Bio Chemistry Exam #2 Practice quizzes
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/118
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
1
New cards
loads DNA Pol delta at sites of single-strand breaks in DNA
PCNA
2
New cards
initiates correction of any chemical base damage within DNA (step \#1)
repair endonuclease
3
New cards
reacts with G to form N-2 ethylguanosine
acetaldehyde
4
New cards
specifically creates an abasic site at ROS-damaged deoxcytosine within DNA
uracil-DNA glycosylase
5
New cards
converts cytosine to uracil
Superoxide
6
New cards
activates the formation of 5,5,6,6-cyclobutane thymine dimers
260 nm light irradiation
7
New cards
metabolic product of smoke that modifies the 2-amino group of guanosine
Benzo(a)pyrene
8
New cards
strips out the damaged strand which in the case of uv damage activates melanogenesis ("tanning")
Helicase
9
New cards
required to convert uracil to thymine on dUMP
N5,N10-Methylene tetrahydrofolate
10
New cards
Double-stranded DNA is the product of
Replication
11
New cards
Once the polymerase is finished producing DNA, it will only return to the task of template guided synthesis when there is a requirement
Prep for cell division and repair
12
New cards
Fidelity is only ensured by amino acids polymerase active site only during what
Durning Synthesis
13
New cards
Fideltiy is ensured AFTER replication by
detection by repair related proteins
14
New cards
When deletion happens it can happen two ways
Removal of U's by Uracil/DNA glycosylase to create an abasic site
cleavage of a damaged strand by repair endonucleases
cleavage of a damaged strand by repair endonucleases
15
New cards
Fidelity requires what
Template strand DNA
16
New cards
What does DNA polymerase do after being recruited to site
Repair to replace the damaged strand
17
New cards
with high levels of base damage, repair endonucleases can produce double-strand breaks which hyperactivate
ATM kinase
18
New cards
When ATM kinase is hyperactive what happens
Apoptosis
19
New cards
The substrate it uses is a nucleotide triphosphate (NTP) which it positions to attach to the end of the growing RNA strand using one phosphate to form a
Phospodiester
20
New cards
What is the by product of growing RNA strand
Pyrophosphate
21
New cards
translated by ribosomes into an amino acid sequence- (PROTEIN
mRNA sequencing
22
New cards
A-OH
Amino-acylation
23
New cards
anticodon segment
I G C
24
New cards
patterns of "stem" stacking and loop folding
TRNA
25
New cards
stylized tertiary structure of tRNAs- backbone
Tube worm
26
New cards
