AP Hug Unit 6
5.0(3)Studied by 85 people
Card Sorting
1/52
Earn XP
Last updated 4:15 PM on 12/5/24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
1
New cards
Site factors
Climate, land forms, availability of water, soil fertility, and other physical factors.
2
New cards
Situation factors
Connections between sites, the relative location often dictates the function of the city.
3
New cards
urbanization
A place that is shirting from rural land use to being more populated.
4
New cards
megacities
Metropolitan areas with populations of more than 10 million people
5
New cards
Metacities
Metropolitan areas with populations of more than **20 million people**
6
New cards
periphery
less developed
7
New cards
semi-periphery
kinda developed
8
New cards
suburbanization
The process of people moving, usually from cities, to residential areas on the outskirts of cities. (exact on quiz def)
9
New cards
urban sprawl
the expansion of cities and urban areas into surrounding rural or undeveloped land. Think of it as an example of urban decentralization.
10
New cards
urban decentralization
Act of spread from the center
11
New cards
edge city
Community located on the outskirts of a larger city with commercial centers, office space, retail complexes, and amenities typically found in an urban center
12
New cards
exurb
Community on the outside edge of traditional suburbs, “exurban.” Function like a suburb, but more rural and less connected to the central city core.
13
New cards
boomburb
Suburb that has grown rapidly into a large and sprawling city with more than 100,000 residents. Typically made up of planned communities that have began to merge together.
14
New cards
world city
Large cities that exert global economic, cultural, and political influence and make up a network of economic, social, and information flows.
15
New cards
urban hierarchy
hamlet, village, town, city, metropolis, and megalopolis
16
New cards
globalization
increasing connection of economic, cultural, and political characteristics across the world
17
New cards
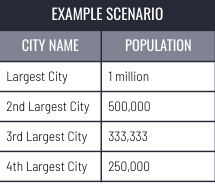
Rank-size rule
Model that illustrates the relationship between population distribution in cities that are interconnected in the urban hierarchy. Typically indicates somewhat even development.
2nd=1/2
3rd=1/3
2nd=1/2
3rd=1/3
18
New cards
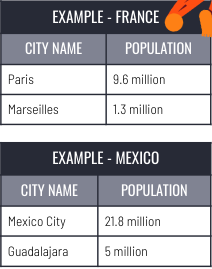
primate city
* Model that illustrates disproportionate population distribution within a state.
* One particular city is extremely large in terms of population size AND economic, cultural and political influence.
* Typically indicates relatively uneven development within a state.
* One particular city is extremely large in terms of population size AND economic, cultural and political influence.
* Typically indicates relatively uneven development within a state.
19
New cards
gravity modle
* Model that illustrates the spatial relationship/amount of interaction between locations of different sizes - flows of people, trade, traffic, communication, etc.
* Considers the distance between two locations and their relative sizes.
* Larger cities interact more often with other large cities, rather than small cities.
* Small cities are drawn to the influence and impact of large cities (gravity tordwwas those bigger cities)
\
\
* Considers the distance between two locations and their relative sizes.
* Larger cities interact more often with other large cities, rather than small cities.
* Small cities are drawn to the influence and impact of large cities (gravity tordwwas those bigger cities)
\
\
20
New cards
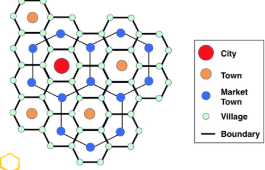
Christaller's central place theory
* Model that illustrates the hierarchical spatial __patterns/order__ of cities and settlements.
* Based on economic functions/consumer behavior - the “central place” is the large city that provides the most goods and services for the surrounding areas.
* Smaller settlements (towns, villages, hamlets) organize around the “central place.”
* Think about hexagons!!!
* try to get to the central spot. (she wrote def)
* URBAN HIERARCHY, TOWNS< VILLAGE
* Based on economic functions/consumer behavior - the “central place” is the large city that provides the most goods and services for the surrounding areas.
* Smaller settlements (towns, villages, hamlets) organize around the “central place.”
* Think about hexagons!!!
* try to get to the central spot. (she wrote def)
* URBAN HIERARCHY, TOWNS< VILLAGE
21
New cards
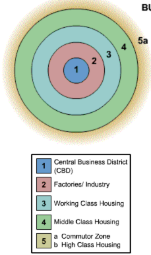
Burgess concentric-zone model
Based on the development of Chicago in the 1920s. Concentric rings are used to classify each type of land use pattern.
