Bacteriology Exam 1
1/381
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
382 Terms
define frank pathogens
capable of causing disease in any host; always considered a pathogen when isolate
define opportunistic pathogens
capable of causing disease given the opportunity; often a commensal and part of the normal host flora, but is capable of causing disease in normally sterile tissues
what group of pathogens is most common?
opportunistic pathogens
define non-pathogens
even weak or non-pathogenic bacteria can cause disease in hosts with weakened immune systems
gram + bacteria appear what color?
purple/ blue
gram - bacteria appear what color?
pink/red
gram + bacteria have a _____ peptidoglycan cell wall
thick
gram - bacteria have a ______ peptidoglycan
thin
acid fast bacteria contain
mycolic acid
LPS is considered an
endotoxin
what receptors does LPS bind to
CD14, TLR4, MD2 receptor
define flagella
filamentous appendages (2-20um) composed for flagellin monomers that allow for motility
Flagella has ____ antigens that can be detected by specific antibodies
H
define glycocalyx
capsule or slime layer that is composed of carbohydrates or glycoproteins
what is the purpose of glycocalyx
inhibits phagocytosis and antibiotic uptake
glycocalyx contains ___ antigens that are detect by specific antibodies
K
define pili
filamentous appendages (0.5-2.0 um) composed of pilin monomers
allow for adhesion (fimbriae) and specialized sex pili allow for transfer of DNA between a donor and a recipient
define thermophiles
optimal temperature 55-75 C
can survive from 40-80 C
define mesophiles
optimal temperature 30-45 C
can survive from 10-47 C
define pyschrophiles
optimal temperature 15-18 C
can survive from -5 to 22 C
define microaerophilic
requires reduced oxygen (low quantities)
define capnophilic bacteria
only grow in air with additional carbon dioxide
characteristics of a surface colony
Surface: smooth & glistening; rough; glanular; wrinkled dry & powdery
Whole colony: circular, filamentous; irregular; rhizoid; punctiform
Elevation: flat; raised; convex; pulvinate; umbonate
Margin: entire, undulate, curled, lovate, serrate, filamentous
