Tissue Locations and Functions
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissues with their locations and functions.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
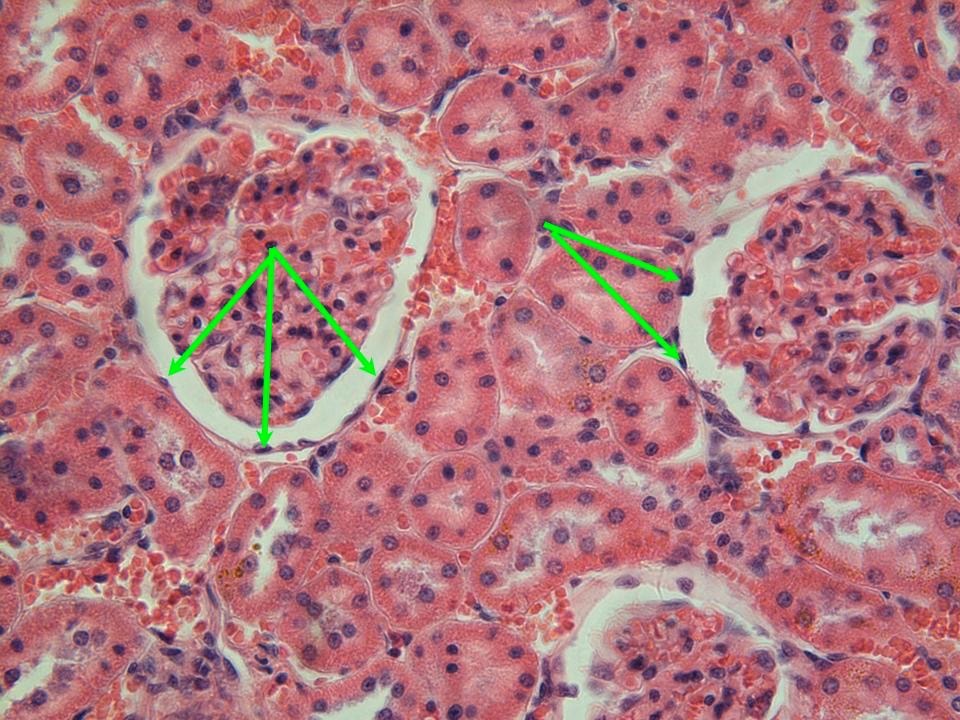
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Location: Alveoli of lungs; glomerular capsules of kidneys; some kidney tubules; inner lining of heart and blood vessels; serous membranes of stomach, intestines, some other viscera; surface mesothelium of pleura, pericardium, peritoneum, and mesenteries. Function: Allows rapid diffusion and transport of substances through membrane; secretes lubricating serous fluid.
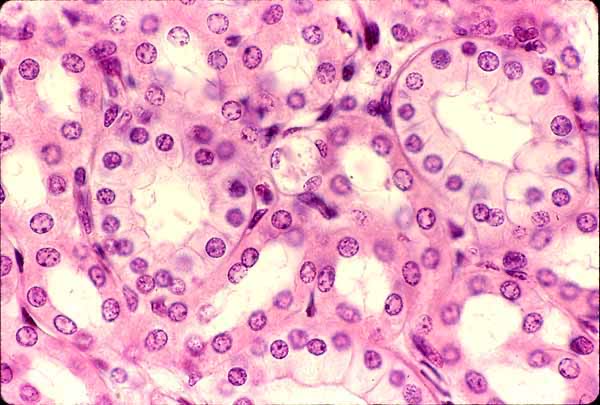
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Location: Liver, thyroid, mammary, salivary and other glands; most kidney tubules; bronchioles. Function: Absorption and secretion; production of protective mucus coat; movement of respiratory mucus.
