Study Guide BFI - History Theme 2: The Post-War Bipolar World and Challenges to Bi-Polarization
Cold War - period of geopolitical tensions between the US and USSR
Legacy of WWII
US emerged as a superpower → didn't do much before ⇒
EU and JAP destroyed in infrastructure → US build EU and JAP to its own image
Increasing tensions between US and USSR
During WW2, USSR seen as convenient ally but did invade POL but once WW2 over they don't leave territories they conquered → commu like it, can liberate the people with commu → leads to emergence of cold war
Eastern EU gets swallowed by USSR
Division of EU - socialists/communists vs capitalists
Bretton Woods 1944 - Conference to deal with problems of currency and exchange in New Hampshire. Creates an international basis for exchanging one currency for another, led to creation of IMF and world bank - dollar will be the international currency of exchange.
Yalta Conference Feb 4-11 1945 - US, UK, USSR - Decision to divide Germany and Berlin by section of countries : FR, BR, US, GER + Disarm Germany → USSR steals the GER factories as a form of reparation = extract GER wealth
Potsdam Conference July 17 - August 2 1945 - Truman (US), Attlee (UK), Stalin (USSR) - Last conference between the great powers before Cold War: Reparation for winners, preserve soviet-western coalition, Germany loses cities, plan to create healthy economic world that doesn't succumb to crisis, support liberalism - USSR never makes peace w/ GER by 1950s→ Stalin bitter about losing so many people
Creation of UN-1945
Part of Atlantic Charter (August 1941) with Churchill and FDR that met to redesign world to look different than age of empires to nation states and diplomacy
Meeting in SF 1945, drew up charter
New organisation designed to maintain international peace and security and encourage cooperation in solving international social, economic, and cultural problems
Structure
General assembly : one nation = 1 vote (change de league of nations) → liberalism
Security council : 5 permanent members, veto (US, USSR, GB, FR, CHI)
UN largely fails to fulfil its role during the Cold War due to conflict between the US and USSR
Issue and use of Atom Bomb
1949→ USSR has the bomb, arms race between them and US
Build huge stockpiles of atomic weaponry, starts arms race
Cold War because with 2 nuclear powers, not viable to have hot war
MAD (mutually assured destruction)
Iron Curtain Speech - March 5, 1946 - “An Iron Curtain has descended across the continent” - Churchill (not PM anymore) warns of a dire threat (communism) at a commencement during presidential campaign in US at a university, communism has created division, BR and US need to act together to fight against communism —> Meaning of speech : US please dont leave EU, no isolation like WW1
Pan-Arabism (get rid of Western Imperialism), Nasser, Non-Aligned Movement
American initiatives at the start of the Cold War
Truman Doctrine
Emerges from strategic importance of Greece and Turkey, Greek Civil War
Churchill and Stalin, cocktail napkin —> Greece and Turkey to be British. After WWII C parties rise and there’s a civil war in both countries where C parties trying to take over the Government. England doesn’t have the money/morale to intervene and contain C so turns to the US.
On March 12, 1947, President Harry S. Truman presented this address before a joint session of Congress. His message, known as the Truman Doctrine, asked Congress for $400 million in military and economic assistance for Turkey and Greece.
