CR Quiz 2 Prep
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/26
Last updated 7:03 PM on 2/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
1
New cards
Where does Glycolysis occur?
Cytosol
2
New cards
How does glycolysis begin cellular respiration?
* Breaks down 6-C glucose molecule into two
* These 3 intermediates(G3P) are oxidized into 2 molecules of pyruvate
* Yield net of 2 ATP and 2 NADH molecules
* These 3 intermediates(G3P) are oxidized into 2 molecules of pyruvate
* Yield net of 2 ATP and 2 NADH molecules
3
New cards
What are intermediates?
* compounds that form between an initial reactant and a final product
* Specific one is G3P
* Specific one is G3P
4
New cards
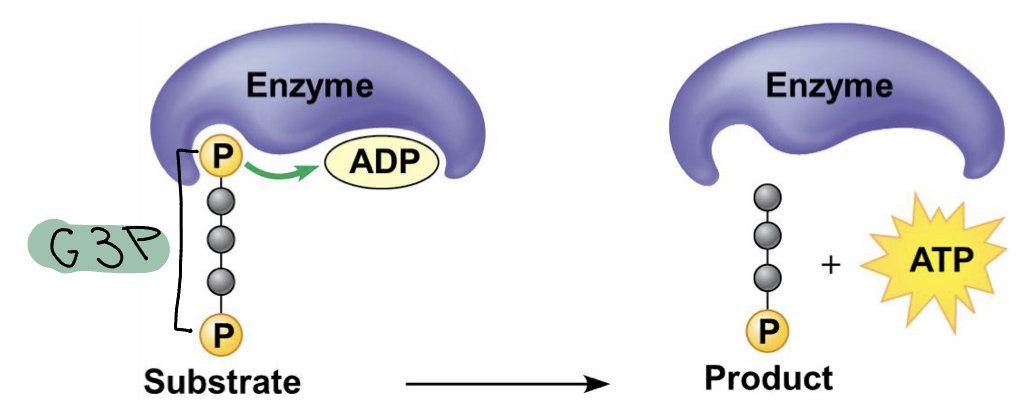
When is substrate-level phosphorylation?
* ATP is formed in which a phosphate is transferred from an organic molecule to ADP
* In other words occurs when phosphate is removed from G3P and given ADP to for ATP
* In other words occurs when phosphate is removed from G3P and given ADP to for ATP
5
New cards
What does the oxidation of glucose to pyruvate release?
Energy stored in ATP and NADH
6
New cards
When can the cell use ATP vs. NADH?
* ATP: Immediatley
* NADH: can be used after electrons from NADH must pass down an electron transport chain in stage 3
* NADH: can be used after electrons from NADH must pass down an electron transport chain in stage 3
7
New cards
What molecules still hold most of the energy in glucose?
Pyruvate which will be oxidized in stage 2 of cellular respiration
8
New cards
What is a metabolic pathway?
each chemical step feeds into the next one
9
New cards
How are intermediates classified?
* Classified by the number of Carbons in backbone
* Do not have specific names
* Do not have specific names
10
New cards
What catalyzes each chemical step in glycolysis?
A specific enzyme
11
New cards
What are the two main phases of glycolysis?
