Topic 2 - Egypt
5.0(1)Studied by 2 people
Card Sorting
1/103
Earn XP
Last updated 1:31 PM on 2/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
1
New cards

Amon-Ra
sun god of Upper + Lower Egypt
2
New cards

Bastet
Goddess who protects Amon-Ra from Apophis (or Chaos)
part cat, part lioness
part cat, part lioness
3
New cards

Ma'at
The Feather of Truth
goddess protects justice
keeps things in balance
goddess protects justice
keeps things in balance
4
New cards
Aten
Not sun, but sun's disk
5
New cards

Thoth
god of learning and thought
patron of scribes
patron of scribes
6
New cards

Tawaret
(The Great One)
Takes care of pregnant women
protected Horus when he was a baby while Isis went to find Osiris
Takes care of pregnant women
protected Horus when he was a baby while Isis went to find Osiris
7
New cards
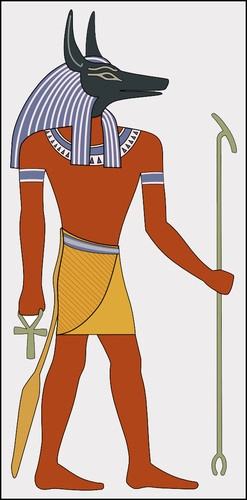
Anubis
Dad: Osiris
Mom: Nepthys
Jackal headed god in charge of mummifying the dead properly
Mom: Nepthys
Jackal headed god in charge of mummifying the dead properly
8
New cards

Horus
Hawk-eyed avenger married to a cow
Son of Osiris and Isis
Fought uncle Set
He's got his EYE on you!
Son of Osiris and Isis
Fought uncle Set
He's got his EYE on you!
9
New cards
Geb
God of Earth
husband of Nut
one of the first Beings of Creation
husband of Nut
one of the first Beings of Creation
10
New cards

Nut
Goddess of the sky and heavens
11
New cards

Shu
God of atmosphere and dry winds
12
New cards

Tefnut
Goddess of Rain (created by Atum's clearing his throat)
Lioness's Head
Lioness's Head
13
New cards

Isis
Egyptian goddess of fertility
Beloved wife of Osiris
Searched high and low for his body, TWICE
Mummified his body parts
Beloved wife of Osiris
Searched high and low for his body, TWICE
Mummified his body parts
14
New cards

Osiris
Egyptian god of the underworld
judge of the dead
Beloved husband of Isis
First to be mummified
judge of the dead
Beloved husband of Isis
First to be mummified
15
New cards
Seth
Jealous brother of Osiris and Isis
Murdered Osiris. TWICE.
Fought Horus for control of Egypt
Murdered Osiris. TWICE.
Fought Horus for control of Egypt
16
New cards

Nephthys
Termed the "lady of the castle," for her role as guardian of the tomb
Isis' sister
also said to be Osiris' mistress + mother of Anubis
Isis' sister
also said to be Osiris' mistress + mother of Anubis
17
New cards

Narmer-Menes
1st pharaoh of Egypt
unites upper and lower Egypt with crown
Palette shows unification by having both crowns
unites upper and lower Egypt with crown
Palette shows unification by having both crowns
18
New cards

Pharaoh Djoser
Ordered his vizier Imhotep to buid the stepped pyramid from stacked mastabas
19
New cards

Vizier Imhotep
Genius who designed the first pyramid in the world, the Stepped Pyramid of Saqqara, for Pharaoh Djoser.
20
New cards

Stepped Pyramid of Saqqara
First pyramid in the world
built by Imhotep for Djoser
built by Imhotep for Djoser
21
New cards

Khufu
Pharaoh who had built the Great Pyramid of Giza, the largest Pyramid in the world
22
New cards
Pyramid building
Twenty year project
very expensive and very complex
Paid for with onerous taxes on product and labor
very expensive and very complex
Paid for with onerous taxes on product and labor
23
New cards

1st intermediate period
2300CE, people of Egypt rebelled because pyramid building demanded too much- money, natural resources, people's time
24
New cards

Middle Kingdom of Egypt
Pharoahs stopped building pyramids
instead built drained
irrigated the Delta
built canals between Nile and Red Sea
focus on public works/infrastructure enriched Egypt and her people.
instead built drained
irrigated the Delta
built canals between Nile and Red Sea
focus on public works/infrastructure enriched Egypt and her people.
25
New cards

