1 - nerve impulses and synaptic transmissions
1/331
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
332 Terms
what are the 2 main parts of the nervous system?
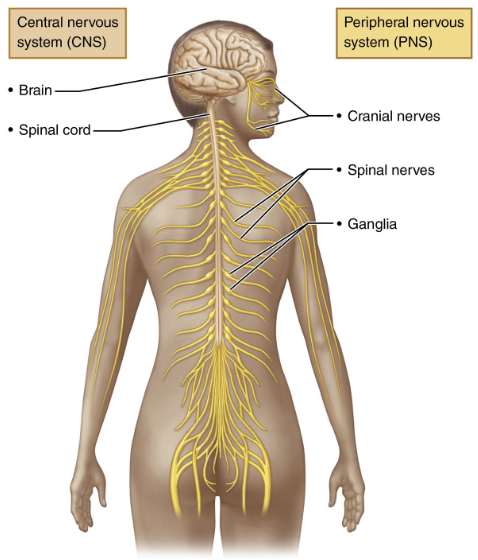
central nervous system (CNS)
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
the CNS includes the _____ and ________
brain and spinal cord
where is the CNS located?
the CNS is located in the dorsal body cavity (back side of body)
what are the main roles of the CNS?
process info (like a control center)
interprets sensory signals (like pain, sound, etc.)
send instructions to muscles/organs (motor output)
the PNS includes ___________
all nerves outside the CNS
what nerves is the PNS made of?
spinal nerves → which connect to the spinal cord
cranial nerves → which connect to the brain
what are the 2 major functions of the PNS?
carry signals between the body and CNS
help body react and function properly
what is known as the “gut brain”?
the enteric nervous system (ENS) is known as the “gut brain”
where is the ENS found?
the ENS is found in the walls of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract
what does the ENS control?
the ENS controls the digestive functions → like food movement and enzyme release
T or F: the ENS can work independently but also connects with CNS
TRUE
what are the 2 main functional divisions of the PNS?
sensory (afferent) division
motor (efferent) division
what does the sensory (afferent) division do?
the sensory (afferent) division carries info TO the CNS (brain and spinal cord)
what are the 2 main types of sensory fibres of the sensory division?
somatic sensory fibers
visceral sensory fibers
the somatic sensory fibers are from the ____, _____, and ____
from the skin, muscles, and joints
example: feeling pain or temperature
the visceral sensory fibers are from the _________
from the internal organs (stomach, heart, etc…)
example: feeling full after eating
what does the motor (efferent) division do?
the motor (efferent) division carries instructions FROM the CNS to body
where does the motor (efferent) division send signals to?
to the muscles and glands → which are the effectors
what are the 2 subdivisions of the motor (efferent) division?
somatic nervous system (SNS)
autonomic nervous system (ANS)
the somatic nervous system controls ______ movements
voluntary
example: moving your hand or walking
the autonomic nervous system controls ______ functions
involuntary
example: heartbeat, digestion, breathing
the nervous tissue consists of 2 principal cell types: ____ and ____
neuroglia (glial cells)
neurons (nerve cells)
what are neuroglia (glial cells)?
neuroglia are small cells that surround and wrap delicate neurons
what are neurons (nerve cells)?
neurons are excitable cells that transmit electrical signals
what are the 4 main types of neuroglia of the CNS?
astrocytes
microglial cells
ependymal cells
oligodendrocytes
T or F: neuroglia do not suport CNS neurons
FALSE; neuroglia DO support CNS neurons
what are the 2 main types of neuroglia of the PNS?