Policy containment of communism
George Kennan US researcher to analyze USSR state and say if its acting as an expansionist imperialist power
US should not investigate a war with soviet union
US should defend other nations from USSR take over (domino effect, communism like a virus) (economic help)
US now doesnt like RUS having Eastern EU so Stalin feels backstabbed
Marshall Plan and containment policy 1948-1951
US conquers JAP and GER and instead of reparation, they give them money → changing world stage !!, bigger person (also to their advantage to impose capitalism instead of communism, buy US goods with $)
George Marshall - secretary of state
13 billion $ to EU, expected to be US allies : support economic growth, fuel, machinery
Precursor to UE, leads to it
Isolate USSR, Stalin thought it was US imperialism
Berlin Blockade 1948/49
Berlin divided into 4 (East Berlin : liberal capitalists) vs West (commu)
Stalin decides to cut off the city → allies pipeline cant reach berlin, famine, allied outnumbered military
Solution : supply city through air, USSR can't shoot because would declare war
Truman could not decide if retreat or war→ got very close to war
Blockade hurt more soviet economy, allies even more allied
Lifted may 1949
A New World Order→ created by US
Atlantic charter→ august 1941
Reborn nation of WIlson's 14 points
Goal: No territorial aggrandizement, Self determination and freedom of seas (trade across oceans), Guaranteed each nation’s security (alliance system), Disarmament (no more arms race), Global cooperation to secure better economic and social conditions for all (traded with all, open up market, GATT, start globalization)
Planned during WWII by Churchill and Roosevelt
NATO 1949 —> West GER became a country ; War of political influence, threat and distance
Soviet Initiatives
Cominform
Socialist international meeting, foster social networking → how to spread commu in countries
Cooperation of commu states, coordinate activities, ideological unity
Spread fear that capital, liberal countries would fall to Coms
COMECON
Council for mutual economic assistance
Facilitate and coordinate the economic development of the eastern European countries belonging to the Soviet bloc → Stalin’s response to marshall plan to help eastern EU economically
Warsaw Pact 1955
Retaliated for the creation of NATO, military alliance among the USSR and other communist alliances
The perspective of Stalin
Protection for slavs→
Stalin gained credibility after war, wide appeal around world,
Red army largest force, West could do nothing to stop them, nothing could, Soviets followed past conquer→ wanted back land (Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania,...),
Argument with US→ USSR supposed to just occupy lands they once had, thought it was spoils of victory, wanted buffer zone against GER
Great powers call the shots→
Stalin saw Napoleon in Hitler, during Yalta and Potsdam conferences→ FDR, Churchill, agree on territory between GER and USSR had to be under Soviet control
Stalinization: eastern EU feels forgotten, stalins comes in and nobody does anything about it
Poland and Hungary under Soviet control
Stalin though capitalist countries would go to war between them, WW3 coming between them had to wait until world collapse in communist rev,
Though they would split on how to handle GER
Stalin fearful of West→ after war got back to industrial dev and military expansion, continue to build 1930s economy
Nuremberg Trials-aug 1945-1949
Crimes against humanity, war crimes punished
4 winners (US, FR, BR, USSR) put on trial losers (GR, JAP)
Put on trial: Herman Göring, Rudolf Hess,...
Executed 12 people→ 3 life sentences, 4 long sentences, set standard for future war crimes
Prblms: Victors get justice? Sovereign nations ? (they were forced to shoot people, so their fault?)USSR had invaded Poland yet judge the Nazis?
Proxy Wars / Conflicts
Korean War 1950-1953
Had japanese rule since 1910, during war:
North: USSR satellite, Kimm II sung leader
South: US satellite -1947, Syngman Rhee leader - repressive, support authoritarianism rather than communism
North invade south in 1950→ US asked security pacts around non-commnuist Asia, but were not trusted because seen as new imperialist power, north wanted to unite country→ USSR boycotts UN → go to war
US defend South when gets approval from UN, puts troops on ground, Truman wanted “Unified independent democratic Korea”
North, armed by USSR, went all the way down to Seoul, 16 countries send military troops to south
October 1950 china enters war→ ends up China vs US - 500 000 chinese
Us retreat back behind 38th parallel (were not going to fight with China), embarrassing → technically still at war today
Casualties: 1 US death= 10 North korea +China death → outnumbered but effective
the DMZ and the 38th Parallel
Armistice signed in 1953
38th parallel → demilitarized land, no side claims side, stop invasion from north to south
Not all koreans were die hard commu, some wanted to stay in South
The Vietnam War
US saw war as anti colonialism, independence vs US that thinks it’s a war against commu, domino theory, people’s war.