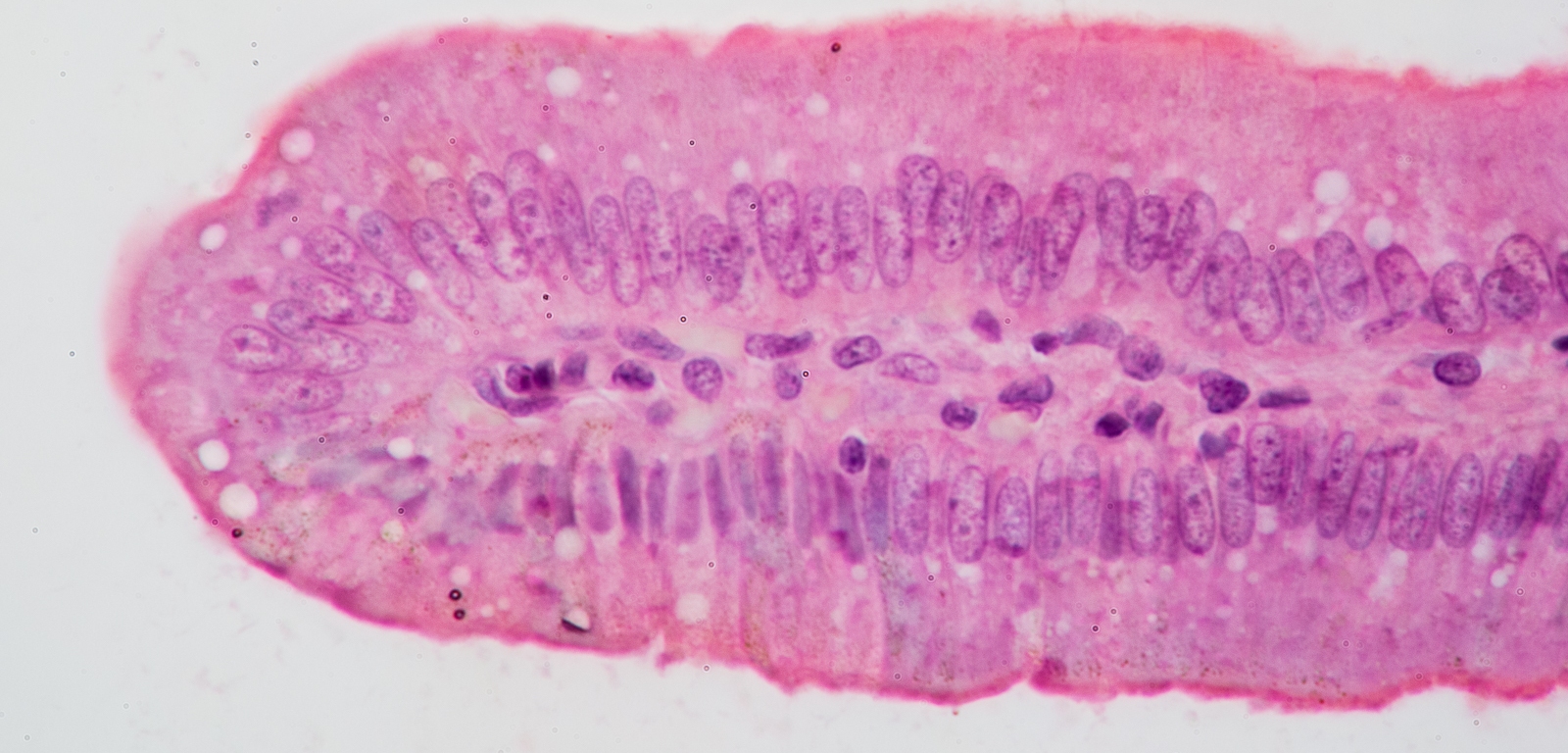
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Location: Inner lining of stomach; intestines; gallbladder; uterus; uterine tubes; some kidney tubules. Function: Absorption; secretion of mucus; secretion of other products; movement of egg and embryo in uterine tube.
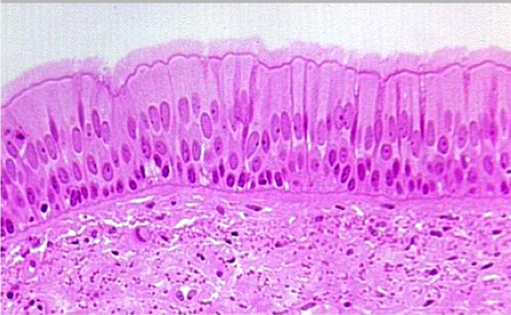
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Location: Respiratory tract from nasal cavity to bronchi; portions of male urethra. Function: Secretes mucus; propels mucus.