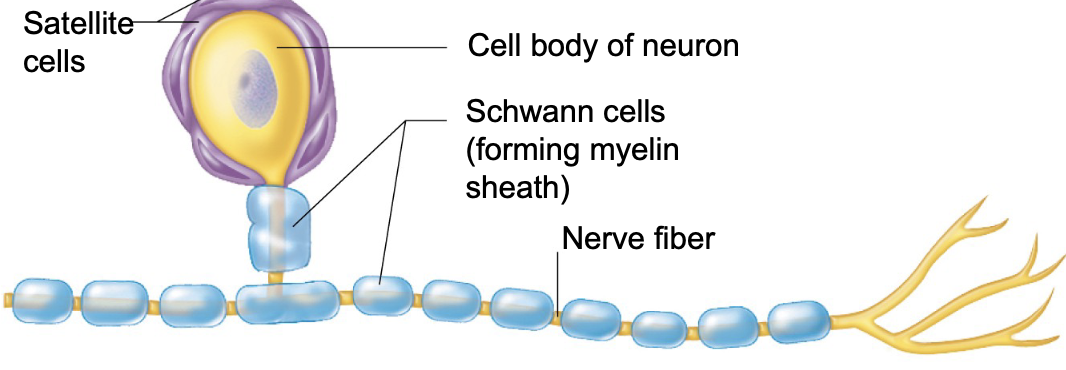
satellite cells
Schwann cells (neurolemmocytes)
T or F: astrocytes are the least common type of glial cells
FALSE; astrocytes are the MOST common type of glial cell
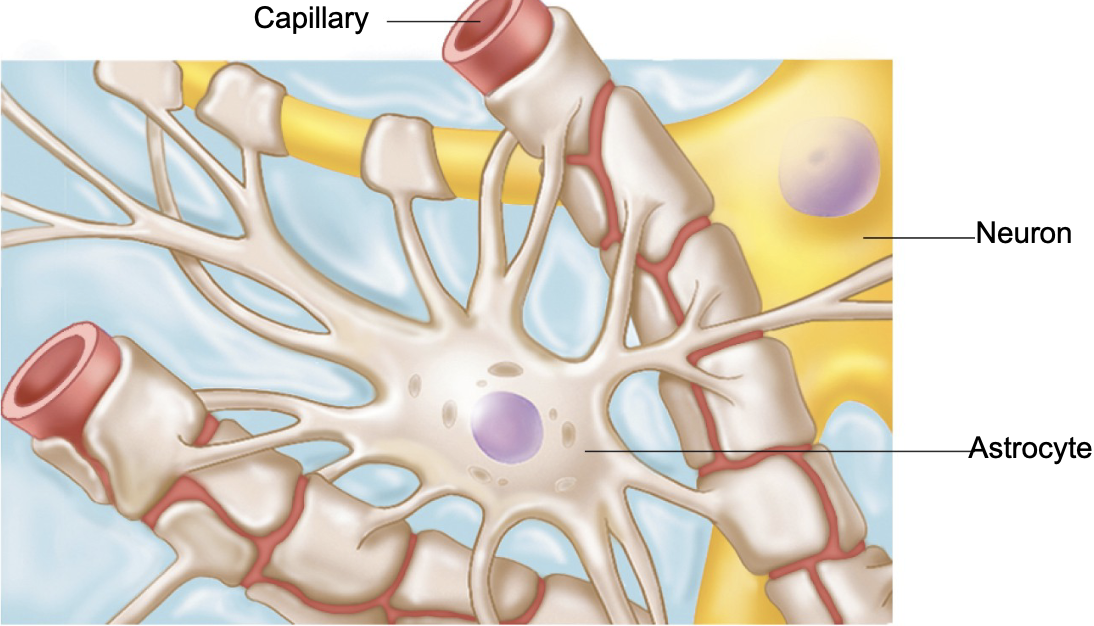
what are the 3 main things astrocytes attach to?
neurons
capillaries
synapses
T or F: astrocytes are star-shaped
TRUE
what are the 6 main functions of astrocytes?
support and hold neurons in place
help with nutrient exchange between blood and neurons
guide young neurons during brain development
keep chemical balance around neurons
respond to nerve signals and chemicals
help with processing info in brain
microglial cells are known as the _____ of the neuroglia cells
defenders
what is the physical description of microglial cells?
