Chapter 8: DNA Electrophoresis
8.1: Basic Principles
- DNA is a negatively charged molecule in an aqueous environment, with the phosphate groups of DNA nucleotides carrying negative charges.
- Electrical Potential: A measure of the work required to move a charged molecule in an electric field, is the force responsible for moving the charged macromolecules during electrophoresis.
- The electrophoretic mobility of macromolecules is primarily determined by their charge-to-mass ratios and their shapes.
8.2: Supporting Matrices
- Matrix: A physical support material used by most variants of electrophoresis.
- It can be used as a molecular sieve for the separation of DNA molecules, and it also reduces diffusion and convection during electrophoresis.
Agarose
- It is a linear polymer composed of alternating residues of D-galactose and L-galactose.
- A gelatinized agarose forms a three-dimensional sieve with pores from 50 to 200 nm in diameter.
- DNA fragments ranging from 50 to 20,000 base pairs in size are best resolved in agarose gels.
- The electrophoretic mobility of double-stranded DNA through agarose gel matrices is inversely proportional to the log10 of the size of DNA fragments ranging from 50 to 20,000 base pairs.
- The electrophoretic mobility of a linear DNA fragment is also inversely proportional to the concentration of agarose in the gel.
- A low concentration of agarose in a gel forms larger pores, allowing the separation of larger DNA fragments.
Polyacrylamide
- It is very effective for the separation of smaller fragments of DNA (5–500 base pairs).
- A single nucleotide difference in the length of a DNA fragment can be resolved with this type of gel.
- Polyacrylamide produces much smaller pore sizes than agarose gels and thus has a much higher resolving power than agarose gels for low-molecular-weight DNA molecules.
- A polyacrylamide gel matrix is formed by polymerization and cross-linking reactions.
- Polymerization Reaction
- Long linear chains of polyacrylamide are polymerized from acrylamide monomers.
- This polymerization reaction is initiated in the presence of free radicals that are generated from the reduction of ammonium persulfate (APS) by N,N,N′,N′— tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED).
- Cross-Linking Reaction
- Three-dimensionally cross-linked polyacrylamide chains can be formed with the use of cross-linking agents, such as N,N′— methylenebisacrylamide.
- The porosity of the resulting gel is determined by the lengths of these chains and the degree of cross-linking between them.
- Denaturing Polyacrylamide Electrophoresis
- Electrophoresis that is performed under the conditions of single-stranded DNA is called denaturing electrophoresis.
- Denatured DNA migrates through the gel as linear molecules at a rate independent of the base composition and sequence.
8.3: Apparatus and Forensic Applications
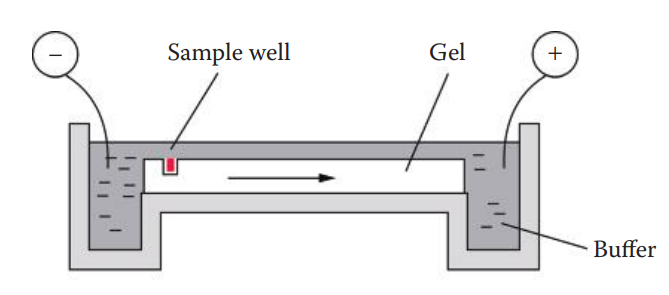
Slab Gel Electrophoresis
Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
One forensic application of agarose gel electrophoresis is restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis of VNTR loci.
An agarose gel is used to separate the DNA fragments by size ranging from 500 to 20,000 base pairs of commonly used VNTR loci for forensic testing.
This type of electrophoresis is done under non-denaturing conditions (double-stranded DNA).
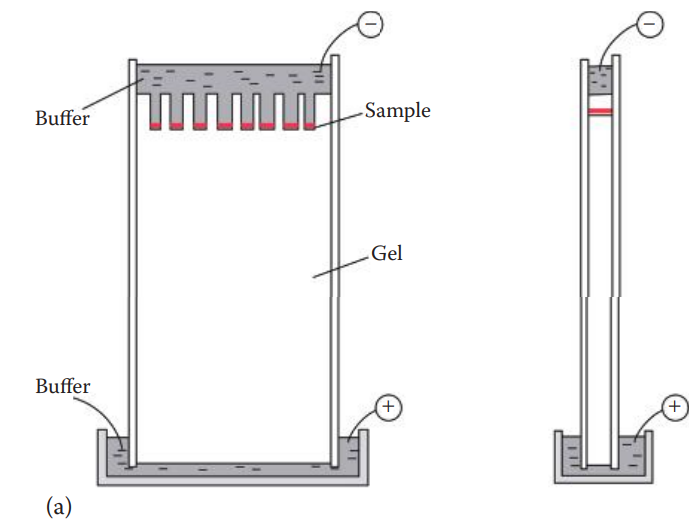
Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
- The forensic application of this apparatus is the separation of STR fragments and DNA sequencing reaction products of mtDNA.
