HUMAN GEO UNIT 1
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Location
Specific position on the Earths surface. Geographic coordinates.
Human Environment Interaction
Relationship between human societies and the natural world
Region
How regions are similar or different based on physical and cultural characteristics
Place
A locations unique physical and human characteristics
Movement
Mobility of goods, people and ideas
Absolute Location(Location)
Coordinates. Latitude and Longitude
Relative Location(Location)
Approximate location. “Next to” “near”.
Site(Location)
Location of a settlement on the Earth “Site Factors”
Situation(Location)
Surrounding features of a city. Both manmade and natural.
Formal/Uniform Region(Region)
Regions defined by physical, cultural or economic traits(ex. Sahara desert)
Functional/Nodal Region(Region)
Regions defined by interactions/activities, united by networks of communication (ex. broadcast area for a radio tower)
Perceptual/Vernacular Region(Region)
Intellectual designs people give to places(ex. “The South”)
Sense of Place(Place)
How we think of a place/what it means to us based on things we’ve experienced with our senses
Perception of Place(Place)
How we perceive a place based on what we have heard or been told
Intervening Opportunity(Movement)
Something diminishing the attractiveness of sites father away (ex. Why go to China when you can go to Chinatown in NYC?)
Sequent Occupance(Movement)
Successive societies leave their imprints on a place (ex. Latin Americans speak Spanish and also follow some aspects of Native American culture).
Cylindrical Map
Used for navigation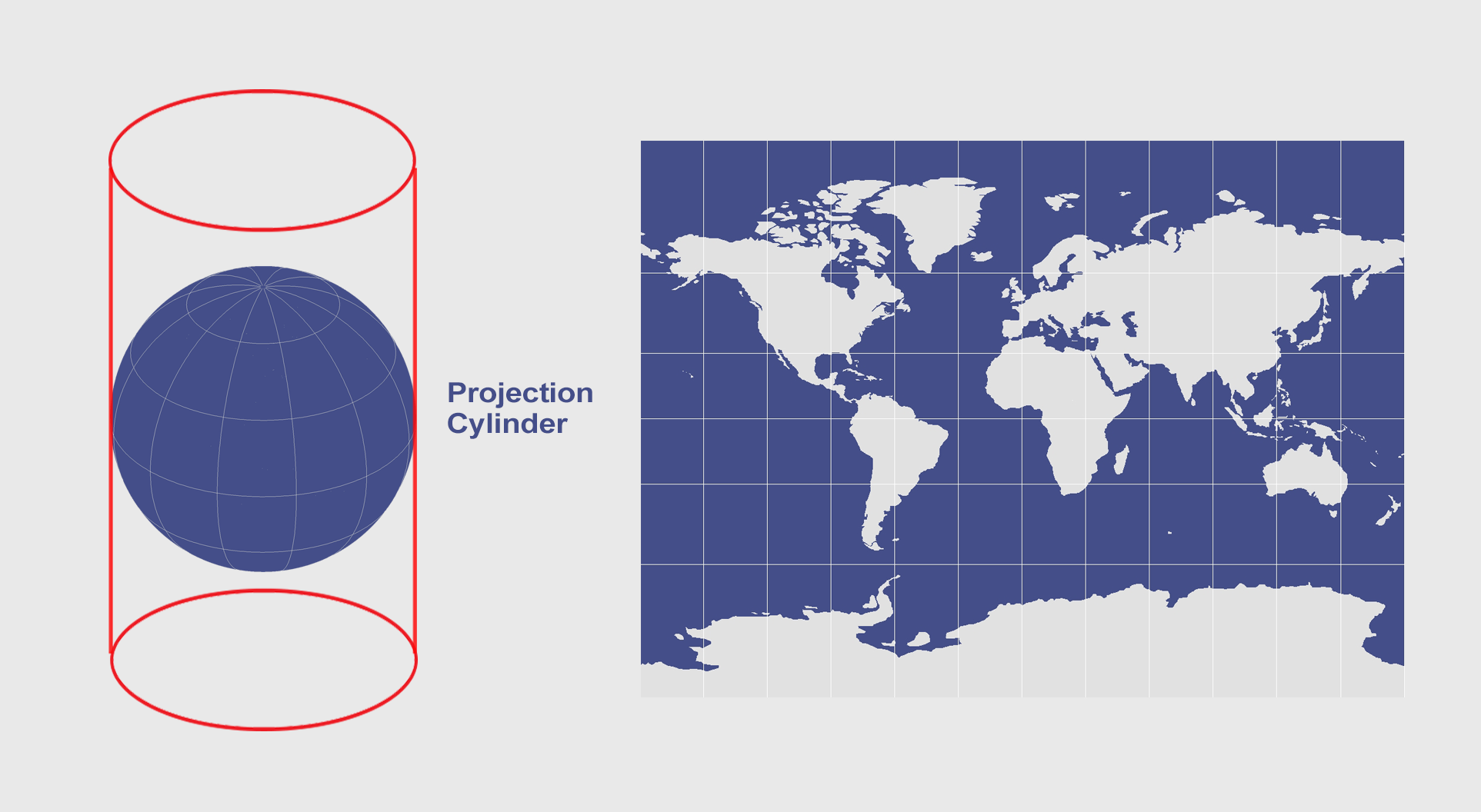
Peters Map
Spatial distribution related to area. Presents countries in their true proportion to one another. 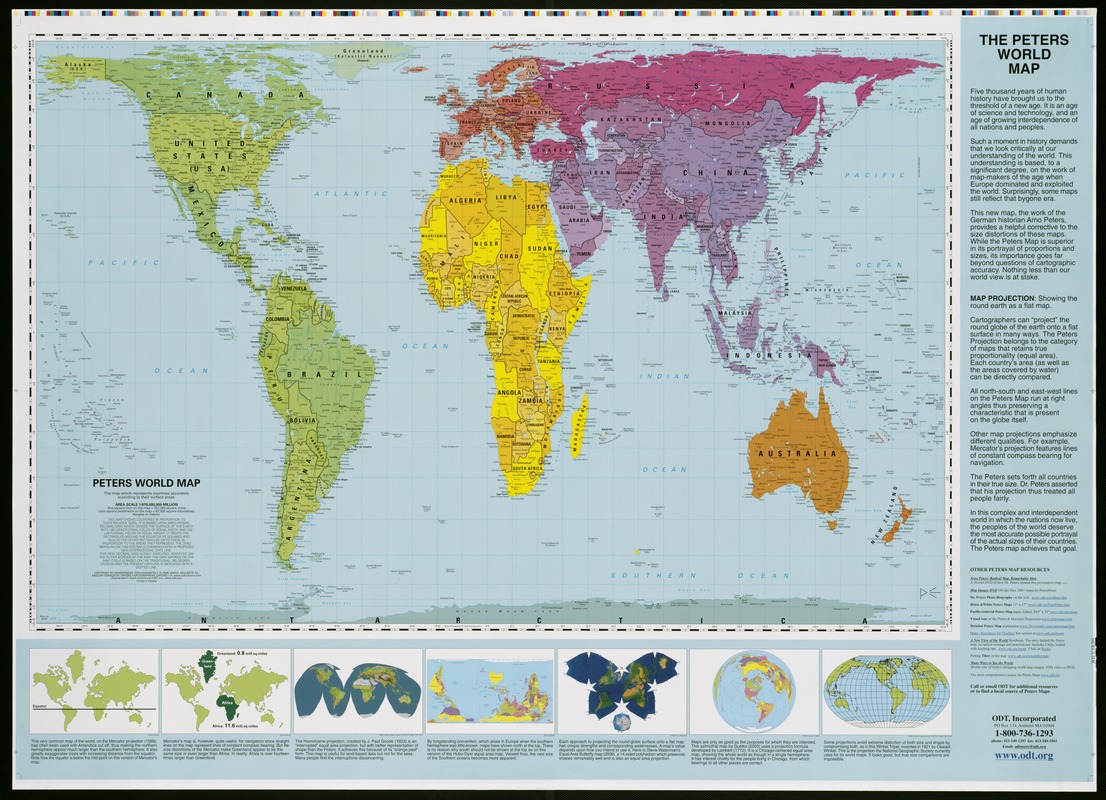
Conic Map
Projections of the Earth onto a cone surface. Best suited to mid latitude regions(distortion increases towards the poles). 
Robinson Map
Designed to minimize distortion in all properties. Most common/general type of map. 