Vietnam proved that US most powerful power could be defeated by guerilla
Ho Chi Minh
Poet, led commu rev
Leads commu party that fought against the french - Vietminh independence league
US declaration of independence
Anti-colonial vs anti-commu, nationalist war for viet
1945 - declares independence, becomes political head
Ho CHI Minh trail→ supplies coming into south for north soldiers through cambodia and laos→ US could not do anything about it because not at war w/ these countries
Brazzaville Declaration 1944
1941 Minh declared overthrow of french rule
De Gaulle plan to keep colonies - brazzaville declaration
Vietcong → north
Viet commu nationalist → viewed south viet gov as puppets in the us
Trained, enthusiastic, under-gunned fighting force
Viet Minh → communist living in the south and Vietcong → soldiers secret fighting against US
Dien Bien Phu 1954
Battle where the french are deflated, get trapped and surrender to Minh
France recognizes vietnam, cambodia, laos
Geneva Accords 1954
US steps in and discuss how to deal with viet
US create a separate independent viet : south and north
Says they will have two years in 1956 until elections where they will choose their gov and unite → doesn't work since commu were gonna win so US doesn't like that
US will train South, money, scared of another korea don't want to fight china
Ngo Dinh Diem
Catholic raised western guy, authoritarian, people unhappy
Begin with his brother raiding buddhist pagodas in South claiming they were harboring commu
Result : massive social protests including self-immolation of many buddhist monks
Diem depicted as US friend
Gets assassinated in 1963 even though JFK knew about this and didn't do anything
THE GULF OF TONKIN INCIDENT —> 1964→ US intelligence missions to determine North Vietnam’s defenses, USS Maddox clashed with coms patrols boats in gulf→ shot at each other, excuse from LBJ to invade north
Guerilla Warfare in Vietnam
Dense terrain→ movement difficult, not running like WW2
Surprise and ambush, booby traps, land mines, hide in the trees→ left psychological effects on soldiers
Not conventional fights→ Vietcong charged as fast as possible, hit and run, ambushes
US had military superiority: had helicopters, medical aid, transportation, rocket ship
Vietcong hid in villages tried to act normal
The Tet Offensive-- Jan 31rst 1968
Big battles→ people in the US ask “how is it that if we are winning, if we still need to fight such big battles?”
Secret attack→ 70 000 Vietcong sneak into south and create huge uprising at US embassy→ expected people in cities to help kick US out, did not → Viet cong lost
My Lai Massacre —> Lots of Civilians die→ US shot them all because did not know who the Vietcong were, 200 women, children and old men, ordered by Lieutenant Calley
Peace with Honor by Nixon
Told North vietnam to not negotiate w/ Johnson (limit treason)
Bombed them into negotiation, bomb cambodia in “secret” in April 1969 because of Ho Shi Minh trail
Vietnamization —> Training the south soldiers with US arms so that they could be self sufficient and run their own government without falling apart
Us pulls troops out of Vietnam in 1973, then north conquers south, then US embassy leaves in 1975
Cuba
Apparition of communism in Cuba
1956 exiles from Cuba came back to overthrow the dictator
Castro appeared, won the war in 1959, promised lands to peasants, introduced nationalist reforms and nationalized american interests
Che guevara as a cult figure
Bay of pigs April 17, 1961