- The sizes of DNA fragments that can be separated range from 100 to 500 base pairs—much smaller than what can be separated efficiently with agarose gels. Single-nucleotide resolution to distinguish similarly sized fragments can be
- achieved with this technique under denatured conditions with only single-stranded DNA.
- Polyacrylamide thin slab gels (0.75–1.5 mm) are usually used.
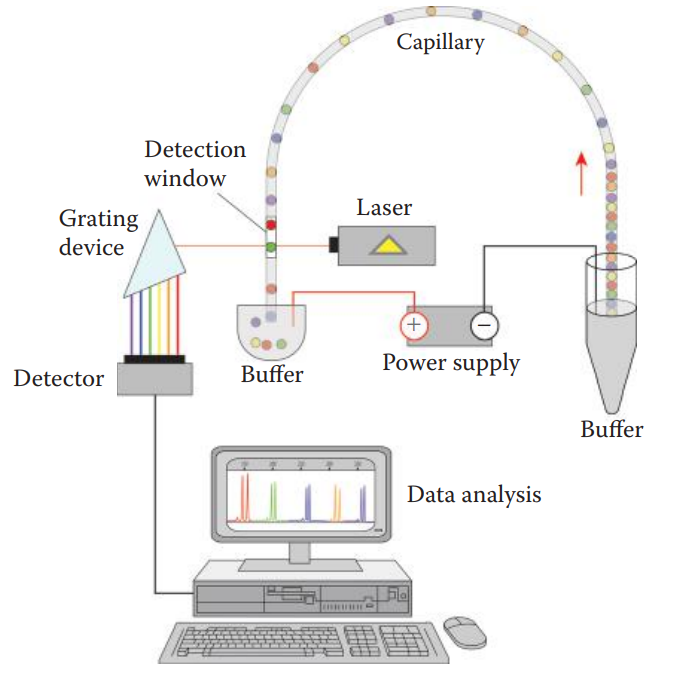
Capillary Electrophoresis
It can be utilized to separate charged macromolecules, such as DNA, RNA, polysaccharides, and proteins.
Capillary: A thin hollow tube made of fused silica.
- It contains a translucent detection window for the instrument to detect signals from the labeled DNA fragments during electrophoresis.
Linear poly-dimethyl acrylamide is used as the matrix.
Electrokinetic Mechanism: An injection based on the charge of molecules.
Microfluidic Devices
- Forensic DNA analysis includes the extraction of DNA from a sample, DNA quantification, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification, capillary electrophoresis, data collection, and genotyping.
- Microfluidic devices control the movement of samples and reagents in a small, geometrically constrained environment and carry out biochemical reactions and analysis.
- These devices are made using microfabrication technology. This technology fabricates miniature structures historically used for integrated circuit fabrication in semiconductor manufacturing.
- Microfluidic devices can be classified as modular and integrated devices.
Modular Microfluidic Devices
- Modular devices are separate devices for DNA extraction, quantitation, amplification, electrophoresis, and so on.
- It is flexible, allowing laboratories to choose the best device suited to the procedure for each step.
- Electrophoretic assay: It is carried out on a modular microfluidic chip format using the same basic principle of capillary electrophoresis.
- Single-use chip: Contains wells for samples, a sieving polymer matrix for electrophoresis, and size standards. The wells are connected through microchannels.
- Polymer matrix: Contains fluorescent dye molecules that intercalate with DNA in a sample, which can be detected by laser-induced fluorescence.
Integrated Microfluidic Devices
An integrated system is a fully automated process. It also reduces the risk of contamination from laboratory sources.
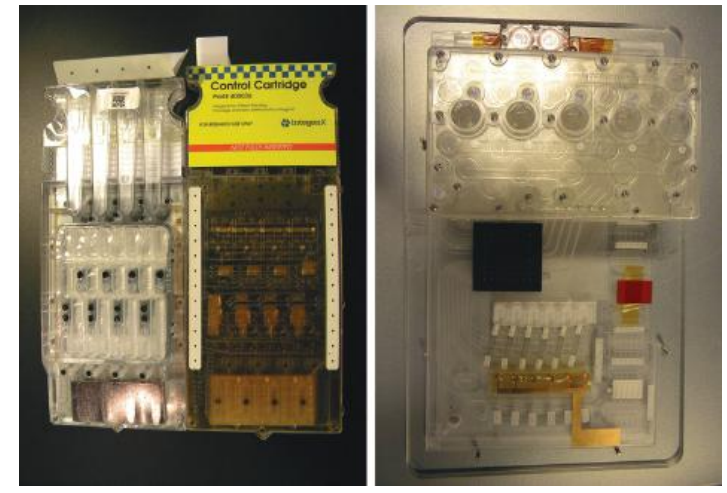
Full integration of all the constituent steps required for forensic STR DNA analysis has been achieved by a rapid DNA instrument.