decoding the mRNA relies on base-pairing
tRNA anticodons
27
New cards
hypoxanthine can base-pair to the other
Bases
28
New cards
3rd position in the code is called the
Wobble position
29
New cards
amino- acylation is preformed by
aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
30
New cards
Step 1
aa + ATP \=\> aminoacyl-AMP + PPi
31
New cards
Step 2
aminoacyl-AMP + tRNA \=\>aminoacyl-tRNA + AMP
32
New cards
this higher energy structure is called an
Acyl phosphate
33
New cards
Iniation
tRNA with mythiene start at AUG
34
New cards
iniation codon
AUG
35
New cards
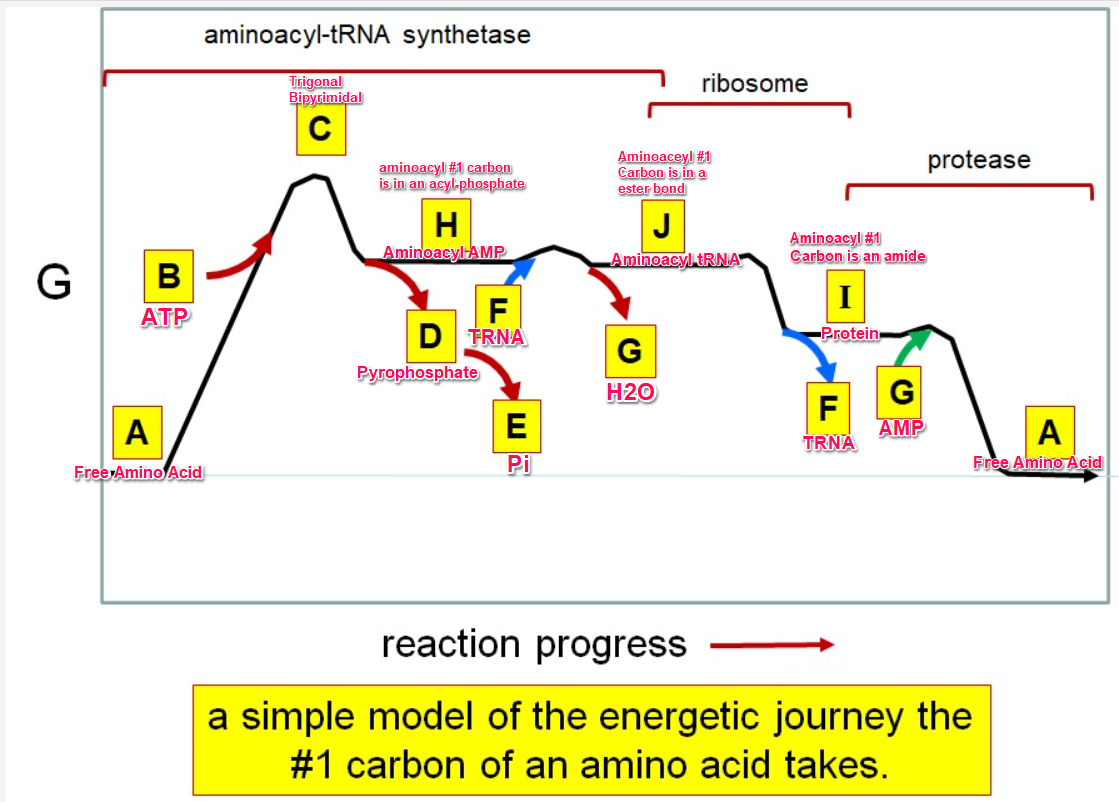
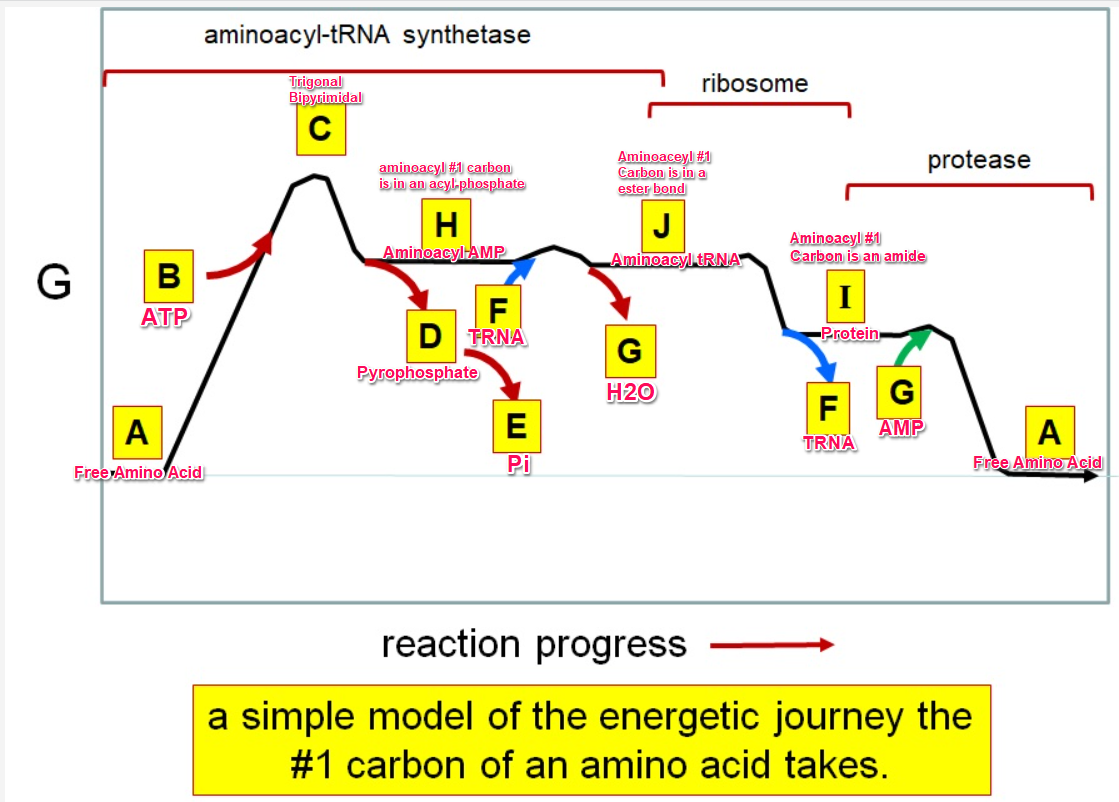
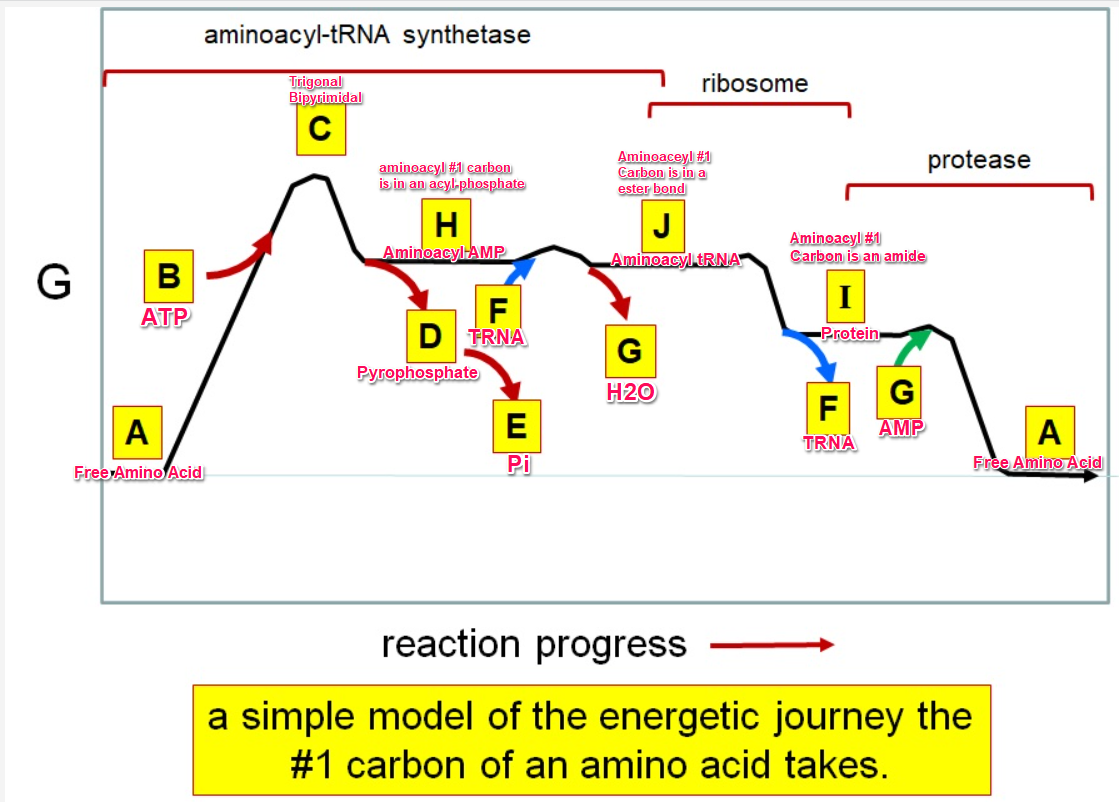
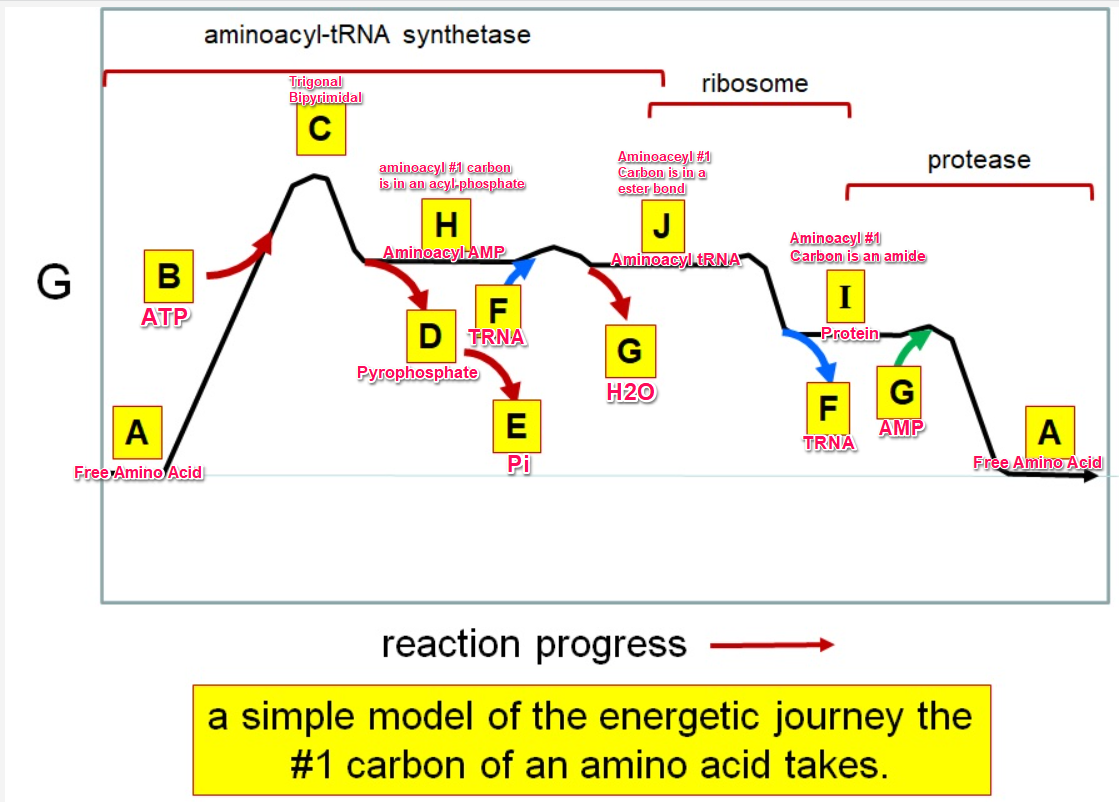
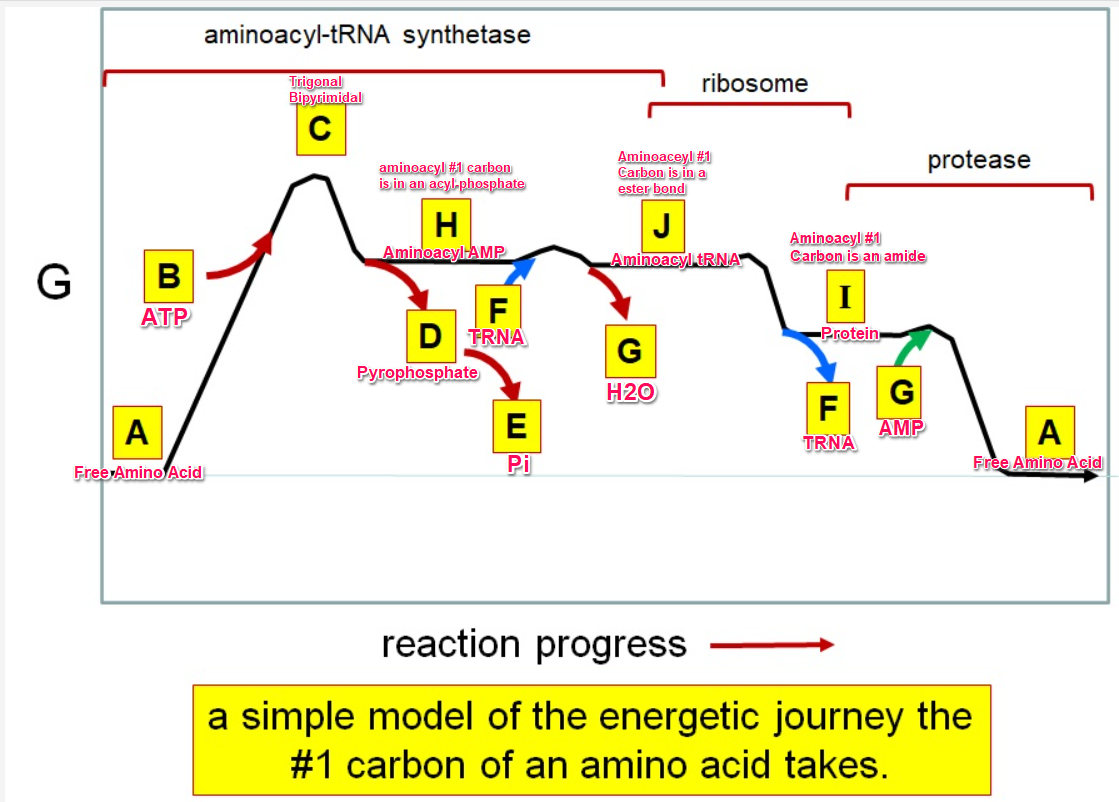
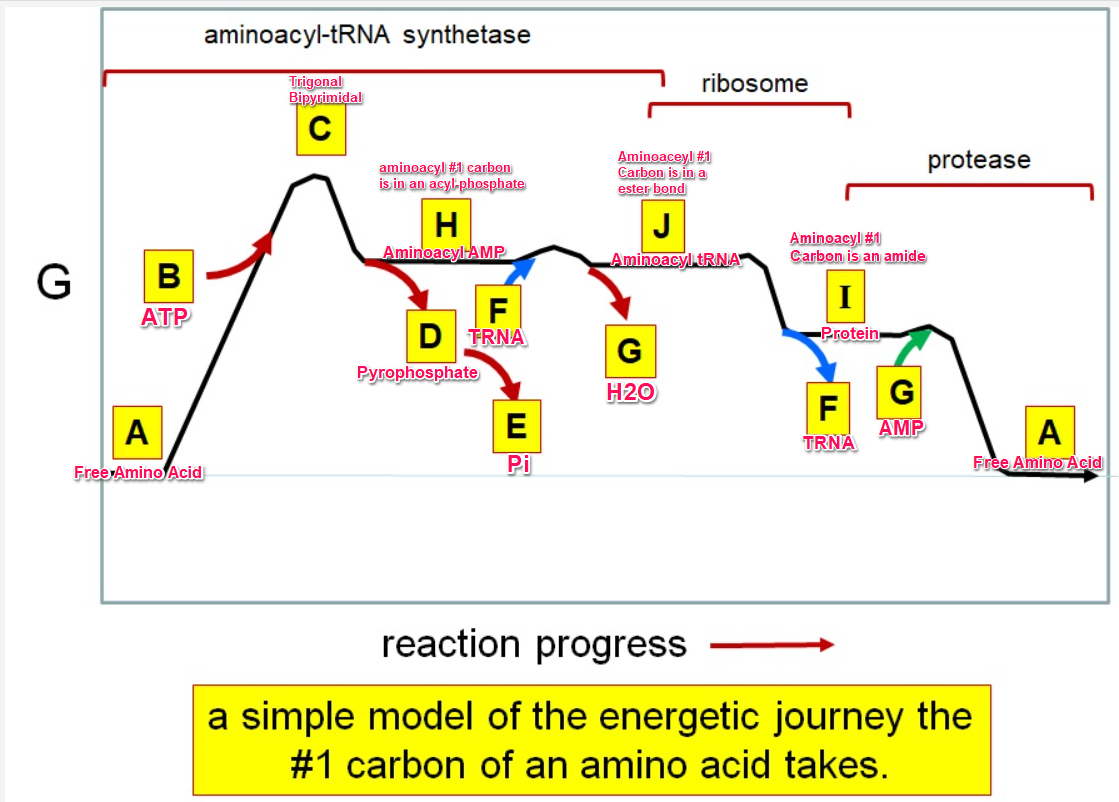
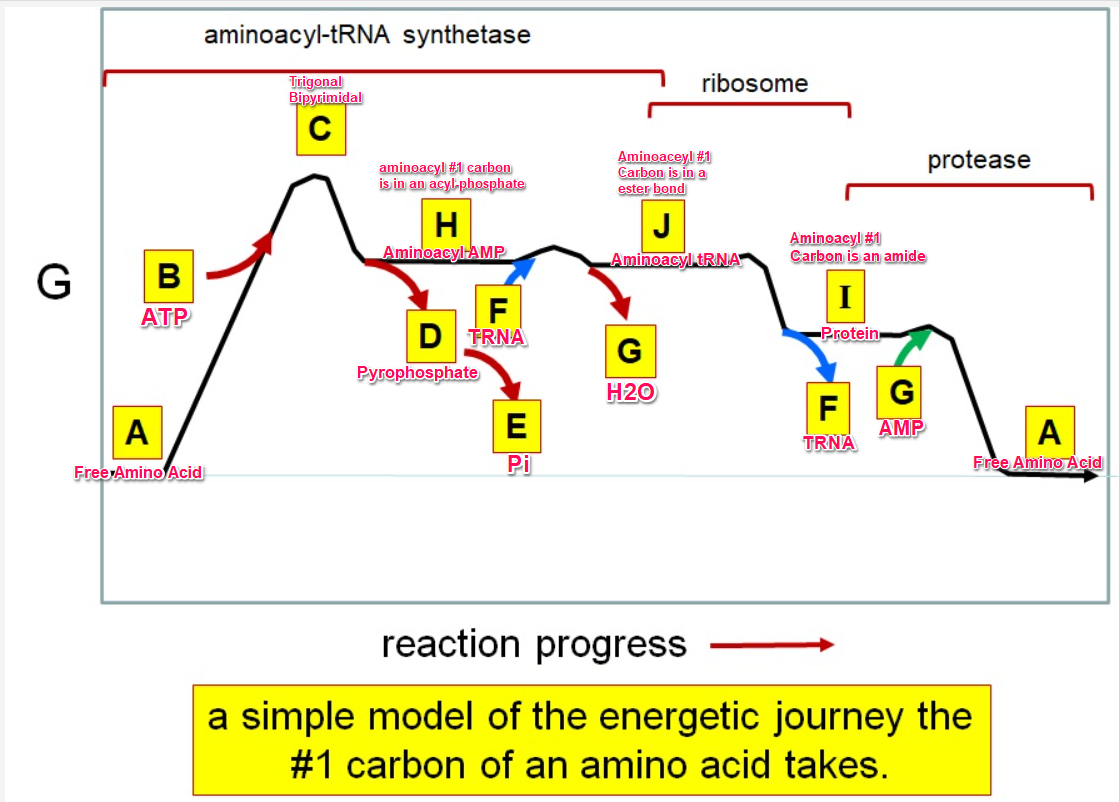
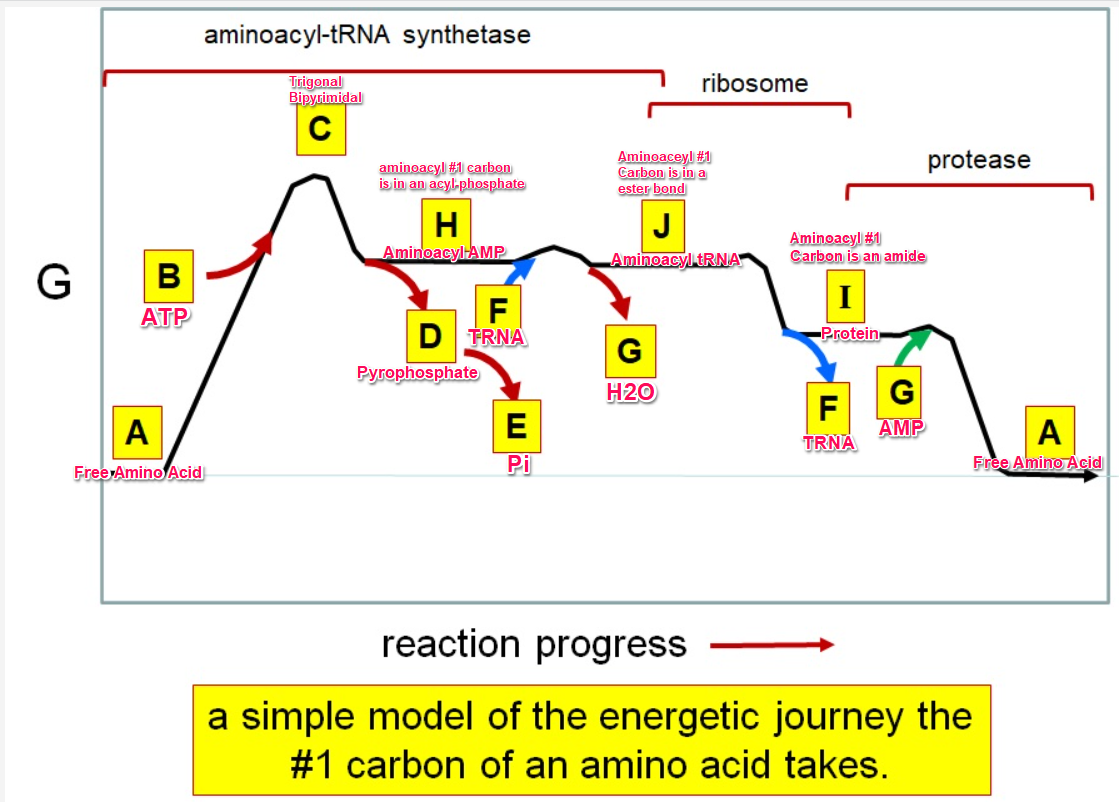
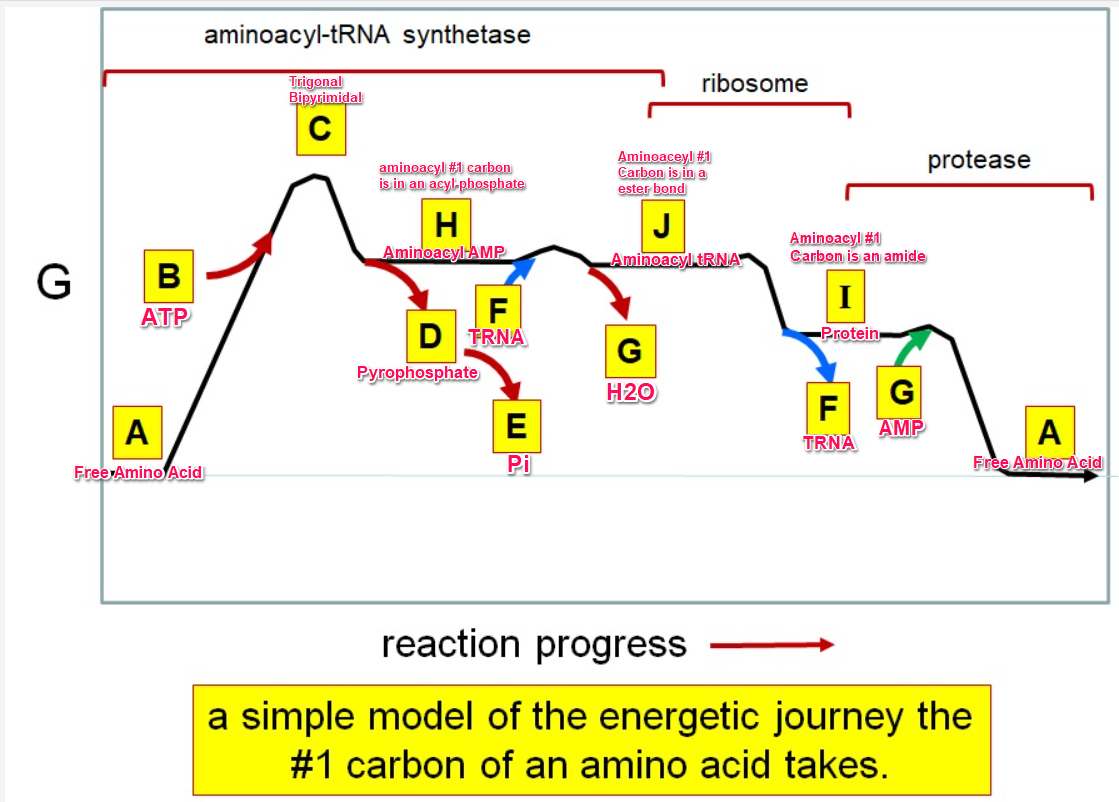
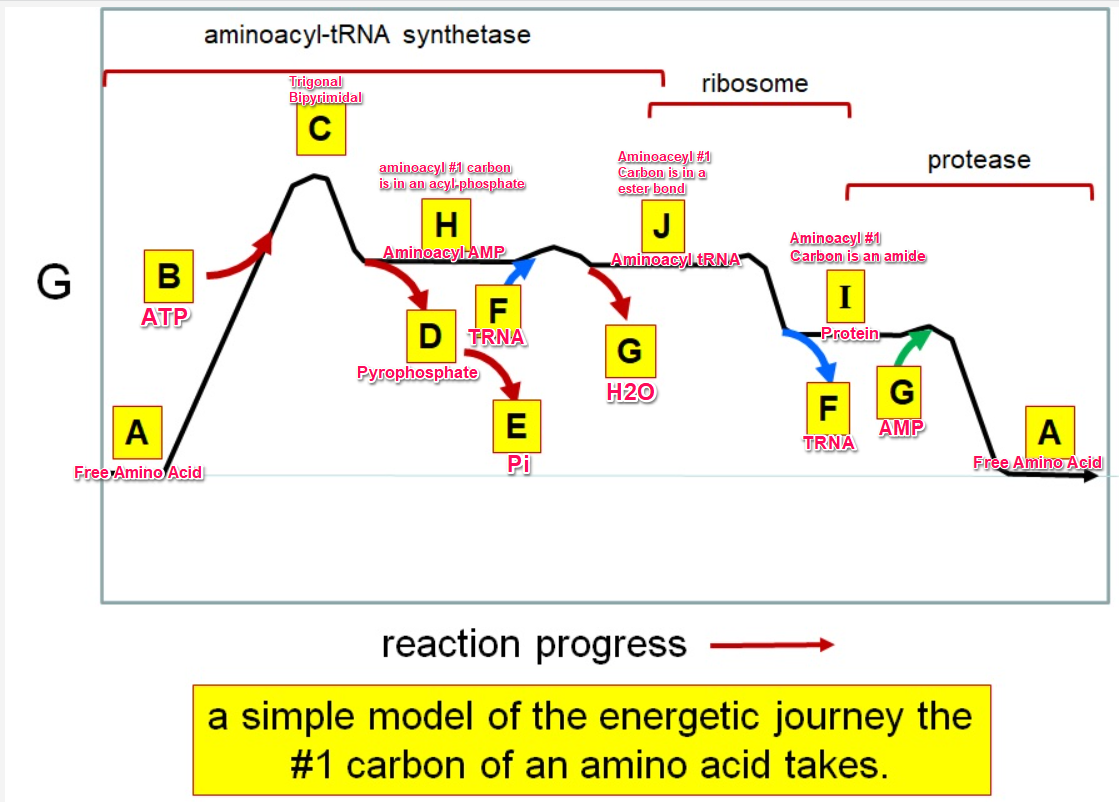
Which letter corresponds with pi
E
36
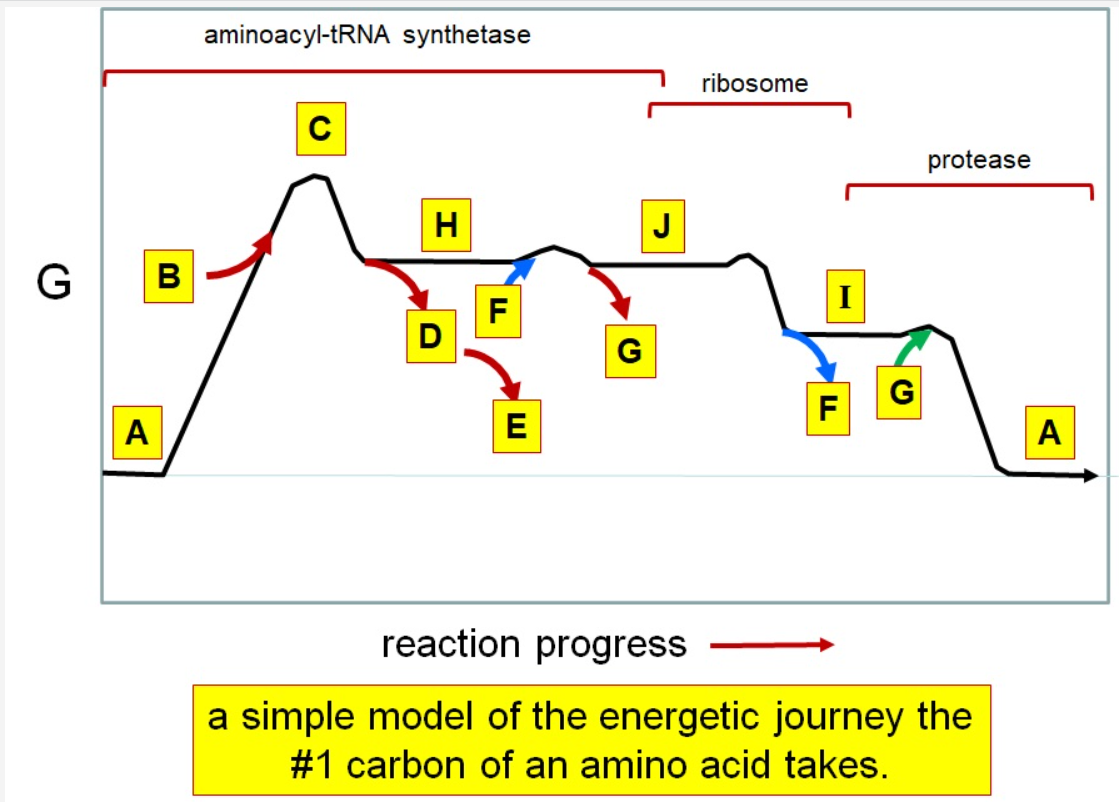
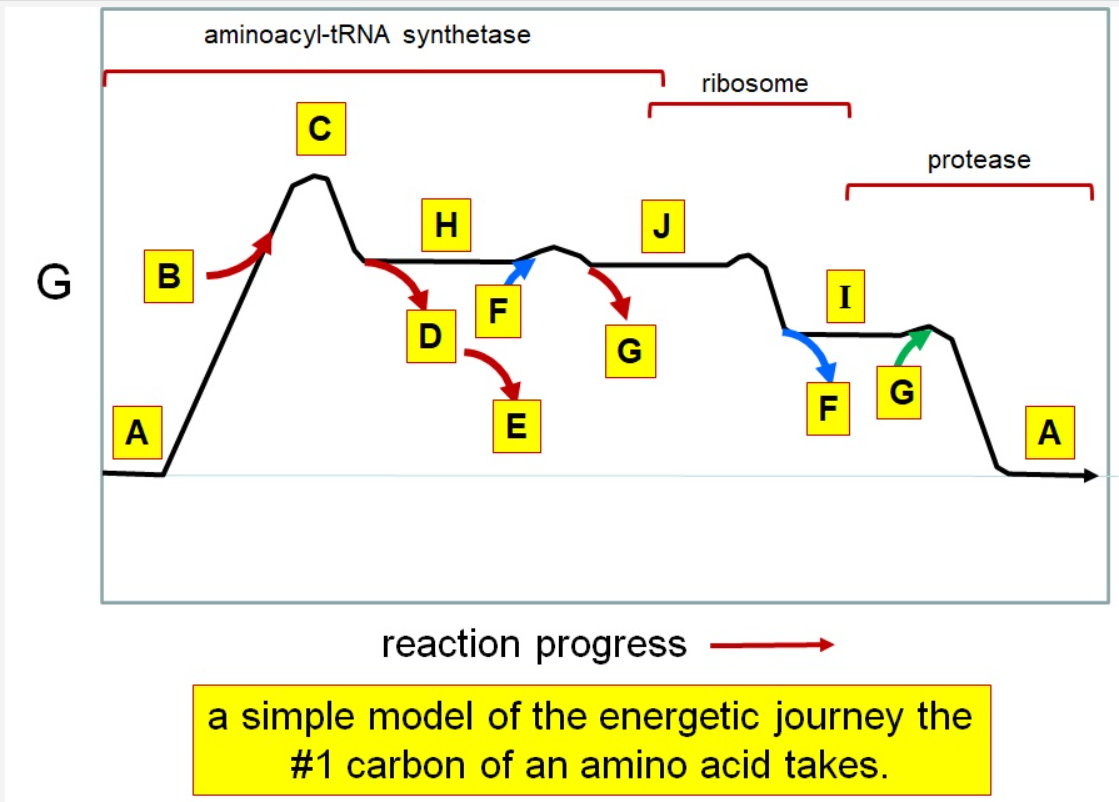
New cards
What letter corresponds aminoacyl tRNA
J
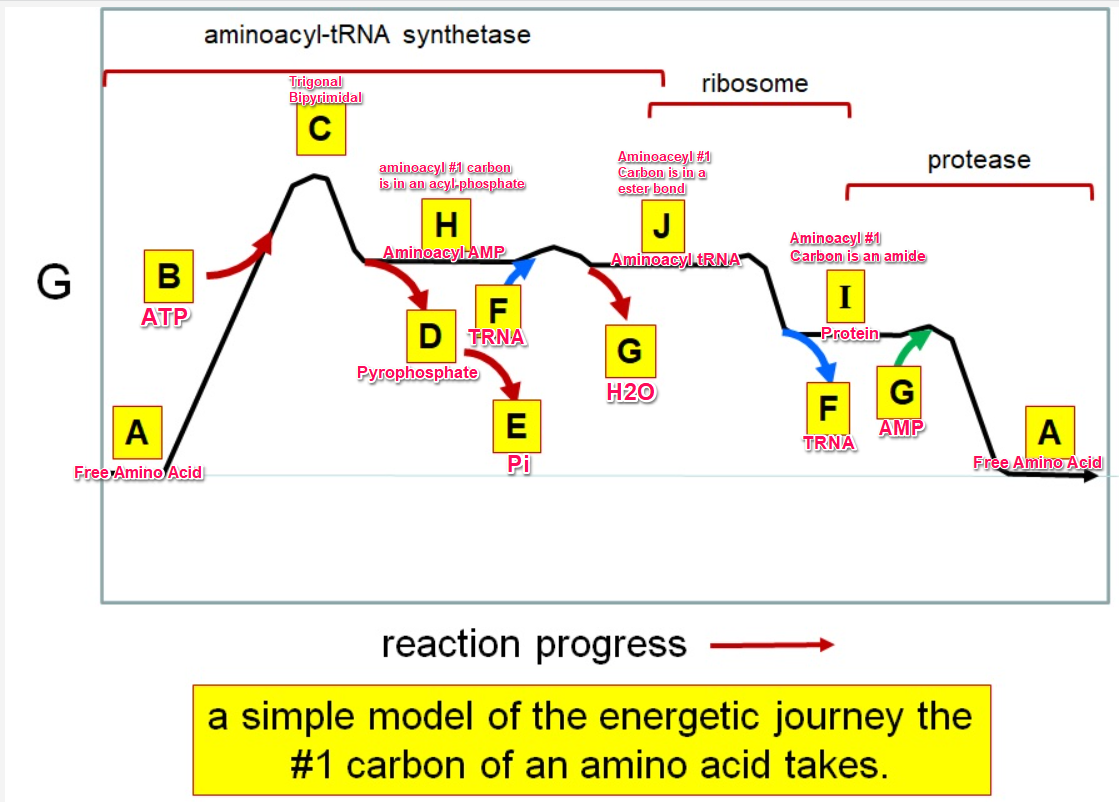
37
New cards
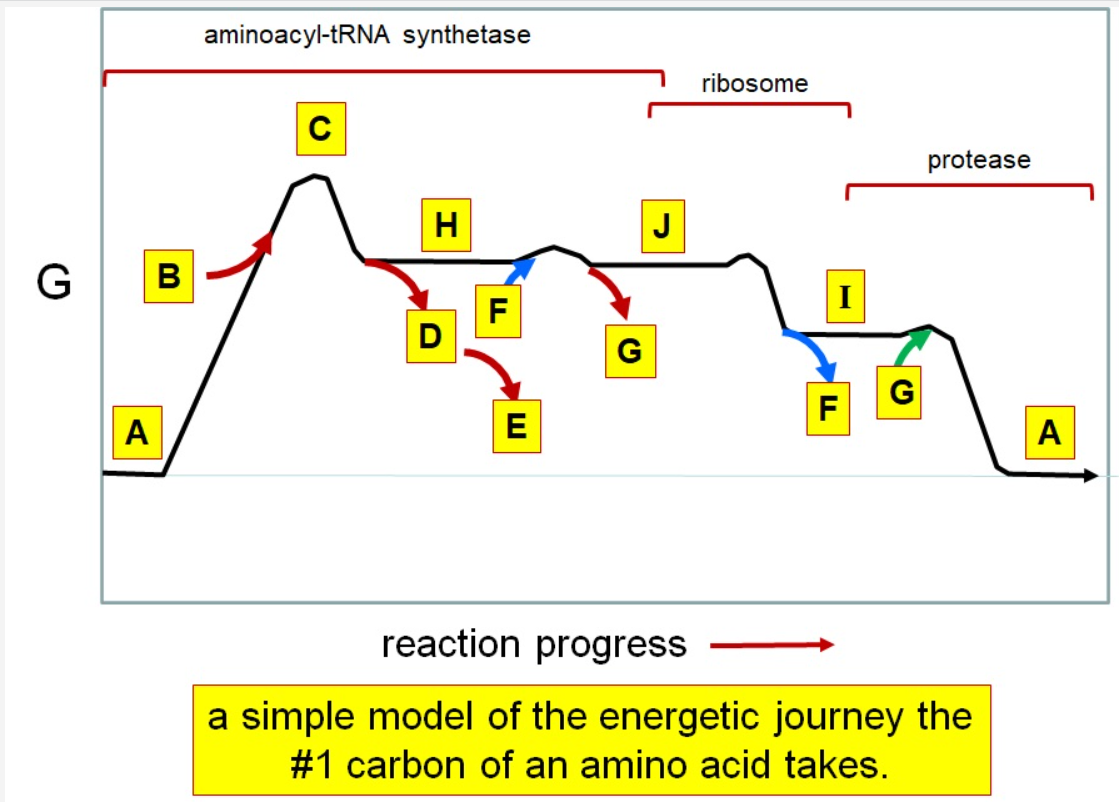
Which letter corresponds to the tRNA
F
