Marketing Final
1/43
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Marketing
activity and process for creating, communicating, delivering and exchanging offerings that have value for customers. involves research, segmentation, targeting, positioning, product, price, place, promotion - drives brand awareness & revenue growth
Segmentation
involves grouping customers by 1 or more characteristics to identify groups with similar demand for similar products/services e.g. demographic, geographic, behavioural, psychographic
Targeting
deciding which segment market to target. ideal: product/service fit, profitability of CLV, growth potential of CLV, competitive position, cost to reach segment and compatibility
Research
any organized effort to gather information on consumers including what they need want or believe. primary/secondary - quantitative/qualitative
Positioning
act of designing company’s marketing so that it occupies a distinct and valued place in the customer’s mind and heart. The CVP is used for this. The CVP communicates the benefit/value the product will bring to the customer/market.
CVP: Functional, emotional, economic, symbolic and end value
Product
can be intangible/tangible that provides satisfaction to the buyer in terms of color, form, function etc. The product adaptation framework is used for developing products to achieve differentiation and innovation - perceived value for money. It entails core product, packaging and service.
Price
Must support the product’s positioning & be consistent with other variables in the marketing mix, fit the realities of the market place (will customers purchase for this price) and achieve profitability (cover the costs of manufacturing, distribution etc. and still make profit)
Place
refers to the distribution system where channel members are responsible for moving information, products and services to a place where it becomes available and convenient for use and consumption by a consumer. Can be direct/indirect. Traditional structures: 0-level, 1-level, 2-level, 3-level or omnichannel (integrated).
Promotion
means by which the firm attempts to inform, persuade and remind customers directly/indirectly about the products they sell. There are 2 strategies - push and pull.
Production concept
customers prefer products that are widely available and inexpensive. Managers of production-oriented businesses concentrate on achieving high production efficiency, low costs, and mass distribution. This concept is still used. Standard products are not customized e.g blue water, sugar.
Product concept
customers favor products offering the most quality, performance, or innovative features. Focuses on the product itself rather than the production of it. A new or improved product will not necessarily be successful unless it is priced, distributed, advertised, and sold properly. e.g smartphones
Selling concept
consumers and businesses if left alone won't buy enough of the organization's products. It is practiced most aggressively with unsought goods that buyers don’t normally think of buying. e.g insurance
Marketing concept
customer-centered philosophy. The job is to find not the right customers for your products but the right product for your customers. e.g. Dell doesn’t prepare a perfect computer for its target market. Designing products from customers' point of view
Holistic concept
Relationship marketing - Aims to build mutually satisfying long-term relationships with key stakeholders -outcome is loyalty.
Integrated marketing - Marketer devises marketing activities that are meant to reinforce and complement each other to achieve a particular objective - e.g online store and brick & mortar store - it communicate w/ logistics to get product to consumer
Internal marketing - Every employee must understand his/her role in the company's marketing. Every department must see other departments as its customers e.g if the clerk is delaying paperwork it will delay the ability to serve the customer
Performance marketing - requires an understanding of the financial and non-financial returns to business and society from marketing activities and programs. Consider the legal, ethical, social, and environmental effects of marketing activities.
Research Methods - Quantitative & Qualitative
Descriptive survey - Most appropriate tool when statistically valid relationships and trends need to be established within a population
Experiment - The most appropriate tool when you need to investigate the subjects’ reaction or feedback under environmental or situational conditions
Focus groups - Most appropriate for exploratory research.
Interviews - Most appropriate for uncovering deep personal views, understanding psychological motivations and underlying perceptions, etc. that would otherwise not be expressed in a focus group or survey
Observations - researchers can measure actual behaviour, opposed to user-reported behaviour. - privacy issue
Sample size
To draw valid conclusions from quantitative research, a representative sample size must be chosen. That is - is a subset of a population that accurately reflects the characteristics of the entire population
Data Analytics
comprise different techniques that use software, machine learning algorithms etc to uncover patterns and extract insights from raw data. today used to uncover trends & patterns “Big Data” structured,(id# in database) semi semi-structured (tweets by hashtags) or unstructured (online reviews)
Benefits of data analytics to marketer
Provides a central location for this data and ensures that your whole customer service team, as well as your sales and marketing teams, are on the same page.