small cells with thorny branches
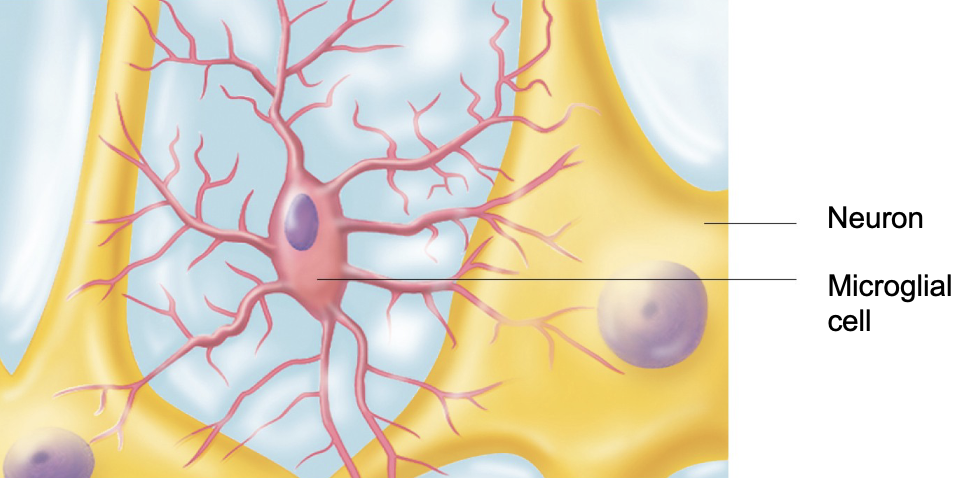
what is the function of microglial cells?
microglial cells constantly monitor neurons and move to injury sites when needed
microglial cells act like _____ cells because they eat _____ and clean up _____
microglial cells act like immune cells because they eat bacteria and clean up dead cells
what are ependymal cells known as?
ependymal cells are known as fluid movers
where are ependymal cells found?
ependymal cells line the brain and spinal cord cavities
what is the shape of ependymal cells?
squamous (flat) or columnar (tall)
may have cilia
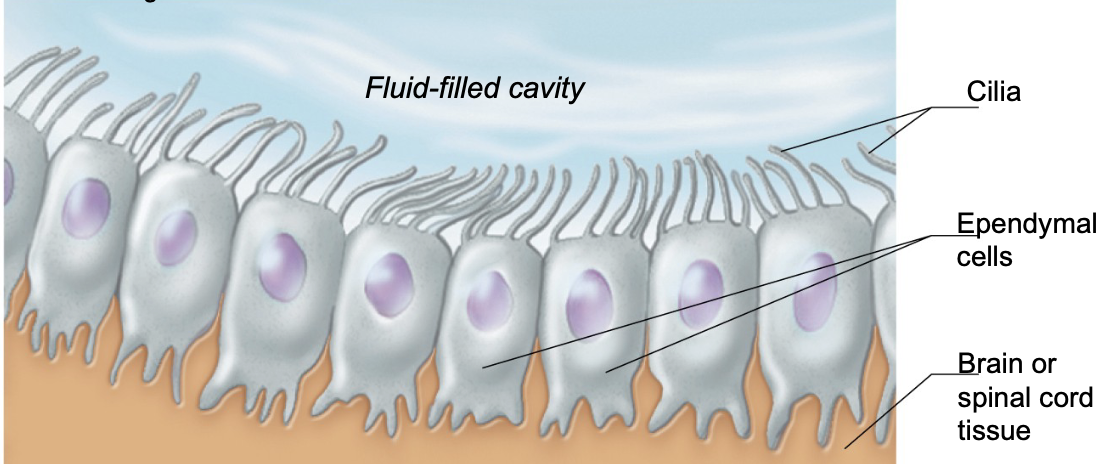
what does the cilia on ependymal cells do?
the cilia on ependymal cells help circulate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
T or F: ependymal cells create a barrier between CSF and brain/spinal tissue
TRUE
oligodendrocytes are the ________ makers of the neuroglia cells
insulation makers
T or F: oligodendrocytes wrap around CNS nerve fibers
TRUE
what is the main function of oligodendrocytes?
