Adv chemistry exam 1
5.0(4)Studied by 58 people
Card Sorting
1/133
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:16 PM on 11/17/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
134 Terms
1
New cards
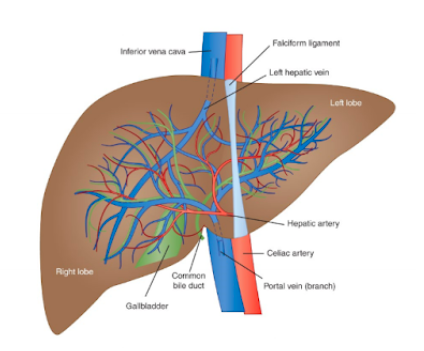
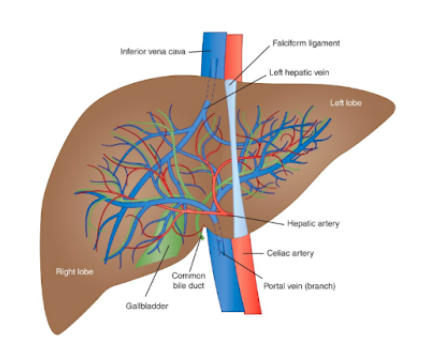
identify structures in the liver
identify structures in the liver
2
New cards
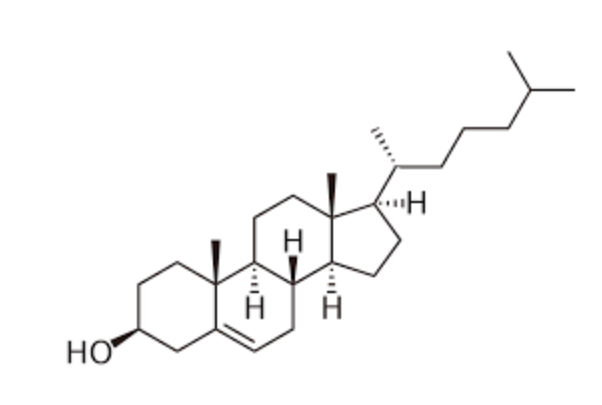
Cholesterol
3
New cards
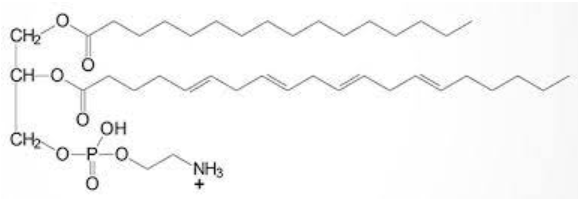
Phospholipid
4
New cards
Triglyceride
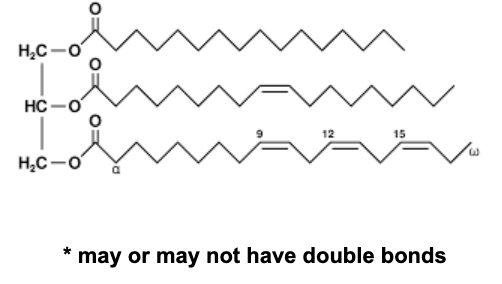
5
New cards
Free fatty acid
6
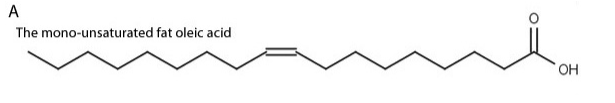
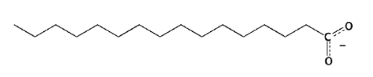
New cards
saturated fatty acid
(saturated with hydrogens)
7
New cards
unsaturated fatty acid
unsaturated: doesn’t have all the hydrogens it could possibly have; has a at least 1 double bond
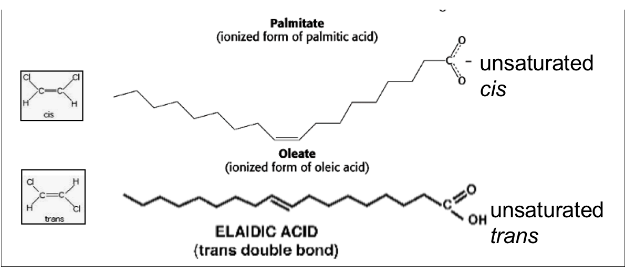
8
New cards
Polyunsaturated fatty acid
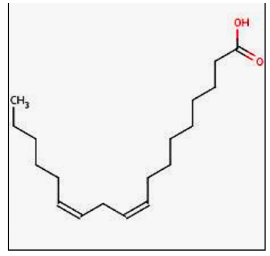
9
New cards
Omega-3 fatty acid
has double bond between 3rd and 4th carbon from far end away from the COO-/COOH
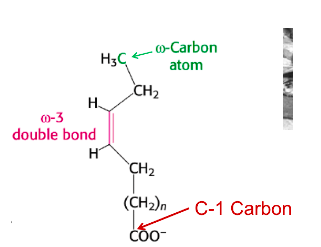
10
New cards
Of glutathione
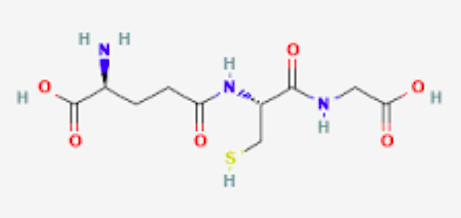
11
New cards
Identify markers of MI on timeline chart
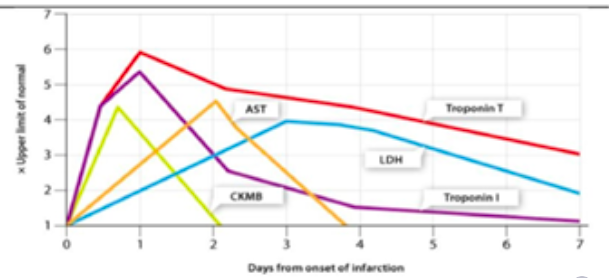
12
New cards
Recognize functions of Kupffer cell and acenstery/derivation
-Macrophages (monocytes that have migrated from blood vessels to tissue) that line the sinusoid (blood vessel in liver)
-Act as scavenger, removing big particulates (complexes of coagulation factors and inhibitors, antibodies and antigens) from circulation, detoxifier, and antimicrobial
-Act as scavenger, removing big particulates (complexes of coagulation factors and inhibitors, antibodies and antigens) from circulation, detoxifier, and antimicrobial
13
New cards
Identify markers of protein nutrition
Prealbumin
-AKA transthyretin (thyroxine-binding prealbumin)
-Transports vitamin A and thyroid hormones
-Sensitive index of protein nutrition
Prothrombin (factor II)
PLT count
-AKA transthyretin (thyroxine-binding prealbumin)
-Transports vitamin A and thyroid hormones
-Sensitive index of protein nutrition
Prothrombin (factor II)
PLT count
14
New cards
synthetic function of the liver
Markers of liver function (synthesis)
-Total protein
-Albumin
-Transports insoluble compounds
-FAs
-Bilirubin
-Calcium
-Lipophilic medications
-Keeps water in vasculature
-Decrease albumin = edema
-Moderately informative of protein nutrition
-3-week half life
-Total protein
-Albumin
-Transports insoluble compounds
-FAs
-Bilirubin
-Calcium
-Lipophilic medications
-Keeps water in vasculature
-Decrease albumin = edema
-Moderately informative of protein nutrition
-3-week half life
15
New cards
synthetic function of the liver (shorter 1/2 life)
factor VII (clotting factor)
-half-life of 4 hours
-Basis of INR, depends on adequate activity and levels of factor 7. No protein = low factor 7 activity
prealbumin
-Half life of 2-3 days
-half-life of 4 hours
-Basis of INR, depends on adequate activity and levels of factor 7. No protein = low factor 7 activity