Invasion planned by the US to invade Cuba and overthrow Castro by sending CUban exiles trained by the CIA
Invasion didn't go as planned, US air force failed to destroy the cuban one, and then troops took too long to get off the ship and cuban air force sunk the ship, paratroopers landed at the wrong place
Makes the US look weak, strengthen Castro’s regime and started Cuba’s alliance with USSR
Cuban missile crisis of october 1962 - kinda like today with UKR
Most dangerous moment during the Cold War
USSR puts nuclear missile base in Cuba because it seemed only fair since US had some in Turkey and Italy aimed towards Moscow
Kennedy opted for naval blockade and put Cuba under “quarantine” meaning that no offensive weapons could enter Cuba and an attack from CUba would declare war from USSR
USSR negotiates with US for 13 days with the US agreeing to never invade Cuba again, remove its nuclear bases in Italy and Turkey and the soviets will remove theirs from Cuba with a UN inspection
Almost made WW3 happen with soviet missile hitting US airplane and soviet submarine hit by US on October 27, 1962, could become a nuclear war
→ restored faith in Kennedy as a great leader and president of the US and victory of diplomacy and the capacity of the two leaders to solve peacefully the crisis
→ superpower confrontation, geostrategic balance of power dynamics
→ transform cuban society, embargo of the US on cuba that stayed for 60 years, removed recently
Castro was in power until 2008
Decolonisation and the NAM
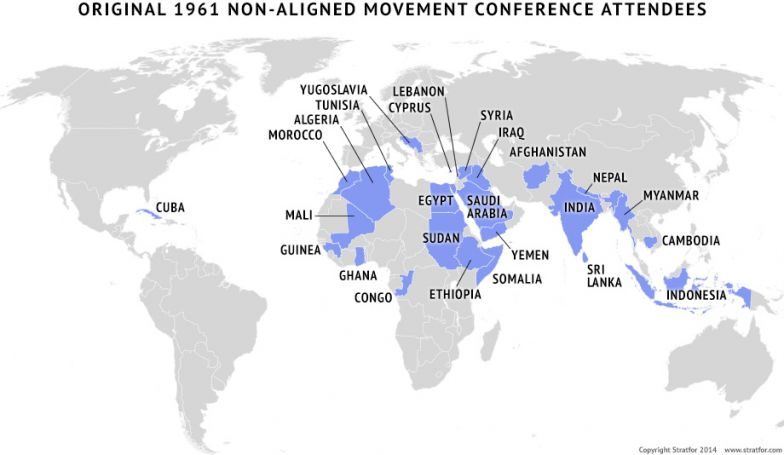
Egypt —> Had declared its independence in 1922 but British troops remained until the Suez Canal Crisis of 1956
The Egyptian Revolution of 1952
Egyptian monarchy was apparently corrupted and king farouk failed to deal correctly with the Israel Arab conflict
Led by the Free officers specifically Nasser that wanted to throw out monarchy and B British
Army forced king to abdicate (faced threats from western imperial powers)
Agrarian reforms and industrialisation, improved infrastructure → socialist economy in the 60s → influenced other countries to do the same
Nasser
Replaced the first president Naguib in 1954 until his death in 1970
Banned all political parties replaced by liberation rally
Gave women right to vote, put a new constitution in place, created the National Union that led to the national assembly and the first assembly and parliament since 1952
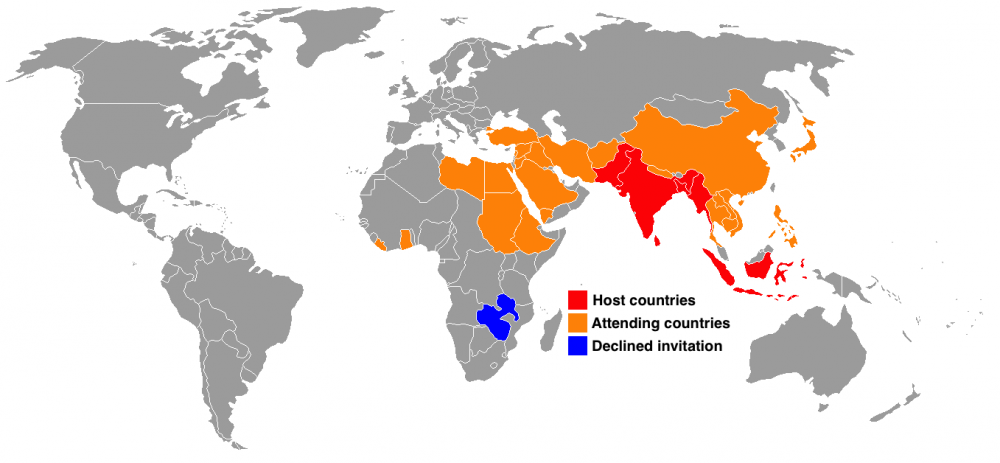
Nasser and the Bandung Conference - non aligned movement
International organisation of 3rd world nations attempting to remain free of cold war competition and imperialism
Founded in 1955 at Bandung conference
Nasser as one of the founding fathers of the movement with Nehru (India), Yugoslavia (Tito), Indonesia and Ghana
Goals of NAM→ mutual non-aggression, respect for each other’s territorial integrity, equality and mutual benefit, peaceful, nor capitalist or Communist
Members of Bandung Conference:
Arab Nationalism / Pan-Arabism and Nasser —> Began to rise during the Egyptian revolution, unite for the glory of the Arab population socioeconomically, politically, and culturally, and learn to develop without the western powers
Suez Crisis 1956
Egypt nationalised the Suez Canal (had been controlled by Britain and France)
Military intervention by BR, FR, and Israel
International pressure, especially US and SU, forced them to withdraw
Significant shift in global power dynamics + decline of European colonial influence in the region —> growth of Arab nationalism