the main function of oligodendrocytes is to make myelin sheaths (fatty layers)
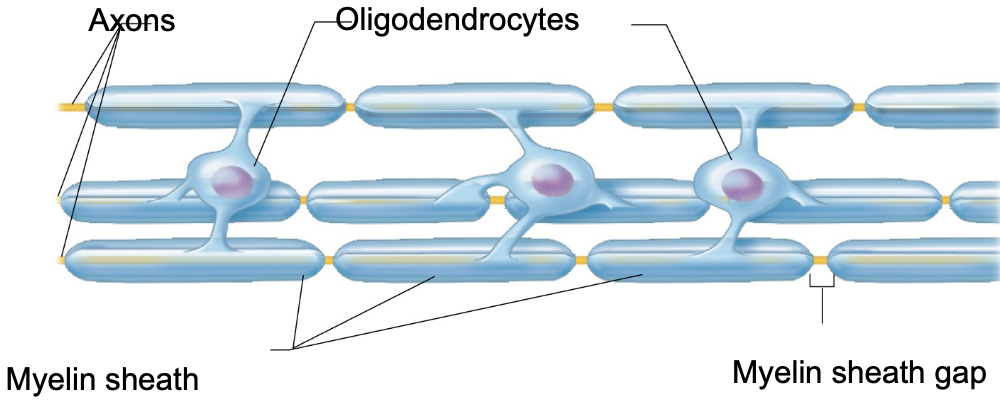
what are myelin sheaths and what is their function?
myelin sheaths = fatty layers
function = help speed up nerve signals
T or F: satellite cells are supportive to the CNS
FALSE; satellite cells are supportive to the PNS
which type of neuroglia cell is known as the bodyguard cells?
satellite cells = bodyguards
satellite cells ____ neuron cell bodies in the PNS
surround
satellite cells in the PNS function like which neuroglia cell in the CNS?
satellite cells of the PNS function like astrocytes of the CNS
what are the 2 major functions of satellite cells?
support and protect neurons
regulate the environment around neurons (nutrients, ions, etc..)
what are Schwann cells of the PNS known as?
Schwann cells of the PNS are known as the myelin markers
Schwann cells (type of neuroglia) belong to which NS: CNS or PNS?
Schwann cells belong to the PNS
schwann cells wrap around ______ in the PNS
nerve fibers
the function of Schwann cells is to make ______
myelin sheath (insulation) → for faster signal transmission
Schwann cells of the PNS are like ________ of the CNS
oligodendrocytes
T or F: Schwann cells have a key role in repair because they regenerate damaged peripheral nerves
TRUE
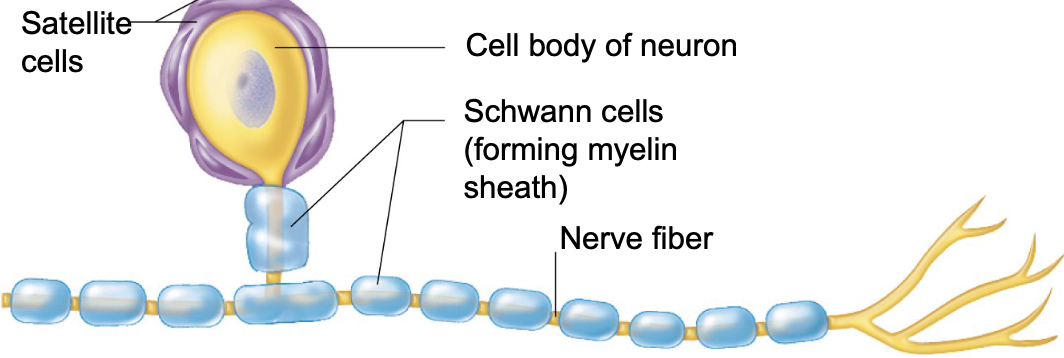
neurons are the ________ of the nervous system
main building blocks
what is the job of neurons (nerve cells)?
neurons send and receive electrical signals (impulses)
T or F: neurons are very large and highly specialized
TRUE
T or F: neurons have a limited lifespan of about 10 years
FALSE; neurons can live a lifetime → they don’t usually die off
T or F: neurons are amitotic
TRUE
amitotic = do not divide → can’t easily replace themselves
T or F: neurons do not require lots of energy
FALSE; neurons require lots of energy
need a constant supply of oxygen and glucose
have a high metabolic rate
what are the 2 basics of a neuron’s structure?
