virus/protist/bacteria/archea
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/44
Last updated 3:42 PM on 2/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
1
New cards
what are viruses?
a particle of nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids that invade living cells and reproduced. they are considered parasites because they need a host to live
2
New cards
examples of viruses
influenza, chicken pox, Ebola, malaria, AIDS
3
New cards
viruses have different…
shapes, sizes, and specificity
4
New cards
what are retroviruses?
viruses made of RNA that is then copied to DNA
5
New cards
types of viral reproduction
lytic infection & lysogenic infection
6
New cards
lytic infection
the virus enters a cell, makes copies of itself, and causes the cell to burst
7
New cards
ways to control viruses
vaccines, interferon, antibodies
8
New cards
vaccines
small injected dose of the virus causes the body to have an immune reaction to prevent later infection
9
New cards
interferon
proteins that attach to your cell and prevent viruses from reproducing
10
New cards
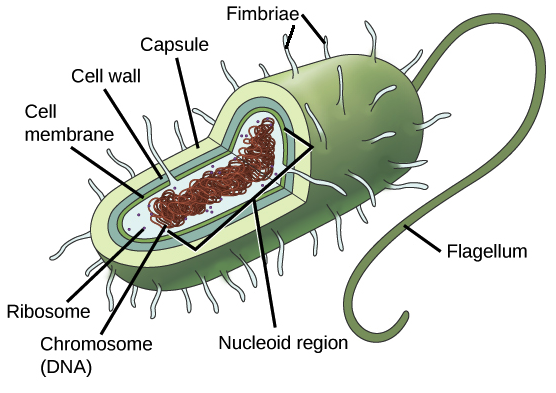
what are bacteria?
single-celled prokaryote organisms with no nucleus
11
New cards
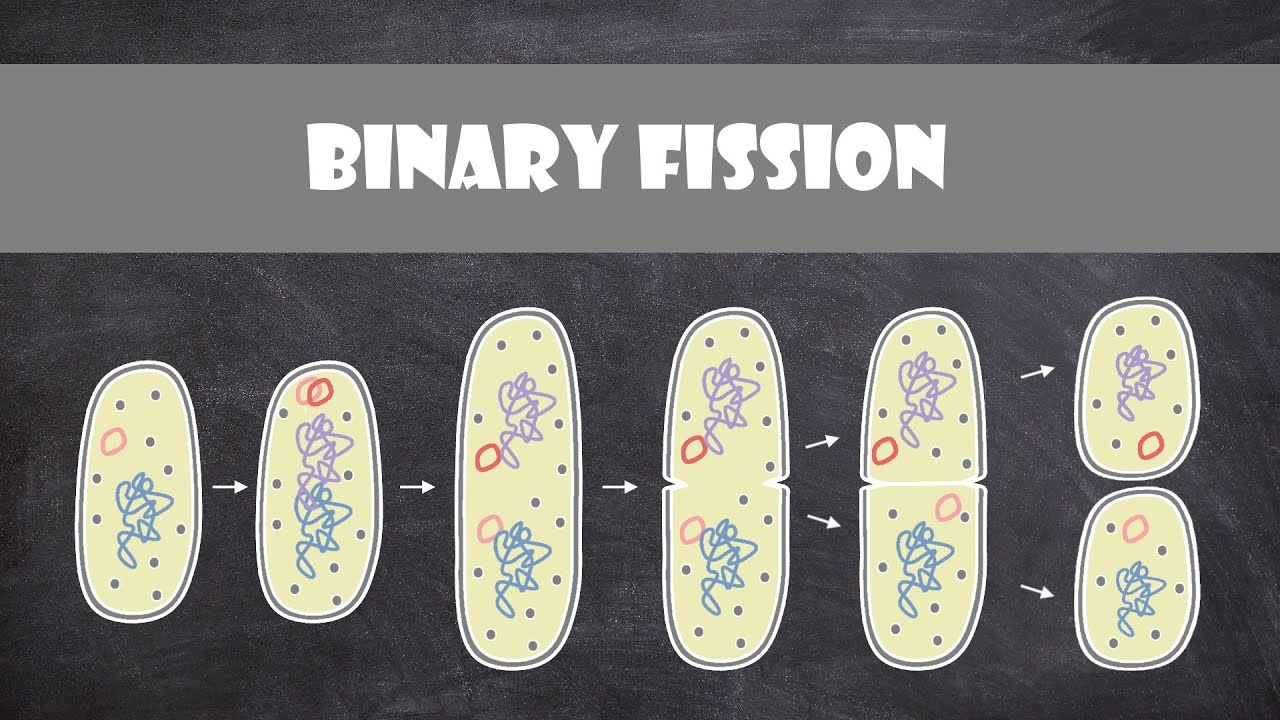
how to bacteria reproduce?