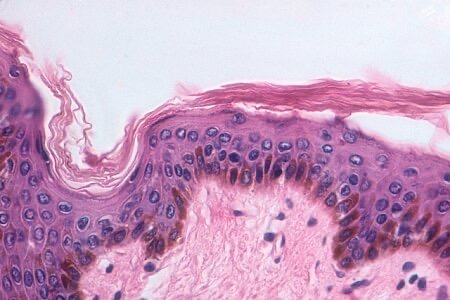
Stratified Squamous Epithelium (Keratinized)
Location: Epidermis. Function: Resists abrasion; resists penetration by pathogenic organisms; retards water loss through skin.
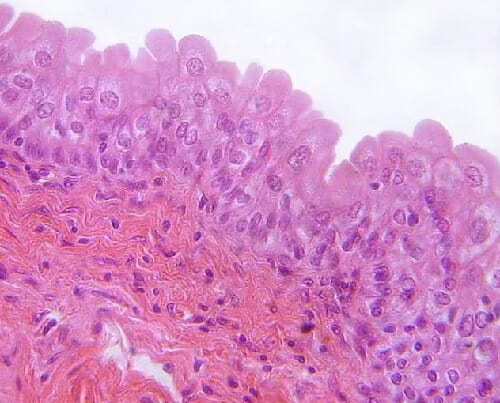
Stratified Squamous Epithelium (Nonkeratinized)
Location: Tongue; oral mucosa; esophagus; anal canal; vagina. Function: Resists abrasion; resists penetration by pathogenic organisms.
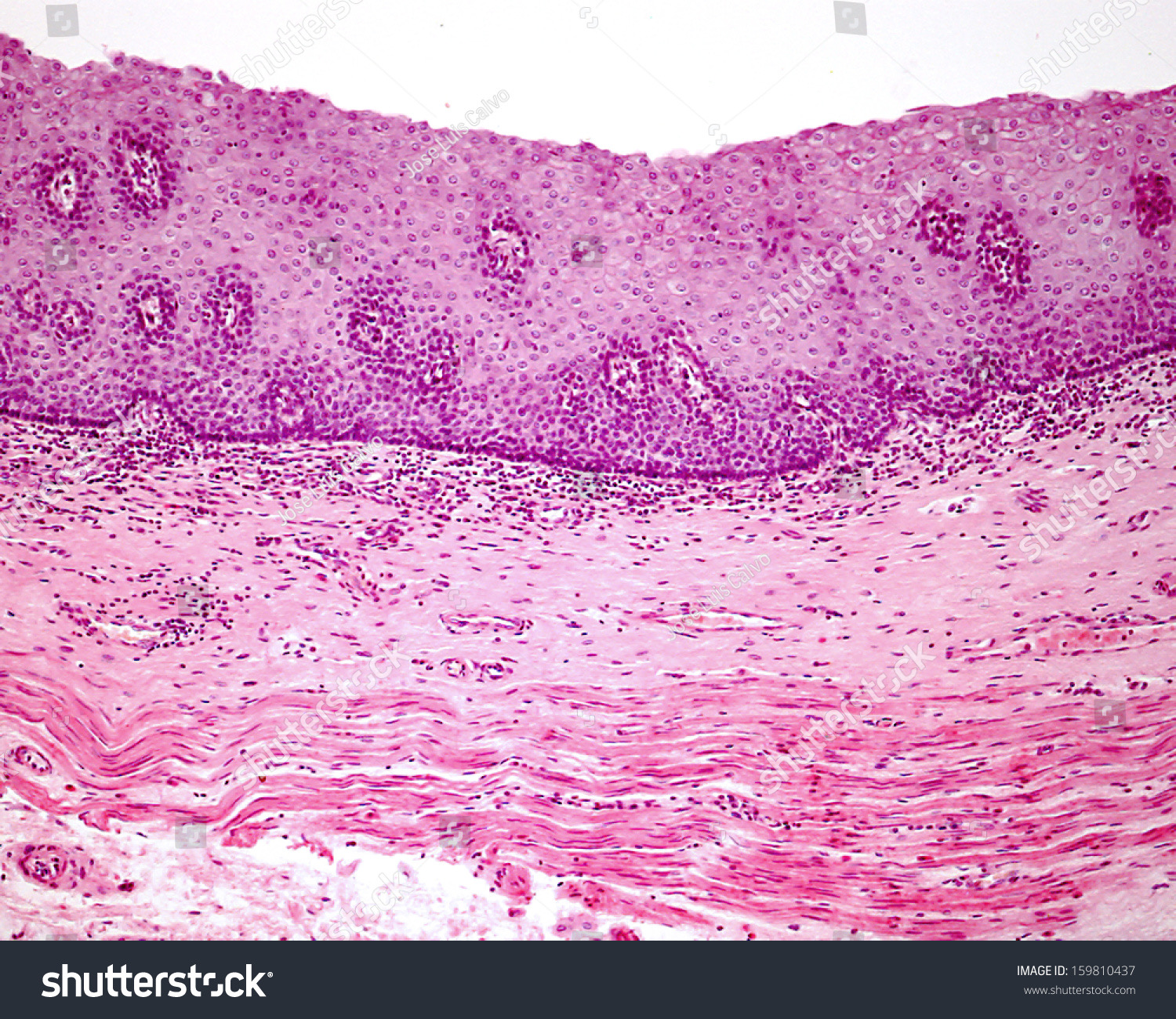
Transitional Epithelium
Location: Urinary tract; part of kidney; ureter; bladder; part of urethra. Function: Stretches to allowing filling of urinary tract; protects underlying tissues from osmotic damage by urine.