* Ring #1. Bid-Rent Theory -> The CBD is the location of major economic activity and the most expensive land.
* Ring #2: Zone of Transition. Factories and industry with a mix of low income apartments.
* Ring #3. Another ring of low income housing. High population density, poor living conditions.
* Rings #4 & 5.As distance from the CBD increases, the cost of land is less expensive -> Larger plots of land -> low population density -> single family homes.
* Ring #1. Bid-Rent Theory -> The CBD is the location of major economic activity and the most expensive land.
* Ring #2: Zone of Transition. Factories and industry with a mix of low income apartments.
* Ring #3. Another ring of low income housing. High population density, poor living conditions.
* Rings #4 & 5.As distance from the CBD increases, the cost of land is less expensive -> Larger plots of land -> low population density -> single family homes.
22
New cards
Hoyt sector model
Based on improving the Concentric Zone Model. Use of sectors/wedges to classify each type of land use pattern.
* Sectors develop along transportation routes.
* Low income housing develops surrounding industry and major transportation routes.
* Middle and high-income housing develops further from the city center and manufacturing so as not to experience heavy traffic, pollution, etc.
* Sectors develop along transportation routes.
* Low income housing develops surrounding industry and major transportation routes.
* Middle and high-income housing develops further from the city center and manufacturing so as not to experience heavy traffic, pollution, etc.
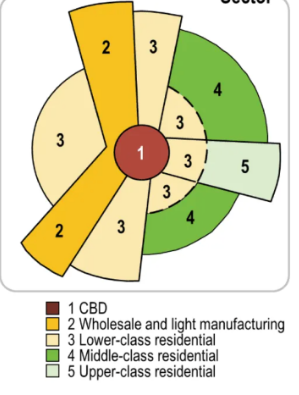
23
New cards
Harris and Ullman multiple nuclei model
Cities develop around multiple focal points and build outwards to create a functional region. Site and situational factors influence land-use patterns.
* CBD remains an important location, however there are other, smaller business districts in various locations.
* Manufacturing & Industry are located near transportation routes for easier shipping.
* Similar businesses locate near each other to take advantage of labor pools, suppliers and communication.
* Middle and high-income housing develops further from the city center and industry so as not to experience heavy traffic, pollution, etc.
* CBD remains an important location, however there are other, smaller business districts in various locations.
* Manufacturing & Industry are located near transportation routes for easier shipping.
* Similar businesses locate near each other to take advantage of labor pools, suppliers and communication.
* Middle and high-income housing develops further from the city center and industry so as not to experience heavy traffic, pollution, etc.
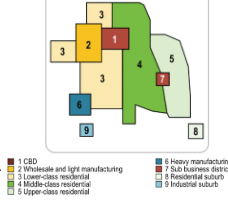
24
New cards
galactic city model
Most modern; developed in the 1980s. Focuses on the decentralization and suburbanization of urban environments.
* As suburbanization and the ownership of cars increased starting in the 1950s, urban areas developed differently than in the past.
Includes edge cities which are like mini-CBDs, which include shopping, entertainment, and offices and are typically located along transportation routes.
* As suburbanization and the ownership of cars increased starting in the 1950s, urban areas developed differently than in the past.
Includes edge cities which are like mini-CBDs, which include shopping, entertainment, and offices and are typically located along transportation routes.
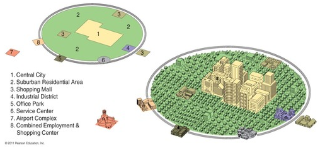
25
New cards
bid-rent theory
The __value__ of land is influenced by its __distance__ from the market/city center (CBD).
26
New cards
Latin American city model
* Shares basic structures of the Concentric Zone and Sector City Models.
* Characteristized by the “spine” that runs from the modernized CBD in the center, through wealthy housing and connects to a secondary urban center called the mall.
* Characteristized by the “spine” that runs from the modernized CBD in the center, through wealthy housing and connects to a secondary urban center called the mall.
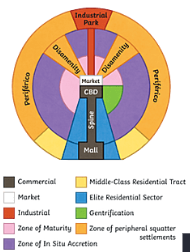
27
New cards
Southeast Asian city model
* Characteristized by a port zone, which was the center of commerce in colonial SE Asia - export oriented, so no CBD.
* History of Chinese immigrants throughout SE Asia - on the model, there is a secondary commercial zone for Chinese business called the Alien commercial zone.