It gives you a 360-degree view of your customers - understand them more fully - better meet their needs.
Gain insights into which audience segments are most likely to interact with a campaign and convert - can be used to adjust your targeting criteria.
Use it to develop different messaging and creative for different segments - Improving your targeting results = more conversions, less ad waste
Helps streamline processes, save money and boost your bottom line - improved understanding of what your audience wants - waste less time and money on creating ads and content that don’t match your audience’s interests
Customer Lifetime Value
Customer Lifetime Value represents the total amount of money a customer is expected to spend in your business, or on your products, during their lifetime.
- takes into account not only the revenue generated from the customer's purchases but also costs associated with acquiring, serving, and retaining that customer
calculate: Convert longevity to yrs - x 350. Then divide that amt of days by time in between purchases. Then multiply by typical purchase amt $.
Advantages of CLV
Customer Acquisition - CLV can improve customer acquisition by identifying the most valuable customers and enabling you to engage them with compelling offerings and incentives.
Marketing Effectiveness - CLV can measure the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns and calculate the return on investment (ROI), helping you optimize your marketing strategies
Disadvantages of CLV
Focus on One Core Group - It is easy for a company to put on blinders and focus only on one core group of customers, potentially neglecting other important customer segments.
Difficult to Predict the Future - The future is difficult to predict, and assumptions must generally be made about a customer's future habits, which may not always be accurate.
Types of Buying behaviour
Habitual - low involvement, few brand differences e.g. buying water, sugar. strategy - make easily accessible
Dissonance reducing - high involvement, few brand differences e.g. loan. this behaviour people take easiest path like dont consider much
Variety-Seeking - low involvement, significant brand differences e.g. restaurant
Complex - high involvement, significant brand differences e.g. buying house. strategy - inspire confidence in their purchase e.g. warranty
Choosing segment (targeting criteria)
Product/Service fit - extent to which they can satisfy the customer needs)
Profitability - Lifetime Value of the customers that make up the segment
Potential for Growth - The extent to which the Lifetime Value of customers can be extended and expanded
Competitive Position - The extent to which a competitive advantage can be sustained in the face of competition
Cost to Reach - The extent to which the company resources can access the customers of the segment on an ongoing basis
Compatibility - how aligned is this market to our goals?
Tactical concept of a brand and the jump to strategic
Tactical - A brand is a name, term, symbol or design, or a combination of them, which is intended to signify the goods or services of one seller or group of sellers and to differentiate them from their competitors.
Jump from tactical to Strategic
While important, these tactical tools are only meant to communicate the brand and do not constitute the brand itself. The brand is what stands behind the name, term or symbol. It defines who you are and what you stand for: People, Processes, Values, and Business culture.
Strategic Concept
A brand is a set of mental associations, held by the consumer, which add to the perceived value of a product or service. A brand is what customers think and feel about your product, service, company or country.
Branding success is no longer measured by how many consumers recognize or are aware of brands and their logos or slogans, but by how strongly consumers feel connected to brands.
Mental Associations & Emotional Connection
When someone is emotionally linked to a company, its products, and services, it is hard for them to let go - translates into customer loyalty. Therefore the objective of every brand manager or marketer should be to make their customers emotionally linked to their brand.
Saliency - suggest a combination of value elements that are relevant to satisfying the needs and wants of that consumer
Exclusivity- suggest something unique about the product/service that differentiates it from its competitors
Desirable - elicit a positive response from the consumer by conveying trustworthiness, likeability and confidence
Product Adaptation Framework
-opportunities for product differentiation from competitors & innovation.