cell body (soma)
contains nucleus and organelles
main centre for cell activity
processes (extensions that come out cell body)
dendrites (receive signals)
axon (sends signals)

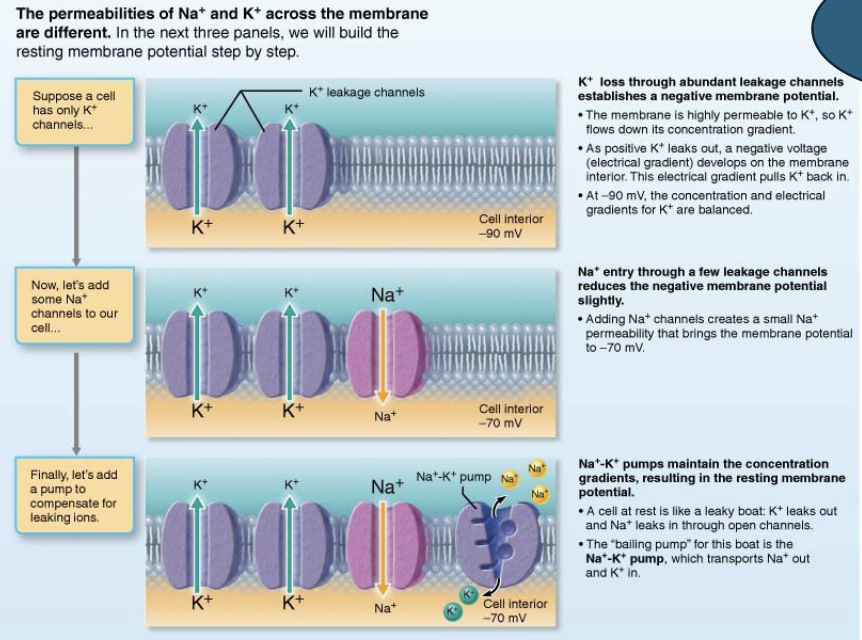
what is resting membrane potential (RMP)?
RMP is the resting voltage across a neuron’s membrane
T or F: RMP is when the neuron is sending a signal
FALSE; RMP is when the neuron is NOT sending a signal
with RMP, the inside of a neuron is _____ compared to the outside
negative
what is the typical RMP?
~ -70 mV
why are neurons called excitable cells?
neurons are called excitable cells because they can change their membrane potential quickly
what does neurons being excitable cells allow them to do?
neurons being excitable cells allows them to send electrical signals (nerve impulses)
all cells have some membrane potential, but neurons use it to ______
communicate
what are the 2 main things that create the RMP?
differences in ion concentration
differences in membrane permeability
what is the ion concentration in the ECF (outside)?
more Na+ (sodium) and Cl- (chloride)
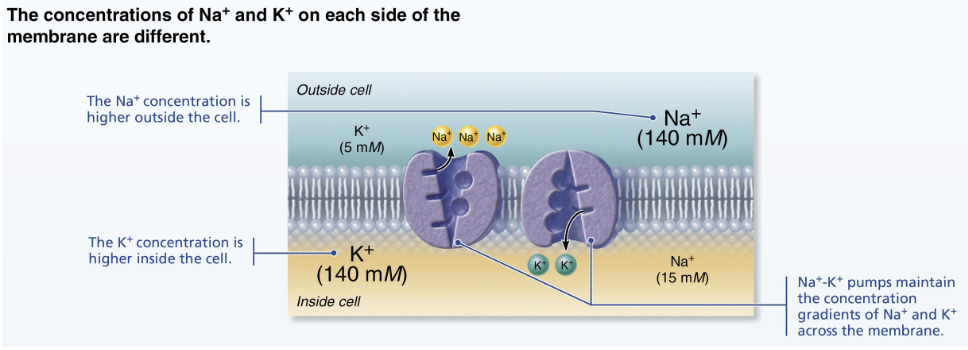
what is the ion concentration in the ISF (inside)?