prealbumin
-Half life of 2-3 days
16
New cards
Markers of hepatobiliary function (will rise when blockage/disease exists)
Total and conjugated bilirubin
ALP activity
gamma-GT
-Participates in glutathione detoxification
ALP activity
gamma-GT
-Participates in glutathione detoxification
17
New cards
Markers of liver cell injury (will rise when cell injury/death present)
AST
ALT
ALT
18
New cards
Recognize metabolic function of liver in regard to blood glucose
-Liver doesn’t metabolize glucose (saves it for brain since fatty acids and lipoproteins can’t cross blood-brain barrier)
-Liver utilizes fatty acids
-Liver utilizes fatty acids
19
New cards
glycogenesis
Conversion of glucose to glycogen (storage form)
Instigated by insulin
Instigated by insulin
20
New cards
Glycogenolysis
Break down of glycogen (storage form) to glucose
Instigated by glucagon
Instigated by glucagon
21
New cards
Lipolysis
Breakdown of cholesterol and triglycerides to form free fatty acids
Instigated by glucagon and epinephrine
Forms 3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol
Transported via blood stream with cholesterol as lipoprotein
Other cells take up FAs, liver uses glycerol
Instigated by glucagon and epinephrine
Forms 3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol
Transported via blood stream with cholesterol as lipoprotein
Other cells take up FAs, liver uses glycerol
22
New cards
Fatty acid synthesis
Synthesis of fatty acids from acetyl CoA
23
New cards
Gluconeogenesis
Formation of glucose-6-phosphate from noncarbohydrate sources
Instigated by glucagon
Instigated by glucagon
24
New cards
Anaerobic glycolysis
Metabolism of a glucose molecule to pyruvate or lactate for production of energy
25
New cards
function of glutathione and importance in RBC and hepatocyte
RBCs use glucose to run salt pumps
-Keeps glutathione in reduced state? (intact glucose-6-phosphate pathway)
Important antioxidant
Can be depleted in G6PD deficiency, acetaminophen overdose
Detoxifies both xenobiotic and endogenous compounds
Facilitates excretion of toxins from cells, body
Directly neutralizes compounds
Scavenges oxidants (superoxide anion, hydroxyl radical, nitric oxide, carbon radicals)
Recycles vitamin C and E
-Keeps glutathione in reduced state? (intact glucose-6-phosphate pathway)
Important antioxidant
Can be depleted in G6PD deficiency, acetaminophen overdose
Detoxifies both xenobiotic and endogenous compounds
Facilitates excretion of toxins from cells, body
Directly neutralizes compounds
Scavenges oxidants (superoxide anion, hydroxyl radical, nitric oxide, carbon radicals)
Recycles vitamin C and E
26
New cards
Differentiate markers of hepatobiliary disease with those sensitive to liver cell injury
AST/ALT = liver cell injury
-Leak out of damaged cells
ALP, gamma-GT: hepatobiliary function
-Induced by biliary stasis or obstruction/hepatobiliary disease
-Leak out of damaged cells
ALP, gamma-GT: hepatobiliary function
-Induced by biliary stasis or obstruction/hepatobiliary disease
27
New cards
Which aminotransferase is used most often to monitor toxic effects of medications?