Size: diameter in mm; pinpoint; small, medium, and large
Color: pigmentation
examples of motility tests
wet mount: direct microscopic observation
motility culture medium: soft agar stab
O antigens can be found in
LPS
H antigens can be found in
flagella
K antigens can be found in
capsule
serological tests for bacterial identification
slide agglutination
counter-immunoelectrophoresis
ELISA
latex agglutination
western blotting
radioimmunoassay
complement fixation
fluorescent antibody
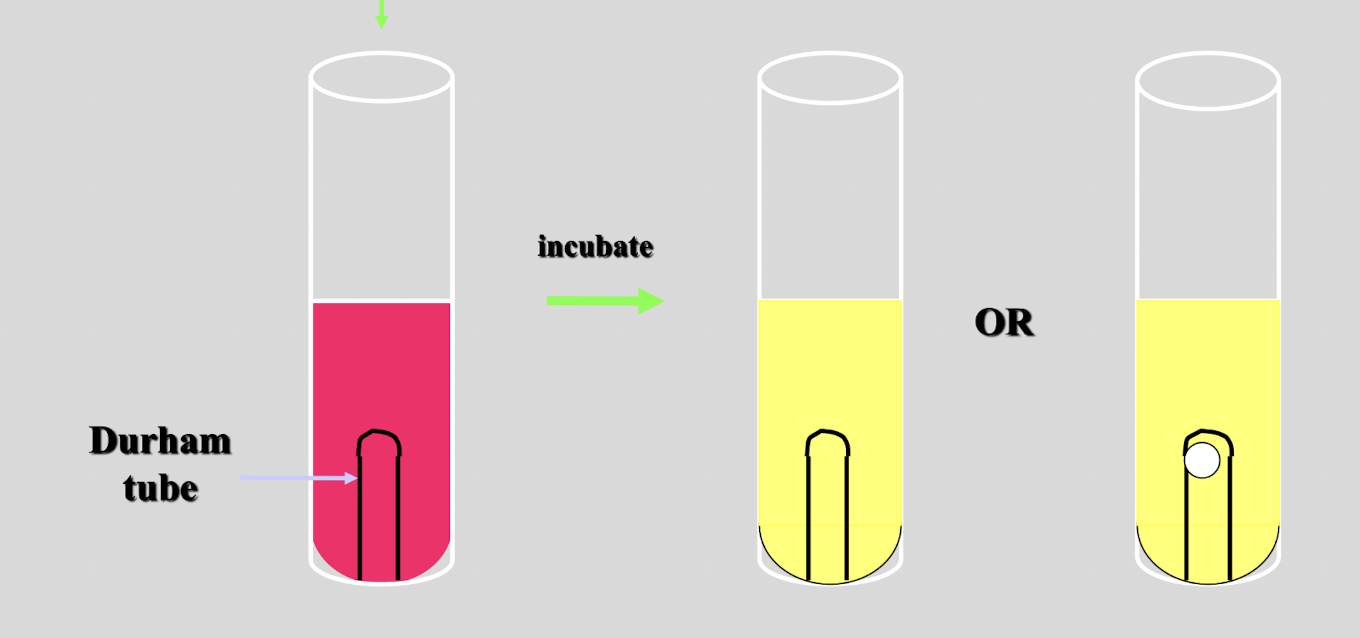
describe the process of detecting carbohydrate utilization
broth culture medium containing specific sugar, pH indicator, and Durham tube
color change to yellow = acid production, able to ferment
color change and gas bubble = able to ferment and gas production
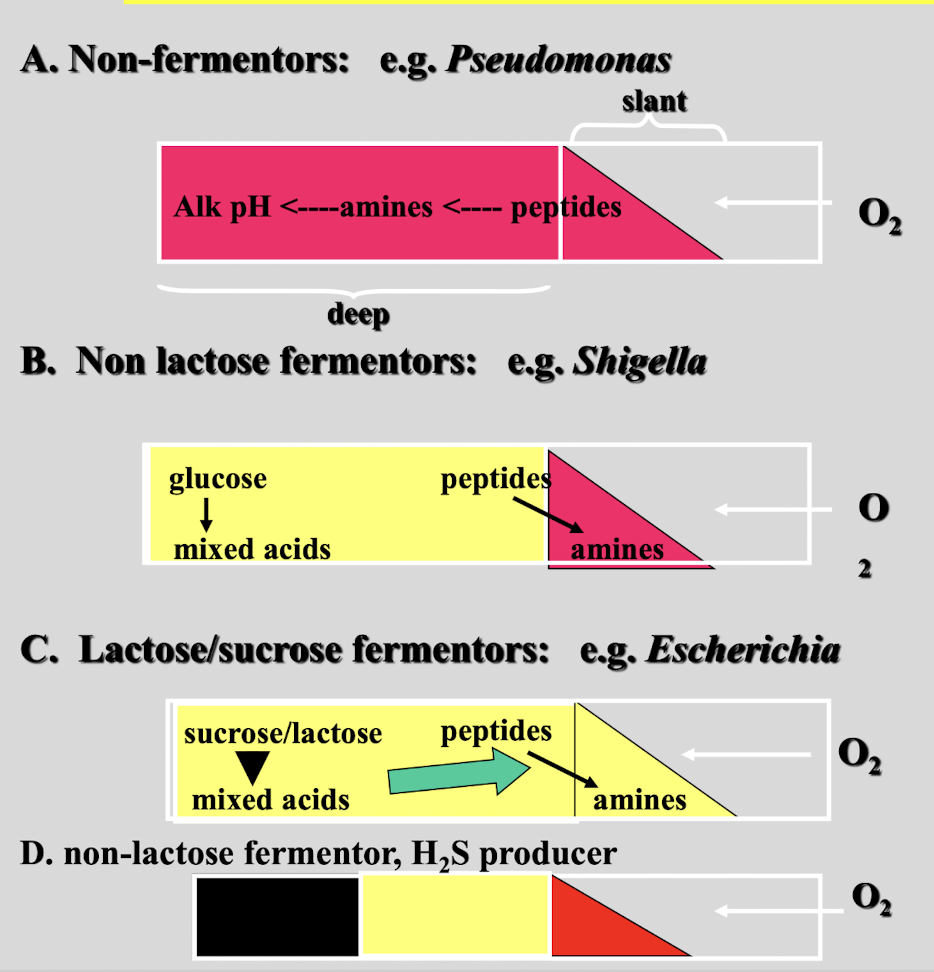
triple sugar iron medium can be used to
differentiate enteric bacteria based on their ability to ferment surgars, produce H2S and/or produce gas
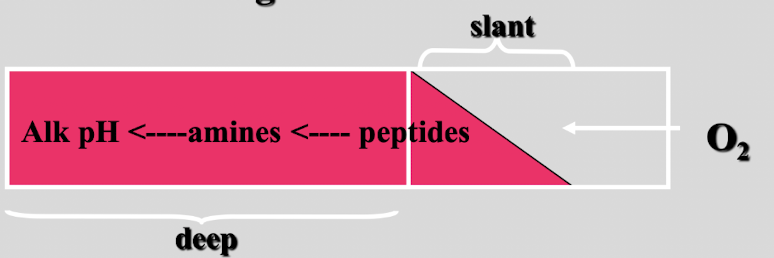
this test shows
non-fermentor
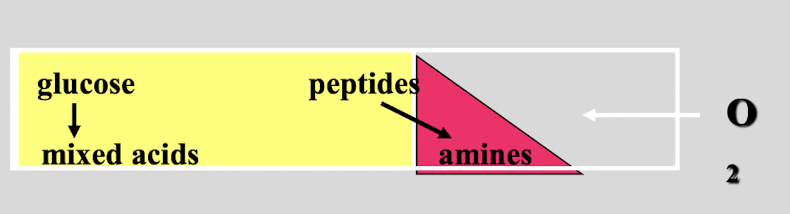
this test shows
non-lactose fermentor
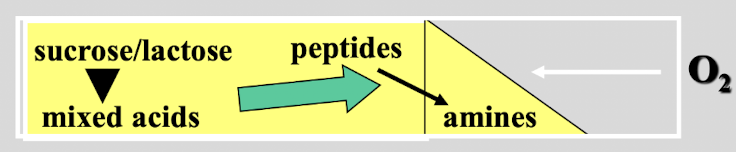
this test shows
lactose/ sucrose fermentor

this test shows
non-lactose fermentor, H2S producer
what does Bromthymol blue test for?
pH of a solution to determine if carbonic acid is formed
yellow solution on bromthymol blue test
acidic solution; carbonic acid formed
green solution on bromthymol blue test
neutral pH
blue solution on bromthymol blue test
basic solution
define decontamination
cleaning and any additional steps required to eliminate risk of infection while handling devices or attire. A reduction in potentially pathogenic organisms to a level that is safe to handle
define disinfection
elimination of most if not all PATHOGENIC organisms, including spores. Most effective when preceded by cleaning
define sterilization
Elimination of ALL living organisms/ agents
describe autoclave
useful for sterilization of heat stable liquids and objects
121 C, 15 min
describe dry heat
160 C (320F) for 1-2 hours
slower than moist heat