2nd intermediate period
HYKSOS INVADE and rule for 150 years
nothing changed because they like the Egypt lifestyle
They had better weapons
nothing changed because they like the Egypt lifestyle
They had better weapons
26
New cards
New Kingdom
Incredibly powerful pharoahs who ousted the Hyksos and built obelisks, school, temples, tombs
Included Ahmose, Hatshepsut, Akhenaten, Tutankhamun, and Ramses the Great
Included Ahmose, Hatshepsut, Akhenaten, Tutankhamun, and Ramses the Great
27
New cards

Ahmose
Upper Egypt pharoah who threw out the Hyksos and reunited Upper and Lower Egypt for the first time in 150 years.
28
New cards
Thutmose I
Non-royal pharaoh and father of Thutmose II & Hatshepsut by different wives.
29
New cards
Thutmose II
Non-royal pharaoh and husband/half brother of Hatshepsut.
30
New cards
Hatshepsut
Only female pharaoh, took power in place of her nephew/step-son when her brother/husband Thutmose II dies.
31
New cards
Thutmose III
Nephew/step-son of Pharaoh Hatshepsut who tried to tried to rid every memory of her rule after she died
32
New cards

Nefer
Part of an Egyptian name, it means "beauty"
Ka-nefer-nefer
Nefertiti
Nefertari
Maathorneferure
Ka-nefer-nefer
Nefertiti
Nefertari
Maathorneferure
33
New cards
Akhenaten
Tries to limit worship in all of Egypt to just the sun's disk god, Aten, (monotheism)
gives a lot of power to Nefertiti
Father to Tut and Anaksenamun
gives a lot of power to Nefertiti
Father to Tut and Anaksenamun
34
New cards
Tutankamen
Pharoah whose tomb in the Valley of the Kings is one of the only tombs found intact (not robbed)
husband to Anaksenamun
husband to Anaksenamun
35
New cards

Anaksenamun
Daughter of Nefertiti and Akhenaten
Married to her father Akhenaten, then her brother Tut and finally her grandfather Ay.
Married to her father Akhenaten, then her brother Tut and finally her grandfather Ay.
36
New cards

Why monotheism by Akhenaten?
The priests of Amun-Ra were even more powerful than the pharaohs so removing Amun-Ra removed the priests rendering them powerless.
37
New cards
Ramses II
Pharoah who ruled for 70 years in the 1200s
Emphasis on military power
famous treaty with Hittites
mortuary temples
Emphasis on military power
famous treaty with Hittites
mortuary temples
38
New cards

Abu Simbel
Worship temple for Ramses placed specifically so that twice a year Ramses and three god faces sitting inside the temple would get lit up (except god of the underworld)
Had to be moved onto higher ground and have a mountain built around it bc it was in flood plain
Had to be moved onto higher ground and have a mountain built around it bc it was in flood plain
39
New cards
Ramesseum
Ramses' mortuary temple complete with a scribe school because it assured that he would always be worshipped
40
New cards

Nefertari
Ramses favorite wife, had a matching (smaller) mortuary temple.
41
New cards

Why are Egypt and Nubia considered frenemies?
Nubia needed crops and wheat from Egypt and Egypt needed gold from Nubia
42
New cards
Opposite geography of Nubia and Egypt
Nubia was very rocky and had gold in the hills,
Egypt was very fertile thanks to the Nile floods and produced wheat and lots of other food.
Egypt was very fertile thanks to the Nile floods and produced wheat and lots of other food.
43
New cards

Medjai (medjay)
Nubians who guarded the tombs of the Pharaohs in the VOK
44
New cards
meriotic
Nubia's written language, still undeciphered
45
New cards
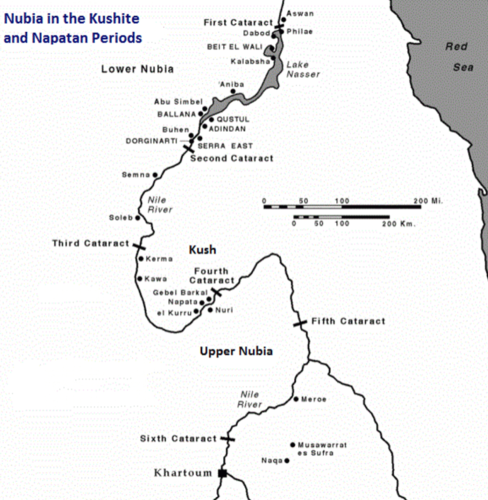
Why Nubia had 3 capitals over time.
Kerma, Napata, Meroë- kept moving farther up the Nile away from Egypt because each capital was too close to the enemy as Egypt expanded
46
New cards
Cultural Diffusion
Nubia copied Egypt -their kings dressed as pharaohs and built tiny pyramids
47
New cards