Product Lifecycle - Embryonic & Growth
Embryonic - product is new to the market and sales are low. No competition.
Creating high awareness (heavy advertising and promotions)
Encouraging customers to try product/service (trial & adoption)
Command premium prices for innovation
Growth - Sales are growing as more customers adopt products. Competition begins to appear
Maintaining awareness
Expanding distribution
Offering incentives for repeat purchase
Product Lifecycle - Maturity & Decay/Product Extension
Maturity - Sales level of - maximum number of customers in the market are using the product. Many competitors offer similar products/services.
Offering customer loyalty rewards programs to maintain number of customers e.g. discounts/points for members
Sales promotions including discounts and rebates
Saturate distribution channels
Decay/Product extension- Sales decline as customers move to newer/more innovative products/services. Competitors have better product/service offerings. if this not acknowledged - decay
Jolting sales into a new phase of growth by redefining aspects of the product to appear ‘fresh’ in the market e.g. new packaging features, label redesign, new flavours, improved quality/quantity, etc. (line extensions/brand extensions)
Well-chosen price point
Achieve the financial goals of the company (e.g., profitability) - cover cost of producing, distributing, and selling the product, and a fair return for effort/risk.
Fit the realities of the marketplace (Will customers buy at that price?)
Support a product's positioning and be consistent with the other variables in the marketing mix e.g high quality positioning requires a high price
Price/Quality Relationship
refers to the perception by most consumers that a relatively high price is a sign of good quality (premium pricing) and the lower price is an indication of basic quality (value pricing).
Problem: The greater the uncertainty surrounding a product, the more consumers depend on the price/quality hypothesis and the greater the premium they are prepared to pay. Difficult for complex products that are hard to test.
Price skimming vs Penetration Pricing
The price of a product is set as high as possible and is gradually lowered to meet the market average price. Used if there’s enough differentiation or innovation to justify a premium price and product/service brand is positioned at the high end of the market
Market penetration strategy is when the product is introduced at a low price to induce a maximum number of consumers. Used when product or service brand is positioned for the mass market or lower end of the market.
Pricing method- Full cost plus cos idc abt marginal
If the firm’s offer contains features not offered by the nearest competitor, it may price just above the competitor If the competitor’s offer contains some features not offered by the firm, the firm may price just below the competitor. (not part of method)
Full cost per unit = Variable cost + Fixed Cost per unit
Variable cost per unit =
Fixed cost portion per unit =TFC/Q
Full cost per unit = VC + FC
Selling price per unit using full cost plus pricing = add the mark up to full cost
Channel member
one part of the organized network of institutions which, in combination, perform all the functions required to link producers with end users.
Channel members may include manufacturers, wholesalers retailers etc. Traditional channel structures can be 1 level where there are no channel members, 2 level with 1 channel member, 3 level with 2 channel members or 4 level with 3 channel members.
Channel conflict reasons
Incompatible goals among channel members - there may be conflicting goals and objectives. E.g. manufacturers may prioritize maximizing market share or brand visibility, while retailers may focus on maximizing sales and profitability
Domain conflict where channel members compete with each other e.g. wholesaler competes with retailers for certain customers/market segments
Poorly defined roles and responsibilities of channel members- Without clear guidelines, channel members may intrude on each other's territory, leading to disputes and inefficiencies e.g issues such as pricing, inventory management, and customer relationships
Strategies for channel conflict
Set and communicate clearly defined goals, objectives, and expectations- helps align everyone's efforts towards common objectives e.g. establishing sales targets
Provide sales and promotional support - helps members achieve their sales targets and effectively market and sell the company's products e.g. advertising materials
Visit channel members and customers regularly - opportunities for relationship-building, problem-solving, and feedback to understand the needs and challenges of its channel members
Invite key channel members to visit home-based operations - provide insights into the company's operations, culture, and values to understand the company's strategic direction, and market positioning, fostering alignment.
Provide updates on products, markets, and company developments - ensure that they remain knowledgeable and up-to-date reducing the likelihood of conflicts arising from miscommunication or misunderstandings.
