Functional groups
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Boiling point of alcohols
Higher than those of alkanes with similar molecular weights
Largely from alcohols being able to form hydrogen bonds
Increases as carbon chain increases due to increased dispersion forces
Solubility of alcohols (3 or less carbons)
Hydrogen bonds are most significant
Form hydrogen bonds with water
Soluble
Solubility of alcohols with more than 3 carbons
Dispersion forces increases as length of non-polar hydrocarbon tail increases
Unable to form hydrogen bonds with water
Solubility in water decreases and solubility in non-polar solvents increases.
Intermolecular forces of ketones and aldehydes
Dispersion forces
Dipole-Dipole interactions between polar groups
Boiling points of ketones and aldehydes
Higher boiling point than alkanes of similar mass due to dipole-dipole interactions
Lower boiling points than alcohol because they don’t form hydrogen bonds
Higher boiling point as the number of carbon atoms and dispersion forces increases
Solubility of aldehydes and ketones
With one to four carbons are soluble in water
With five or more carbons are not very soluble in water
Form hydrogen bonds with water between carbonyl oxygen and hydrogen atoms in water
Boiling point of carboxylic acids
Pure carboxylic acids form hydrogen bonded dimers
Dimers are stable species with a molar mass double that of a single carboxylic acid molecule
Increase in size results in an increase in dispersion forces
Boiling point of carboxylic acid is much higher than that of other organic molecules of similar molar masses
Solubility of carboxylic acid
Short chain carboxylic acids are soluble in water
Hydrogen bonding occurs between the water molecules and both the groups on the carboxylic acid molecule
Intermolecular bonding of esters
Have lower melting and boiling points than carboxylic acids of similar size because of hydrogen bonding
Esters only form dispersion and dipole-dipole forces
Esters have poor solubility in water
Esters in an acid solution
If an ester is boiled in acid solution, then the ester bond will be broken, reforming the alcohol and carboxylic acid
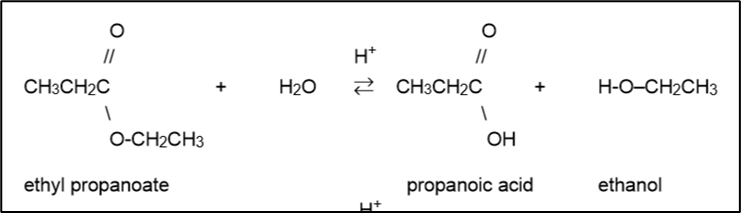
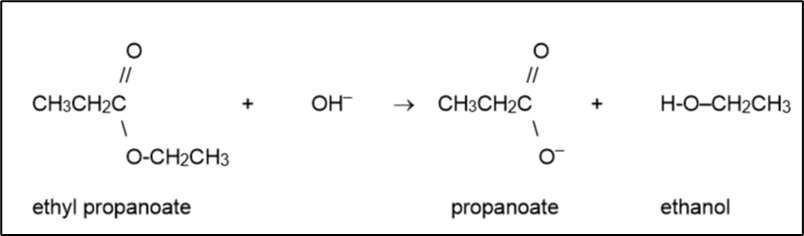
Esters in a basic solution
If an ester is boiled in a basic solution, then the ester bond will be broken, reforming the alcohol and conjugate base of the carboxylic acid (a carboxylate ion)
Functional group of amide
-CONH2 like carboxylic acid but replace the OH group for amino group