ALT
More liver specific
More liver specific
28
New cards
End result of severe urea cycle defects
Build-up of ammonia
29
New cards
Function of UDP-glycosyl transferases
Transport (derivative of glucose) glucuronic acid
Catalyze covalent addition of sugars to lipophilic molecules
Eliminates exogenous chemicals and by-products of endogenous metabolism
Controls levels and distribution of endogenous signaling molecules
Liver attaches polar and charged glucose (glucuronates) to facilitate excretion through bile
Catalyze covalent addition of sugars to lipophilic molecules
Eliminates exogenous chemicals and by-products of endogenous metabolism
Controls levels and distribution of endogenous signaling molecules
Liver attaches polar and charged glucose (glucuronates) to facilitate excretion through bile
30
New cards
Gibert
Defect in bilirubin uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase (bilirubin UGT)
Mild
Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia is induced by stress/illness
Mild
Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia is induced by stress/illness
31
New cards
Crigler-Najjar syndrome
Rare
Autosomal recessive disorder
Loss of UGT1A1
Severe unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia and kernicterus
Autosomal recessive disorder
Loss of UGT1A1
Severe unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia and kernicterus
32
New cards
Identify the type of large complexes cleared from blood by the liver
Haptoglobin
-scavenges free heme from blood
Removes coagulation-inhibitor complexes, hemopexin-heme, haptoglobin-globin complexes
-scavenges free heme from blood
Removes coagulation-inhibitor complexes, hemopexin-heme, haptoglobin-globin complexes
33
New cards
Identify conditions or disorders other than MI/ACS which result in elevations in plasma Troponins
Renal failure
Trauma
CHF
Aortic valve disease
Pulmonary embolism
Renal insufficiency
Pneumonia
Septic shock
Trauma
CHF
Aortic valve disease
Pulmonary embolism
Renal insufficiency
Pneumonia
Septic shock
34
New cards
Chylomicrons
Transports dietary triglycerides
35
New cards
Chylomicron remnant
Remnant of chylomicron after delivery of triglyceride to adipose tissue
Taken up by liver
Taken up by liver
36
New cards
VLDL
Transports endogenous triglyceride to adipose
37
New cards
IDL
Intermediate density lipoprotein
Remnant of VLDL after delivery of triglycerides
Taken up by liver
Remnant of VLDL after delivery of triglycerides
Taken up by liver
38
New cards
LDL
Transports cholesterol
Size is clinically significant
Receptor-mediated uptake in liver and adipose (LDL-R)
Size is clinically significant
Receptor-mediated uptake in liver and adipose (LDL-R)
39
New cards
HDL
Important in reverse cholesterol transport
40
New cards
Lipoprotein lipase
“Digests” triglycerides transported to adipose
enzyme
enzyme
41
New cards
LCAT
Enzyme
Transports cholesterol out of blood and tissues via cholesterol esterification
Uses phosphatidylcholine
Transports cholesterol out of blood and tissues via cholesterol esterification
Uses phosphatidylcholine
42
New cards
ACAT
Enzyme
Uses acyl-CoA