Call to Action
Call to action refers to any design that prompts an immediate response or encourages an immediate sale. A CTA most often refers to the use of words or phrases that can be incorporated into sales scripts, advertising messages, or web pages, which compel an audience to act in a specific way. e.g. “Buy Now”
Promotions
means by which the firm attempts to inform, persuade and remind customers directly/indirectly about the products they sell. There are 2 strategies - push and pull.
Push Strategy
Maximizes the use of all available channels of distribution to "push" the ofering into the marketplace. Requires generous discounts to give the channels incentive to promote the offering, thus minimizing your need for advertising.
Pull strategy
Requires direct interface with the end user of the offering. The objective is to "pull" the customers to the various channel outlets creating a demand the channels cannot ignore, thus maximizing the need for advertising.
Factors influencing Merchandising Decisions
Target Market Preferences & Demographics - Different customer segments - diff preferences regarding product assortment, pricing, and presentation e.g if the target market consists of health-conscious individuals, the retailer should prioritize stocking organic, sustainable products and offer promotions on fitness-related items.
Level of competition influences the need for retailers to differentiate themselves and offer unique value propositions to attract customers e.g. Intense competition requires innovative merchandising strategies, such as exclusive product offerings.
Retailer’s image, store positioning & strategic objectives - Merchandising should align with ‘’ ‘ ‘’’ to ensure consistency and authenticity in the customer experience e.g. a retailer with a high-end positioning needs to focus on curating a selection of high-quality products and create a sophisticated store environment to reinforce its brand identity.
Store location determines the customer demographic. Retailers need to adjust their product assortment, pricing, and promotions to cater to the specific needs and preferences of customers in different geographic areas.
Stock turnover & Profitability - Retailers may use sales forecasts and inventory management tools to ensure that products are replenished efficiently to meet demand while minimizing carrying costs.
Visual Merchandising and Purpose
This is the activity of developing floor plans and three-dimensional displays in order to maximise sales by highlighting their features and benefits - purpose: to attract, engage and motivate the customer towards making a purchase.
Make it easier for the customer to locate the desired category and merchandise - organizing products in a logical and intuitive manner for easy navigation e.g. Clear signage, aisle markers - don’t feel overwhelmed/confused.
Make it easier for the customer to self-select - organizing products to invite customers to interact with them e.g. Open displays, product testers, and sample stations allow customers to touch, feel, and experience the products firsthand, aiding in their decision-making process.
Make it possible for the shopper to co-ordinate and accessorise - by showcasing products in coordinated sets, outfits, or collections that demonstrate how items can be mixed and matched
Recommend, highlight and demonstrate particular products at strategic locations e.g. in high-traffic areas or focal points - maximize visibility - showcases to draw attention to specific items
Effective Marketing Communications
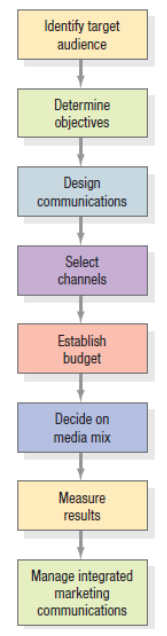
Identify target market → Determine objectives (e.g brand awareness) → Design Communications (CTA, what to say, who will say and how to say it) → Select Channels (tv, radio)→ Establish Budget (cost of all promo) → Decide on media mix→Measure results → Manage integrated marketing communication
Think Global Act Local (GLOCAL Strategy)
“Think Global” - standardized elements that will not change from one country to the next - Branding - Restaurant Format - Franchising model
Benefit: builds consistent international image and consumer confidence, economies of scale in production and distribution, lower marketing costs
“Act Local” - customized elements: -menu items - Local promotions - Local employees
Benefit: International Brand gains local acceptance
Why?: Differences in culture, consumer needs, wants, competitive environment, legal environment, marketing infrastructure, administrative procedures