more K+ (potassium) and negative proteins
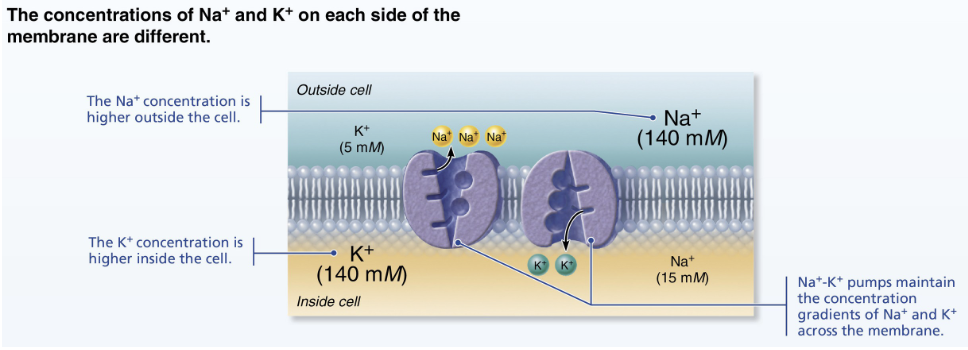
uneven distribution of ion concentrations in RMP creates a __________
charge difference
in RMP, the neuron’s membrane is ____ permeable to ____ than Na+
more permeable to K+
K+ leaks out of the cell easily
Na+ can’t enter as easily
in RMP, the membrane being more permeable to K+ makes the inside _______
more negative
what mineral/chemical element plays the main role in setting up RMP?
K+ (potassium)
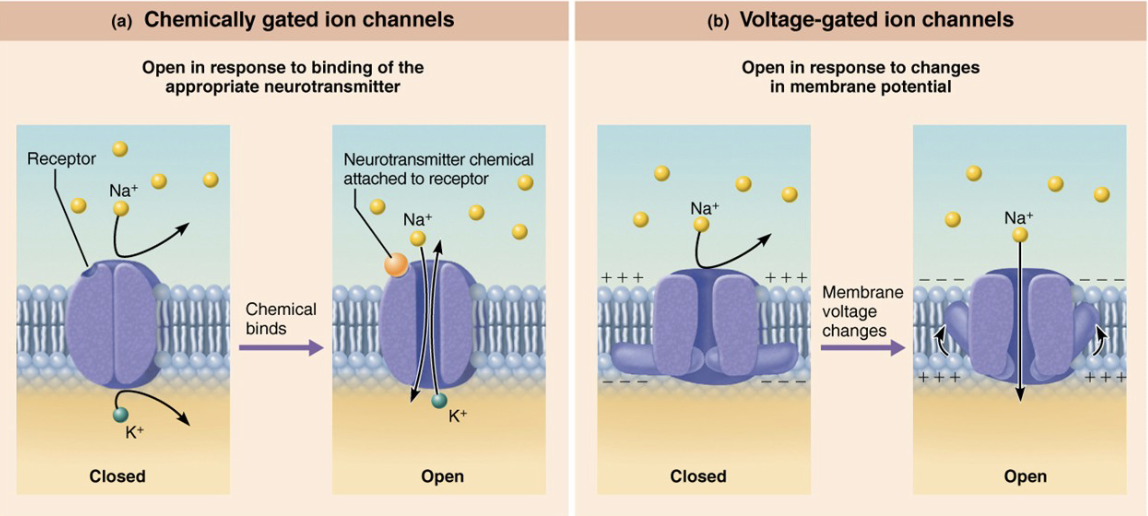
what are gated ion channels?
gated ion channels are special protein “doors” in the membranes (of neurons, excitable cells, muscle cells, etc…)
T or F: gated ion channels only open when triggered (by voltage, chemicals, etc.)
TRUE
when open, ions move based on what 2 major factors?
concentration gradient (high → low)
electrical charge (opposites attract)
gated ion channels are key for sending ________
nerve impulses
movement of ions = _______
changes in membrane potential
T or F: channels are ion specific
TRUE
what is the difference between chemically gated and voltage gated ion channels?
chemically gated ion channels: open in response to binding of appropriate NTM
voltage-gated ion channels: open in response to changes in membrane potential
generating RMP: diagram explanation (no question)
what is action potential (AP)?
action potential is a brief reversal of membrane potential with a change of voltage of ~100mV → from -70mV (resting) to +30mV (spike)
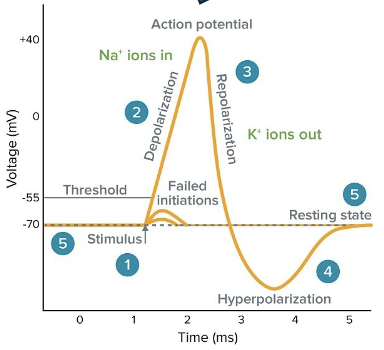
action potential is the main way _______ over long distances
neurons send signals
action potential occurs only in _________ (neurons and muscle cells)
excitable cells
where does action potential happen?