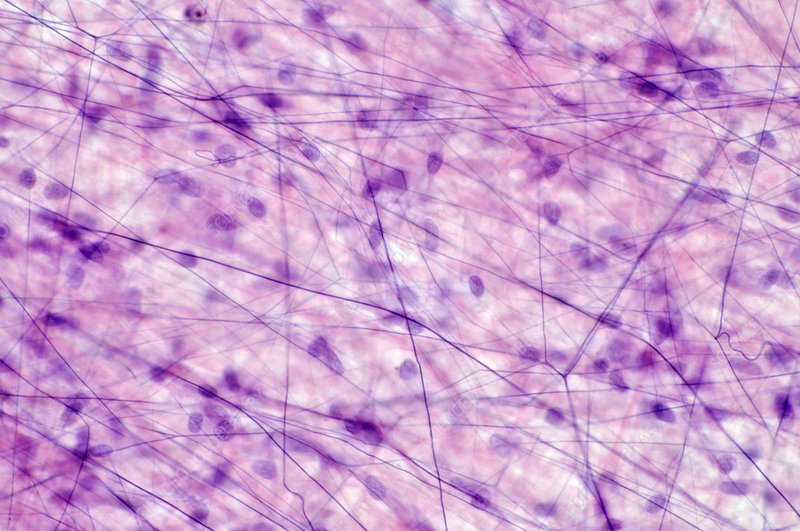
Loose Connective Tissue
Location: Underlies nearly all epithelia; surrounds blood vessels; surrounds nerves; surrounds esophagus; surrounds trachea; fascia between muscles; mesenteries; visceral layers of pericardium and pleura. Function: Loosely binds epithelia to deeper tissues; allows passage of nerves and blood vessels through other tissues; provides arena for immune defense; houses blood vessels which provides nutrients and waste removal for overlying epithelia.

Dense Connective Tissue, Regular Type
Location: Tendons; ligaments. Function: Ligaments tightly bind bones together and resist stress; tendons attach muscle to bone and transfer muscular tension to bones.