1) **energy investment phase**
2) **energy payoff phase**
2) **energy payoff phase**
12
New cards
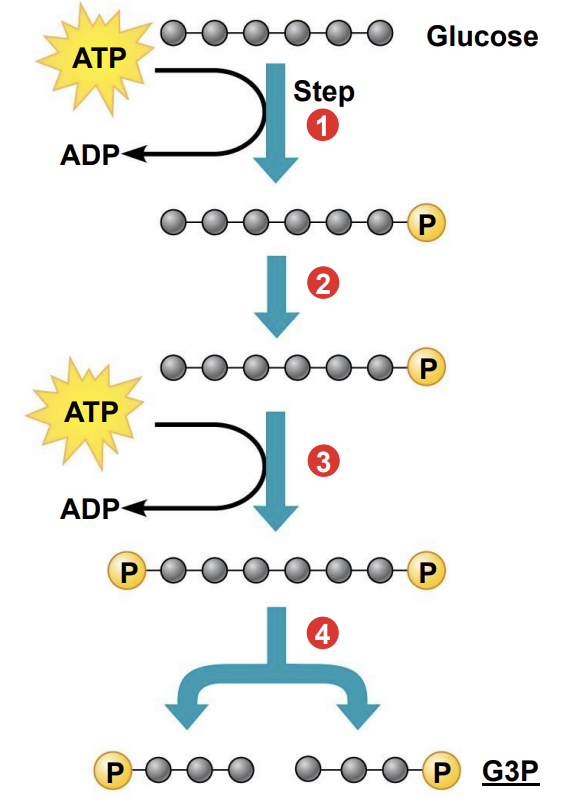
Describe the energy investment phase in greater detail.
(1-3) Glucose is energized using 2 molecules of ATP
* Step 1 and 3: ATP hydrolysis where ATP breaks into ADP and adds phosphate to glucose
(4) A six-carbon intermediate(glucose) splits into two three-carbon intermediates(G3P)
* G3P is oxidized
* Step 1 and 3: ATP hydrolysis where ATP breaks into ADP and adds phosphate to glucose
(4) A six-carbon intermediate(glucose) splits into two three-carbon intermediates(G3P)
* G3P is oxidized
13
New cards
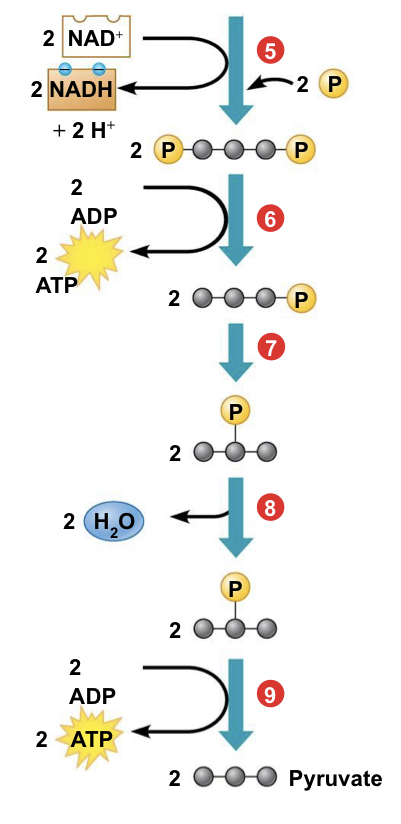
Describe the energy payoff phase in greater detail.
(5) a redox reaction generates NADH
* reduction reaction following oxidation of G3P
(6-9) ATP and Pyruvate are produced
* Step 6 and 9: Substrate Level Phosphorylation
* Step 8: lost water will go back to ATP hydrolysis(1 or 3)
* *yield 2 NADH and 4 total AP molecules*
* reduction reaction following oxidation of G3P
(6-9) ATP and Pyruvate are produced
* Step 6 and 9: Substrate Level Phosphorylation
* Step 8: lost water will go back to ATP hydrolysis(1 or 3)
* *yield 2 NADH and 4 total AP molecules*
14
New cards
What happens at the end of glycolysis?
1) pyruvate is transported from the cytosol into a mitochondrion where Kreb cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation occur
15
New cards
What does the oxidation of pyruvate yield?
acetyl CoA, CO2, and NADH
16
New cards
What are the products for each turn of the citric acid cycle?
