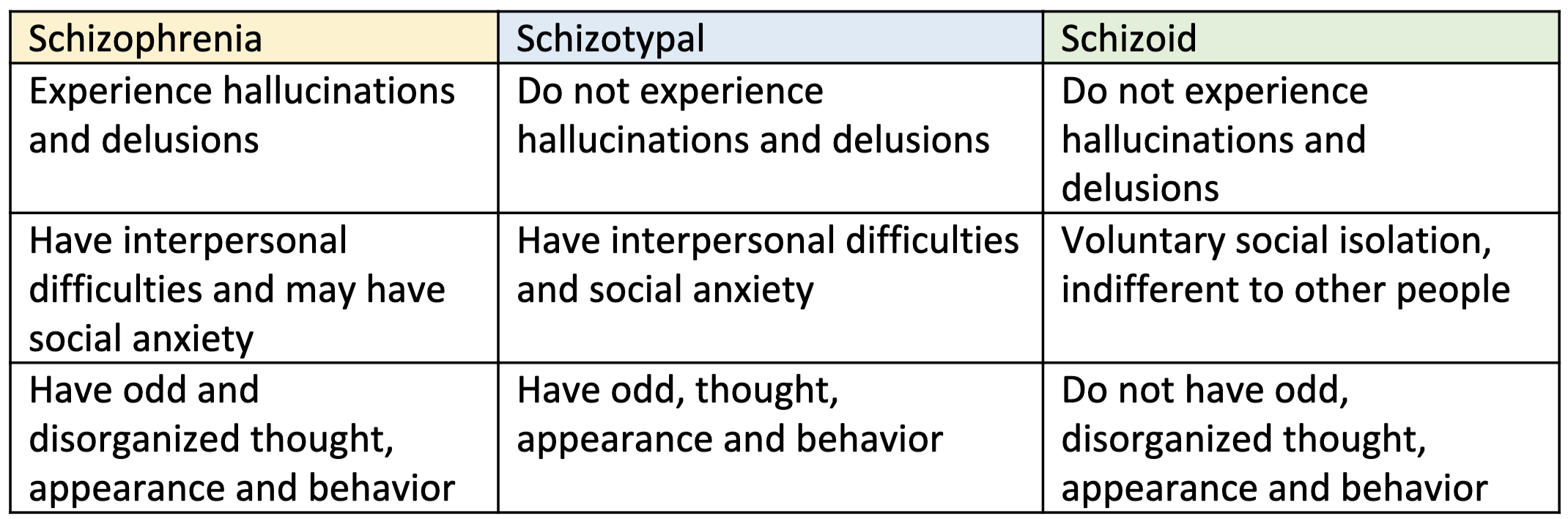
72
New cards
Cluster B Personality Disorders
dramatic or overly emotional behaviors (AKA the dramatic, emotional, and erratic cluster)
\
* all characterized by a pattern of unstable relationships, self-image, and impulsivity
\
* all characterized by a pattern of unstable relationships, self-image, and impulsivity
73
New cards
Antisocial personality disorder
Cluster B Personality Disorder
= person consistently shows no regard for right and wrong and ignores the rights and feelings of others
\
1) symptoms
* tend to purposely make others angry or upset and manipulate or treat others harshly or with cruel indifference. They lack remorse or do not regret their behavior
2) prognosis
* There is no cure for antisocial personality disorder. People generally manage the condition throughout their lives. But medication and therapy can help you cope with certain aspects of the disorder
3) any differences by demographic group?
\
* People with an antisocial or alcoholic parent are at increased risk.
* more men than women are affected. The condition is common among people who are in prison
How is Anti-Social Personality disorder different than Conduct disorder?
same except conduct disorder is typically **diagnosed in children**, so if an adult meets the criteria for both disorders, then they would be given the antisocial personality disorder diagnoses instead of conduct disorder
= person consistently shows no regard for right and wrong and ignores the rights and feelings of others
\
1) symptoms
* tend to purposely make others angry or upset and manipulate or treat others harshly or with cruel indifference. They lack remorse or do not regret their behavior
2) prognosis
* There is no cure for antisocial personality disorder. People generally manage the condition throughout their lives. But medication and therapy can help you cope with certain aspects of the disorder
3) any differences by demographic group?
\
* People with an antisocial or alcoholic parent are at increased risk.
