NU FS 223: The Mediterranean Diet, Olives and Olive oil, Legumes and Wheat in the Mediterranean diet
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Mediterranean Components
- High in: Plant foods (primary plant based), Fruits/Veggies, Minimally refined Grains, Potatoes, beans, Nuts/seeds, Locally grown fresh foods, Olive oil (Virgin/extra-virgin, primary fat)
- Moderate in: Fish, dairy, Poultry, Wine, Eggs (low-moderate)
- Low: Read Meat (animal consumption 50-60% lower), added sugars, saturated fats
- Nutrition components: High fibre, Healthy fats, Low added sugar, variety in proteins
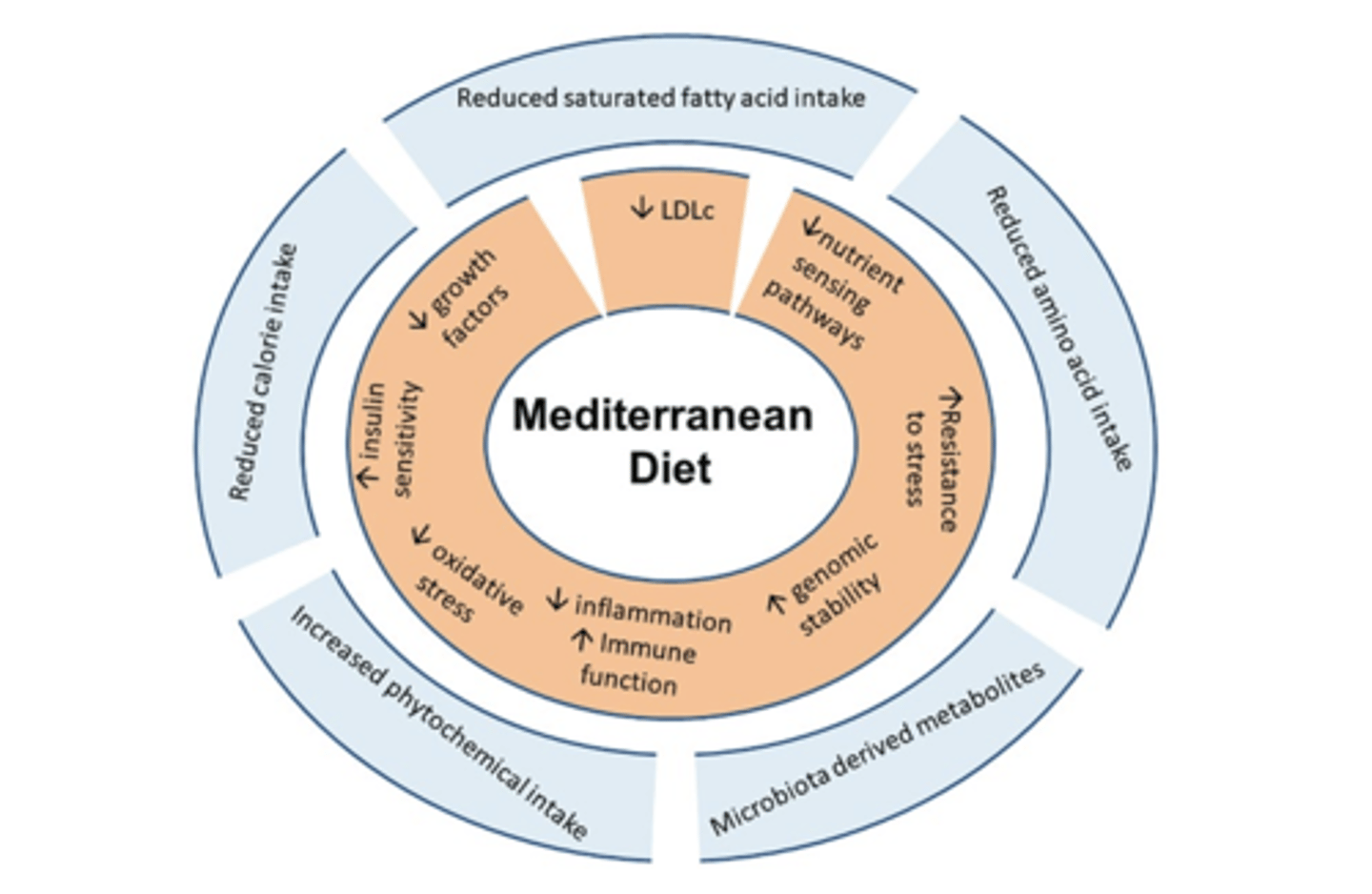
Mediterranean health factors
- Protects against lots, obesity, CVD, etc.
