8- Movement Analysis
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Purposeful movement is:
-complex
-requires a series of tasks directed toward a goal behavior (ex. STS)
-occurs within a specific context (influenced by social, environmental, and personal factors)
PTs are responsible for:
Evaluating, managing, diagnosing, interventions
reasons PTs perform movement analysis
treatment efficacy, provide person-centered care, focus intervention, treatment strategies, avoid pathoanatomical diagnosis, justify skilled intervention
What is the big picture of movement analysis?
• Observe the movement
• Describe the movement, noting abnormalities
• Hypothesize cause(s) of any abnormalities
• Test your hypotheses
• Treat the problems you identify
• Re-assess
• Modify and repeat as needed
Motor control framework steps
movement examination, movement analysis, plan of care to address movement dysfunction, outcome
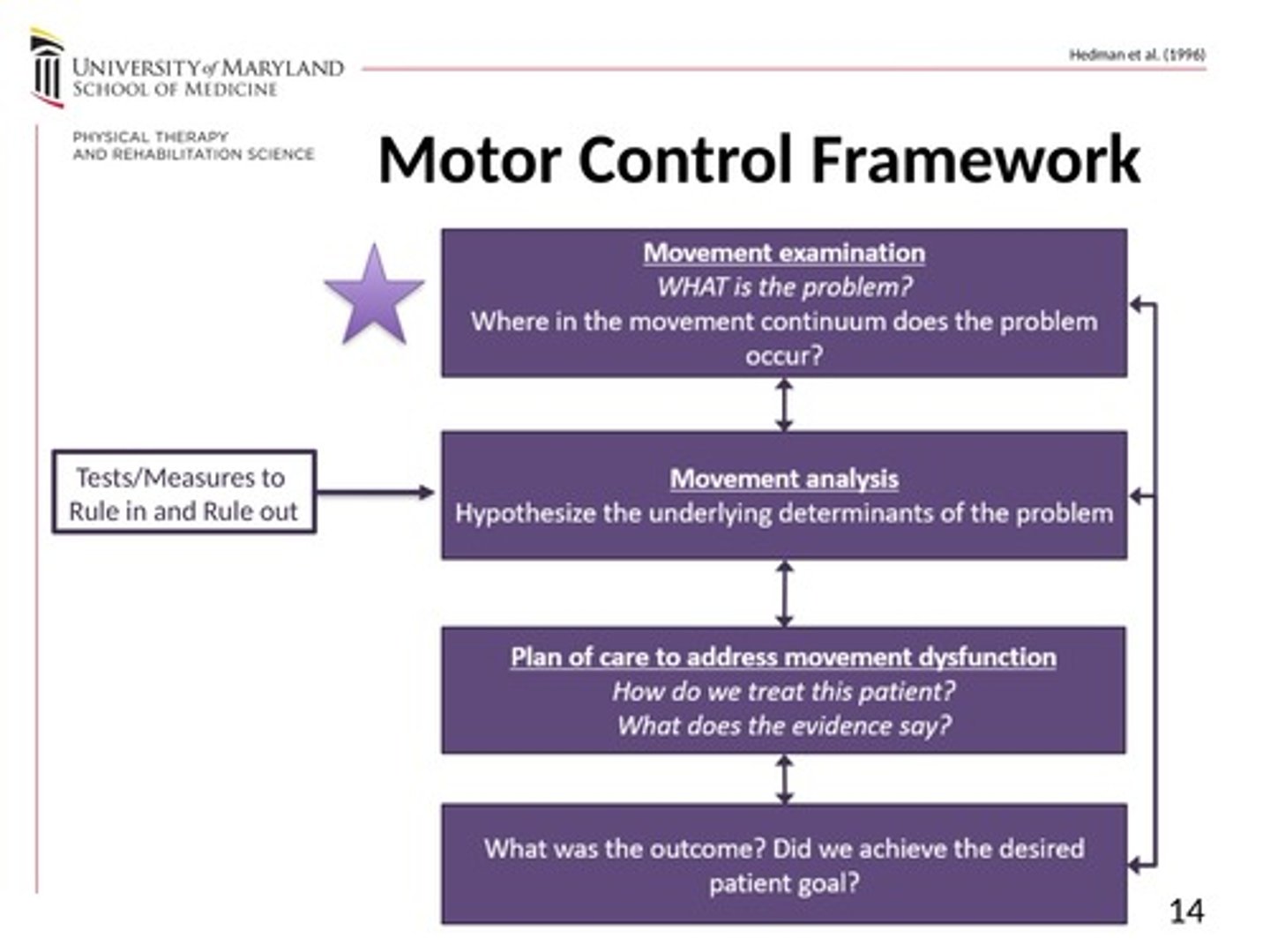
Motor control framework step: __________________
- What is the problem?