* more men than women are affected. The condition is common among people who are in prison
How is Anti-Social Personality disorder different than Conduct disorder?
same except conduct disorder is typically **diagnosed in children**, so if an adult meets the criteria for both disorders, then they would be given the antisocial personality disorder diagnoses instead of conduct disorder
74
New cards
Borderline personality disorder
Cluster B Personality Disorder
= mental illness that severely impacts a person's ability to regulate their emotions
\
1) symptoms
* Fear of abandonment. People with BPD are often terrified of being abandoned or left alone. ...
* Unstable relationships. ...
* Unclear or shifting self-image. ...
* Impulsive, self-destructive behaviors. ...
* Self-harm. ...
* Extreme emotional swings. ...
* Chronic feelings of emptiness. ...
* Explosive anger.
2) prognosis
**BPD symptoms gradually decrease with age.** **Some people's symptoms disappear in their 40s**
3) any differences by demographic group?
\
* 1.6% of the adult U.S. population has BPD, but that number may be as high as 5.9%. Nearly 75% of people diagnosed with BPD are women. Recent research suggests that men may be equally affected by BPD but are commonly **misdiagnosed** with PTSD or depression
* no significant difference among ethnic groups
= mental illness that severely impacts a person's ability to regulate their emotions
\
1) symptoms
* Fear of abandonment. People with BPD are often terrified of being abandoned or left alone. ...
* Unstable relationships. ...
* Unclear or shifting self-image. ...
* Impulsive, self-destructive behaviors. ...
* Self-harm. ...
* Extreme emotional swings. ...
* Chronic feelings of emptiness. ...
* Explosive anger.
2) prognosis
**BPD symptoms gradually decrease with age.** **Some people's symptoms disappear in their 40s**
3) any differences by demographic group?
\
* 1.6% of the adult U.S. population has BPD, but that number may be as high as 5.9%. Nearly 75% of people diagnosed with BPD are women. Recent research suggests that men may be equally affected by BPD but are commonly **misdiagnosed** with PTSD or depression
* no significant difference among ethnic groups
75
New cards
Histrionic personality disorder
Cluster B Personality Disorder
\
= condition marked by intense, unstable emotions and a distorted self-image. The word “histrionic” means “dramatic or theatrical.
1) symptoms
* self-esteem depends on the approval of others and doesn’t come from a true feeling of self-worth.
* They have an overwhelming desire to be noticed
* behave dramatically or inappropriately to get attention
2) prognosis
* can improve with talk therapy and sometimes medicines
3) any differences by demographic group?
\
* Women and people assigned female at birth (AFAB) are more commonly diagnosed with histrionic personality disorder than men and people assigned male at birth (AMAB), but researchers think that **men and people AMAB may be underdiagnosed**
\
= condition marked by intense, unstable emotions and a distorted self-image. The word “histrionic” means “dramatic or theatrical.
1) symptoms
* self-esteem depends on the approval of others and doesn’t come from a true feeling of self-worth.
* They have an overwhelming desire to be noticed
* behave dramatically or inappropriately to get attention
2) prognosis
* can improve with talk therapy and sometimes medicines
3) any differences by demographic group?
\
* Women and people assigned female at birth (AFAB) are more commonly diagnosed with histrionic personality disorder than men and people assigned male at birth (AMAB), but researchers think that **men and people AMAB may be underdiagnosed**
76
New cards
Narcissistic personality disorder
Cluster B Personality Disorder
\
= mental health condition in which people have an unreasonably high sense of their own importance.
\
1) symptoms
* Sense of self-importance.
* Preoccupation with power, beauty, or success.
* Entitled.
* Can only be around people who are important or special
2) prognosis
* difficult to treat and resistant to change. Because the behavioral patterns especially with regard to how the person relates to others are difficult to change, the prognosis for NPD is poor
3) any differences by demographic group?
* affects more males than females, and it often begins in the teens or early adulthood
How do clinicians distinguish between Histrionic PD and Narcissistic PD?
\
people with NPD have an inflated sense of self and expect others to have the same view of them, while people with HPD wants the approval and attention of others
\
= mental health condition in which people have an unreasonably high sense of their own importance.
\
1) symptoms
* Sense of self-importance.
* Preoccupation with power, beauty, or success.
* Entitled.
* Can only be around people who are important or special
2) prognosis
* difficult to treat and resistant to change. Because the behavioral patterns especially with regard to how the person relates to others are difficult to change, the prognosis for NPD is poor
3) any differences by demographic group?
* affects more males than females, and it often begins in the teens or early adulthood
How do clinicians distinguish between Histrionic PD and Narcissistic PD?