limited to inanimate, heat resistant objects
describe incineration
300 C until completely oxidized
fast but expensive
useful in elimination of pathogen contaminated materials (bandages, carcasses, tissues)
for liquid filtration what size filter should be used?
0.2 micrometers
define HEPA (high efficiency particulate air filter)
99.999% of 0.12 micron particles are filtered
face masks, sterile hoods, room air filters
define cleaning
removal of foreign material
define minimum effective concentration (MEC)
concentration of a germicide require to achieve advertised microbicidal activity
define low-level disinfectants
germicide that kills most vegetative bacteria and lipid-enveloped and medium size viruses
define intermediate level disinfectant
kills all microbial pathogens except spores
define high level disinfectant
kills all microbial pathogens except large number of bacterial spores
what is the order of bacteria affected by disinfectants (most to least)?
gram +
gram -
acid fast
spore formers
what is the concentration of ethanol that is most effective as a disinfectant?
70%
what is the role of alcohol as a disinfectant?
denature proteins and solubilize lipids
what is the role of alkalies as a disinfectant?
destroys cell walls and membranes
used in inanimate objects not sensitive to alkaline pH
what is the role of heavy metals (HgCl2 (0.001%), AgNO3, and copper) as a disinfectant?
metals poison enzyme activities by interacting with sulfhydryl groups of cysteine residues
the basis for merthiolate and mercurochrome uses as skin antiseptics; “burns” open tissue as it is solubilized in alcohol!!!
what are the different classes of chemical disinfectants?
alcohols
alkalines
heavy metals
oxidizing agents
surface active agents
phenolic compounds
aldehydes
what is the role of oxidizing agents as a disinfectant?
inactivate enzymes by converting functional -SH groups to oxidized S-S forms; can attack -NH groups, indole groups and tyrosine residues
what is the role of surface active agents as a disinfectant?
induce a reduction of surface or interfacial tension (ex. wetting agents, detergents)
what are the most commonly used aldehydes?