Catalyzes formation of cholesteryl esters from cholesterol
Uses acyl-CoA
Catalyzes formation of cholesteryl esters from cholesterol
43
New cards
Apo B-100
Atherogenic
Structural protein for VLDL and LDL
Ligand for binding to LDL receptor
Mainly on VLDL, IDL, LDL
Structural protein for VLDL and LDL
Ligand for binding to LDL receptor
Mainly on VLDL, IDL, LDL
44
New cards
Apo A-IV
Mainly on HDL, chylomicrons
Activator of LPL and LCAT
Activator of LPL and LCAT
45
New cards
Apo C-II
Mainly on chylomicrons, VLDL
Essential cofactor for LPL
Essential cofactor for LPL
46
New cards
Apo a
Structural protein for Lp(a)
Inhibitor fo plasminogen activation
Increases risk for heart disease and stroke
Similar to LDL
-Has aspoB and aspo(a) attached to surface
-Contains oxidized phospholipids
Inhibitor fo plasminogen activation
Increases risk for heart disease and stroke
Similar to LDL
-Has aspoB and aspo(a) attached to surface
-Contains oxidized phospholipids
47
New cards
Clinical significance of increased circulating Lp(a)
Increased risk of heart disease and stroke
Genetic predisposition
Genetic predisposition
48
New cards
Small dense LDL
Associated with raised triglycerides and decreased HDL-c levels
Adiposity and diabetes
Genetic predisposition
Adiposity and diabetes
Genetic predisposition
49
New cards
Oxidized LDL
atherosclerosis
50
New cards
mutated LDL-R
Coronary artery disease
51
New cards
Table 6 from AACE, match LDL goals to risk category
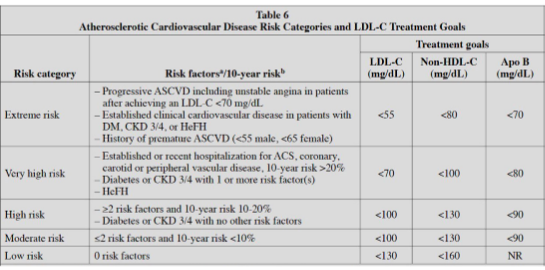
52
New cards
Familial hypercholerolemia
Changes in LDLR gene
Results in increased LDL
Caused by mutations in APOB, LDLRAP1, or PCSK9 gene
LDLR is unable to remove cholesterol from blood
Results in increased LDL
Caused by mutations in APOB, LDLRAP1, or PCSK9 gene
LDLR is unable to remove cholesterol from blood
53
New cards
Abetalipoproteinemia
Very low LDL and VLDL
Cause by genetic variants in MTTP gene; autosomal recessive
-Makes microsomal triglyceride transfer protein
-Produces beta-lipoproteins (carry dietary fats and cholesterol)
Cause by genetic variants in MTTP gene; autosomal recessive
-Makes microsomal triglyceride transfer protein
-Produces beta-lipoproteins (carry dietary fats and cholesterol)
54
New cards
Friedewald formula
LDLC = (Total Cholesterol) − (HDLC) − (TGs/5)
TGs/5 = VLDL
TGs/5 = VLDL
55
New cards
Identify conditions that invalidate the use and calculation of the Friedewald formula
Triglycerides >400,
56
New cards
Frederickson phenotypes I
Type I: impaired chylomicrons
57
New cards
Frederickson phenotypes IIa
Type IIa: Receptor defects in CSK9 protein
58
New cards
Frederickson phenotypes IIb
Type IIb: Impaired clearance of VLDL
59
New cards
Recognize technique to routine measurement of HDL
Precipitation
-Add precipitant
-All non-HDLs precipitate
-Centrifuge sample
-Measure HDL in supernatant
colorimetry
-Add precipitant
-All non-HDLs precipitate
-Centrifuge sample
-Measure HDL in supernatant
colorimetry
60
New cards
Recognize two systems that utilize receptor mediated endocytosis as a vehicle to deliver their goods to the inside of target cells
LDL
Cholesterol
Cholesterol