* History of colonialism results in a Western commercial zone in which merchants from European countries are located.
Market gardening zone is distinctive due to the climate and agricultural land use in SE Asian locations.
* History of Chinese immigrants throughout SE Asia - on the model, there is a secondary commercial zone for Chinese business called the Alien commercial zone.
* History of colonialism results in a Western commercial zone in which merchants from European countries are located.
Market gardening zone is distinctive due to the climate and agricultural land use in SE Asian locations.
28
New cards
African city model
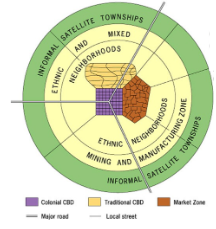
* Characteristized by 3 CBDs, and reflects the influence of colonialism throughout the continent.
* Traditional CBD: Small shops, narrow streets
* Colonial CBD: Big streets, straight, often in grid-like patterns, with government buildings with European architectural styles. \*Sense of place!
* Market Zone: Traditional open-air markets.
* Mostly outdated, but the 3 CBDs can still be seen on the \*cultural landscape today in some African countries.
* Traditional CBD: Small shops, narrow streets
* Colonial CBD: Big streets, straight, often in grid-like patterns, with government buildings with European architectural styles. \*Sense of place!
* Market Zone: Traditional open-air markets.
* Mostly outdated, but the 3 CBDs can still be seen on the \*cultural landscape today in some African countries.
29
New cards
infilling
Redevelopment of vacant land to improve the surrounding area. (it is controversial)
30
New cards
infrastructure
Refers to the basic support systems needed to keep a society and economy running smoothly.
31
New cards
sustainable design
Reducing the city’s impact on the environment. Ex: bike paths, less parking, high density places for easy access to everything you need.
32
New cards
mixed land use
Planned urban development that includes multiple uses such as retail, residential, educational, recreational and businesses. Only one type of development - residential, commercial, or industrial.
33
New cards
urban walkability
Walkability provides urban residents with safe, convenient and efficient ways to walk or bicycle to important places.
34
New cards
transportation-oriented development
Public transportation. Decreases air pollution, reduces traffic congestion and allows for valuable urban land to be used to create mixed-use developments instead of parking lots.
35
New cards
smart-growth policies
Types of sustainable urbanism design policies - are oftentimes used interchangeably. Increase the use of already existing urban structures, create walkable and liveable cities. (The step to create new urbanism) (not on quiz)
36
New cards
New Urbanism
Reducing urban sprawl and develop urban spaces that are sustainable, efficient, and environmentally conscious. (not on quiz)
37
New cards
De facto segregation
Low income families and people of color can no longer afford to live in the city and are forced to move out.
38
New cards
quantitative data
involves descriptive depictions or characteristics of a research topic - often based on people’s perceptions or opinions.
39
New cards
Quantitative Data
involves numbers and statistics - can be measured
40
New cards
Census Data
A survey for info about America
41
New cards
survey data
Quantitative data example. population or development statistics
42
New cards
field study
Qualitative data example. Out of the books.
43
New cards
field narrative
Description of the field work. Qualitative data.
44
New cards
housing discrimination
Segregating people in their land ownership
45
New cards
redlining
Housing discrimination maintained by banks - starting in the 1930s, refusal to grant home loans in certain areas because of the ethnic or racial composition
46
New cards
blockbusting
Housing discrimination maintained by real estate industry - white families were encouraged to rapidly sell when African-American families moved into neighborhoods.
47
New cards
housing affordability
Rising mortgage rates, expensive home prices, low inventory and inflation have made it more difficult for the average American family to afford a home.
48
New cards
environmental injustice
Communities of color and the poor are more likely to be exposed to environmental burdens such as air and water pollution
49
New cards
disamenity zone
Locations that are typically physically unsafe with dangerous terrain that are not connected to city services.
50
New cards
zone of abandonment
Locations that have been abandoned due to a lack of jobs, housing opportunities, decline in land values or falling demand.
51
New cards
squatter settlement
Residential areas that are situated on undesirable/ abandoned land that are built with found materials and not connected to city services. (not on test)
52
New cards
Local food movement
Using city-owned land or abandoned areas to plant community, urban gardens to provide fresh fruit and vegetables to people living in food deserts. (not on test)
53
New cards
urban renewal
Programming funded by federal government grants after WWII intended to redevelop and modernize blighted, abandoned and/or industrial urban areas (not on test)