Chapter 14 - Conflict & negotiation
A definition of conflict
- @@Conflict@@: process that begins when one party perceives that another party has negatively affected, or is about to negatively affect, something that the first party cares about.
- @@Traditional view of conflict@@: belief that all conflict is harmful and must be avoided.
- @@Interactionist view of conflict@@: belief that conflict is not only a positive force in a group but that it is also an absolute necessity for a group to perform effectively.
- @@Functional conflict@@: conflict that supports the goals of the group and improves its performance.
- @@Dysfunctional conflict@@: conflict that hinders group performance.
Types and loci of conflict
- Three types of conflict
- @@Task conflict@@: conflict over content and goals of the work.
- @@Relationship conflict@@: conflict based on interpersonal relationships.
- @@Process conflict@@: conflict over how work gets done.
- Three types of conflict loci
- @@Dyadic conflict@@: conflict that occurs between two people.
- @@Intra-group conflict@@: conflict that occurs within a group or team.
- @@Inter-group conflict@@: conflict between different groups or teams.
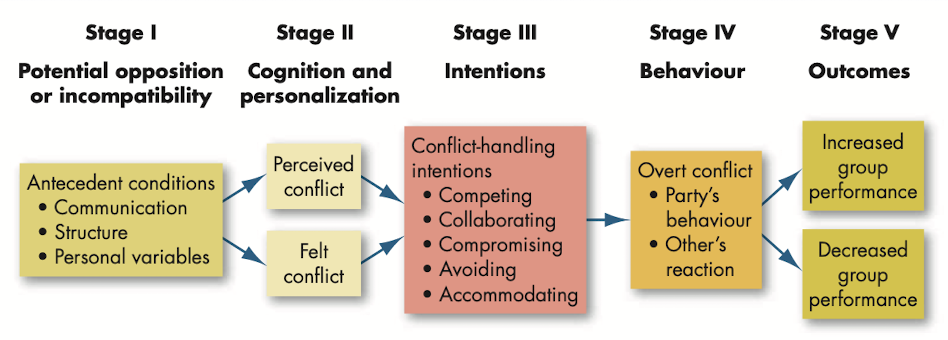
The conflict process
@@Conflict process@@: process that has five stages - potential opposition or incompatibility, cognition and personalization, intentions, behavior and outcomes.
- Stage 1: Potential opposition or incompatibility
- Stage 2: Cognition and personalization
- Perceived conflict: awareness by one or more parties of the existence of conditions that create opportunities for conflict to arise.
- Felt conflict: emotional involvement in a conflict that creates anxiety, tenseness, frustration or hostility.
- Stage 3: Intentions
- Intentions: decisions to act in a given way.
- Competing: desire to satisfy one’s interests, regardless of the impact on the other party to the conflict.
- Collaborating: situation in which the parties in a conflict each desire to satisfy fully the concerns of all parties.
- Avoiding: desire to withdraw from or suppress a conflict.
- Accommodating: willingness of one party in a conflict to place the opponent’s interests above their own.
- Compromising: situation in which each party to a conflict is willing to give up something.
- Stage 4: Behavior
- Conflict management: use of resolution and stimulation techniques to achieve the desired level of conflict.
- Stage 5: Outcomes
Negotiation
- @@Negotiation@@: process that occurs when two or more parties decide how to allocate scarce resources.
- Bargaining strategies
- @@Distributive bargaining@@: negotiation that seeks to divide up a fixed amount of resources; a win/lose situation.
- Fixed pie: belief that there is only a set amount of goods or services to be divvied up between the parties.
- @@Integrative bargaining@@: negotiation that seeks one or more settlements that can create a win/win solution.
- The negotiation process
- @@Preparation and planning@@
- BATNA: the best alternative to a negotiated agreement; the least the individual should accept.
- @@Definition of ground rules@@
- @@Clarification and justification@@
- @@Bargaining and problem-solving@@
- @@Closure and implementing@@
- Third-party negotiations
- @@Mediator@@: neutral third party who facilitates a negotiated solution by using reasoning, persuasion and suggestions for alternatives.
- @@Arbitrator@@: third party to a negotiation who has the authority to dictate an agreement.
- @@Conciliator@@: trusted third party who provides an informal communication link between the negotiator and the opponent.
- @@Consultant@@: impartial third party, skilled in conflict management, who attempts to facilitate creative problem solving through communication and analysis.