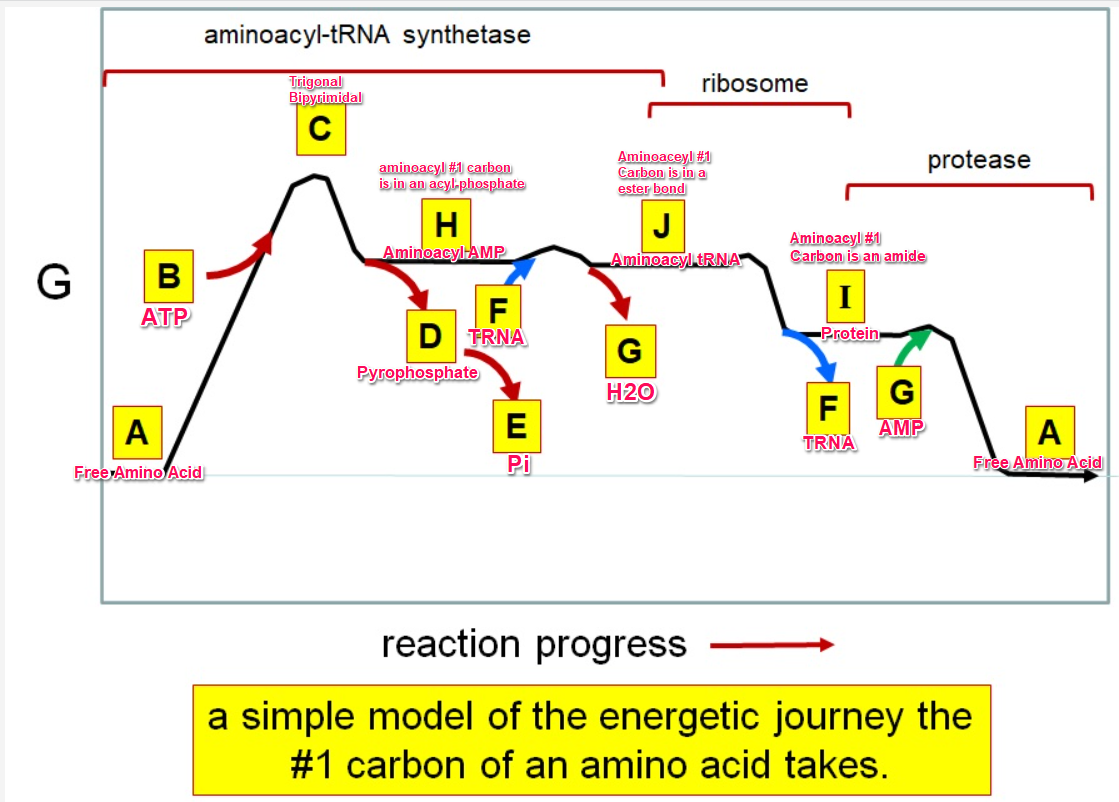
38
New cards
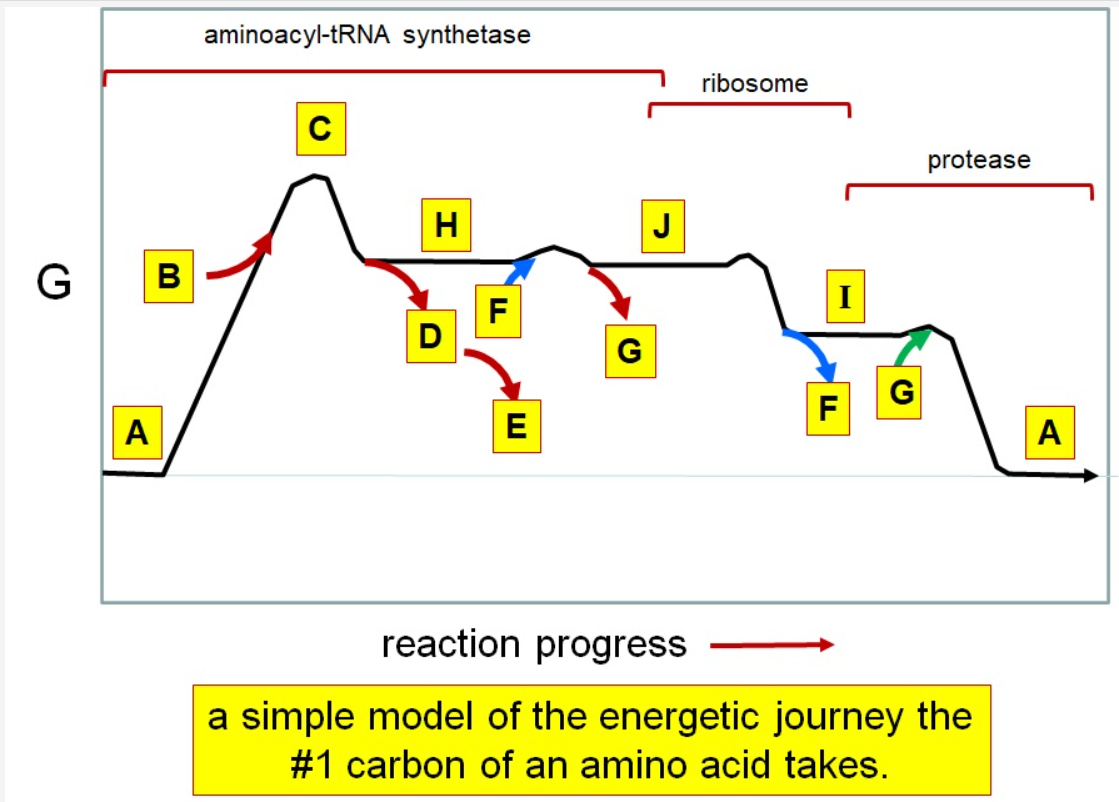
Which letter corresponds with the aminoacly #1 carbon is an amide bond
*I*
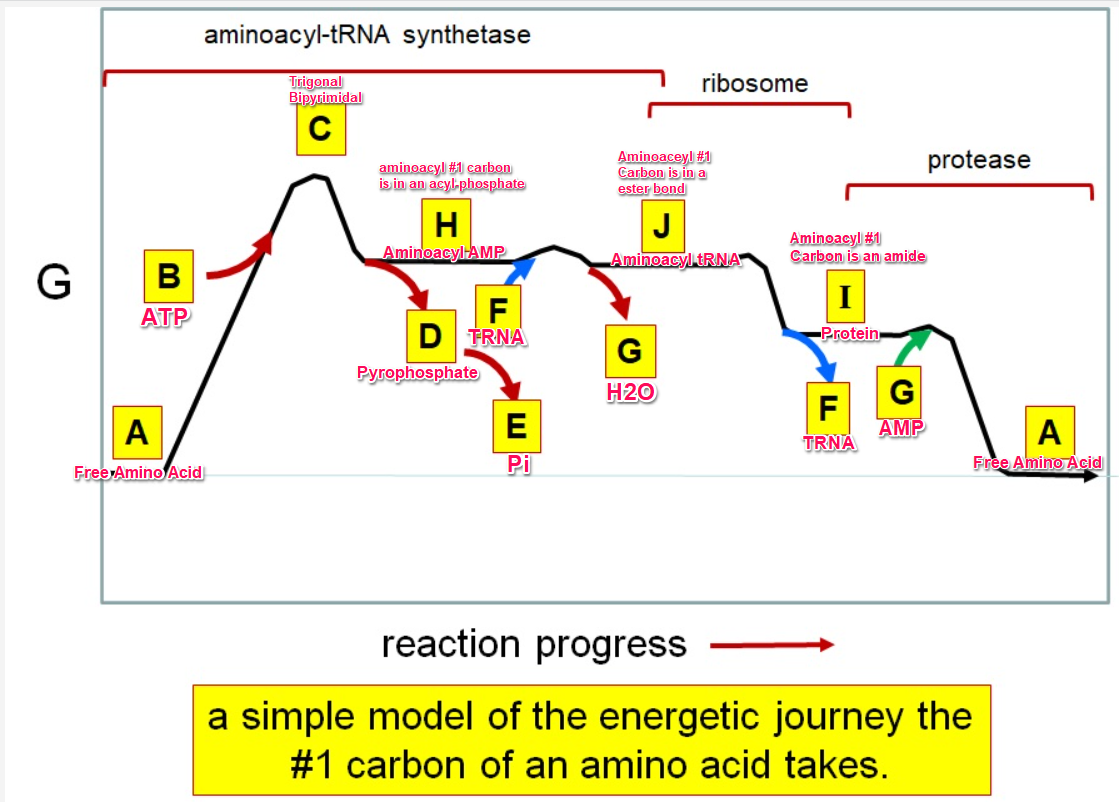
39
New cards
Which letter corresponds with the aminoacyl #1 carbon of the ester bond
J
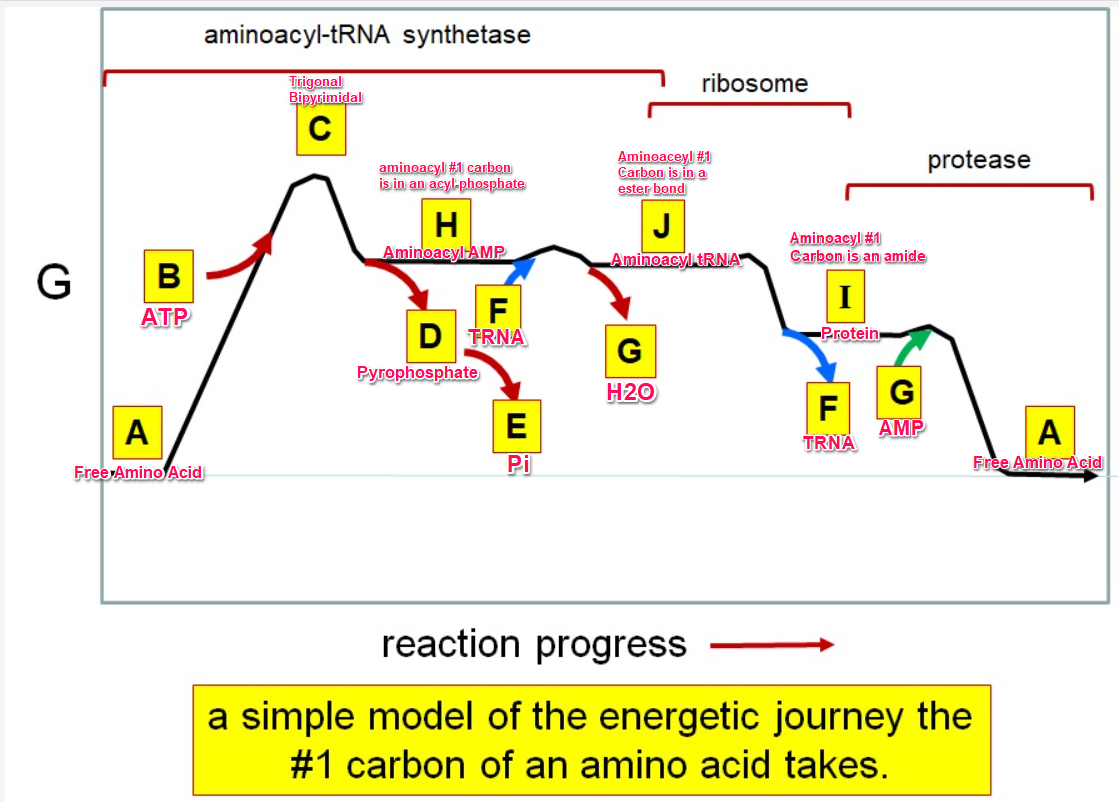
40
New cards
Which letter corresponds to the free amino acid
A
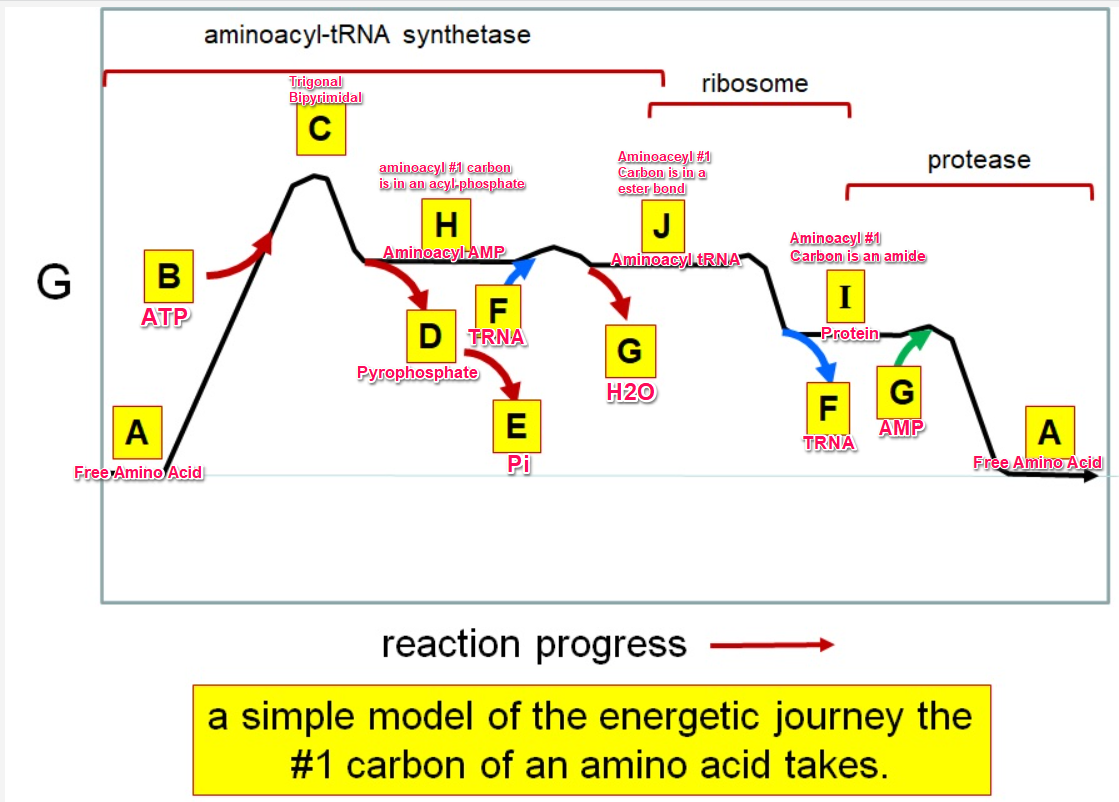
41
New cards
Which letter identifies where the amino acyl #1 carbon is in a carboxylate
A
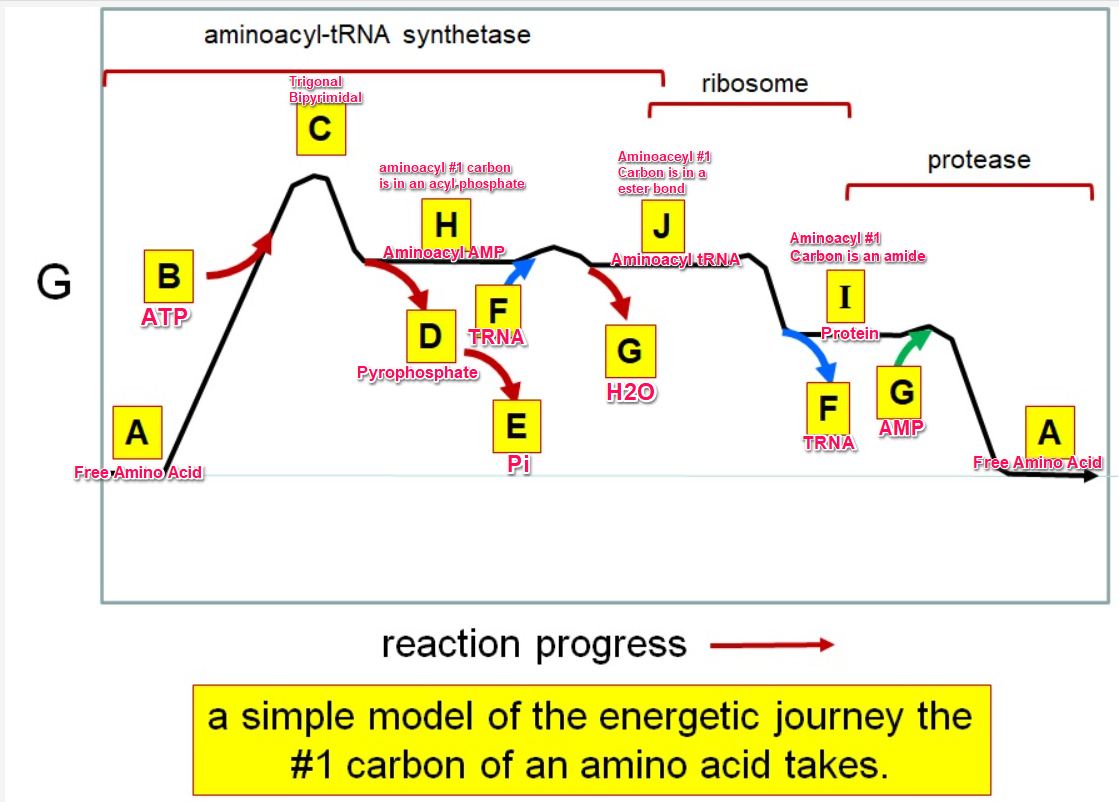
42
New cards
Which letter corresponds to H2O
G green
43
New cards
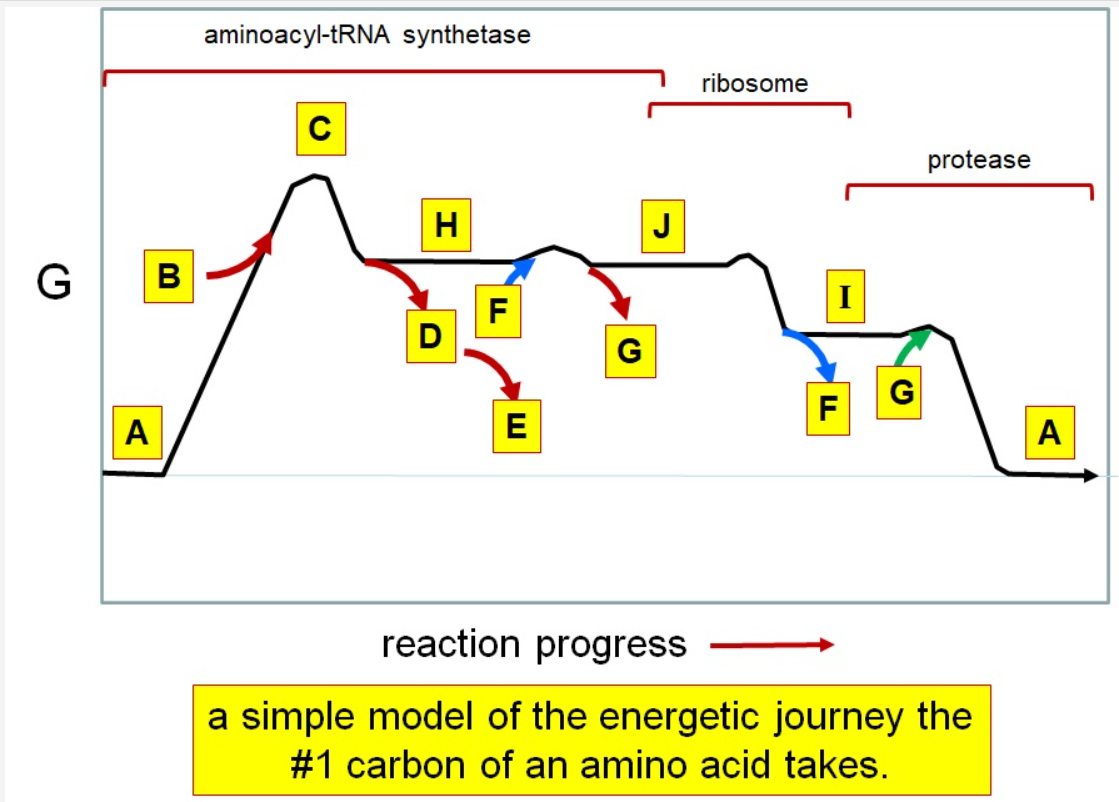
Which letter identifies where the amino acyl #1 carbon is an acyl-phosphate
H
44
New cards
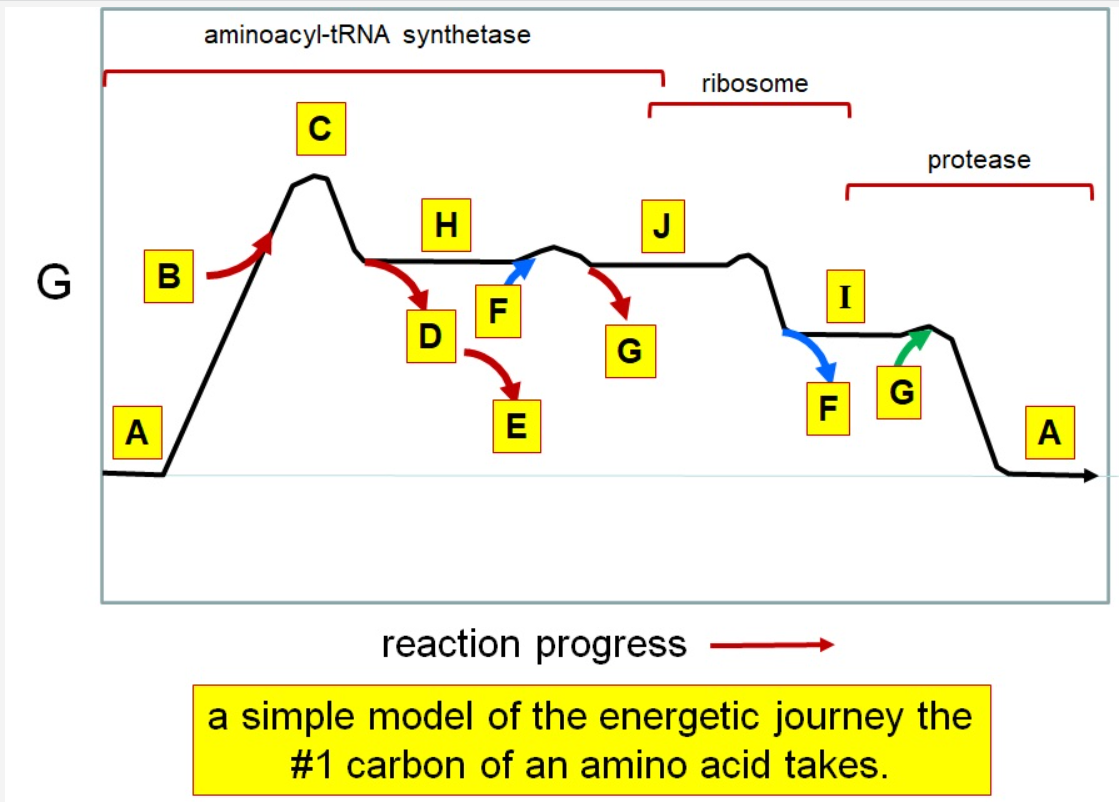
Which letter corresponds to protein
I
45
New cards
Which letter corresponds to trigonal bipyramidal geometry
C
46
New cards
Which letter corresponds with amino acyl AMP
H
47
New cards
Which letter corresponds with AMP
G red
48
New cards
Which letter corresponds with ATP
B
49
New cards
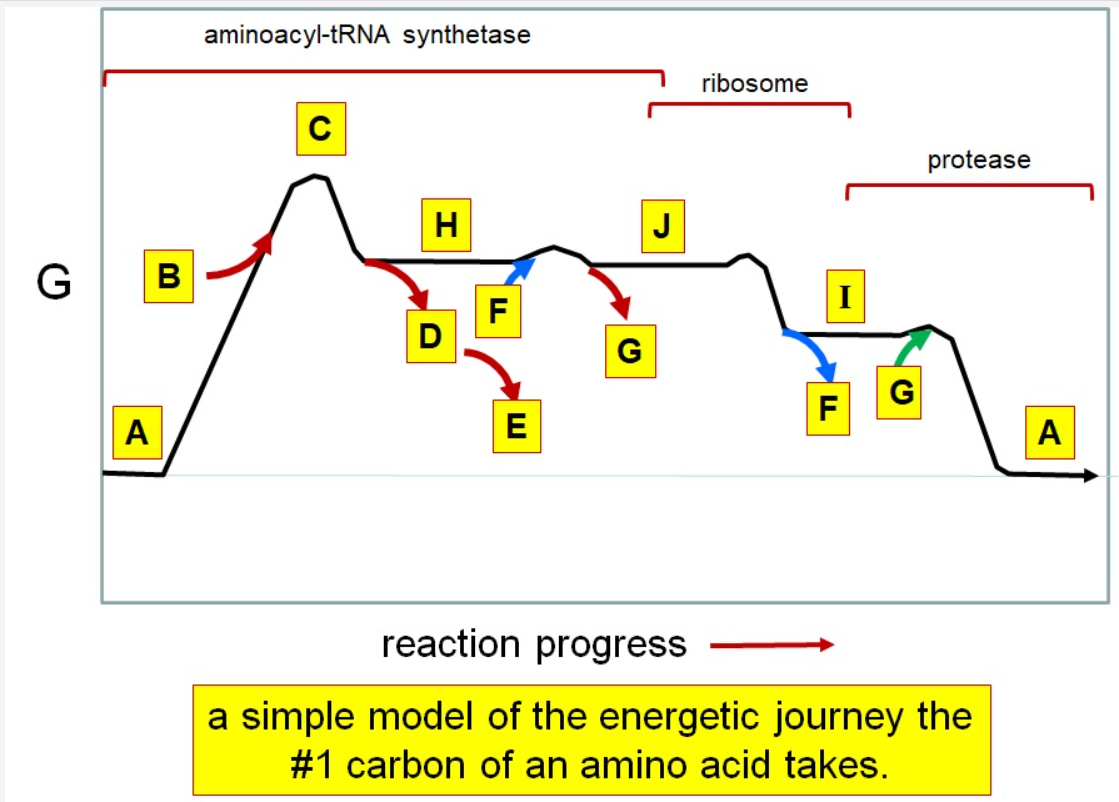
Which letter corresponds to pyrophosphate
~~D~~
50
New cards
tumor-suppressor protein which is the most studied protein in scientific research
P 53
51
