CHEM EXAM #3
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
How can hydrocarbons be classified as, and how many bonds are in each type of hydrocarbon?
Saturated single bonds and unsaturated double bonds
What is a type of saturated single bonds?
Alkane
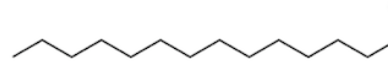
What are different types of unsaturated double bonds?
Alkene (2) and Alkyne (3)

Aldehyde

Ketone

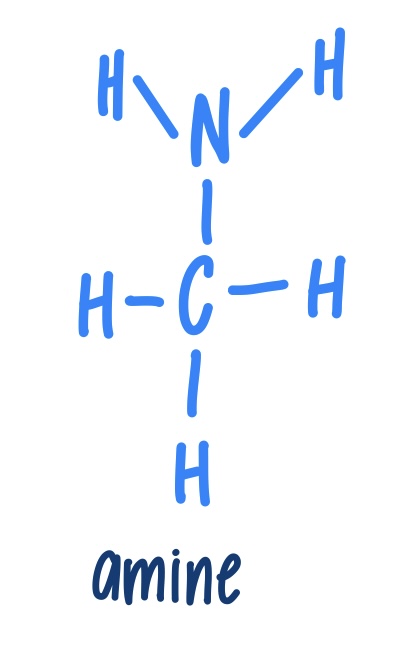
Amine
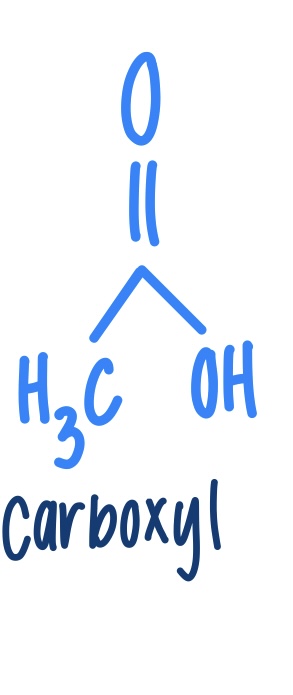
Carboxyl
In the synthesis of aspirin, what compound was used as a catalyst, and what is the role of a catalyst?
The compound that was used as a catalyst was sulfuric acid. The role fo a catalyst is to speed up the reaction
What is a limiting reactant?
It limits the amount of product formed
Aspirin + SA —> pills
What is an excess reagent?
Something that remains when the reaction is over/ stops and the laminating reactant is consumed
How can salicylic acid be detected?
Salicylic acid can be detected by iron (|||) chloride
What is the chemical reaction used to make soap referred to as?
The chemical reactions used to make soap is referred to as saponification
How are fatty acids categorized based on their carbon-carbon bonds?
Saturated fatty acids have single bonds, while unsaturated fatty acids have double bonds (D)
What distinguishes hard water from soft water in terms of its interaction with soap?
Hard water contains a higher concentration of magnesium and calcium ions, which form a precipitate with soap called “soap scum” (A)
How do detergents differ from soaps with respect to their interactions with water containing magnesium and calcium ions?
Detergents have a charged tail group and a non-polar head group (B)
What does a Baeyer’s test tell you?
It tests for unsaturated compounds or double bonds
It changes from pink to brown
Pink- single bonds are present
Brown- double bonds are present
What test is done to distinguish between an aldehyde and ketone? What is the color change?