- Where in the movement continuum does the problem occur?
- How is the pt CURRENTLY performing the specific movement tasks - observe and describe the movement (seeing/hearing, how can it be qualitatively described, quantitatively?)
- How does movement compare with premorbid or expected performance?
movement examination
How long a pt takes to do an exercise is an example of
Quantitative description of movement
Review slides 18-24: motor control framework...
****
Within the movement continuum, what is one thing you look at during the termination phase?
Timing of stopping, balance or stability
Which component of the movement continuum corresponds to the time period when the movement is being organized (mental processes)?
Preparation
Motor control framework: ________________
- Hypothesize the underlying determinants of the problem (test/measure to rule in and rule out)
- Develop hypotheses for why the movement dysfunctions exist (consider ICF, what DOMAIN is the problem occurring?)
- CLINICAL COMPONENTS of movement
- ultimately leads to PT DIAGNOSIS (Dx)
Movement Analysis
Medical Dx vs. PT Dx?
Medical Diagnosis: Causes of diseases, disorders, injuries
Physical Therapy Diagnosis: Consequences of diseases, disorders, injuries (Movement system impairments, activity limitations, and participation restrictions)
What are examples of Medical Dx?
Stroke, TKR, adhesive capsulitis
What are examples of PT Dx?
Muscle weakness, difficulty walking, shoulder pain
What are the 4 Domains of movement?
Neural, Biomechanical, Physiological, Behavioral
neuronal structures, pathways, and processes that participate in the control of the movement
Neural domain
Weakness due to stroke, or lack of sensation due to peripheral neuropathy from diabetes, are examples of problems with what domain?
Neural
structure and properties of muscles, joints, and soft tissues and the physical laws governing movement
Biomechanical domain
This is an example of problems with what domain?
Muscle tightness limiting joint range of motion or Ligamentous laxity affecting joint stability
Biomechanical
mechanisms of various systems of the body that contribute to the production of movement
physiological domain
This is an example of problems with what domain?
Impaired cardiopulmonary endurance or decreased metabolic efficiency, or skin is too tight after burn (integumentary system)
Physiological
cognitive, motivational, perceptual, and emotional processes, & the outcome of movement in terms of either solving a motor problem or satisfying a goal in a particular environmental context
behavioral domain
Impaired attention and cognition, or Fear of falling are examples of problems with what domain?
Behavioral
What are the clinical components of movement?
Mobility, force generation, muscle tone, sensory information, pain, speed, endurance, posture, balance, coordination, selective capacity, adaptive capacity, cognitive and psychology
Identify the difference between medical diagnosis and PT diagnosis?
Medical: causes of disease
PT: consequences
Abnormal movement patterns due to a leg length discrepancy would be categorized under which domain of movement?
Biomechanical
Motor control framework: _________________
How do we treat this pt? What does the evidence say?
- Aim to optimize movement and minimize activity limitations and participation restrictions (ICF)
- Identify interventions linked to underlying determinants
- directly target underlying determinant (assistive devices, pt education, referrals)
Plan of care to address movement dysfunction
Motor control framework: ___________
What is the result? Did we achieve the desired pt goal?
- Re-eval to assess effectiveness of interventions
- Goals achieved?
- Return to movement examination if needed
outcome
Identify the big picture: How does the motor control framework help you to get from what you observe to how you design your plan of care?
Identify where in the movement continuum they have dysfunction, try to identity the cause of the problem, and design the plan of care, reevaluate, refer if needed
10 min walk gait analysis
IC: posture standing upright with cane, leaning towards the cane, left arm IR (muscle tension), BOS is narrow but normal, environment: in hallway, flat surface
Preparation: pt understood directions well, no modification needed
Initiation: cane moves first, movement initiated at the hip
Execution: stomping more weight the left foot leading, eye gaze on the ground, toe in posture of the right foot, no excessive leaning, left arm in flexed position, knee in extension, leg circumducts)
Termination: ends in same position as start, elbow ended in flexion, elevated shoulder