Egyptian writing system
Hieroglyphics
48
New cards
Isis, Osiris and Horus myth
Seth kills Osiris b/c of jealousy
puts him in a box which lands in a tree and grows into it
Tree gets moved to Tyre (Phoencia)
Isis get it back
Seth kills Osiris again and spreads body parts
Isis finds the body parts and puts them together in the world's 1st mummy
Horus avenges Osiris by fighting his uncle Seth for control of Egypt
puts him in a box which lands in a tree and grows into it
Tree gets moved to Tyre (Phoencia)
Isis get it back
Seth kills Osiris again and spreads body parts
Isis finds the body parts and puts them together in the world's 1st mummy
Horus avenges Osiris by fighting his uncle Seth for control of Egypt
49
New cards
feather of truth test
They would weigh their hearts compared to a feather
If they were lighter they would be saved
if it was heavier, they would go to the underworld
If they were lighter they would be saved
if it was heavier, they would go to the underworld
50
New cards
mummification
canopic jars held your guts, spread with salt and then herbs and oils, wrapped in linen
51
New cards
tomb decorations
They were filled with a lot of gold and jewelry- everything the person would need for the afterlife
52
New cards

Egyptian soul
Ba: the bird - part that can travel between life and death
others
Khet (physical body)
Sah (spiritual body)
Ib (heart)
Ka (vital essence)
Shut (shadow)
Sekhem (form)
Ren (name)
others
Khet (physical body)
Sah (spiritual body)
Ib (heart)
Ka (vital essence)
Shut (shadow)
Sekhem (form)
Ren (name)
53
New cards
negative confession
"I have NOT..."
54
New cards

Nubian pharaohs
Copies Egypt with same fake beard, jewelry, crown, eye makeup, but not same skin color
55
New cards
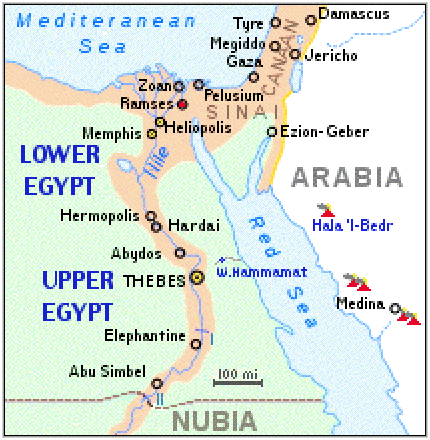
Upper Egypt capital
Thebes
56
New cards
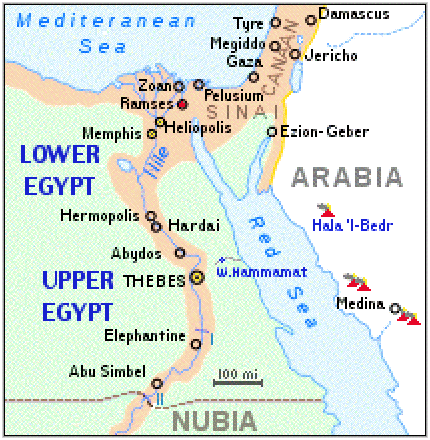
Lower Egypt capital
Memphis
57
New cards

Valley of Salt
Wadi Natron
58
New cards
Natural Borders of Egypt
Cataract, Mediterranean, Eastern and Western deserts
59
New cards
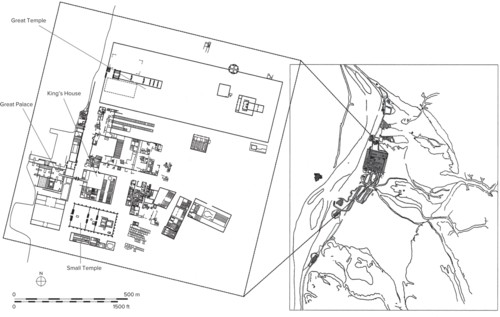
City of Aten
Akhetaten (Amarna)
60
New cards
Canopic Jars (sons of Horus)
Containers in which the ancient Egyptians preserved the internal organs of a deceased person usually for burial with the mummy
61
New cards