Fibre
- High Fibre diets (Healthy GI tract)
- Legumes/Pulses, Fruits, Veggies, Whole grains
- Helps you live longer, increasing dietary fibre intake associated with reduced risk of dying from CVD and cancers
- 30-40g/day
Plant Antioxidants
- Tomato: Lycopene (red pigment - carotenoid)
- Lemon juice: Ascorbic acid
- Allium Vegetables (garlic, onions): sulfur components (pungent)
- Rosemary, basil, oregano, thyme, lemon balm, sage, mint: Rosmarinus acid
- Sofrito: Sauce made from frying tomatoes, onions, garlic and aromatic herbs in olive oil
Alcohol
- In moderation, associated with reduced risk of heart disease in some research studies (debatable)
- Diet typically includes some kind of wine
- No more than 5 ounces (150ml) of wine a day for women/men over 65, no more than 10 ounces (300ml) of wine a day for men under 65
- Drink with meals
Diet Pattern vs Single Nutrients, Lifestyle
- Used often to examine relationship between adherence to the Mediterranean diet and disease
- Do not focus on single nutrients or single foods, but examine overall diets
- No super foods/magic bullets
- Foods may act synergistically/interactively on the risk of developing disease
lifestyle
- Socializing with friends
- Eating together/sharing
- Everyone involved with cooking
- Close to nature
- Physically active
- Adequate sleep
Olive tree and Olives
- OT:
- Mediterranean origins, agricultural expansion
- long lived, slow growing, survives harsh weathers