61
New cards
PCSK9
Dismantles LDLR
62
New cards
Evolocumab (Repatha)
Inhibits PCSK9
LDLR not broken down; cholesterol/LDL taken into cells and plasma levels lowered
Monoclonal antibody against PCSK9
LDLR not broken down; cholesterol/LDL taken into cells and plasma levels lowered
Monoclonal antibody against PCSK9
63
New cards
Statins
Competitive inhibitors of HMGCoA reductase
Starves cells of cholesterol; increases expression of LDLR
Starves cells of cholesterol; increases expression of LDLR
64
New cards
Vitamin C
Keeps iron in reduced state
Increases iron absorption
Deficiency
-Low iron
-scurvy
Excess
-Iron overload
Increases iron absorption
Deficiency
-Low iron
-scurvy
Excess
-Iron overload
65
New cards
ethanol
Increases iron absorption
66
New cards
Hemolytic anemia
Increases absorption
67
New cards
Phytate (vegetable) intake
Decreases absorption
68
New cards
Elevated inflammatory cytokines
Decreases absorption
69
New cards
Elevated inflammatory cytokines
Decreases absorption
70
New cards
Anemia of chronic inflammation
Decreases absorption
71
New cards
Anemia of chronic disease
Decreases absorption
72
New cards
Hereditary hemochromatosis
Increased absorption
73
New cards
Transferrin
Transports iron
Chelates iron to be rendered soluble
Prevent formation of reactive oxygen species
Chelates iron to be rendered soluble
Prevent formation of reactive oxygen species
74
New cards
Ferritin
Increases with hereditary hemochromatosis
Stores iron inside cells
Stores iron inside cells
75
New cards
Transferrin receptor 1
Transfers iron from circulation (transferrin) into cells
76
New cards
Transferrin receptor
Senses iron status
On hepatocytes
On hepatocytes
77
New cards
Dcytb
Duodenal ferric reductase
Reduces iron from 3+ to 2+ for absorption
Reduces iron from 3+ to 2+ for absorption
78
New cards
DMT-1
Divalent metal transporter-1
Absorbs Fe2+
Absorbs Fe2+
79
New cards
Hepcidin
Liver hormone
Regulates iron absorption and mobilization
Increased hepcidin = decreased iron
Regulates iron absorption and mobilization
Increased hepcidin = decreased iron
80
New cards
Hephaestin
Transmembrane copper-dependent ferroxidase
Effective iron transport from intestinal cells to circulation
Dependent on hepcidin levels
Effective iron transport from intestinal cells to circulation
Dependent on hepcidin levels
81
New cards
Ceruloplasmin
With hephaestin: oxidizes and binds ferric iron to transferrin
82
New cards
Ferroportin
Transports iron across the membrane from cell to circulation
Bound by hepcidin (which decreases iron absorption)
Bound by hepcidin (which decreases iron absorption)
83
New cards
Hemojuvelin
Controls levels of hepcidin
84
New cards
HFE
Controls levels of hepcidin
Mutation causes hereditary hemochromatosis
Mutation causes hereditary hemochromatosis
85
New cards
Identify function of lactoferrin in neutrophils
Keeps tight hold on iron to prevent parasites/bacteria from getting ahold of it
86
New cards
Calculate transferrin saturation given appropriate variables
Serum iron/TIBC x 100
Example:
Serum iron = 100 micrograms/L
TIBC = 300 micrograms/L
100/300 * 100 = 33% transferrin saturation