sarcophagus
coffin in Egypt
62
New cards
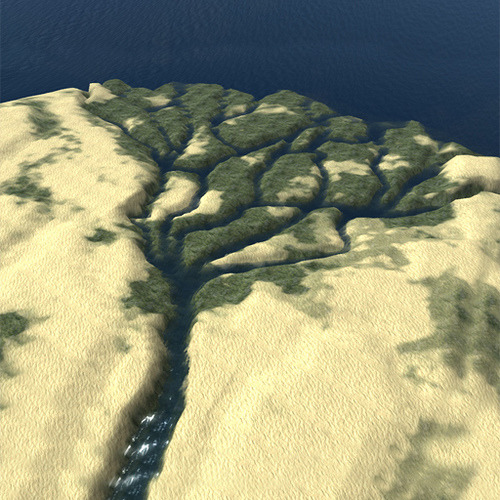

Nile Delta
The most fertile area of land in Egypt located end of the Nile River where it empties into the Mediterranean Sea
63
New cards
Valley of the Kings
An area were many tombs where built after the great pyramids because it allowed for easier guarding and less grave robbery.
64
New cards
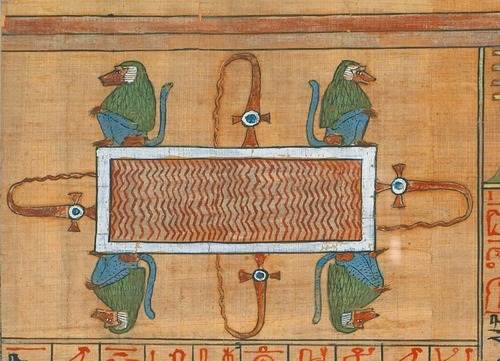
Book of the Dead
Collection of religious spells which were thought to be helpful to the deceased in the afterlife.
65
New cards

Herodotus
Greek Historian
considered the father of History
came from a Greek community in Anatolia and traveled extensively, collecting information in western Asia and the Mediterranean lands
considered the father of History
came from a Greek community in Anatolia and traveled extensively, collecting information in western Asia and the Mediterranean lands
66
New cards

Dua-Khety
Wrote Satire of the Trades -a letter to his son Pepy encouraging him to stay in school -become a scribe and thus avoid entering the trades (HARD work)
67
New cards

scribe
A professional writer who works for those with money, power and position.
68
New cards
royal blood
Believed to be elite, containing special properties that commoners' blood did not have, thus enabling royal descendants to control aspects of nature that common people could not.
69
New cards
Ta-Seti
Name of Nubia that means Land of the Bow (Archers)
refers to the excellence of the Archers of Nubia
their ability to win wars by shooting at their enemies with bow and arrow
refers to the excellence of the Archers of Nubia
their ability to win wars by shooting at their enemies with bow and arrow
70
New cards

Augustus Caesar (Octavian)
Enemy of the Nubia Kandake, Amirenas.
founder of the Roman Empire and its FIRST Roman Emperor
Part of a statue of him was the footrest of Amirenas' throne
Also enemy of Cleopatra
founder of the Roman Empire and its FIRST Roman Emperor
Part of a statue of him was the footrest of Amirenas' throne
Also enemy of Cleopatra
71
New cards

Palermo Stone
A fragment of the Royal Annals of the Old Kingdom, ca. 2300 BCE, a record of military campaigns by Egypt against Nubia. Egyptian artifact held hostage in Palermo, Italy.
72
New cards
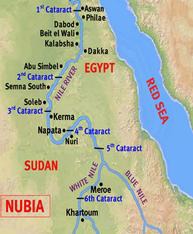
Kerma, 2400BCE
1st Kingdom of Kush capital, created when the more powerful Nubian villages gradually took over the weaker ones
73
New cards
Hyksos alliance with Nubia, 1700BCE
Agreement between them to attack Upper Egypt and defeat the forces of Kamose (last Pharaoh of 17th Dynasty)
74
New cards
Nubian alliance with Phoenicia and Judah, 700s BCE
Agreement between them to defend against expanding Assyrians (Sennacherib, Esarhaddon and finally Ashurbanipal). Led by Taharqa of Kush
75
New cards