- This instrument integrates various microfluidic devices including DNA extraction, PCR amplification, electrophoresis, detection, and genotyping steps into a single process on a cartridge.
Microquantitative PCR utilizes the Taqman real-time quantitative PCR technique. During amplification, multiplex PCR is accomplished using commercial STR kits.
The fluorescently labeled DNA fragments are detected based on laser-induced fluorescence.
Rapid DNA instruments: Are fully automated platforms that are designed to process a single-source sample such as a buccal swab to generate a DNA profile and database search in less than 2h.

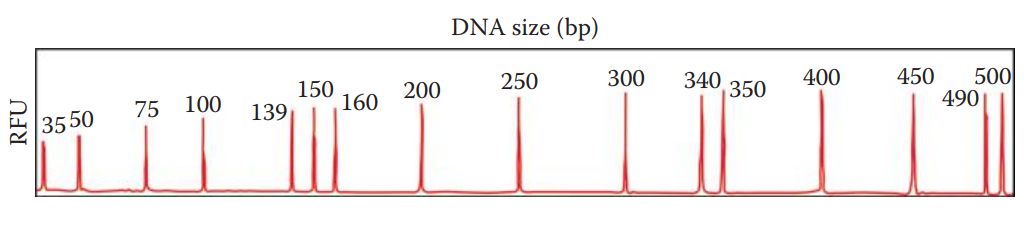
8.4: Estimation of DNA Size
Relative Mobility
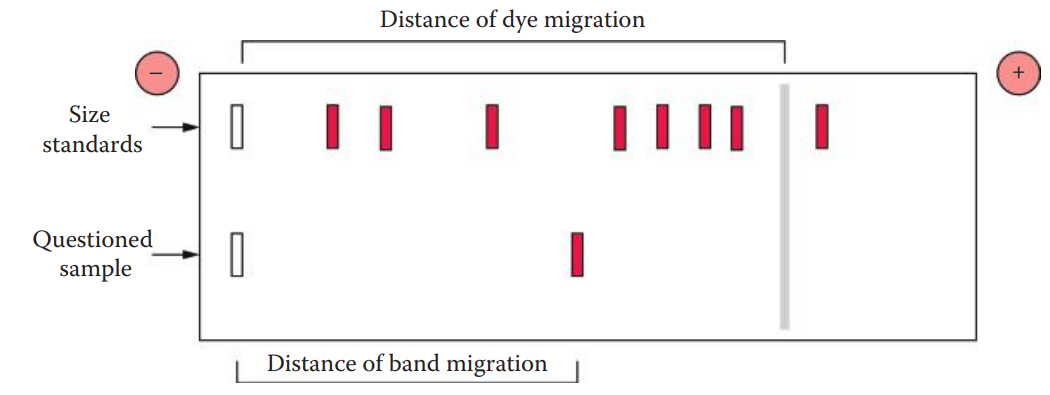
Relative mobility (Rf) of a DNA molecule during electrophoresis can be calculated as the distance of band migration divided by the distance of tracking dye migration.
DNA band migration: The distance from the sample origin to the center of the band. The tracking dye migration distance extends from the sample origin to the center of the dye band.
To estimate the size of the DNA, standards containing DNA of known size and questioned samples are run on the same gel at the same time. The standards can be used to estimate the size of an unknown DNA molecule.
Local Southern Method
Local Southern method: Used to generate standard curves for determining the sizes of DNA fragments.
The size of a DNA fragment is determined by an internal size standard that is a set of synthetic fragments with known molecular weight.
The standard is labeled with a different colored dye so that it can be spectrally distinguished from DNA fragments of unknown size.
The sample including the internal size standard is then mixed in with DNA samples and is analyzed by electrophoresis.
To determine the sizes of DNA fragments, a standard curve using the internal size standards must be established based on the reciprocal relationship between the electrophoretic mobility and the sizes of DNA fragments. This relationship is not exactly linear; instead, it appears to be sigmoidal.