Example:
Serum iron = 100 micrograms/L
TIBC = 300 micrograms/L
100/300 * 100 = 33% transferrin saturation
87
New cards
interpret transferrin saturation
70-100% saturation = iron overload (hemochromatosis)
10% saturation = iron deficiency
35% = normal
10% saturation = iron deficiency
35% = normal
88
New cards
Both should agree, differences in methodology
TIBC
-Radiated iron is added to a sample
-The more radiated iron is attached to transferrin, the more open spaces there are on transferrin
-Excess iron is removed
-Iron is dissociated from transferrin
-Measurement of iron is indication of transferrin levels
-More iron after dissociation = more transferrin
Immunochemical
-Anti-transferrin antibody attaches to transferrin
TIBC
-Radiated iron is added to a sample
-The more radiated iron is attached to transferrin, the more open spaces there are on transferrin
-Excess iron is removed
-Iron is dissociated from transferrin
-Measurement of iron is indication of transferrin levels
-More iron after dissociation = more transferrin
Immunochemical
-Anti-transferrin antibody attaches to transferrin
89
New cards
Iron panel
TIBC
Ferritin
Transferrin
Hemoglobin
Ferritin
Transferrin
Hemoglobin
90
New cards
ACD
TIBC is low
Stores are high
Stores are high
91
New cards
IDA
TIBC is high
Stores are low
Stores are low
92
New cards
Iron overload
TIBC low or normal
Iron high
Ferritin high
Iron high
Ferritin high
93
New cards
Hemachromatosis
TIBC high
Ferritin high
Serum iron high
Ferritin high
Serum iron high
94
New cards
Ceruloplasmin
In plasma
Catalyze oxidation and binding of ferric iron to transferrin
Catalyze oxidation and binding of ferric iron to transferrin
95
New cards
Hephaestin
Basolateral membrane of RBCs
Catalyze oxidation and binding of ferric iron to transferrin
Catalyze oxidation and binding of ferric iron to transferrin
96
New cards
Identify what is meant by a negative acute phase reactant
Quantity goes down in inflammation
Example: ferritin, transferrin
Example: ferritin, transferrin
97
New cards
Identify the earliest and most sensitive marker of iron deficiency
Ferritin
-Storage form of iron
-Use all storage when absorption of iron is low
-Low ferritin = early sign of iron deficiency
-Storage form of iron
-Use all storage when absorption of iron is low
-Low ferritin = early sign of iron deficiency
98
New cards
Identify the earliest and most sensitive marker of iron overload
Ferritin increased
99
New cards
Hepcidin
Regulates ferroportin
High hepcidin turns off ferroportin
Keeps iron inside of cells
Potentiates excretion of iron; soughs enterocytes into feces
High hepcidin turns off ferroportin
Keeps iron inside of cells
Potentiates excretion of iron; soughs enterocytes into feces
100
New cards
hepcidin in ACD/ACI? Hereditary Hemochromatosis?
Is positive acute phase reactant
-Increases in inflammation
-Keeps iron inside of cells to keep it away from parasites/bacteria
Increases in ACD
Decreases in hemochromatosis
-Increases in inflammation
-Keeps iron inside of cells to keep it away from parasites/bacteria
Increases in ACD
Decreases in hemochromatosis