Relocation/Migration(Diffusion)
Ideas and practices carried with people are they immigrate from place to place. Diffuse into society in the new place they go to. (ex. Religious statute carried with an immigrant as they move to another country)
Hierarchical(Diffusion)
Diffusion as a result of a societal hierarchy. The more power a culture has over other cultures, the faster and wider it spreads. (ex. Roman Empire resulted in the spread of Roman culture in everything they conquered)
Contagious(Diffusion)
Spread of a cultural trait through direct contact. Usually rapid spread and requires close proximity. (ex. disease transmission, social media trends)
Stimulus(Diffusion)
Spread of an underlying principal, but traits are altered. Adapting a foreign culture to a local cultures norms. Diverse manifestations of an original idea. (ex. Indian McDonald's serving veggie burgers due to a high vegetarian population)
Reference Maps
Maps that show absolute locations of places
Thematic Maps
Maps that tell stories by showing some attribute or movement.
Time Zones
Every 15 degrees of longitude traveled east and west accounts for 1 hour difference 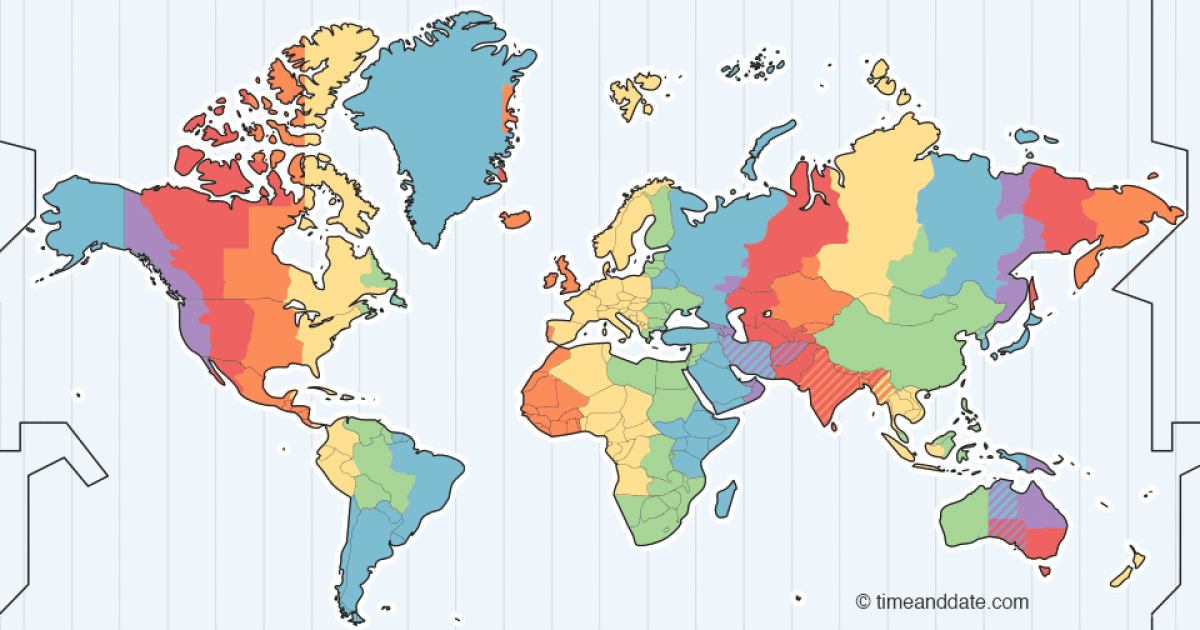
GPS
satellite technology used to get you from point a to point b.
GIS
uses computer technology to create maps with “patterns” and other relationships. 
Determinism
Belief that physical environment determines human actions and culture
Possibilism
Belief that the physical environment may impact human actions and culture but does not decide it, in the end people choose what to do
Cartograms
chart and assign data by size so they distort places on a map
Cloropleth maps
Uses patterns or colors
Dot Maps
Dots represent a certain number of phenomena
Flow-Line Maps
Show data based on thickness and can be drawn from one base to another.
Isoline Maps
Uses continuous lines to join points of the same value. Such as a topographic map. 
Graduated Symbol Map
Uses symbols of different sizes to indicate amounts.