New cards
activates Chk2 kinase
ATM kinase
52
New cards
tag for proteins destined for proteolysis
Ubiquitin
53
New cards
phosphorylates S20 of p53 to block binding by Mdm2
Chk2 kinase
54
New cards
becomes attached in an amide bond between its own C-terminal carboxylate to a lysine on a target protein
Ubiquitin
55
New cards
wobble base of the anticodon of phenylalanine tRNA that base-pairs to ONLY UUU and UUC
Guanine
56
New cards
responds directly to single-strand and strongly to double-strand breaks in DNA
ATM kinase
57
New cards
wobble base of the anticodon of alanine tRNAs that base-pairs to GCX where X is any base
Hypoxanthine
58
New cards
produces "cuts" upstream (5') and downstream (3') on a chemically-damaged DNA strand
Repair endonuclease
59
New cards
directs covalent attachment of ubiquitin to p53
Mdm2
60
New cards
cut by caspase 3 to promote the cutting up of genomic DNA into nucleosome sized fragments, effectively killing the cell
ICDA
61
New cards
trimeric protein that is assembled by p21 to load DNA polymerase delta at sites of repair
PCNA
62
New cards
domain of CBP that bonds to acetyl-lysines to continue the spread of acetylation towards the start of transcription
Bromo
63
New cards
pro-apoptotic protein that is expressed in response to high levels of p53 binding to weaker response element binding sites