* two carbons from acetyl CoA are added,
* 2 CO2 are released
* 3 NADH and 1 FADH2 are produced
* 2 CO2 are released
* 3 NADH and 1 FADH2 are produced
17
New cards
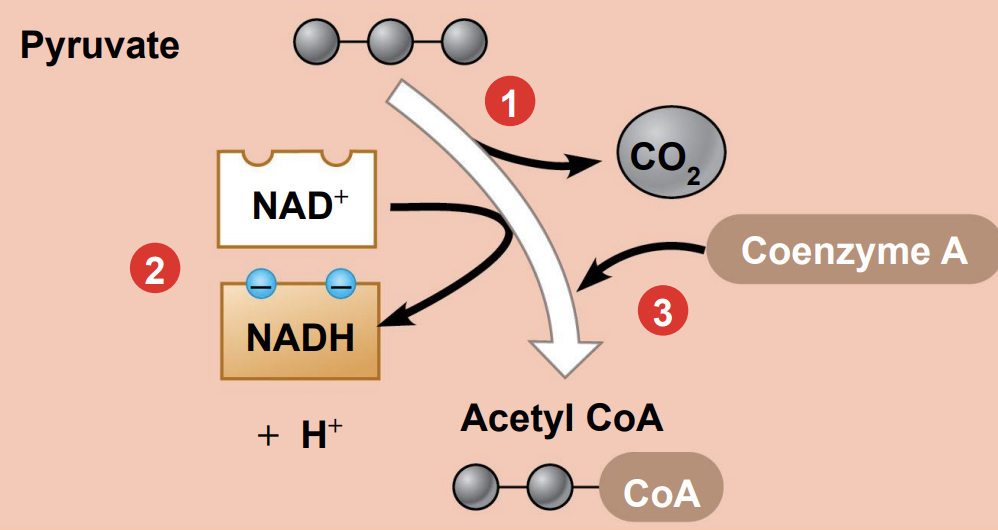
What are the steps of pyruvate oxidation?
* Step 1- a carboxyl group is removed from pyruvate and given off as a molecule of CO2
* Step 2- the 2-C compound remaining is oxidized while a molecule of NAD+ is reduced to NADH
* Step 3- coenzyme A joins with the 2-C compound to form acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA)
* Step 2- the 2-C compound remaining is oxidized while a molecule of NAD+ is reduced to NADH
* Step 3- coenzyme A joins with the 2-C compound to form acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA)
18
New cards
Products of pyruvate oxidation
each molecule of glucose makes , 2 molecules of pyruvate, so 2 are oxidized, thus 2 molecules of acetyl CoA are ready to enter the citric acid cycle
19
New cards
What does the Kreb cycle complete?
* oxidation of organic fuels (only energy carriers passed to stage 3)
20
New cards
What is a common charecteristic among all steps of Kreb cycle?
* Each step is catalyzed by a specific enzyme located in the mitochondrial matrix or embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane
21
New cards
What actually enters the citric acid cycle?
* Only the 2-C of acetyl CoA actually enter the citric acid cycle
* coenzyme A splits off and is recycled
* coenzyme A splits off and is recycled
22
New cards
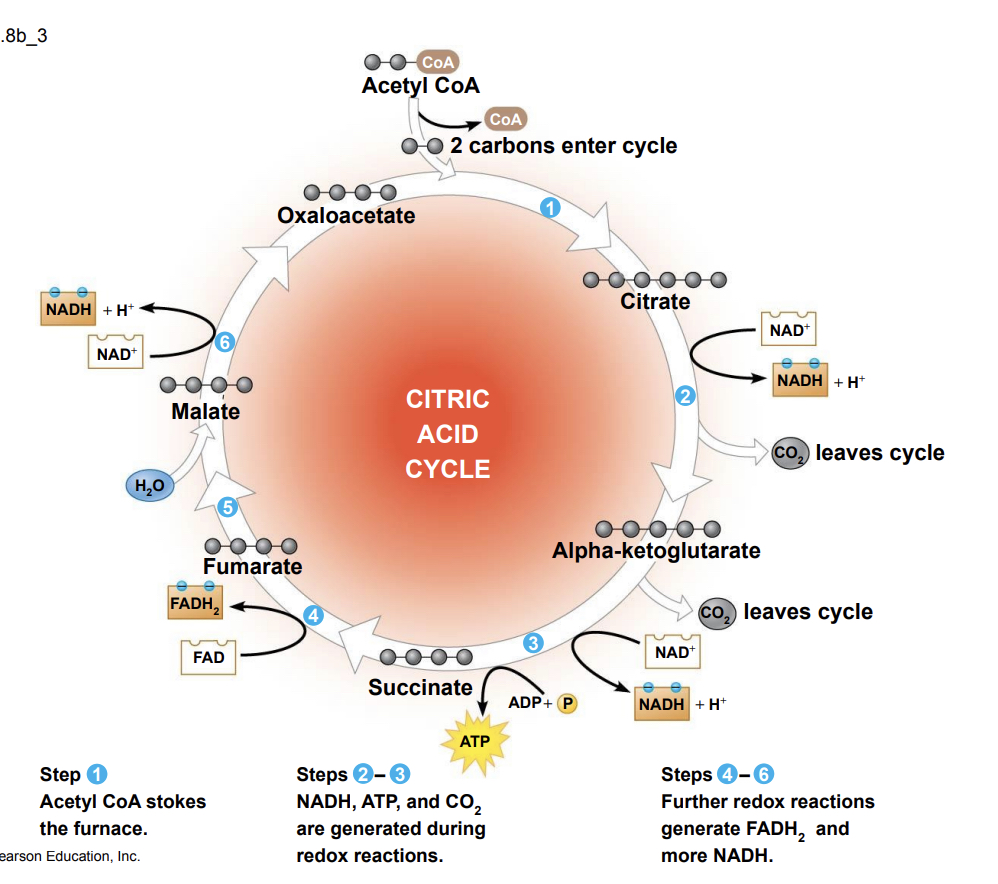
What are the steps of the Citric Acid Cycle
* Step 1- the 2-C molecule (acetyl) joins to a 4-C molecule (oxaloacetate) processed through a series of redox reactions forming citrate (citric acid)
* Steps 2 and 3- two carbon atoms are removed as CO2, and the 4-C molecule (succinate) is regenerated. Two NAD+ are reduced to NADH and one ATP generated via Substrate-level phosphorylation