Fehlging’s Test- testing for aldehydes
Turns from blue to red- (positive for aldehyde)
Remains blue- ketone (does not have an aldehyde)
How are acid and base groups tested? What is this test called?
pH test
Blue litmus paper: turns RED (acid)
Red litmus paper: turns BLUE (base)
What does iron (III) chloride do? What does it tell us?
Test for purity of acid
Yellow- NOT pure (no aspirin is present or it is not pure)
Blue- pure (aspirin is present and it is pure)
Explain what a catalyst is. What is the catalyst for aspirin?
Catalyst speeds up a reaction. The catalyst for aspirin is sulfuric acid.
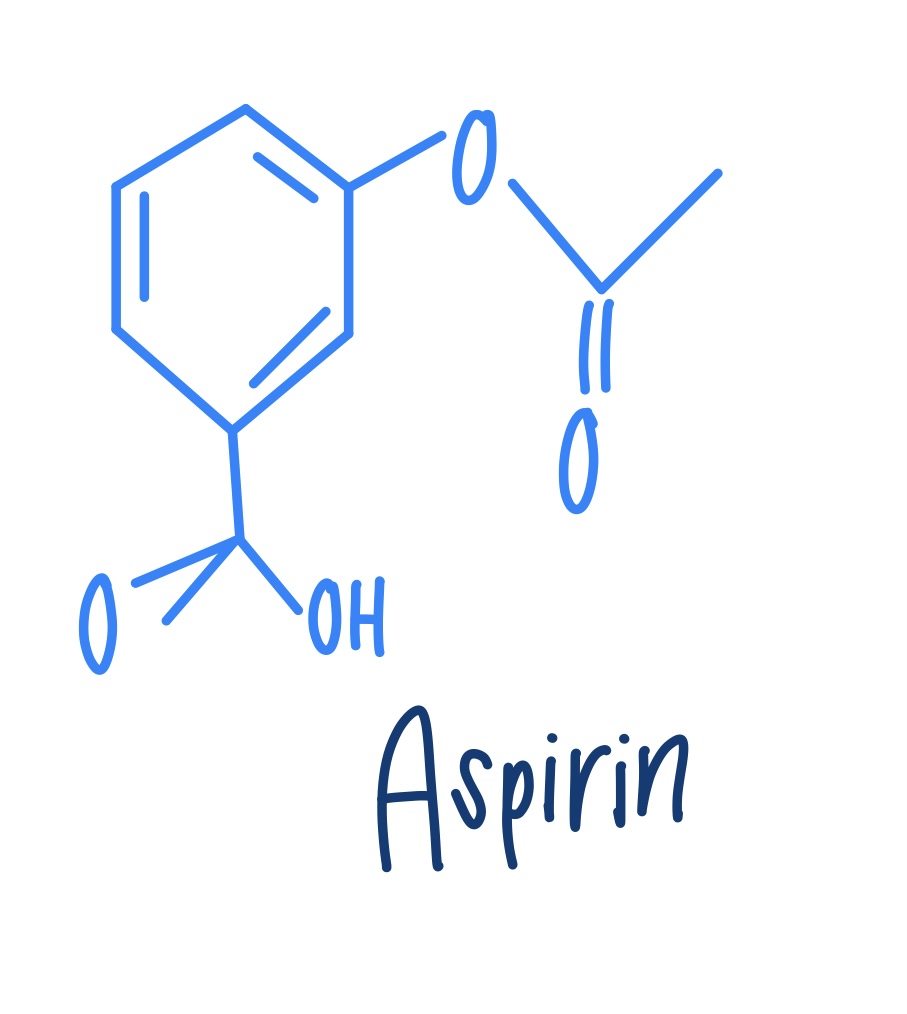
Write the names of the synthesis of aspirin
SA (salicylic acid) + acetic anhydride —> acetic acid + aspirin
Salicylic Acid (structure)
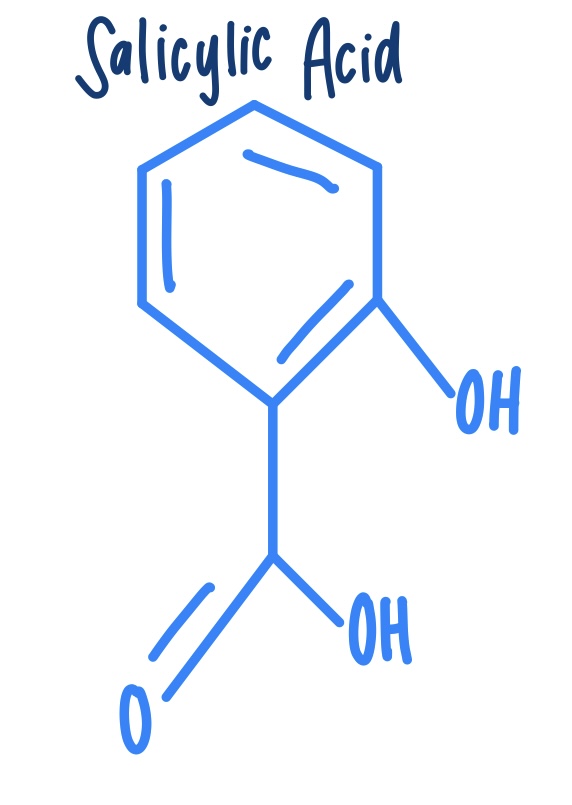
Aspirin (structure)
What is the difference between hard and soft water?
Hard:
does not lather with soap
leaves stains
clothes are dingy
hair is dull
only minerals
Soft:
lathers with soap
does not leave stains
clothes look fresh
hair is healthy
water has sodium
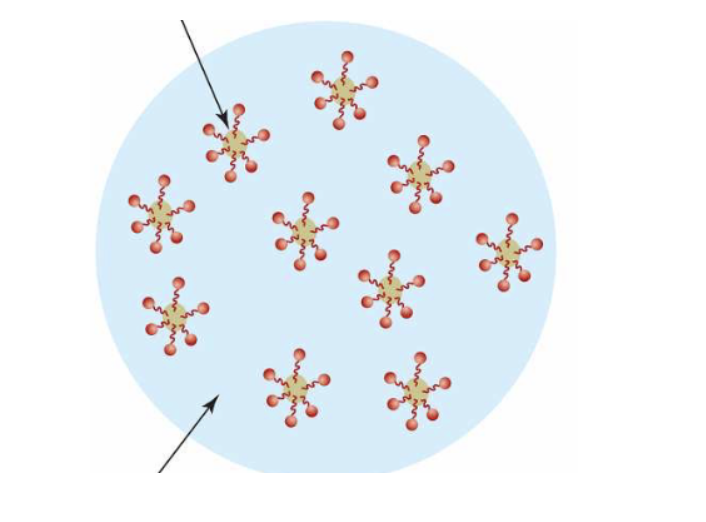
Label the two arrows shown in this picture:
Top: oil, hydrophobic, non-polar
Botton: water, hydrophilic, polar
What occurred during the aspirin lab
Materials used:
Filter flask
Buchner funnel
Ice water
We vacuum this
During this process of vacuuming, we are recrystallizing the aspirin
When we are recrystallizing, it helps get out purities, thus making the aspirin more pure
What chemicals are used to make soap?
Oils, NaOH, and fats
How did we create wintergreen? What are the steps to create wintergreen?
Combine SA and methanol together in a test tube
Heat up the test tube , making the catalyst H2SO4 during this process of heating up
Once the test tube has cooled down, smell it thus wintergreen has been created. It should smell minty and fresh
Formula for percentage of yield
actual/ theoretical x 100