The United Arab Republic 1958-1961
Egypt with syria joined this in the goal to create a larger pan-arab state
Ba’ath egypt party supported this union
Syria agreed reluctantly suffering in 1957 from the syrian crisis
Syria became more commu, egypt didn't like it, nasser gets involved, stops commu takeover, puts in place a new constitution
Nasser slowly took out all syrians from government
Syria revolts, got money from Saudi Arabia to go against Nasser → UAR not successful, led to full domination by Egypt
Sadat
After Nasser’s death from 1970-1981, VP under Nasser
Free officers thought they could manipulate Sadat but not the case
Sadat gov purged the extremists and nasserists
For the islamist mvt
Allied with the US instead of SU, invited to camp david
Economic policy of “open door” where gov controls economy and encourages private investment → led to Bread Riots, didn’t help
Went to Israel in 1977 → lead to peace of 1979
Sadat brought to trial the former gov officials under nasser → discontent arised, got assassinated in 1981
1973 October War (Yom Kippur War)
Since egypt lost six day war in 67, convinced arab nations and syria to fight israel
Lost again in 1973 but seen as a victory → restored egyptian pride → led to negotiations with Israel to get back sinai in exchange for peace → rejected later by arab nations
Reagan - Outspends during the cold war
RUS economy during Cold War
Economy was based on manufacturing, bi-lateral trade
RUS built 1950 century planned economy, but didn’t create consumer industry with companies competing → no variety for consumers
Ex : CZ was complex eco, West bought precise machinery from it but with RUS choice to focus on shoes it made them recess
With the centralised economy, RUS and EU missed 4 decades of economic dev
RUS economy was not growing
People noticed it with shortage of tampons and toilet paper argument, most essential goods→ made people lose faith in ability of commu to keep up, people realised it was a centralised economy
End of cold war USSR / fall of communism
Nationalists movements
Baltic states - Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia, Moldavia, Armenia, Georgia, Poland, Ukraine → want greater cultural autonomy + own language
High profile dissidents
Andrey Sakharov demanded reform openly
Writer Alexander Solzhenitsyn exposed the brutal gulag life in the Life of Ivan Denisovich
Economic crisis in 1988
Because of this, it convinced members of the SU that commu couldn’t deliver on its promise to improve their material conditions
Overspending in Afg war
Gorbachev’s decisions to not use violent suppression against democratic reform mvts (POL in 87, end commu in 90, Hungary in 89, CZ, Bulgaria, Romania …) → all got free elections and vote commu down
Wanted more humanistic approach → believed in commu with a nice face
Not the same gov compared to CHI with Tiananmen square who rolled the tanks, removed military, suppress police
Gov lost authority
END OF COMMUNISM = FAILURE TO SUPPRESS BREAKAWAY MOVEMENT
Gorbachev —> tries to reform the Soviet Union in 1985 due to being behind to the West
Wanted more openness, greater free expression = glasnost, drop central planning of agriculture in favor of free market economy, looked for FDI in 1987 from the west, slowed down arm race bc couldn’t afford it
Perestroika, "restructuring" —> the restructuring of the political and economic systems of the Soviet Union, in an attempt to end the Era of Stagnation.
