"AP Chemistry - Electronic Structure of Atoms and Quantum Theory Review"
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
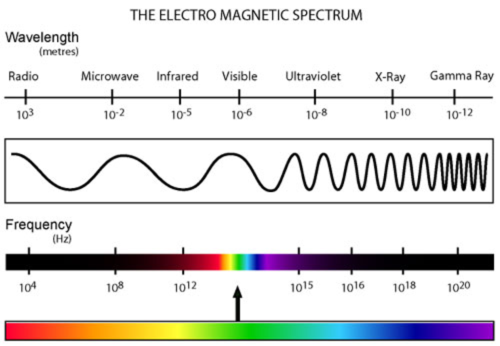
Electromagnetic Spectrum
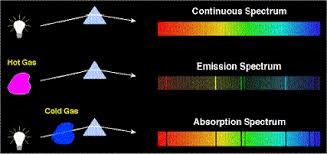
Continuous Spectrum
Spectrums from light containing all wavelengths.
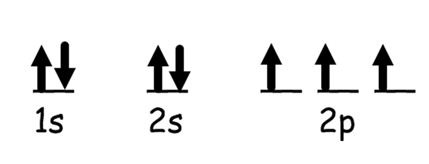
Orbital Notation
This image represents?
Electron Configuration
This image represents?
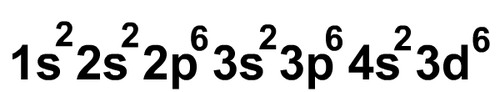
Noble Gas Notation
This image represents?

Shielding effect
The decrease in attraction between an electron and the nucleus of an atom.
-Atomic radius increases.
-Ionization Energy decreases.
-Electronegativity decreases.
-Zeff (effective nuclear charge) decreases.
-Harder to remove electrons.
Atomic Radius
Half the distance between the nuclei in covalently bonded atoms.
-Decreases left to right
-Increases downward.
Ionization Energy
The energy required to remove electrons.
-Increases left to right.
-Decreases downward.
Electronegativity
Measure of an atom's bond to another atom.
-Increases left to right.
-Decreases downward.
Electron Affinity
The energy change that results in the addition of electrons
-Increases left to right.
-Decreases downward.
Metallic charcter
An element that has the physical and chemical properties of metals.
-Decreases left to right.
-Increases downward.
Repulsion of paired electrons.
As the e- moves to enter an orbital already having 1e- they
pair with opposite spins so the IE drops.
-Outweighs the increased attraction from the nucleus so less energy to remove the e-.
Paramagnetism
The magnetic state of an atom with one or more unpaired electrons.
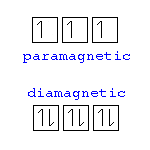
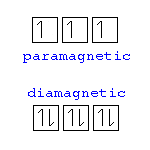
Diamagnetism
The magnetic state of an atom with paired electrons with no magnetic attraction.
Coulomb’s Law
The strength of the interaction between two electrical charges depends on the magnitudes of the charges and on the distance between them.