Bax
64
New cards
cut by active caspase 9 to promote apoptosis
Pro caspase 3
65
New cards
anti-apoptotic protein which forms inactive heterodimers with Bax to prevent apoptosis
Bcl2
66
New cards
uses phenylalanines to pry open A-T rich, double stranded DNA to expose single-stranded template to RNA Polymerase II
TBP
67
New cards
dimerized by the apoptosome so as to perform cross-proteolytic cleavage
Pro caspase 9
68
New cards
leaked out of the intermembrane space of the mitochondrion to the cytoplasm with cytochrome c to form the apoptosome
Apaf1
69
New cards
inhibited directly by p21 so as to prevent progression through the cell cycle
Start kinase
70
New cards
Contribution of SRP receptor alpha to SRP54 that induces the formation of trigonal bi pyramid intermediate
Arginine finger
71
New cards
As SRP 54 is released the nascent peptide is looped into the opened
Transcolon
72
New cards
The SRP complex stalls translation by preventing the ribosomes interaction with
eEF2
73
New cards
Cuts the polypeptide chain between the pre and the peptide B sections of preproinsulin
Signal peptidase
74
New cards
Bonds with high affinity of the pre portion of preproinsulin to stall translation
SRP54
75
New cards
Acts as a GAP on SRP54 to release it from the nascent peptide
SRP receptor alpha subunit
76
New cards
Small molecule that is bound to SRP54 when it's bound to the nascent peptide
GTP
77
New cards
Cofactor used in redox reactions that produce hydrogen peroxide
FAD
78
New cards
Portion of the nascent peptide that is most important for binding to SRP54
Hydrophobic leucine-rich sequence
79
New cards
ROS produced durning formation of the functional form of pro insulin
Hydrogen peroxide
80
New cards
Enzyme which oxidizes reduced PDI in the rER lumen
Ero1
81
New cards
The most abundant mRNA in the islet beta cell encodes
Preproinsulin
82
New cards
Enzyme that oxidizes the cystines of preproinsulin
Protein disulfide isomerase
83
New cards
organizes the assembly, movement and delivery of transport vesicles moving from the rER to the Golgi
Rab 1
84
New cards
organizes the assembly, movement and delivery of Islet beta cell secretory granules/vesicles from the Golgi to the plasma membrane
Rab 37
85
New cards
motor protein that moves secretory vesicles through the actin cortex to the plasma membrane
myosin5a
86
New cards
cargo receptor carrying BiP, PDI, and Ero1 recognizes what on those proteins to load them into vesicles going from the cis Golgi to the rER
KDEL-COO-
87
New cards
at the delivery point, acts as a GAP on Rabs