Jebel Barkal
A city built to worship Amun
site of Nubian pillars that have the history of the Napatan period of Nubian/Kush history inscribed on them in hieroglyphics.
Beautiful temple built during the age of the Black (Nubian/Kush) Pharaohs,
modeled after the temples at Abu Simbel, and is the burial site of Piye and Shabaka. 700s BCE
site of Nubian pillars that have the history of the Napatan period of Nubian/Kush history inscribed on them in hieroglyphics.
Beautiful temple built during the age of the Black (Nubian/Kush) Pharaohs,
modeled after the temples at Abu Simbel, and is the burial site of Piye and Shabaka. 700s BCE
76
New cards

Taharqa
A Kushite king he was one of the most powerful leaders in history.
His Kushite kingdom grew to include Egypt and prospered under his reign.
He built many large temples in and around Egypt and Kush. Driven out of Egypt by the conquering Assyrians under King Esarhaddon,
returned to reclaim Egypt until he was later defeated by the next Assyrian king, Assurbanipal. 600s BCE
His Kushite kingdom grew to include Egypt and prospered under his reign.
He built many large temples in and around Egypt and Kush. Driven out of Egypt by the conquering Assyrians under King Esarhaddon,
returned to reclaim Egypt until he was later defeated by the next Assyrian king, Assurbanipal. 600s BCE
77
New cards
Alara, King of Kush
Very first King of Kush (Nubia)
78
New cards
Kashta
Kushite king who attacked Egypt.
Made the Kushite Kingdom into an Empire by conquering Upper Egypt and capturing Thebes.
Father of High Priestess Amenirdis I.
Founder of 25th Dynasty of Egypt.
Made the Kushite Kingdom into an Empire by conquering Upper Egypt and capturing Thebes.
Father of High Priestess Amenirdis I.
Founder of 25th Dynasty of Egypt.
79
New cards

Amenirdis I
Nubian princess, daughter of King Kashta, she became High Priestess in newly conquered Thebes.
She was called "God's Wife of Amun".
Super powerful
She was called "God's Wife of Amun".
Super powerful
80
New cards
Piye
King of Kush around 750 B.C., who gained control of all of Egypt, becoming pharaoh and uniting Egypt with Kush. Got the Delta princes of Egypt to promise allegiance with Kush.
81
New cards

Shabaka
Piye and Amenirdis' brother.
Pharaoh over Kush and Egypt. Avenged his brother Piye, by punishing the rebel Egyptian princes from the Delta region.
Pharaoh over Kush and Egypt. Avenged his brother Piye, by punishing the rebel Egyptian princes from the Delta region.
82
New cards
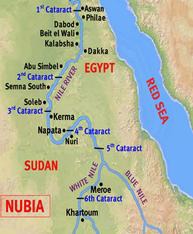
Meroe
Capital of a flourishing kingdom in southern Nubia from the 4th century B.C.E. to the 4th century C.E.. In this period Nubian culture shows more independence from Egypt and the influence of Sub-Saharan Africa. Known for its manufacture of iron weapons and tools.
83
New cards

kandake
Sister of the current king ("Qore" in Kush), she would be the mother of the next king/Qore.
This is matrilineal succession. Often a very powerful female leader who ruled alongside her husband and/or her son.
We use the name Candace for our daughters because it means QUEEN.
This is matrilineal succession. Often a very powerful female leader who ruled alongside her husband and/or her son.
We use the name Candace for our daughters because it means QUEEN.
84
New cards
Powerful Nubian Kandakes:
Shanakdakhete, 177-155BC;
Amanirenas, 40-10BC;
Amanishakheto, 10BC-1AD;
Amanitore, 1-20AD;
Amantitere, 22-41AD \[\*might be the Kandake of reference in the book of Acts\];
Amanikhatashan, 62-85AD;
Maleqorobar, 266-283AD;
Lahideamani 306-314AD.
Amanirenas, 40-10BC;
Amanishakheto, 10BC-1AD;
Amanitore, 1-20AD;
Amantitere, 22-41AD \[\*might be the Kandake of reference in the book of Acts\];
Amanikhatashan, 62-85AD;
Maleqorobar, 266-283AD;
Lahideamani 306-314AD.
85
New cards