glutaraldehyde, ortho-Phthalaldehyde, and formaldehyde
describe glutaraldehyde in disinfection
high level disinfectant that is compatible with many materials, and so is the agent of choice for chemical disinfection of hospital materials
describe ortho-Phthalaldehyde as disinfectant
a 0.55% solution for 12 min is a high level disinfectant, is also compatible with many materials, is more active than glutaraldehyde against mycobacterium
describe formaldehyde as a disinfectant
high level disinfectant used as a liquid or gas. Not used as commonly as previously due to irritation and potential carcinogenicity
bacteria transfer DNA through
transformation
conjugation
transduction
define transformant
cell that have taken up recipient DNA by transformation
define competent
bacteria that can take up DNA naturally (ex. without artificial treatment)
define homologous recombination
identical or similar regions of DNA align and exchange each other by excision-repair
also known as allelic exchange or strand replacement
define transfection
uptake of viral DNA
define complementation
the mutated DNDA expressed on a plasmid (in trans) will correct the mutation
define transduction
is the process of transferring DNA from one bacterium to another by a phage
virulence factor of Salmonella
O antigens (in LPS) can vary as a function of the phage lysogenizing them → serologically different!
virulence factors for Clostridium botulinum
types C and D are toxigenic only when infected with a specific phage
virulence factors for Escherichia coli
lysogenic lambda phage expresses a gene encoding a host cell envelope protein that provides serum resistance! (ex. resistance to antibodies and complement)
virulence factors for Corynebacteriym diphtheriae
the beta prophage carries the diphtheria toxin tox gene, which is expressed only when the bacterium infects its host
virulence factors for Vibrio cholera
cholera toxin genes are on a prophage (phage that has integrated into the genome). Such cells are known as lysogenes
define plasmids
genes of unknown origin and often not necessary for growth; others contain genes encoding virulence factors
define F-factor
fertility factor; genes promote replication and transfer of the factor to recipient cells (ex. conjugation)
define R-factor
F-factor + genes encoding resistance to specific antibodies
R-factor plasmid contained two types of genes including
resistance transfer factor (RTF): encodes origin of replication, sex pilin genes
r-determinants: genes encoding antibiotic resistance, heavy metal resistance or other virulence factors (determinants), insertion sequences (IS)
define transposons
are mobile genetic elements designated as “Tn”
effects of transposon movement
mutation resulting from insertion into middle of another gene
neutral event; insertion next to an intact gene
excision; can carry along a neighboring gene → virulence gene
what are the 5 bacteria classes based on cell wall structure?
mycoplasma
gram +
mycobacterium
gram -
chalmydia
describe mycoplasma cell wall
no cell wall
sterols in cell membrane
describe gram + cell wall
have a thick cell wall with peptidoglycan and lipoteichoic acid
describe the cell wall of mycobacterium
cover their cell wall with mycolic acid
describe cell wall of gram - bacteria
cover cell wall with lipopolysaccharides (lipid A and sugars or endotoxins)
describe the cell wall of chlamydia
have a cell wall with little to no peptidoglycan but covered with lipopolysaccharides (lipid A and sugars or endotoxins
what are the 6 mechanisms of actions of antimicrobials
(1) DNA gyrase/ topoisomerase responsible for DNA synthesis.
(2) RNA polymerase which is responsible for mRNA synthesis.
(3) 30S subunit of ribosome which is responsible for protein synthesis.
(4) 50S subunit of ribosome which is responsible for protein synthesis.
(5) metabolism which produced folic acid
(6) cell wall synthesis
antimicrobials that act on DNA gyrase/ topoisomerase
Flouroquinolines
Nitroimidazoles
antimicrobials that act on RNA polymerase
Rifamycins
antimicrobials that act on 30S subunit
Tetracycline
Aminoglycosides
antimicrobials that act on 50S subunit
Mycolides
Chloroamphenicol
antimicrobials that act on bacterial metabolism
Sulfonamides
Trimethoprim
antimicrobials that act on cell wall synthesis
B-lactams
Penicillinis
Cephalosporins
Carbapenems
Monobactams
define therapeutics
if an individual is sick, treat the patient to cute
define metaphylactics
if one patient is noticed in herd, treat the whole herd and control the spread
define prophylactics
seasonal prescription of drug to prevent the most susceptible population within a herd
what is the non-traditional use of antibiotics that has been banned?
growth promotion
mechanisms of bacterial resistance to antimicrobials
reduced permeability: shrink/ narrow or close porins so that the antimicrobial drug can not enter
efflux pumping (vomiting): once the antimicrobial enters the cell, it will vomit to eject the antimicrobial
drug inactivation by enzymes: if the drug enters the cell, enzymes are present to break it down immediately
target site change, modification, or protection: binding site on the cell changes so drug can not recognize
biofilm formation: joining of several bacteria in order to fight against the drug
naturally become AMR depending on absence of cell wall structure (ex. mycoplasma): some bacteria naturally lack a cell wall, which is one less place in which a drug can act
tetracycline is blocked by
efflux pumping from bacteria