HOPS complex
88
New cards
organizes the assembly, movement and delivery of transport vesicles moving from the Golgi to the rER
Rab 2
89
New cards
Cargo receptor that recognizes proinsulin's peptide B/C boundary to load it into secretory granules at the trans Golgi
Prohormone convertase 1
90
New cards
cargo receptor that recognizes proinsulin to load it into vesicles in the rER
Surf4
91
New cards
concentrates protons into the secretory granule in order to mature proinsulin into insulin
V-ATPase
92
New cards
when the secretory vesicle lumen pH is low this cuts the proinsulin molecule between the C and A peptides
Prohormone convertase 2
93
New cards
holds together the B and A peptides in mature insulin
Disulfide bridges
94
New cards
motor that moves vesicles from the rER to the Golgi
kinesin
95
New cards
most directly "snaps" together vesicle and target membranes to effect fusion
snares
96
New cards
motor that moves vesicles from the Golgi to the rER
dynein
97
New cards
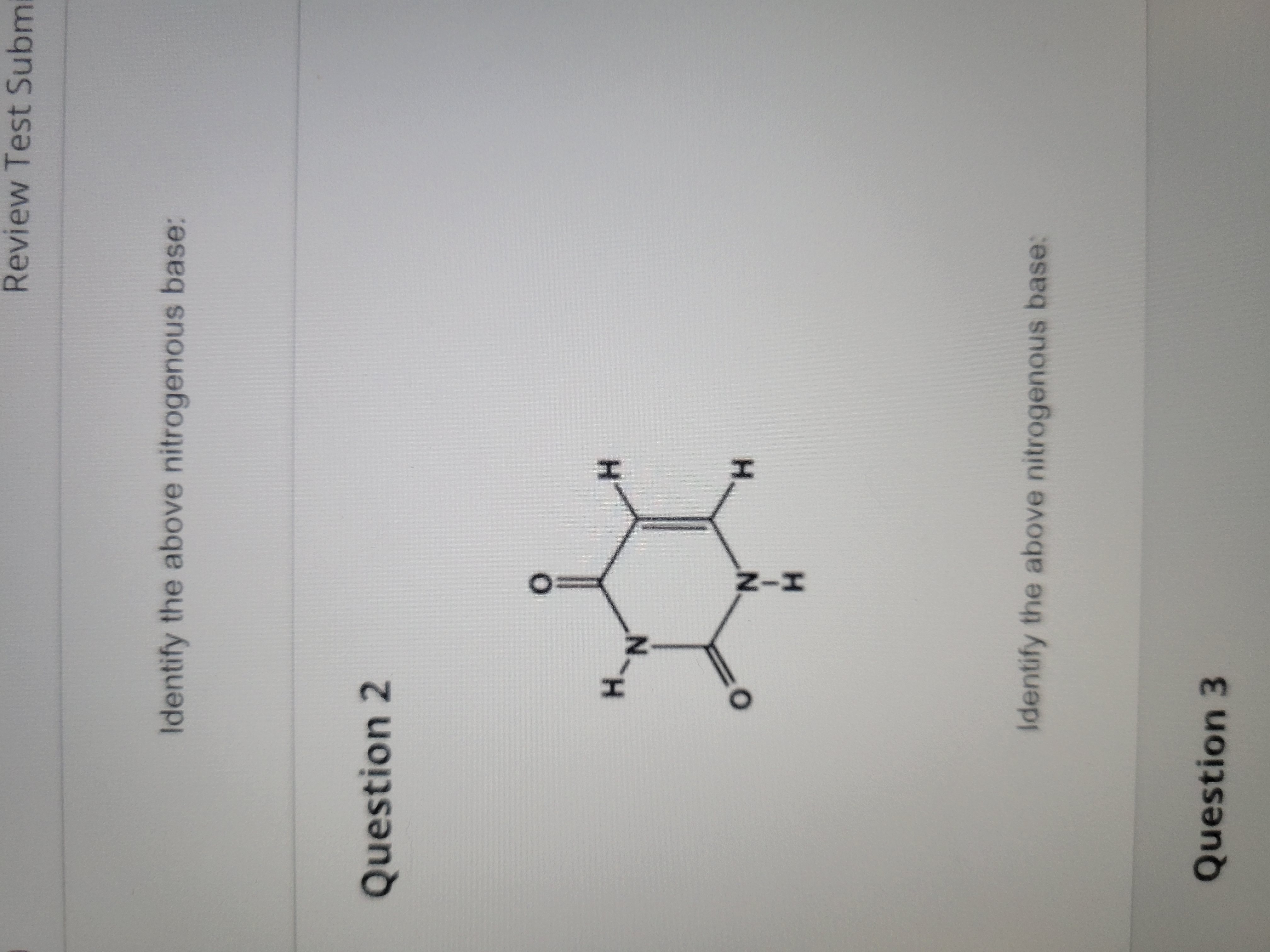
Uracil (pyrimidine)
98
New cards
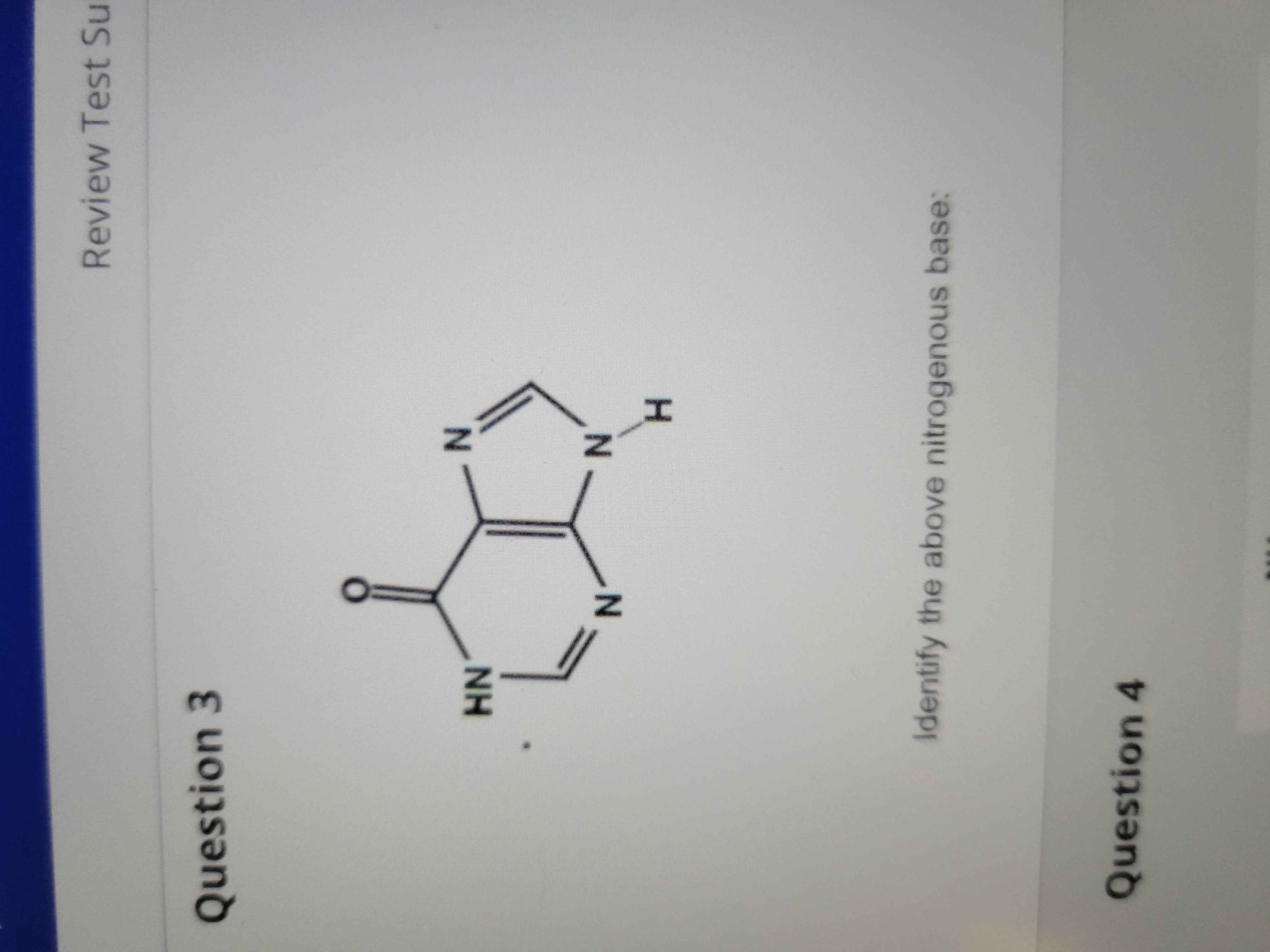
Hypoxanthine (purine)
99
New cards
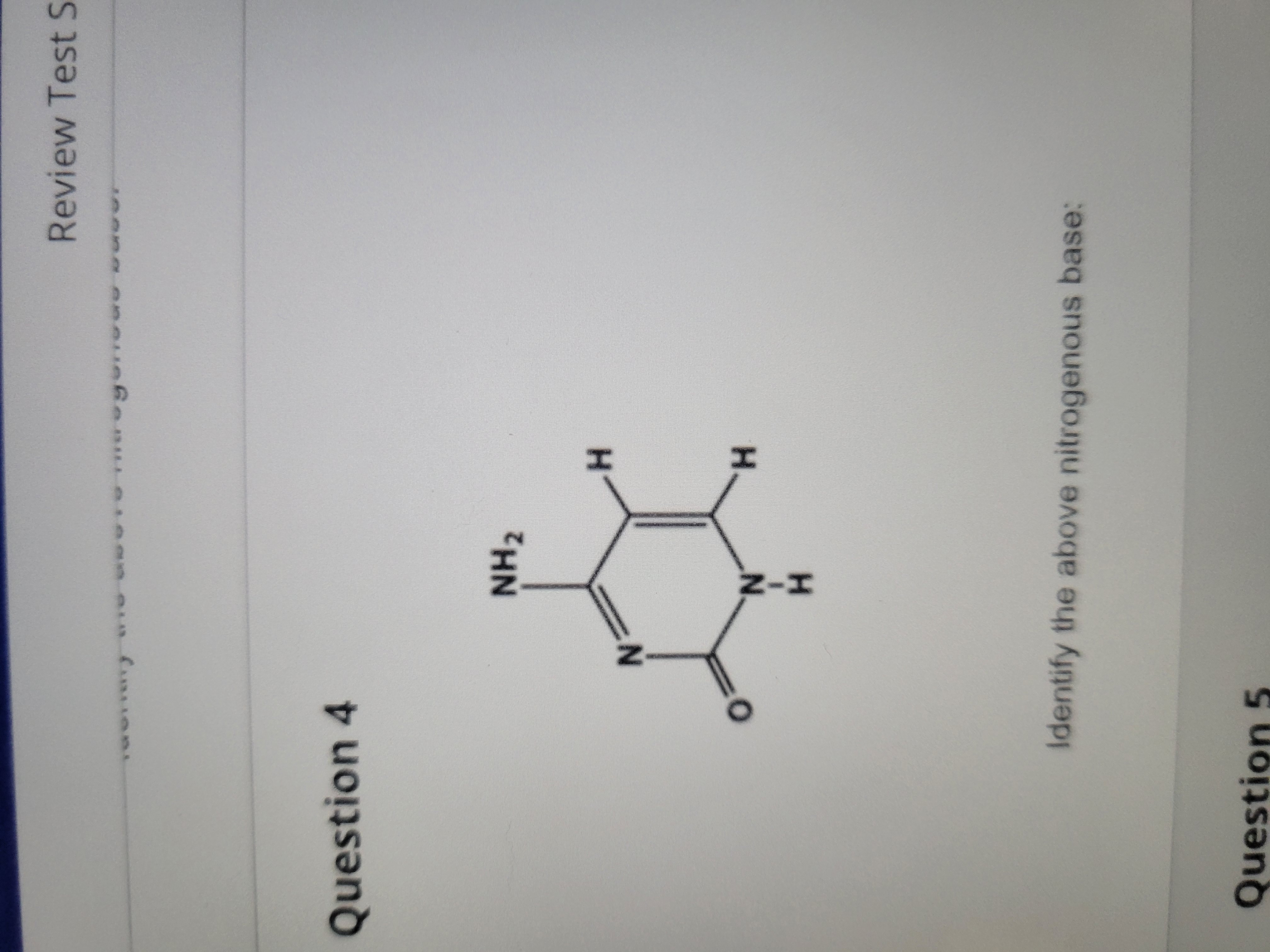
Cytosine (pyrimidine)
100
New cards
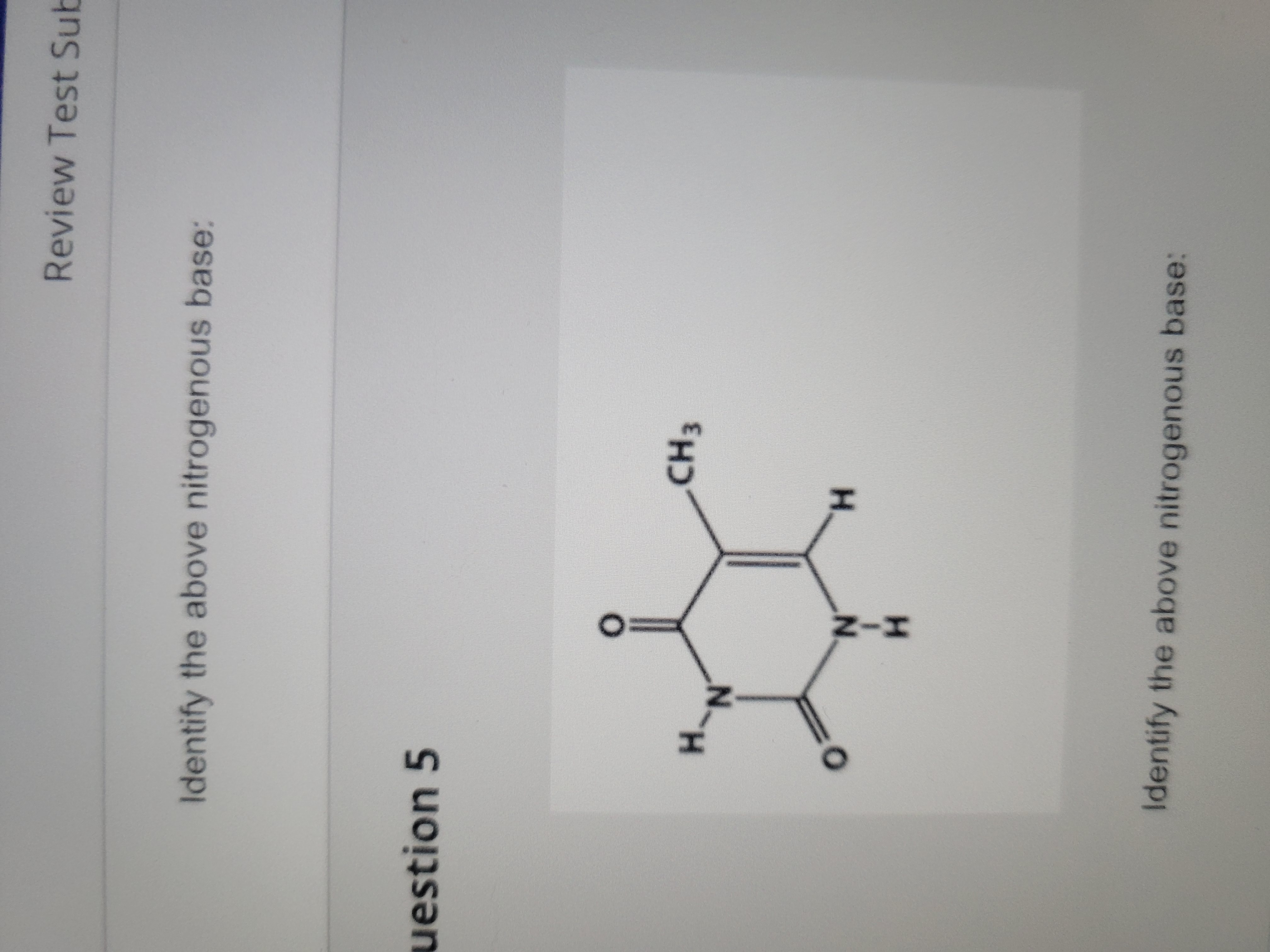
Thymine (pyrimidine)