\
people with NPD have an inflated sense of self and expect others to have the same view of them, while people with HPD wants the approval and attention of others
77
New cards
Cluster C Personality Disorders
= the anxious, fearful cluster
78
New cards
Avoidant personality disorder
Cluster C Personality Disorder
\
= People with avoidant personality disorder have chronic feelings of inadequacy and are highly sensitive to being negatively judged by others
\
1) symptoms
* oversensitive and easily hurt by criticism or disapproval
* They experience extreme anxiety (nervousness) and fear in social settings and relationships, leading them to avoid activities or jobs that involve being with others.
* They tend to be shy, awkward, and self-conscious in social situations due to a fear of doing something wrong or being embarrassed.
* They tend to exaggerate potential problems.
* They seldom try anything new or take chances
2) prognosis
* **cannot be cured**. However, symptoms can be managed and reduced, and quality of life improved, with the help of psychotherapy
3) any differences by demographic group?
\
none
\
= People with avoidant personality disorder have chronic feelings of inadequacy and are highly sensitive to being negatively judged by others
\
1) symptoms
* oversensitive and easily hurt by criticism or disapproval
* They experience extreme anxiety (nervousness) and fear in social settings and relationships, leading them to avoid activities or jobs that involve being with others.
* They tend to be shy, awkward, and self-conscious in social situations due to a fear of doing something wrong or being embarrassed.
* They tend to exaggerate potential problems.
* They seldom try anything new or take chances
2) prognosis
* **cannot be cured**. However, symptoms can be managed and reduced, and quality of life improved, with the help of psychotherapy
3) any differences by demographic group?
\
none
79
New cards
Dependent personality disorder
Cluster C Personality Disorder
\
1) symptoms
* Avoidance of personal responsibility.
* Difficulty being alone.
* Fear of abandonment and a sense of helplessness when relationships end.
* Oversensitivity to criticism.
* Pessimism and lack of self-confidence.
* Trouble making everyday decisions.
\
2) prognosis
* **Someone with DPD can live an emotionally healthy life if they receive treatment from a mental health provider**
3) any differences by demographic group?
\
none
\
\
1) symptoms
* Avoidance of personal responsibility.
* Difficulty being alone.
* Fear of abandonment and a sense of helplessness when relationships end.
* Oversensitivity to criticism.
* Pessimism and lack of self-confidence.
* Trouble making everyday decisions.
\
2) prognosis
* **Someone with DPD can live an emotionally healthy life if they receive treatment from a mental health provider**
3) any differences by demographic group?
\
none
\
80
New cards
Obsessive-Compulsive personality disorder
Cluster C Personality Disorder
\
= mental health condition that causes an extensive preoccupation with perfectionism, organization and control
\
\
1) symptoms
* Over-devotion to work.
* Not being able to throw things away, even when the objects have no value.
* Lack of flexibility.
* Lack of generosity.
* Not wanting to allow other people to do things.
* Not willing to show affection.
* Preoccupation with details, rules, and lists
2) prognosis
* Outlook for OCPD tends to be better than that for other personality disorders. The rigidness and control of OCPD may prevent many of the complications, such as substance use, which are common in other personality disorders.
3) any differences by demographic group?
* more common in men
How is Obsessive-Compulsive PD different from OCD?
\
OCD is ruled by intrusive thoughts called, obsessions that cause anxiety and force the person to perform compulsions for relief. OCPD is ruled by perfectionism and detail. Unlike individuals with OCD, people with OCPD are not self-aware and can hurt the people around them
\
= mental health condition that causes an extensive preoccupation with perfectionism, organization and control
\
\
1) symptoms
* Over-devotion to work.
* Not being able to throw things away, even when the objects have no value.
* Lack of flexibility.
* Lack of generosity.
* Not wanting to allow other people to do things.
* Not willing to show affection.
* Preoccupation with details, rules, and lists
2) prognosis
* Outlook for OCPD tends to be better than that for other personality disorders. The rigidness and control of OCPD may prevent many of the complications, such as substance use, which are common in other personality disorders.
3) any differences by demographic group?
* more common in men
How is Obsessive-Compulsive PD different from OCD?
\
OCD is ruled by intrusive thoughts called, obsessions that cause anxiety and force the person to perform compulsions for relief. OCPD is ruled by perfectionism and detail. Unlike individuals with OCD, people with OCPD are not self-aware and can hurt the people around them
81
New cards
Diathesis Stress Model
= model to explain why some people might develop an illness while some people don’t
2 factors:
* differences in genetic predisposition
* differences in environmental stress
2 factors:
* differences in genetic predisposition
* differences in environmental stress