Amanirenas, 40-10BCE
Most famous kandake of Kush because of her role leading Kushite armies against the Romans in a war that lasted five years, from 27 BC to 22 BC.
After an initial victory when the Kushites attacked Roman Egypt and sacked Thebes, the Kushites were driven out of Egypt by the Romans and forced Amanirenas to make a treaty restoring the prior status quo.
She was described as a tremendous warrior and leader, very brave, and blind in one eye!
After an initial victory when the Kushites attacked Roman Egypt and sacked Thebes, the Kushites were driven out of Egypt by the Romans and forced Amanirenas to make a treaty restoring the prior status quo.
She was described as a tremendous warrior and leader, very brave, and blind in one eye!
86
New cards
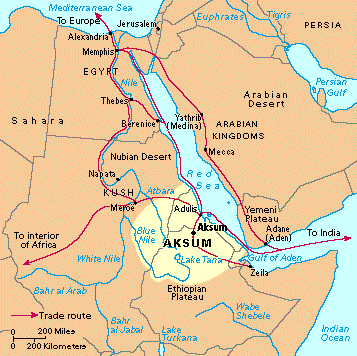
Aksum (Axum)
Early African civilization located southeast of Nubia (in Ethiopia, Eritrea, Sudan);
oldest Christian empire in the world;
traded goods such as ivory, emeralds, tortoise shells, silk, and spices with India, China, Rome, and Byzantium.
Remained Christian even during Muslim expansion.
oldest Christian empire in the world;
traded goods such as ivory, emeralds, tortoise shells, silk, and spices with India, China, Rome, and Byzantium.
Remained Christian even during Muslim expansion.
87
New cards
Lalibela, Ethiopia
Major Christian center of early Ethiopia.
Key church in this city is made of one single rock.
11 rock-hewn churches connected by rock tunnels, near the Great Rift Valley still exist today.
Key church in this city is made of one single rock.
11 rock-hewn churches connected by rock tunnels, near the Great Rift Valley still exist today.
88
New cards
Queen of Sheba
The queen of a wealthy country (Aksum/Ethiopia) who came to test Solomon's wisdom.
Their son, Menelik, returned to Sheba (Aksum/Ethiopia) with the Ark of the Covenant.
Their son, Menelik, returned to Sheba (Aksum/Ethiopia) with the Ark of the Covenant.
89
New cards
Kebra Nagast
Work of sacred literature written in the Ge'ez language in the 1300s AD that documents Menelik and his successors in the Solomonic Ethiopian ruling dynasty.
Considered historically reliable.
Followed by Ethiopian Christians and Jamaican Rastafarians.
Considered historically reliable.
Followed by Ethiopian Christians and Jamaican Rastafarians.
90
New cards
King Ezana of Axum
He brought Christianity to Africa and made it the official religion of Axum. 300s AD
91
New cards
Trade with Axum
Arabia, Sub-Saharan Africa, Red Sea, Arabian Sea, China, India, Persia, Egypt and Nubia
92
New cards
Frumentius
This man and his brother were captives in Aksum and became the tutors of King Ezana, eventually converting Ezana and all of Aksum to Christianity in 333AD (32 years after Armenia, 47 years before Rome)
93
New cards
Athanasius of Alexandria
(d. AD 373) Bishop/Patriarch of the Church in Alexandria, Egypt. Responsible for the Christian community in North Africa. \#2 Patriarch after Patriarch in Rome (Pope)
94
New cards
Ezana Stele
Standing stele (hawulti/obelisk) from Axum carved from a block of granite, marks the tomb of King Ezana, the 1st Christian leader of Aksum.
95
New cards
Ezana Stone
The Ezana Stone documents the conversion of King Ezana to Christianity and his conquest of various neighboring areas, including Meroë, commemorating his victories in praise of God.
Written in various ancient languages, including the Ethiopian Semitic Ge'ez, the South Arabian Sabaean, and Greek, the king's engravings in stone provided a trilingual monument in different languages, similar to the Rosetta Stone.
Written in various ancient languages, including the Ethiopian Semitic Ge'ez, the South Arabian Sabaean, and Greek, the king's engravings in stone provided a trilingual monument in different languages, similar to the Rosetta Stone.
96
New cards
Deir al Bahri, Egypt
Queen Hatshepsut's mortuary temple in the Valley of the Kings
97
New cards
Aswan, Egypt
Trade city in Upper Egypt at the 1st Cataract. The name means TRADE.
98
New cards
Narmer
Egyptian King who is believed to have brought 2 Egyptian Kingdoms together.
99
New cards
Double Crown of Egypt
the crown of unification that combined the white Ibis crown of Upper Egypt with the red Asp crown of Lower Egypt.
100
New cards
Nefertiti
queen of Egypt and wife of Akhenaten (14th century BC)