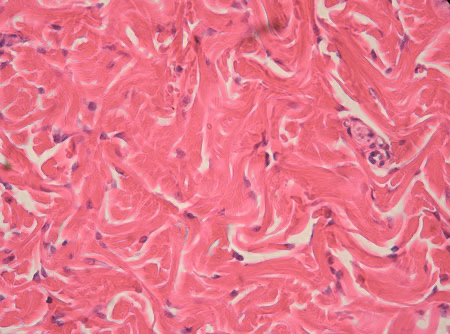
Dense Connective Tissue, Irregular Type
Location: Deeper portion of dermis of skin; capsules around viscera (liver, kidney, spleen, etc.); fibrous sheaths around cartilages and bones. Function: Withstands stresses applied in unpredictable directions; imparts durability to tissues.
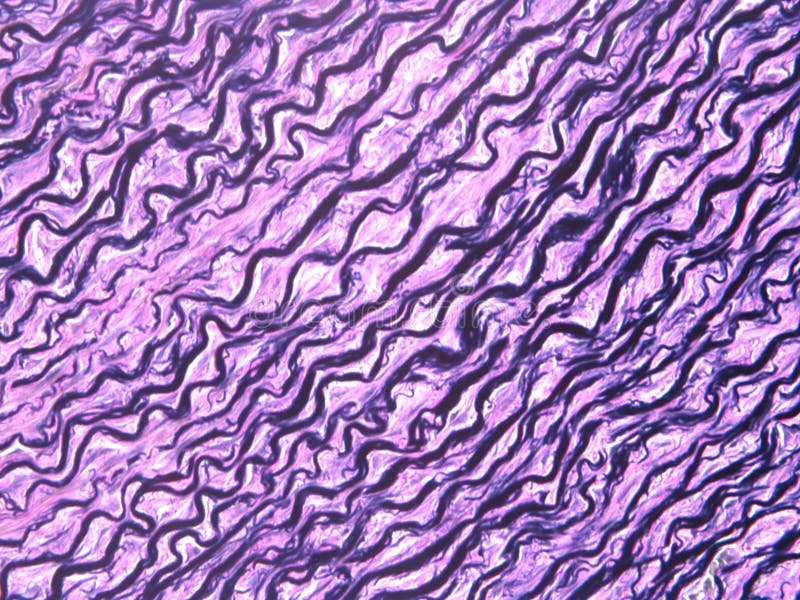
Elastic Tissue (Dense CT)
Location: Vocal cords; some spinal ligaments; medium and large arteries; within bronchial tubes. Function: Allows arteries to expand and relieve some pressure on smaller vessels downstream; allows recoil of tissue after stretching; maintains pulsatile flow of blood in arteries; aids passive recoil of lungs after inspiration.
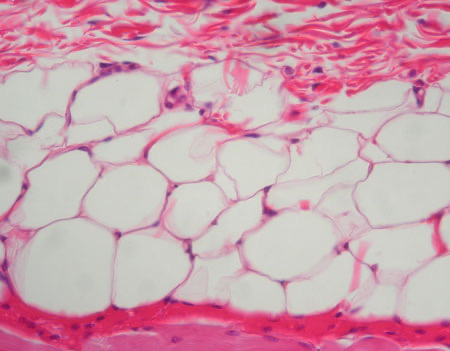
Adipose Tissue
Location: Subcutaneous fat beneath skin; breast; surface of heart; mesenteries; surrounding organs such as kidney and eyes. Function: Energy storage; thermal insulation; heat production by brown fat; protective cushion for some organs; fills space; shapes body.
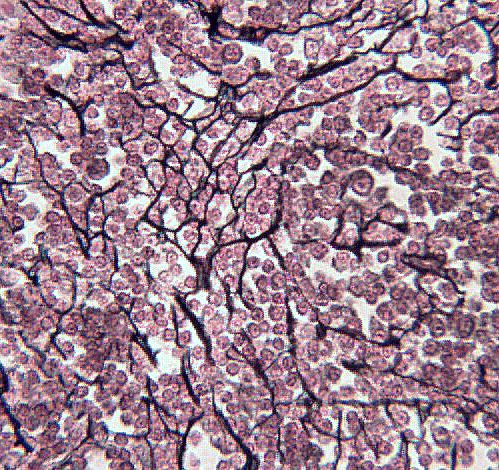
Reticular Tissue
Location: Lymph nodes; spleen; thymus; bone marrow. Function: Forms supportive framework (stroma) for lymphatic organs.
