P4 Electric Circuits - AQA Trilogy Physics
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
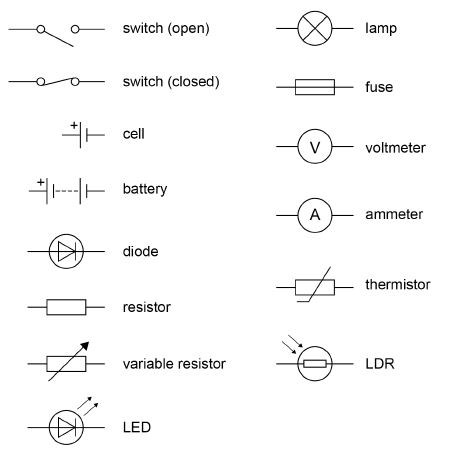
Circuit Symbols
Current
electrons passing through a circuit
charge flow (C) = current (A) x time (s)
Q = I x t
Potential Difference / Voltage
potential difference (V) = energy transferred (J) / charge (C)
V = E / Q
Resistance
resistance (Ω) = potential difference (V) / current (A)
R = V / I
Ohm’s Law
the current through a resistor at a constant temperature is directly proportional to the potential difference across the resistor
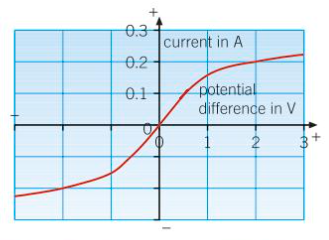
Filament Lamp
the resistance increases if the temperature increases
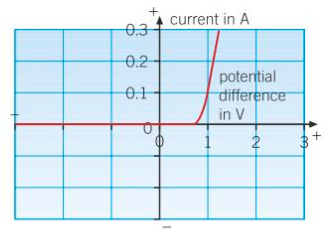
Diode
Thermistor
resistance decreases if the temperature increases
Light-Dependant Resistor (LDR)
resistance decreases as the light intensity increases
Series Circuit
the current in each component is the same
the total potential difference is shared between components
adding components resistances gives the total resistance
adding more resistors increases the total resistance - the current through the resistors is reduced and the total pd across them is unchanged
Parallel Circuit
the total current is the sum of the currents through the separate components
the pd across each component is the same
the bigger the resistance of a component, the smaller the current that will pass through
adding more resistors decreases the total resistance - the total current through the resistors is increases and the total pd is unchanged