action potential happens on axons
T or F: action potential weakens as it travels
FALSE; action potential does not weaken as it travels
action potential is triggered by which type of gated channel?
voltage-gated channels
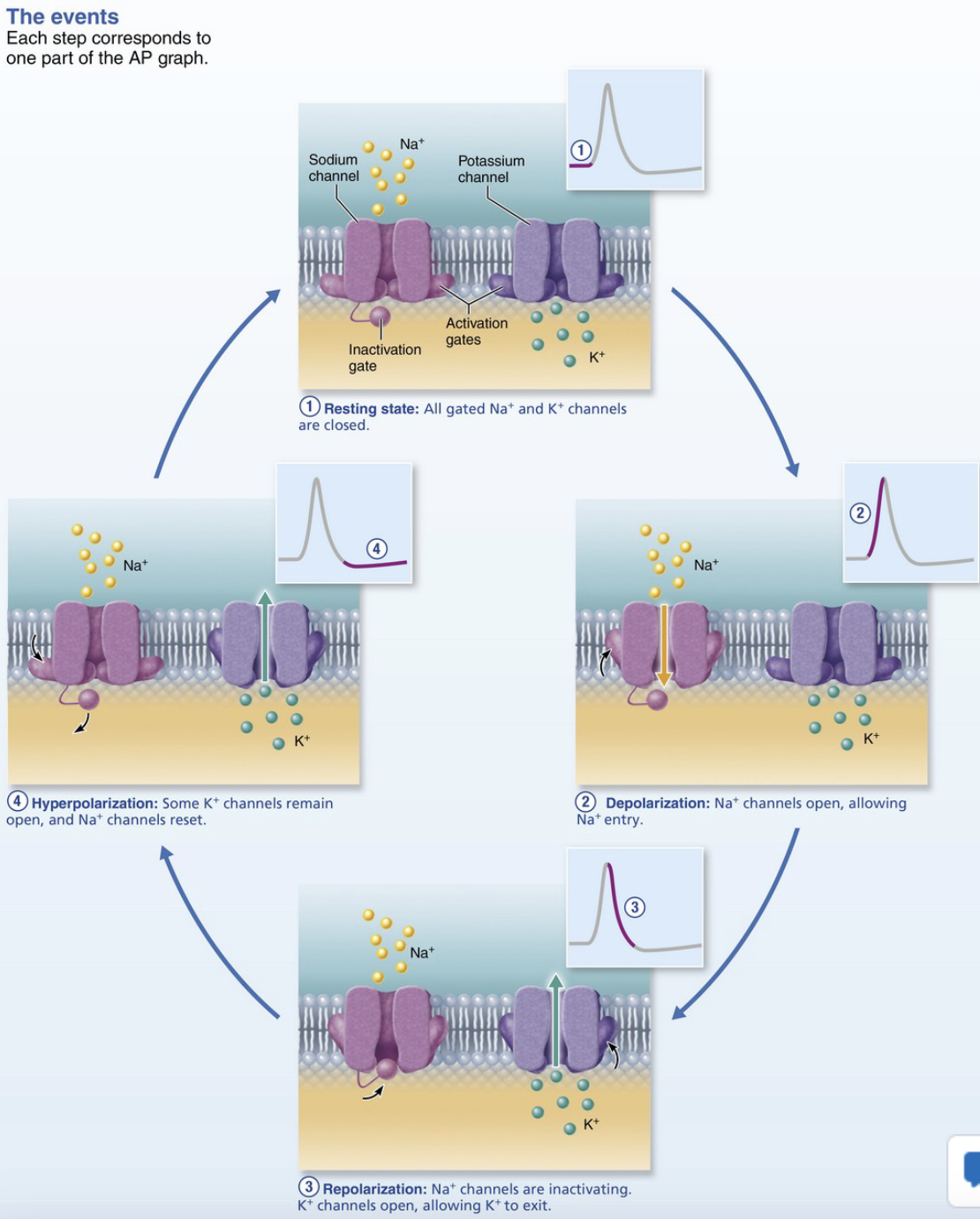
what are the 4 steps of generating an action potential?
resting state
depolarization (rising phase)
depolarization (falling phase)
hyper polarization (undershoot)
what is the membrane potential voltage for resting state in action potential?