* Steps 4 thru 6- oxidation of succinate and other 4-C intermediates allows for the reduction of NAD+ and FAD forming NADH and FADH2 after the addition of a water molecule. Oxaloacetate is regenerated and the cycle is ready to begin again
* Steps 2 and 3- two carbon atoms are removed as CO2, and the 4-C molecule (succinate) is regenerated. Two NAD+ are reduced to NADH and one ATP generated via Substrate-level phosphorylation
* Steps 4 thru 6- oxidation of succinate and other 4-C intermediates allows for the reduction of NAD+ and FAD forming NADH and FADH2 after the addition of a water molecule. Oxaloacetate is regenerated and the cycle is ready to begin again
23
New cards
What stage accounts for most energy extraction?
* Stages 1 and 2 produce only 4 ATP per glucose molecule via SLP (2 from glycolysis, 2 from Krebs).
* At the end of stage 2, molecules of NADH and FADH2 account for most of the energy extracted from each glucose molecule
* At the end of stage 2, molecules of NADH and FADH2 account for most of the energy extracted from each glucose molecule
24
New cards
What happens to electrons from NADH and FADH^2 in oxidative phosphorylation?
passed down the electron transport chain within the inner membrane of the mitochondria toward O2, which picks up H+ to form water within the matrix
25
New cards
What is the energy released used for?
* Energy released by these redox reactions is used to pump H+ into the intermembrane space
26
New cards
What occurs in chemiosmosis?
In chemiosmosis, the H+ concentration gradient
drives H+ back through ATP synthase in the inner
membrane, synthesizing ATP
drives H+ back through ATP synthase in the inner
membrane, synthesizing ATP
27
New cards
What are the unique parts of each step?
1 and 3: energy in
6 and 9: energy out
5: NADH
8: remove water
6 and 9: energy out
5: NADH
8: remove water