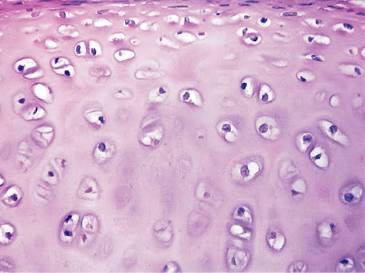
Hyaline Cartilage
Location: Articular cartilage over ends of bones at moveable joints; lacks perichondrium; supportive rings and plates around trachea and bronchi; boxlike enclosure around larynx; fetal skeleton; costal cartilage connecting ends of ribs to breastbone. Function: Eases joint movements; holds airway open during respiration; moves vocal cords during speech; precursor of bone in fetal skeleton and growth zones of long bones.
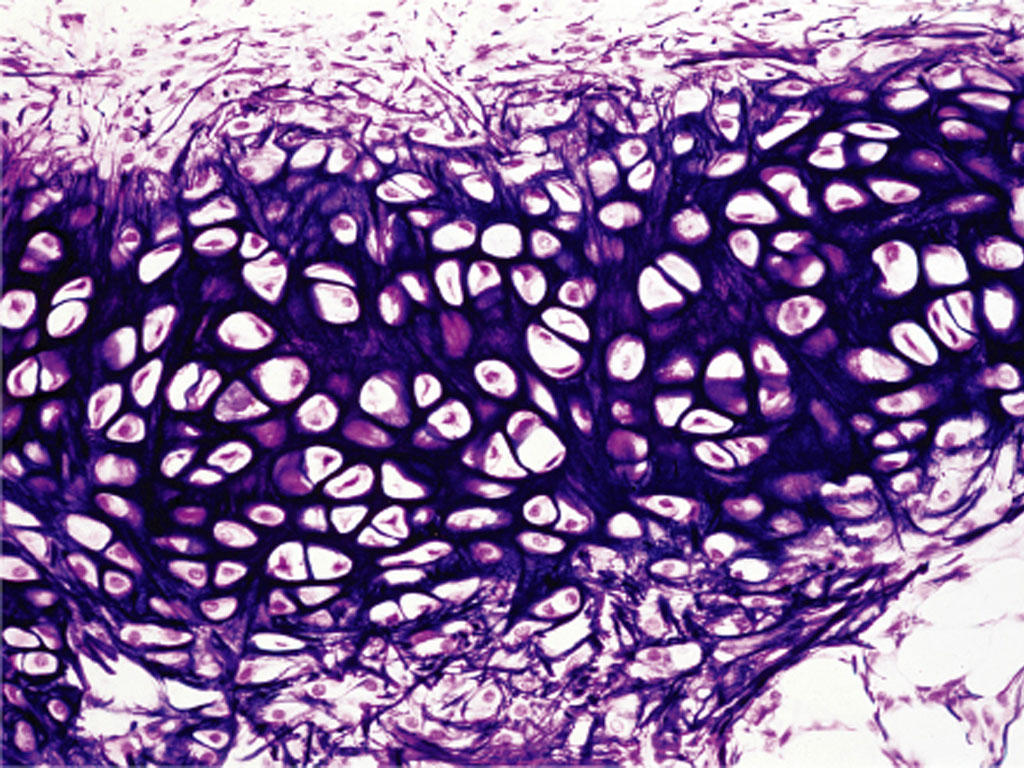
Fibrocartilage
Location: Pubic symphysis; intervertebral discs; menisci of knee joint; at points where tendons insert on bones near articular hyaline cartilage. Function: Resists compression and absorbs shock in some joints; serves as a transitional tissue between dense CT and hyaline cartilage.