Berlin wall fell in 1989 → elections sent commu packing, eastern Germany will be a weight to the west Germany
Eastern eu countries started to want their independence
Boris Yeltsin critiqued Gorbachev and announced that RUS would be a sovereign, independent State → people supported him
Gorbachev sent military to overthrow Yeltsin, Yeltsin did the same, supreme court ended powers accorded to Gorbachev, Gorbachev gave up and Yeltsin was elected President of the “Russian Federation”, implement a market economy in RUS
Looks like everyone is going towards liberalism, end of commu, all republics left SU
—> SU washed away by a tide of reform and nationalism
China
Period of Humiliation
1839→ loose Opium war w/ BR
1850-64→ Taipling Rebellion (christian people come over) → devastates China, Christians leader forms rebellion, lost, chrisitianry crushed in China
1894-1895→ Japan defeated China in 6m. , take Korea and Manchuria
1899 → Open door policy by west who has ports in Chi
1912→ liberal democratic overthrows monarch→ China falls apart in struggle of warlords (not united until 1928 with Chiang Kai-Sheck)
1928→ Chiang Kai-Sheck rises out of this and becomes leader, civil war, commu emerge
Jap in country until 1945
1949→ communist takeover , Sheck goes to Taiwan, comms caused downfall
Sun Yat-sen
Liberal Reformer, first president in 1911
Chiang Kai-Shek
Came out as leader in 1928 after china was broken from 1910-1920, leaves in 1949
Took Beijing and united China
From the Kuomintang (nationalust Party) dynasty, supported by Sun Yat-Sen
Mao Zedong
Leader of China from 1949-1976
Saw revolutionary potential for chinese peasantry, impoverished, oppressed parasitic landlords
Converted to comm in 1918, started out as librarian then urban labor organiser
1925→ Chinese textiles strikes spread from Coastal cities to rural China, see peasants
Why Communists won in China
Overturned Feudalism→ peasants paid 50% of crops to landlords
Half of all land owned by 4% pop, 70% owned 1/6
Land Hunger→ offer land, will follow
Mao gets following of masses because offers to redistribute wealth
History: Sheck pushed them out, but Stalin helped them so came back in, fight together to get rid of Jap, 1934-1935→ Sheck chased coms to North, forced them to make long march, Sheck stop chasing them because Stalin had his son and stalin was aligned with the comms of china
1949→ Communist win civil war w/ Mao
China and the Korean War→see cold war
Seen as chinese victory for propaganda, held back imperialism and capitalism
US worried about chinese involvement in vietnam so beg of diplomatic relation, 1970 Nixon establishes relationship with China
Sino-soviet split 1956-1966
Soviets critique reform plan of mao → saying its not working, useless reforms so they break their relation
illiberal aspects of making the communist state (looks a little like USSR)
800k enemies killed 1949-54
Forced labor camps, re-education through propaganda, self-criticism sessions
Destroyed opposition
Civil, political rights abolished (life, liberty, property not protected), freedom of press dies
temples/ churches closed
Gov controls info→ removed prostitution and drug abuse
Women full equality outside of home
Keep capitalists in cities for factories
Rise to Power: 1950-1953→ China defeats North Korea against US → triumph
1962→ border disput w/ India→ wins again
1970→ Nixon establishes relation w/ china → gets seat on security council
Let a Hundred Flowers Bloom 1956
How can we make commu better ?