-70mV
in resting state of AP, voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels are: open or closed?
closed
T or F: only leak channels (small Na+/K+ flow) maintain resting potential
TRUE
in resting state of AP, are the Na+ channel activation and inactivation gates open or closed?
activation gates = closed
inactivation gates = open
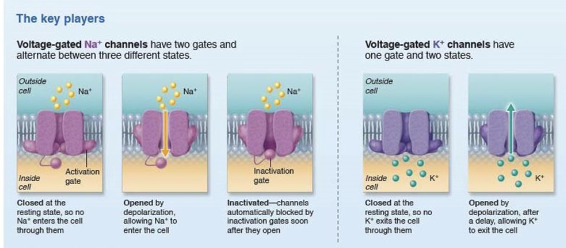
in resting state of AP, K+ channels are: closed or open?
closed
what triggers membrane depolarization in AP?
local graded potential
temporary change in membrane potential in a small, specific area of the neuron
triggered by a stimulus (signal from another neuron or sensory input)
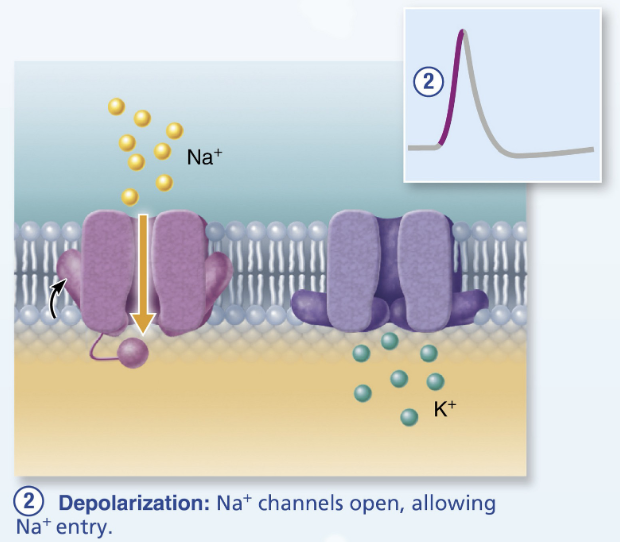
what gated channels in depolarization of AP open?
voltage-gated Na+ channels open
Na+ rushes in
type of positive feedback mechanism (more Na+ channels open)
what is the depolarization minimum threshold voltage?
~ -55mV
once reached, all Na+ channels open → leads to large spike to +30mV
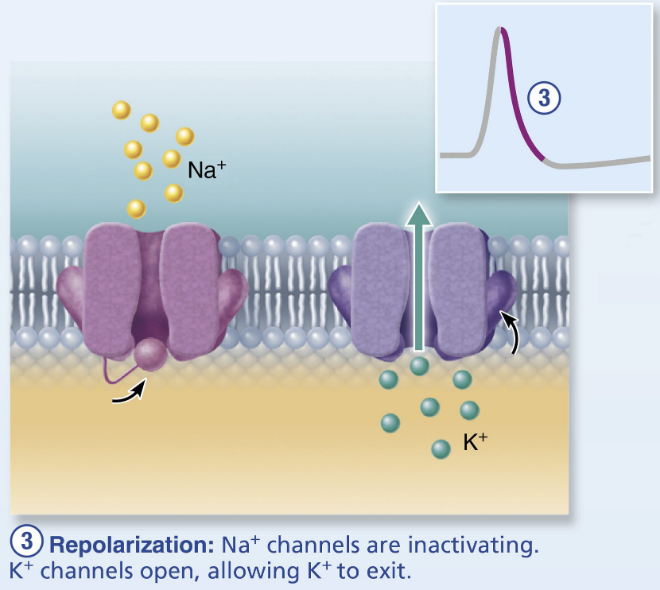
in the repolarization of AP, the Na+ channels: inactivate or activate?
inactivate → stop Na+ entry