through binary fission
12
New cards
bacterial appendages
* pilli are the small hair-like proteins used for attachment
* the flagellaares used as a motor to move the bacteria
* the flagellaares used as a motor to move the bacteria
13
New cards
glycocalyx
sugarcoat that protects and prevents drying
14
New cards
cell shape is determined by…
the genetic code of the bacteria. this allows for genetic ID
15
New cards
bacterial cell membrane
regulates what moves in and out of the cytoplasm
16
New cards
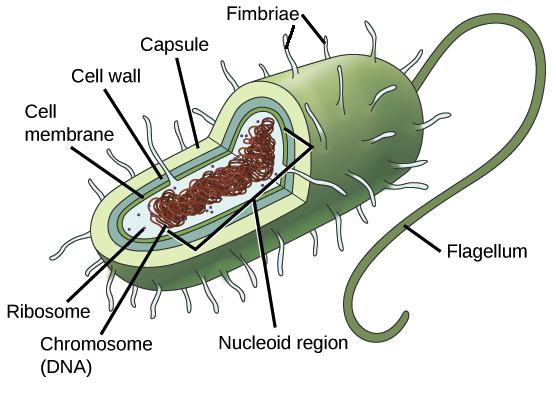
plasmid
extrachromosomal DNA is not a part of the genome with different DNA
17
New cards
around how long have archaea existed?
around 3.5 billion years
18
New cards
are archaea heterotrophs or autotrophs
they are producers who make their own food so they are autotrophs
19
New cards
carbon fixation
the process that converts gaseous carbon dioxide to solid carbon compounds
20
New cards
what types of environments do archaea live in?
extreme or adverse conditions
21
New cards
what is the cell wall of archaea made from?
glycoproteins and polysaccharides
22
New cards
how are they different from other bacteria?
16S rRNA and 18S rRNA sequences were totally different in archaea from other bacteria
23
New cards
similarities between archaea and bacteria:
* both reproduce through binary fission
* they are unicellular organisms
* they are unicellular organisms
24
New cards
differences between archaea and bacteria:
* there are no pathogenic archaea
* they have no peptidoglycan in their cell walls
* genetically different due to ribosomal and rDNA differences
* they have no peptidoglycan in their cell walls
* genetically different due to ribosomal and rDNA differences
25
New cards
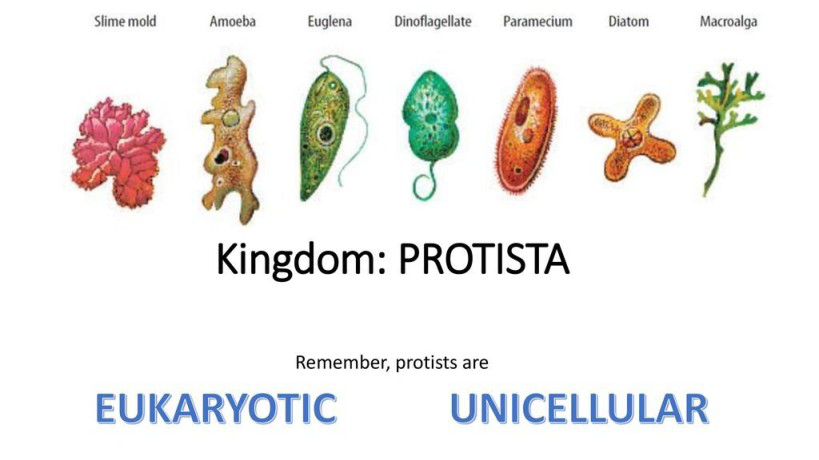
what is a protist?