- Cultural significance
- O:
- Fruits produced by trees from the family Oleaceae
- belong to fruits called drupes
- color depends on maturity (unripe is green, ripe is purple-black)
- Too bitter to be eaten off tree (phenolic compounds)
- Must be cured to reduce bitterness (packed in salt and soaking in brine (salty water) or using alkaline solution such as lye (sodium hydroxide) water solution)
- Most harvested for oil, minority for table olives
- Spain #1 producer, Canada does not grow Olives
Olive Nutrition
- Monounsaturated fat (oleic acid, n9)
- 15-30% of weight is made up of fat
- Vitamin E
- Phytochemicals
- Phenolic compounds
- Fibre
- Sodium
- Green olives lower fat than purple-black
- Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory
How is Olive oil Made?
- Traditional (mechanical and cold pressing, no high heat or chemicals, pressed soon after harvest )
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil, highest grade/most expensive (Obtained by mechanical means without high heat/chemicals, No additives, No more than 0.8g of free Oleic acid in 100g oil, excellent flavor and odor characteristics (fruity, peppery, bitter, not musty/earthy))
- Virgin Olive oil, lesser grade than EVOO, same first 2 steps, free acidity of up to 2g of oleic acid per 100g, reasonable odor and flavor
- Refined Olive Oil, poor quality (heat, chemicals, high free acidity, poor flavors/odors, blended with EVOO or VO, can be labelled as olive oil, pure olive oil, or light olive oil, flavorless/odorless, refinement reduces % of bioactive compounds)
Benefits of EVOO
- Vitamin K
- Vitamin E (tocopherols), an antioxidant (prevents oxidative reactions in the human body, prevents rancidity and extends shelf-life of the oil)
- Carotenoids (e.g. B-carotenoid, lutein)
- Contains several polyphenols, including oleocanthals (antioxidant and anti-inflammatory organic compound), which is responsible for pepperiness
- preventative role against age-related degenerative diseases such as CVD and some cancers
- Usable to fry foods
Olive oil fraud
- EVOO most susceptible of fraud/adulteration
- Oils may be labelled as EVOO but:
- do not contain olive oil
- refined olive oil, or a blend
- Diluted with cheaper oils like soybean oil, peanut oil, palm oil, or canola oil
- Look for dark bottle, harvest date, expensive, bitter and pungent taste with a peppery finish to ensure real
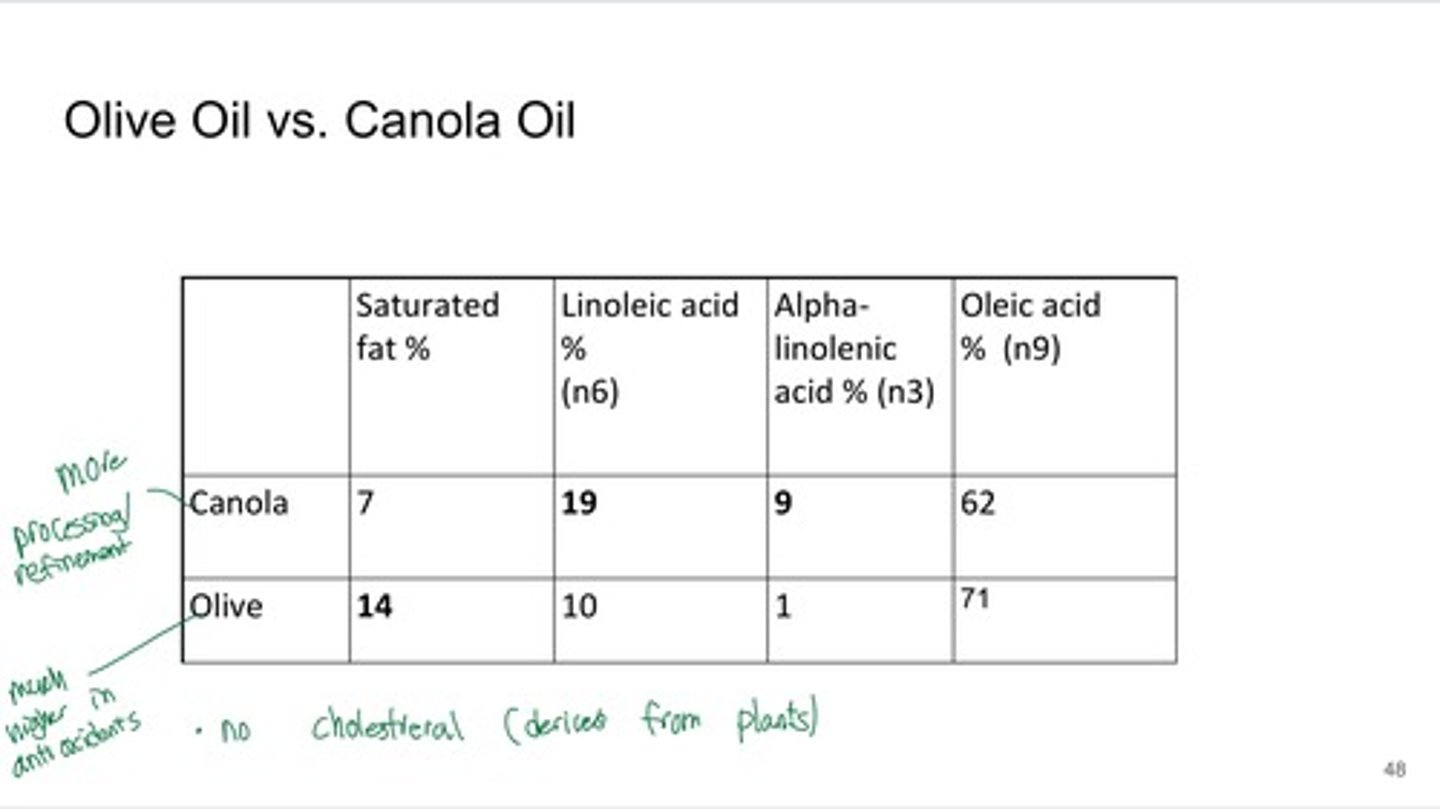
Canola Oil
- Rich source of monounsaturated fats
- lowest amount of saturated fat of all common culinary oils
- Rich in omega-3-fatty acids, reduce CVD
- Low n6/n3 ratio of 2:1
- One serving = 16% RDA of Vitamin for adults
- Cheaper than Olive oil because it does not have to be imported
- Canada produces canola oil
- supports Canadian farmers
Legumes
- From Fabaceae botanical family