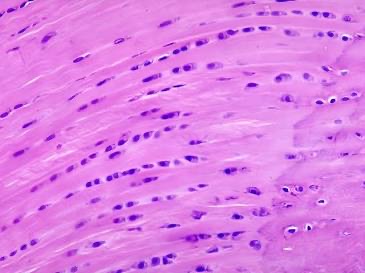
Elastic Cartilage
Location: External ear; epiglottis. Function: Provides flexible, elastic support.
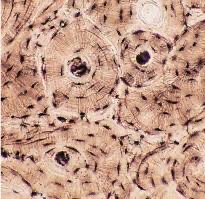
Bone Tissue
Location: Skeleton. Function: Physical support of body; leverage for muscle action; protective enclosure of viscera; reservoir of calcium and phosphorus.
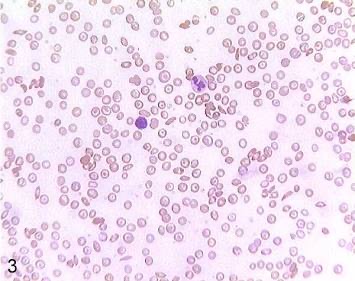
Blood
Location: Contained in heart; contained in blood vessels. Function: Transport of gases, nutrients, wastes, chemical signals, and heat throughout body; provides defensive leukocytes; contains clotting agents to minimize bleeding; platelets secrete growth factors that promote tissue maintenance and repair.
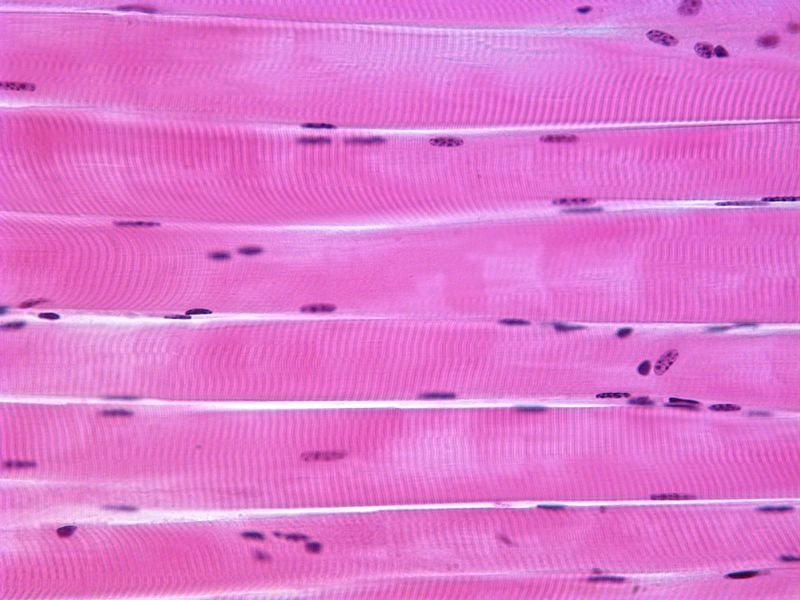
Skeletal Striated Muscle
Location: Skeletal muscles; attached to bones; tongue; esophagus; around lips; eyelids; urethra; anus. Function: Only voluntary muscle; body movements; facial expression; posture; breathing; speech; swallowing; control of urination/defecation; assistance in childbirth.