Mao believed that so much, he would let people talk / discuss freely
Once critics emerged, shuts it down → intellectual, artists, counter revolutionaries sent to camp
Flirting with democracy but as soon as he has it, shuts it down
The Great Leap Forward 1958-61 = fast industrialization
Adopts soviet five year plan - expansion of industry instead of consumer goods
Coincides with famine
GLF (1958-1961): abolishes private poverty, land redistribution to the peasants, collectivization, state control of industrial production
GLF backfires due to chaos and failures to produce → Mao loses influence in Politburo (party leader group)
Great Famine in China during GLF
Tries to mass produce steel with small industry but doesn't work →makes shawty product, break
Communes lied about stats so china continued to export and 30 millions die of famine
The Cultural Revolution 1966-1976
Mao’s attempt to appeal directly to the people not the party → support from the masses
Mao’s ascension to power until he dies in 76
Youth joined, accused older people→ chance for students to be part of something big
Creation of red guards - young people ran tribunals against people not commu enough, want confession of people, lack of purity to commu → put on trial to confess sins
Elimination of enemies
Persecution of intellectuals, teachers, artists→ 500 000 lost their lives
Wanted to remove “feudal” or “bourgeois” thoughts and culture
Fails economy and creates chaos→ caused shift to the right
Mao Personality Cult
People went around quoting him, heavy use of propaganda
Mao became increasingly isolated - emperor lifestyle, lives in forbidden city like emperor
Declining health - swims in river to seem vibrant
Deng 1981-1989 / same time as Reagan
2nd generation comms party, father of Socialist Market Economy
“Dare to be rich”--> not like Mao, pragmatist not ideological , does what works
Destroyed the old China→ build skyscrapers
Pull china to 20th century
Father of the socialist market economy
1984→ negotiates return of Honk Kong from BR
1997→ “one China, two systems”
"No matter if it is a white cat or a black cat; as long as it can catch mice, it is a good cat." → no matter the party→ if helps economy you do it
Illiberal state capitalism→ Deng’s revolution
Made china’s entry into world economic system → allows trade
Open china’s market to world
Turned away from Marxist class struggle ideology
Favored progressive policy, broke up collectivization ( have small farmer private land, private property → people do better than before, provides incentive for farmers to get rich = capitalism )
Lifted 800 millions of chinese out of poverty, pursue self interest
Special Economic Zones (SEZ)
Zones where people build factories at port cities→ brings trade- works→ start doing it everywhere else
Get FDI in these places (allows business from other countries to come in here)
Four Modernizations
Agriculture, Industry (private industry), Science and Tech (Start using western education, send students to other countries), Military, national defense
Lifted the restrictions against private business, made hard work benefit the people first
China the middle class and poverty
Food production increased 50% after 1978
1978-1987→ per capita income doubled
Deng lifted 200m people out of poverty
Encouraged chinese to pursue self interest rather than state sacrifices
2020 → eliminated absolute poverty
New woman / new man under Mao
Socialist personality, rejected individualism and traditional family
Experimented with communal living→ evil of family ties
Communes→ free the woman from the house- loyal to commun not family- sacrifice for the collective
Socialist Market Economy
Gov still own some businesses → mixed economy, not really fair from other countries where companies are not propped up by government
Free markets, some competition, profit incentives
Capitalism without calling it that, led to four modernizations
Bilan - becomes important with center of exports in 2000, don't overstate its importance until the 21th century, not a superpower in 20th century
Key terms :
● Bretton Woods
● Yalta and Potsdam Conferences
● Iron Curtain
● Berlin Blockade and Airlift
● Containment
● Truman Doctrine
● Cominform
● COMECON
● NATO
● Warsaw Pact
Define it
Marshal Plan and Containment
Causes for its emergence
Areas of conflict - eastern europe gets swallowed by USSR
Conflicting ideologies of liberal capitalism vs. Soviet communism
Reagan outspends
Gorbachev tries to reform the Soviet Union
Pan-Arabism
Zionism
Maoism
Sino-Soviet Split