mostly single-celled eukaryotes some are multi-cellular
26
New cards
three categories of protist
Animal-like, Plant-like, Fungus-like
27
New cards
about animal-like protist
* called protozoans
* are heterotrophs
* can move to get food
* made of cells with a nucleus and no cell wall(like animals)
* unicellular
* are heterotrophs
* can move to get food
* made of cells with a nucleus and no cell wall(like animals)
* unicellular
28
New cards
what are the four animal-like groups of protists?
Sarcodines, Ciliate, Flagellates, Parasites
29
New cards
sacrodines
* feed using their fake feet or pseudopods
* they have a contractile vacuole that takes and expels water
* ex. an amoeba
* they have a contractile vacuole that takes and expels water
* ex. an amoeba
30
New cards
ciliates
* uses cilia, which are projections that move in a wave-like motion to move the cell, to eat
* ex. paramecium
* ex. paramecium
31
New cards
flagellates
* use a flagella, or whip-like tail structure, to move
* ex. peranema
* ex. peranema
32
New cards
parasites
* feeds on the body fluids and bodies of their slows
* ex. plasmodium(causes malaria)
* ex. plasmodium(causes malaria)
33
New cards
plant-like protists
* commonly known as algae
* autotrophic
* unicellular and multicellular
* there are 7 main types
* autotrophic
* unicellular and multicellular
* there are 7 main types
34
New cards
7 types of protists
Algae, Diatoms, Dinoflagellates, Euglenoids, Red Algae, Green Algae, Brown Algae
35
New cards
algae
* most live in water or damp surfaces
* some contain chlorophyll to photosynthesize
\
* some contain chlorophyll to photosynthesize
\
36
New cards
diatoms
* unicellular organisms that have glass-like cell walls
* floats on surfaces of bodies of water
* used in scouring products
* floats on surfaces of bodies of water
* used in scouring products
37
New cards
dinoflagellates
* unicellular
* have two flagella
* responsible for red tides
* have two flagella
* responsible for red tides
38
New cards
euglenoids
* can be autotrophs or heterotrophs
* unicellular an green in color
* uses flagella for movement
* unicellular an green in color
* uses flagella for movement
39
New cards
red algae
* multi-cellular seaweed
* contains red chlorophyll, only needs a small amount of sunlight
\
* contains red chlorophyll, only needs a small amount of sunlight
\
40
New cards
green algae
* unicellular, multicellular, or colonial
* closely related to plants
* closely related to plants
41
New cards
brown algae
* seaweed with many pigments
* contains many plant-like structures
\
* contains many plant-like structures
\
42
New cards
fungus-like protists
* heterotrophs
* have cell walls
* they use spores to reproduce
* there are two main types
* have cell walls
* they use spores to reproduce
* there are two main types
43
New cards
slime mold
* brightly colored
* lives in moist environments
* can be very small or as big as several meters
* lives in moist environments
* can be very small or as big as several meters
44
New cards
water molds and downy mildews
* most live in water
* they grow in tiny threads that look like fuzz
* they grow in tiny threads that look like fuzz
45
New cards
lysogenic infection
The virus replaces parts of the cell’s DNA with the virus’s DNA causing the cell to produce the virus. kills the cell after a prolonged period because it may remain inactive in the cell