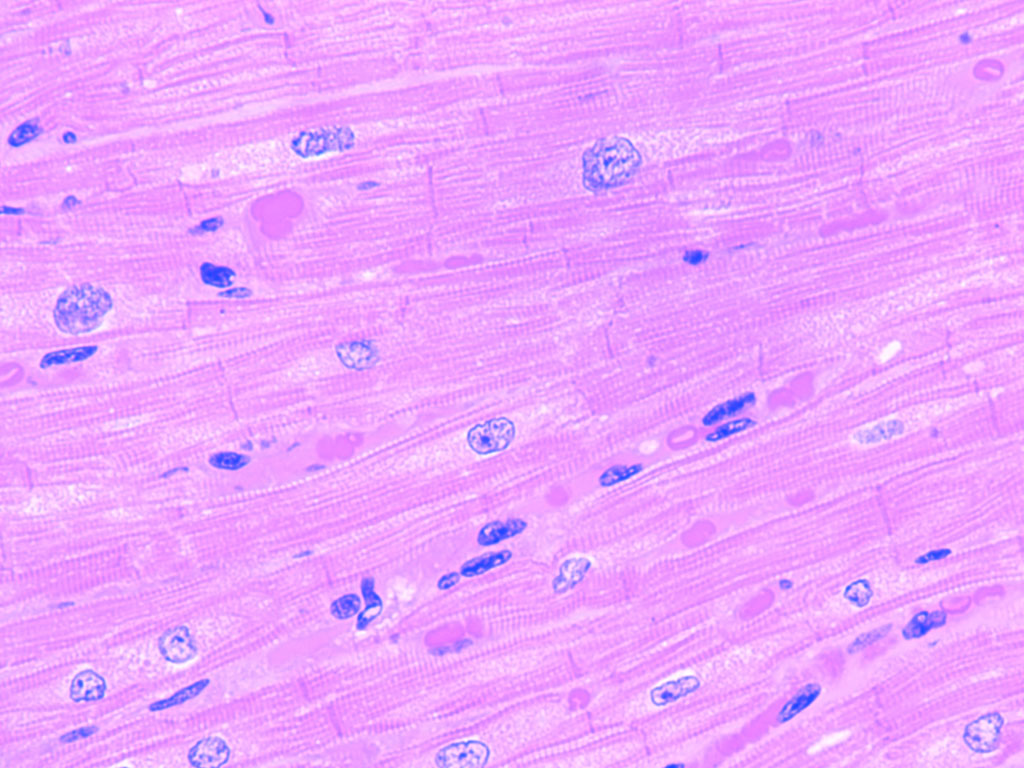
Cardiac Striated Muscle
Location: Heart. Function: Involuntary; pumping of blood.
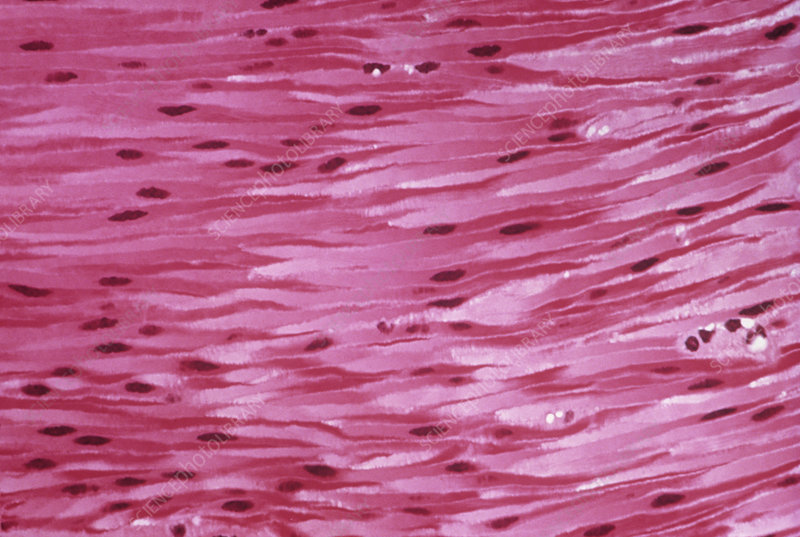
Smooth Muscle
Location: Walls of blood vessels and viscera; iris; associated with hair follicles; sphincters of urethra and anus. Function: Involuntary; swallowing; contraction of stomach/intestines; expulsion of feces/urine; control of blood pressure and flow; control of respiratory airflow; control of pupil diameter; erection of hairs.
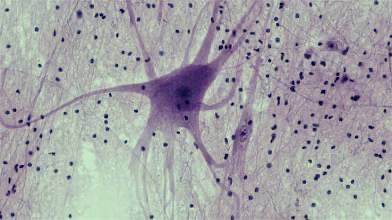
Nerve Tissue
Location: Nervous system; brain; spinal cord; nerves; ganglia. Function: Internal communication.