- Include all forms of beans peas and lentils
- Plant based proteins
- High fibre
Whole grains
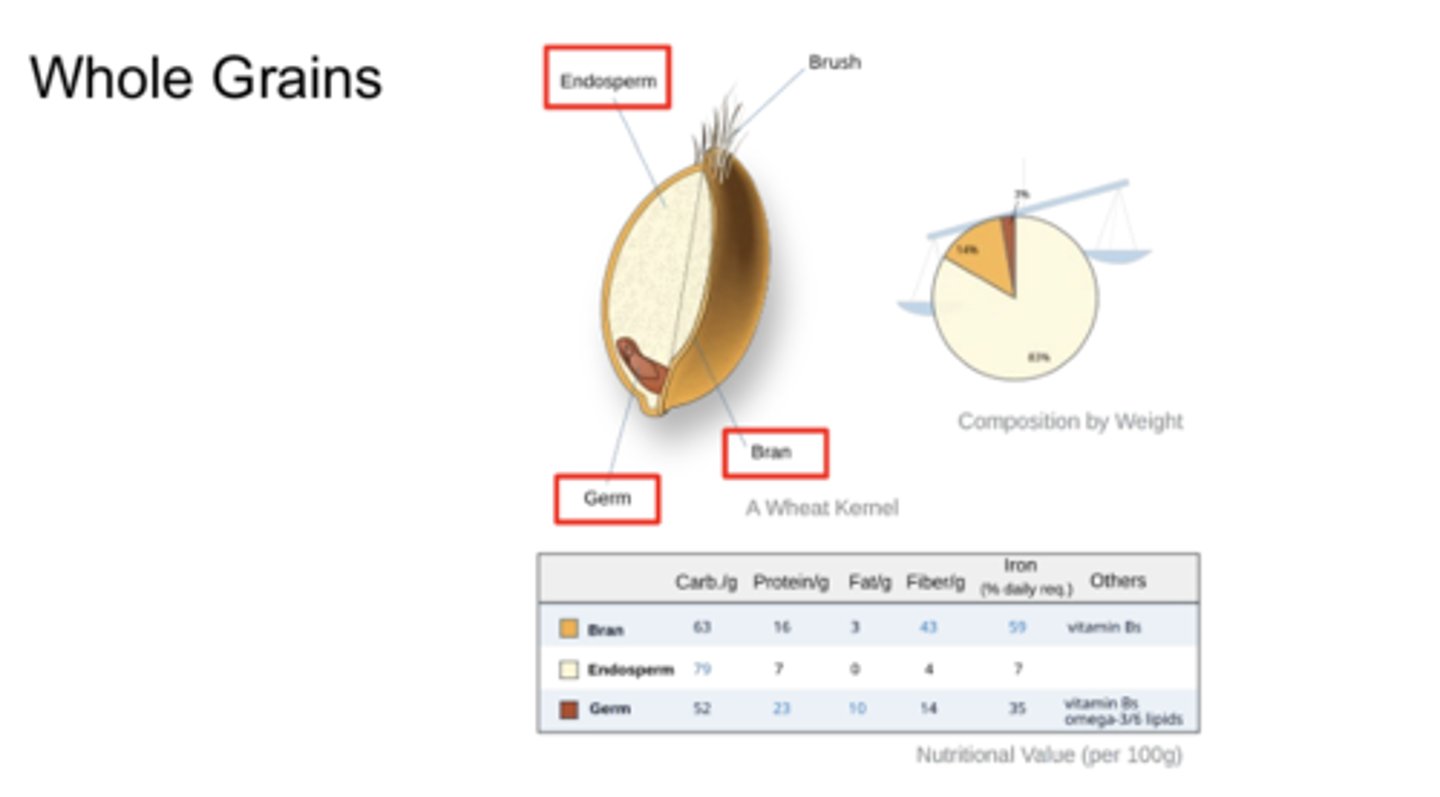
Whole Grain vs Refined Grain
WG:
- Contain the entire grain kernel
- Ex. Whole-wheat flour, bulgur, cracked wheat, oatmeal, whole cornmeal, brown rice
RG:
- milled to remove bran and germ
- EX. white flour, de-germed cornmeal, white rice
Wheat products
- Bulgur, whole wheat, made into pilaf (Whole wheat, parboiled, dried, and ground, minimal cooking)
- Durum wheat, made into couscous and pasta (often yellow)
- Bread Wheat made into bread, staple of Mediterranean diet (Pita, leavened bread, sourdough)
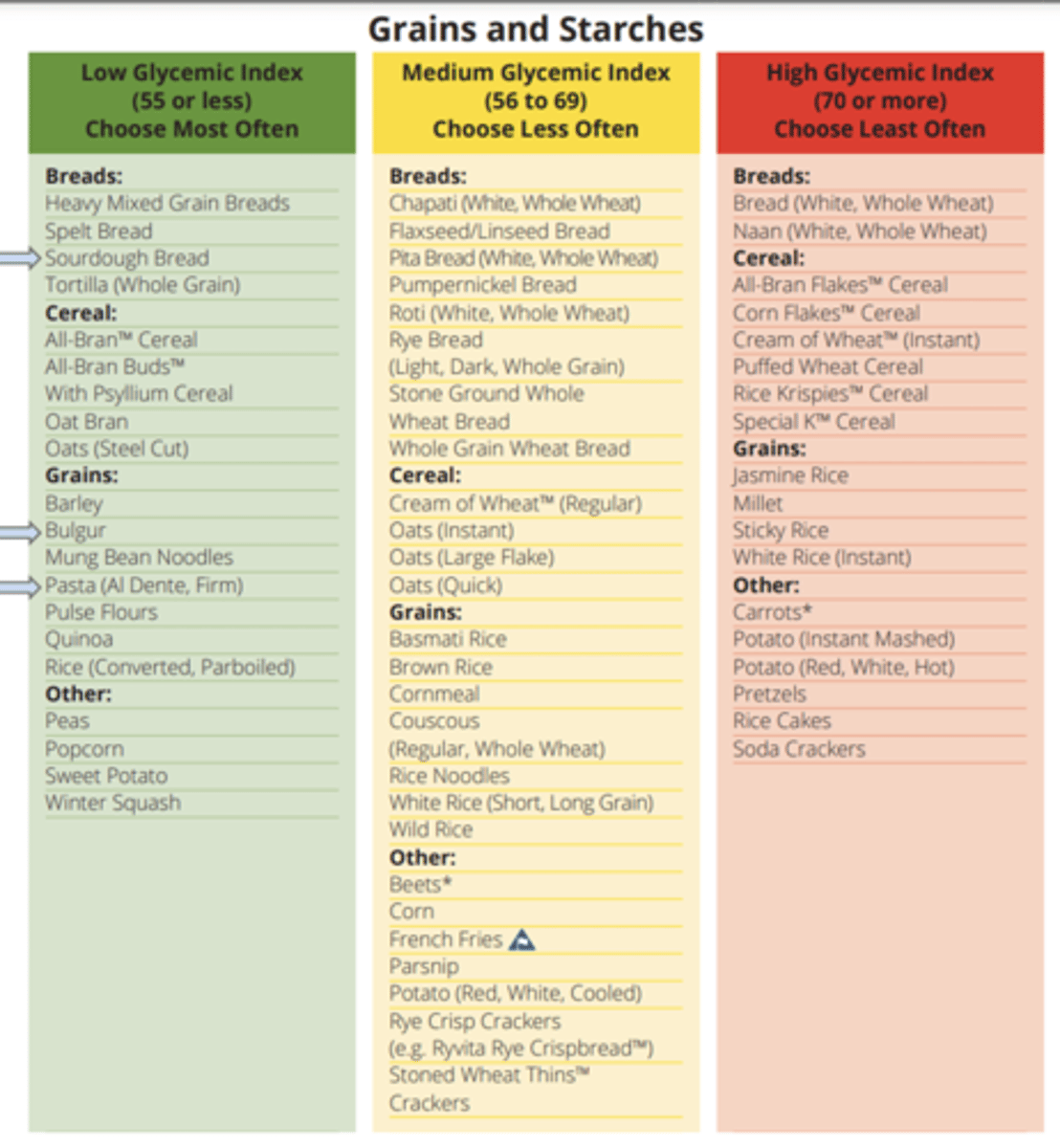
Glycemic index
- ranks a carb-containing food or drink by how much it raises blood sugar levels
- Foods with higher GI increase blood sugar higher and faster than foods with a low GI
- Benefits:
- Decrease risk of type 2 diabetes
- decrease risk of heart disease and stroke
- feel full faster and longer
- Weight management
- High GI diet associated with increased risk of overall cancer, colon and bladder cancer

GI and Mediterranean diet
- preparing foods with an acid lowers the Glycemic response by slowing stomach emptying
- combine a high-GI food with low GI foods (fat and protein) to decrease GI value
- Couscous has medium glycemic index, but when served with a low GI food like chickpea's, the meal is a low GI meal
- Mediterranean diet is a medium-low GI diet